PATHO Ch. 15 Structure and Function of the Neurologic System
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
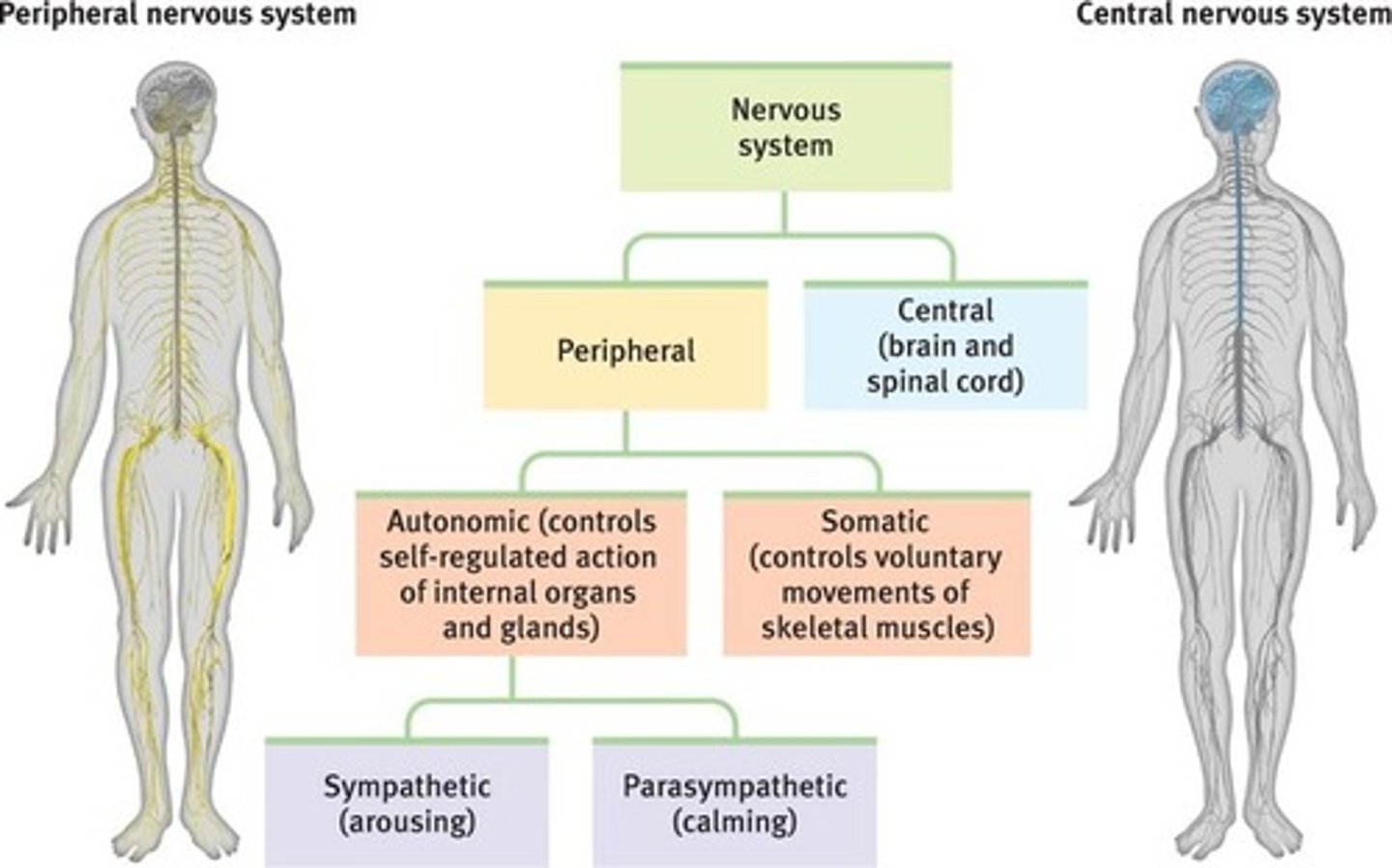
The two main divisions of the nervous system are
central nervous system (CNS)
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
KEEPS US ALIVE
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
spinal and cranial nerves
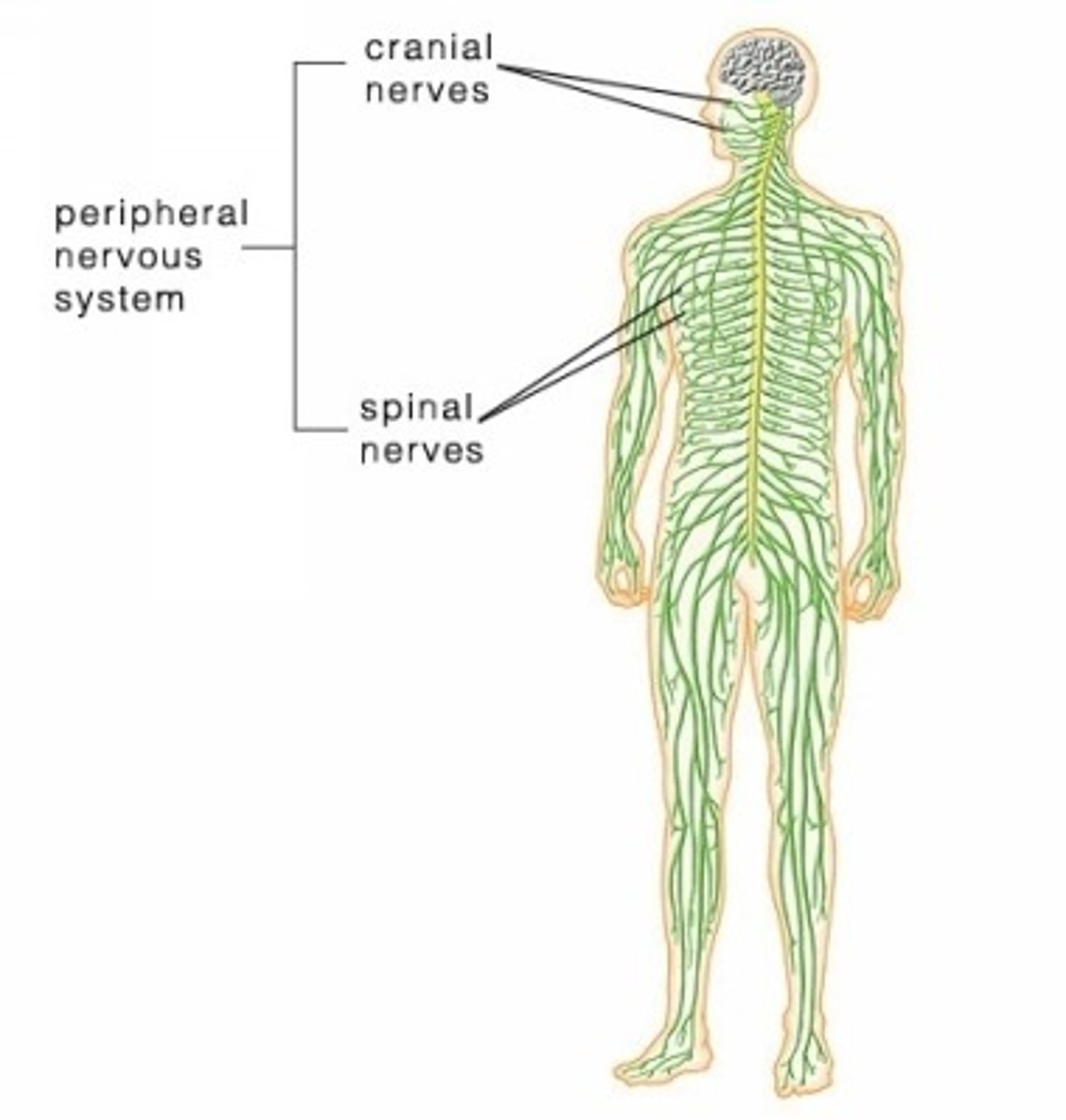
PNS: afferent
carry information toward the CNS
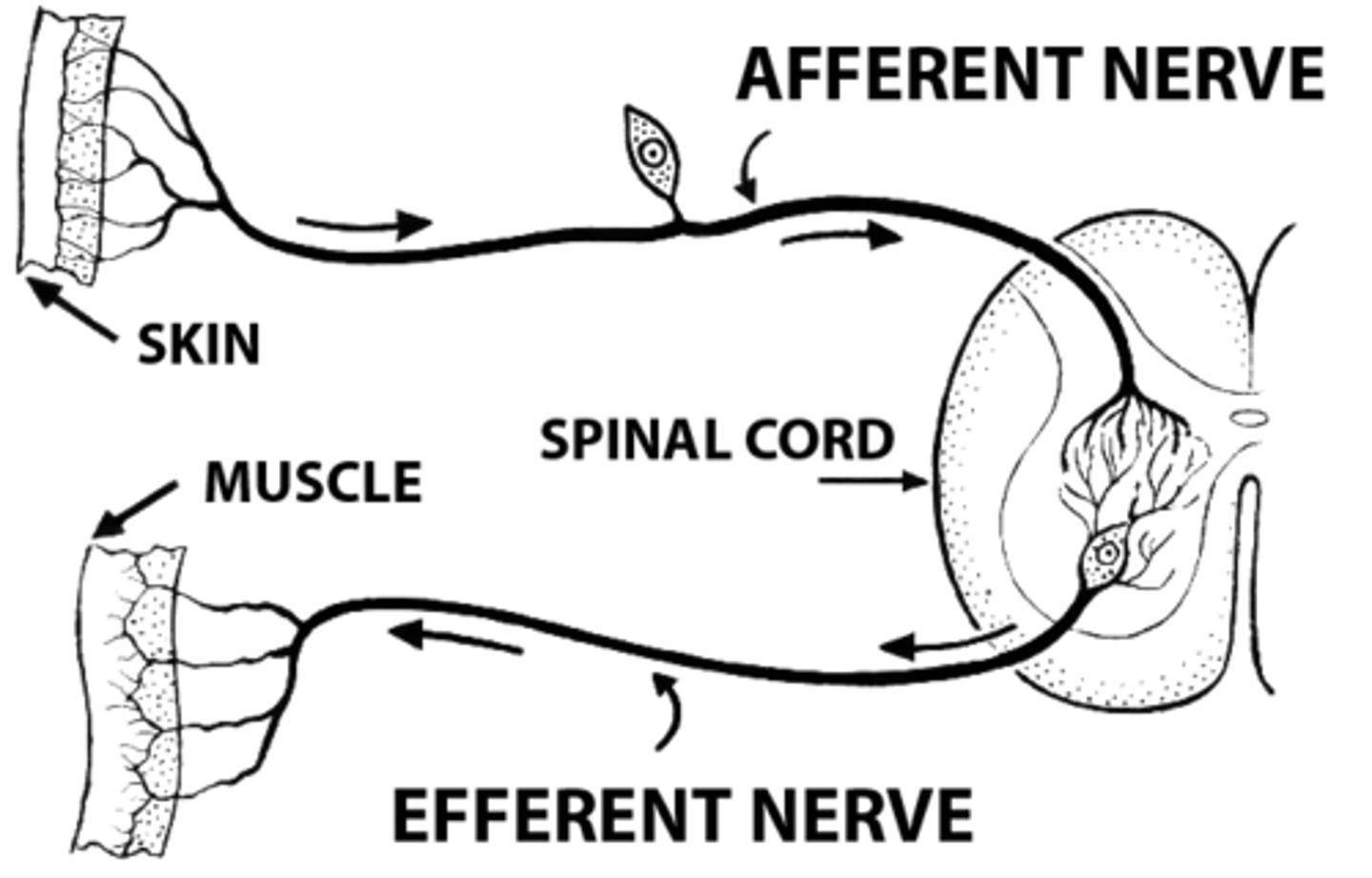
PNS: efferent
carry information away from the CNS
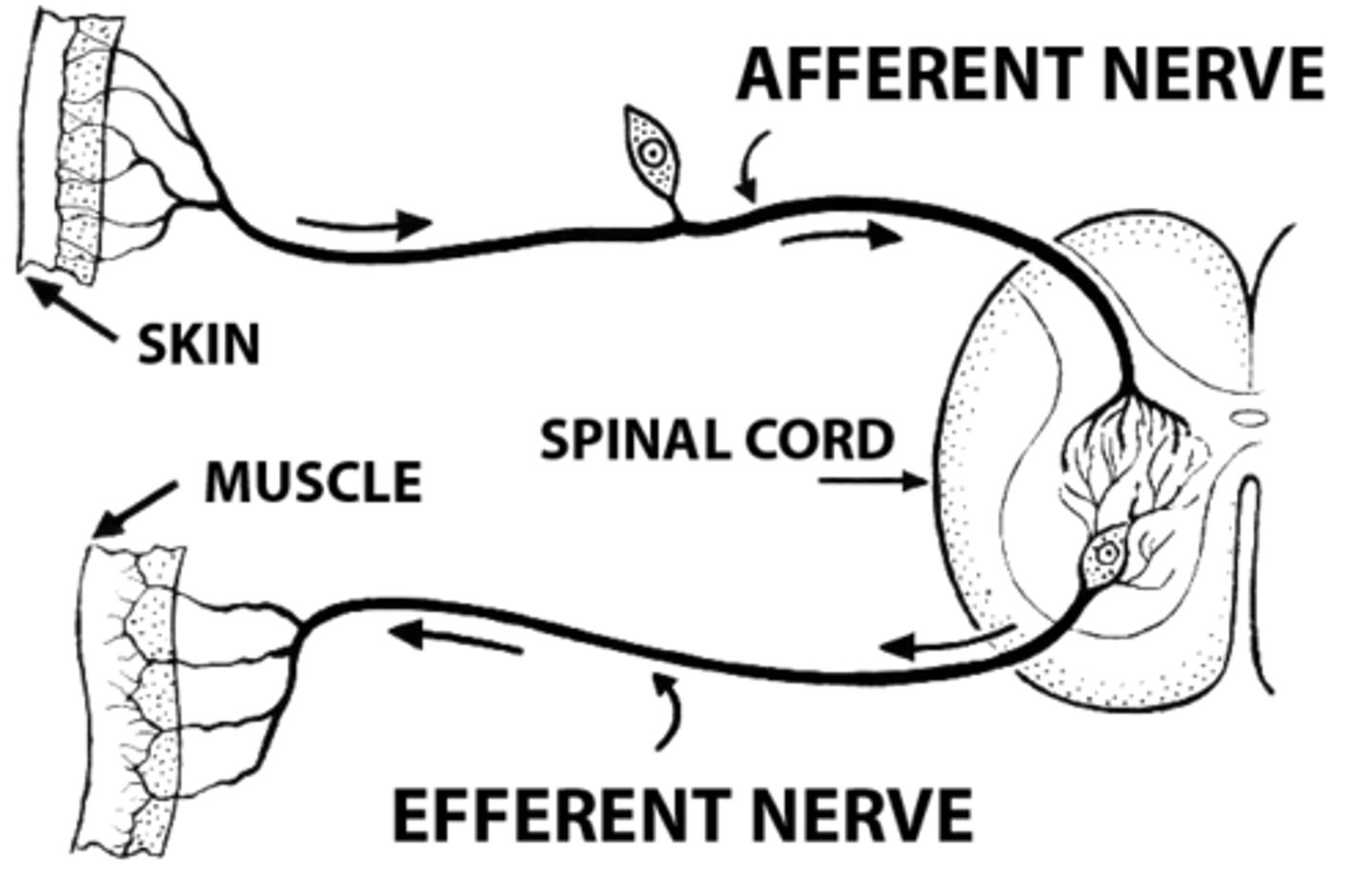
somatic nervous system
part of the PNS
controls:
- skeletal muscles
- somatosensory (touch)
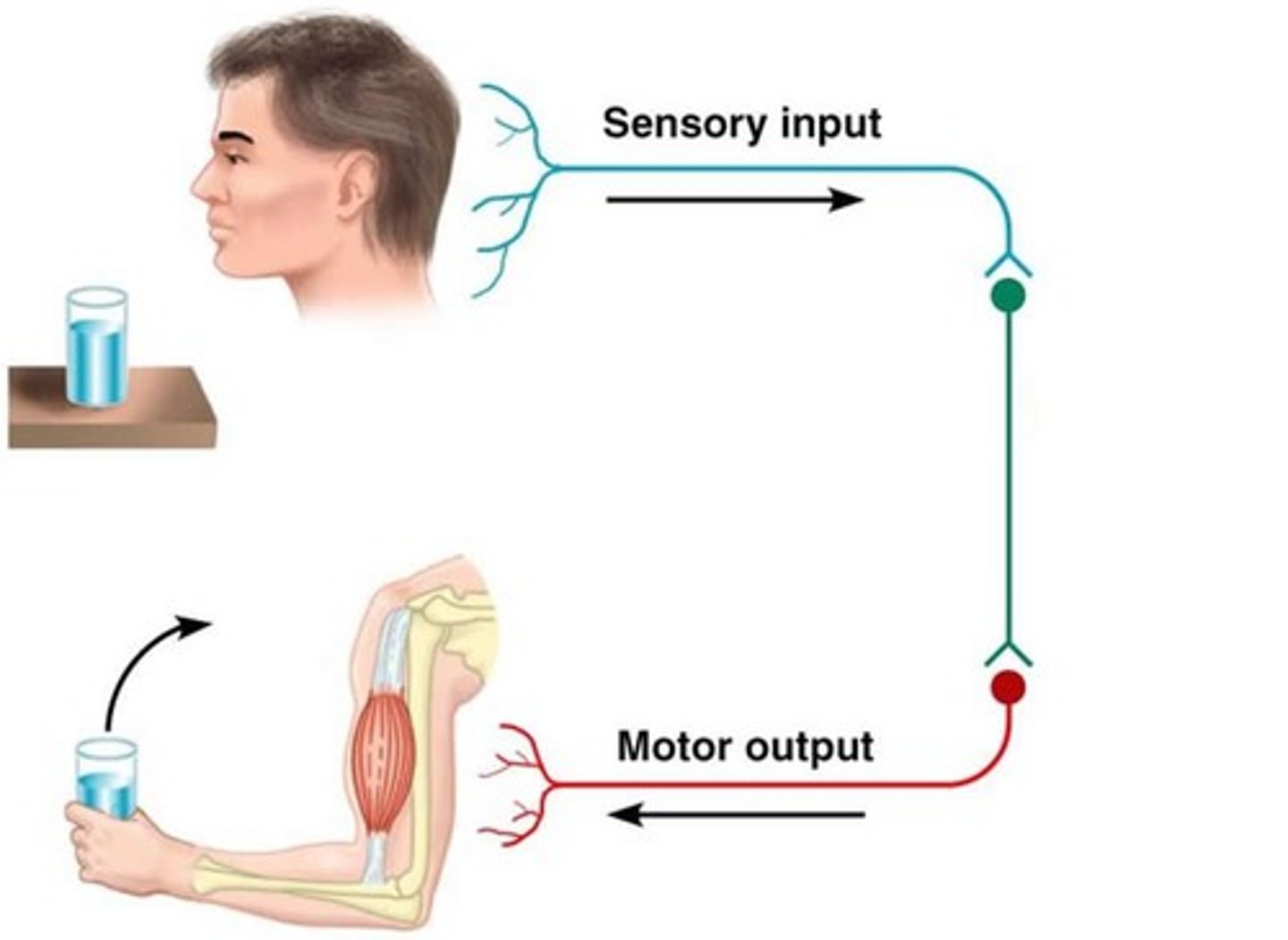
autonomic nervous system
part of the PNS
controls:
- glands + muscles of the internal organs (heart)
- automatic
sympathetic division arouses
parasympathetic division calms.
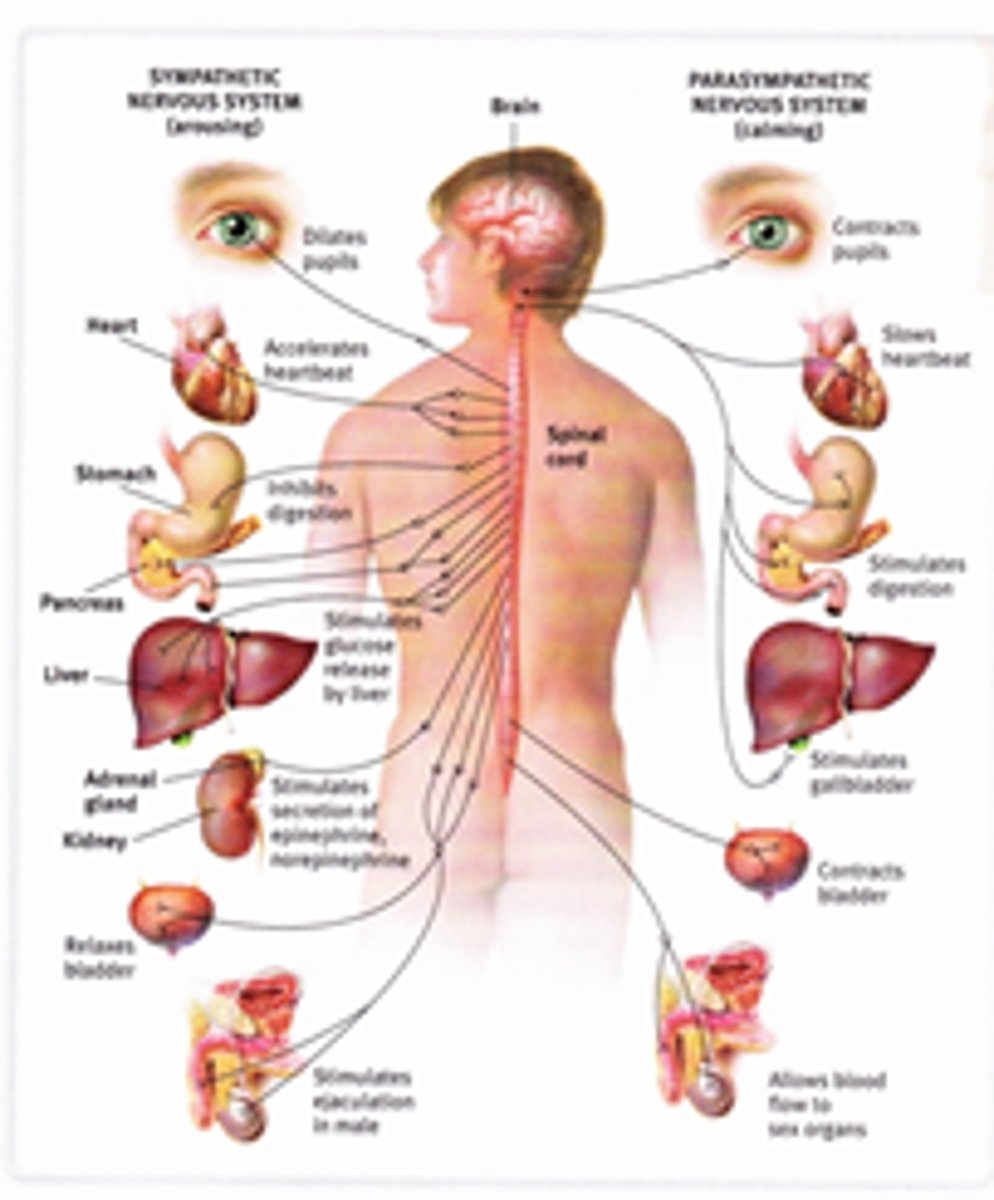
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight

parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest
homeostasis

The neurotransmitter released by preganglionic parasympathetic fibers is:
acetylcholine
vestibular
balance

auditory
hearing
olfaction
smell

gustatory
taste
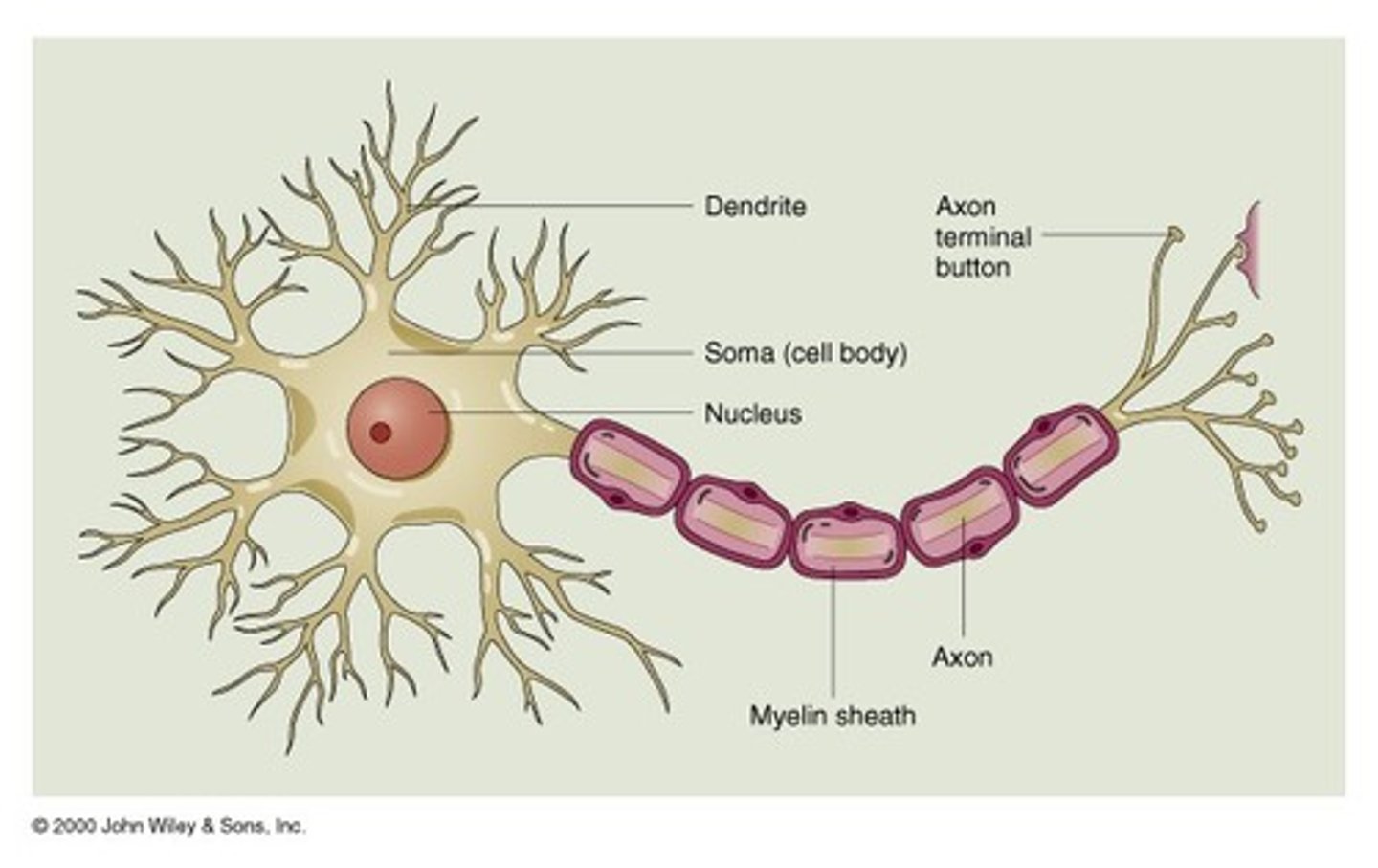
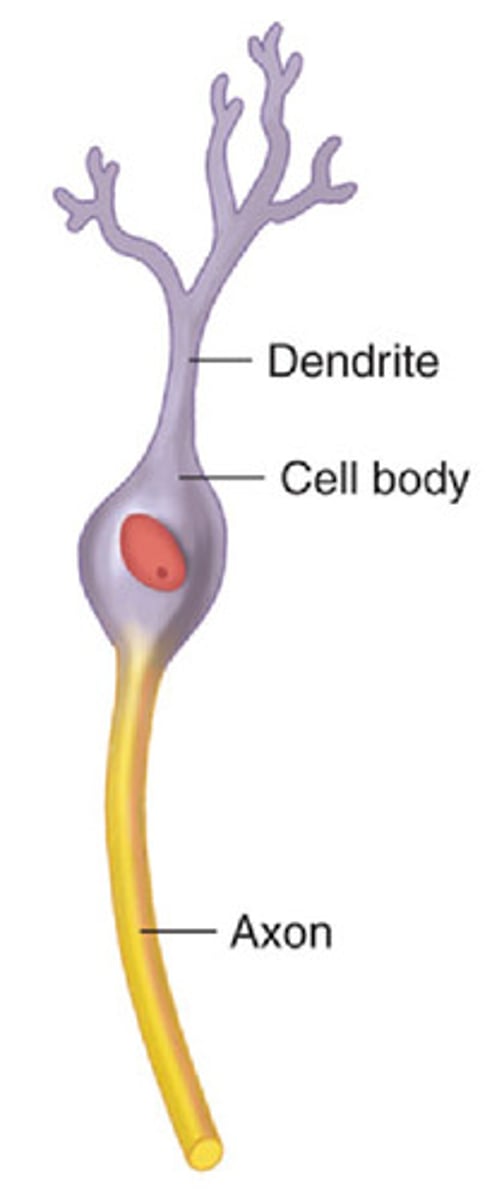
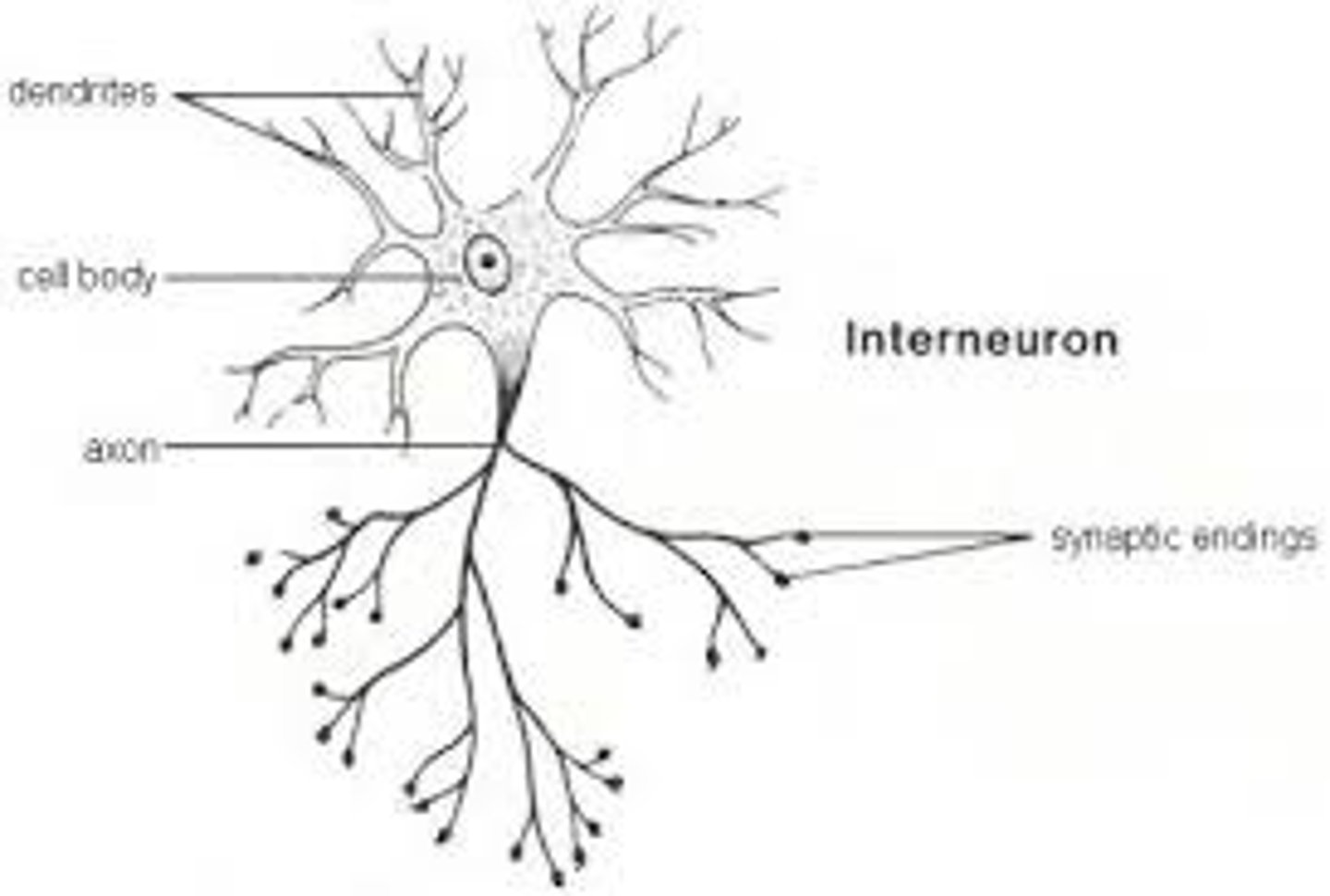
neurons
nerve cell
primary communicating cell
specialized
polarized (axons: send, dendrites: receive)
different shapes and types
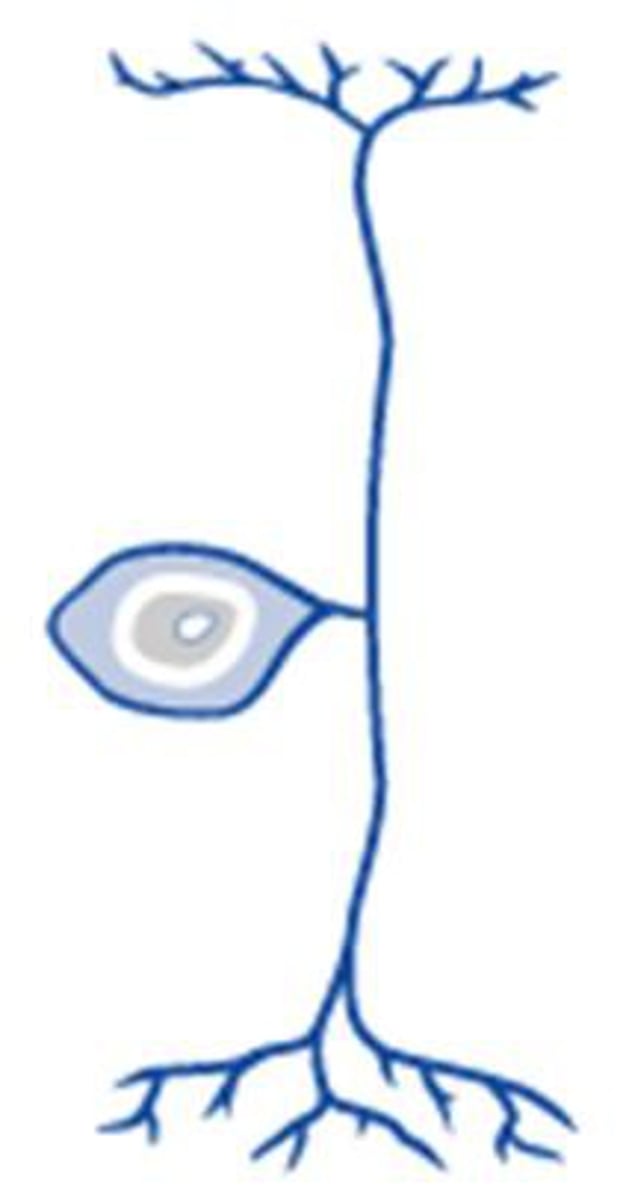
pseudounipolar neurons
have only one fused axon that extends from cell body and divides into TWO processes:
- one process carries sensory information FROM sensory receptors TO cell body;
- other process carries sensory information FROM cell body TO spinal cord;
bipolar neurons
A neuron that has only two projections (one axon/one dendrite) from the cell body
found in: retina
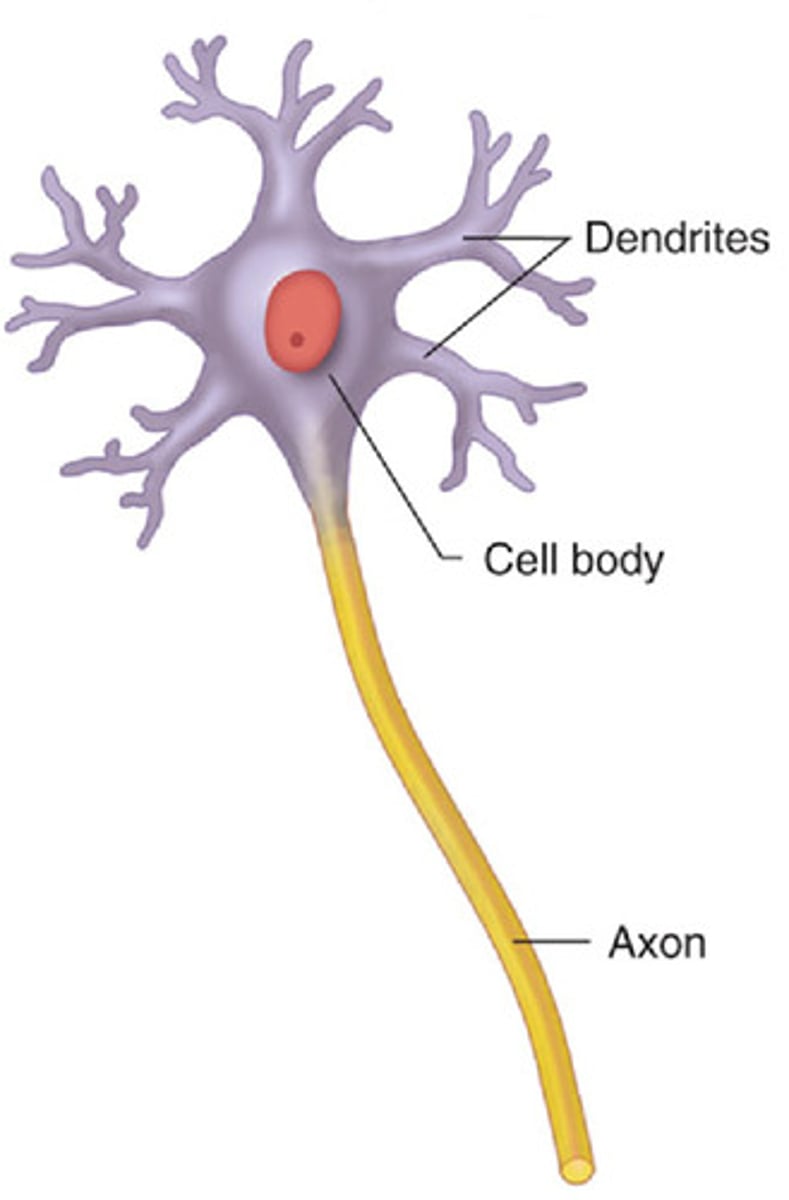
multipolar neuron
a nerve cell that has many dendrites and a single axon
- most common body neuron
every neuron in our body has only ONE
axon
we do NOT have _____ neurons in our body
true unipolar neurons
axon
A long, tail-like part that sends signals to other neurons, muscles, or glands
axon hillock (trigger zone)
acts like a trigger point that decides whether or not to send an electrical signal (action potential) down the axon.
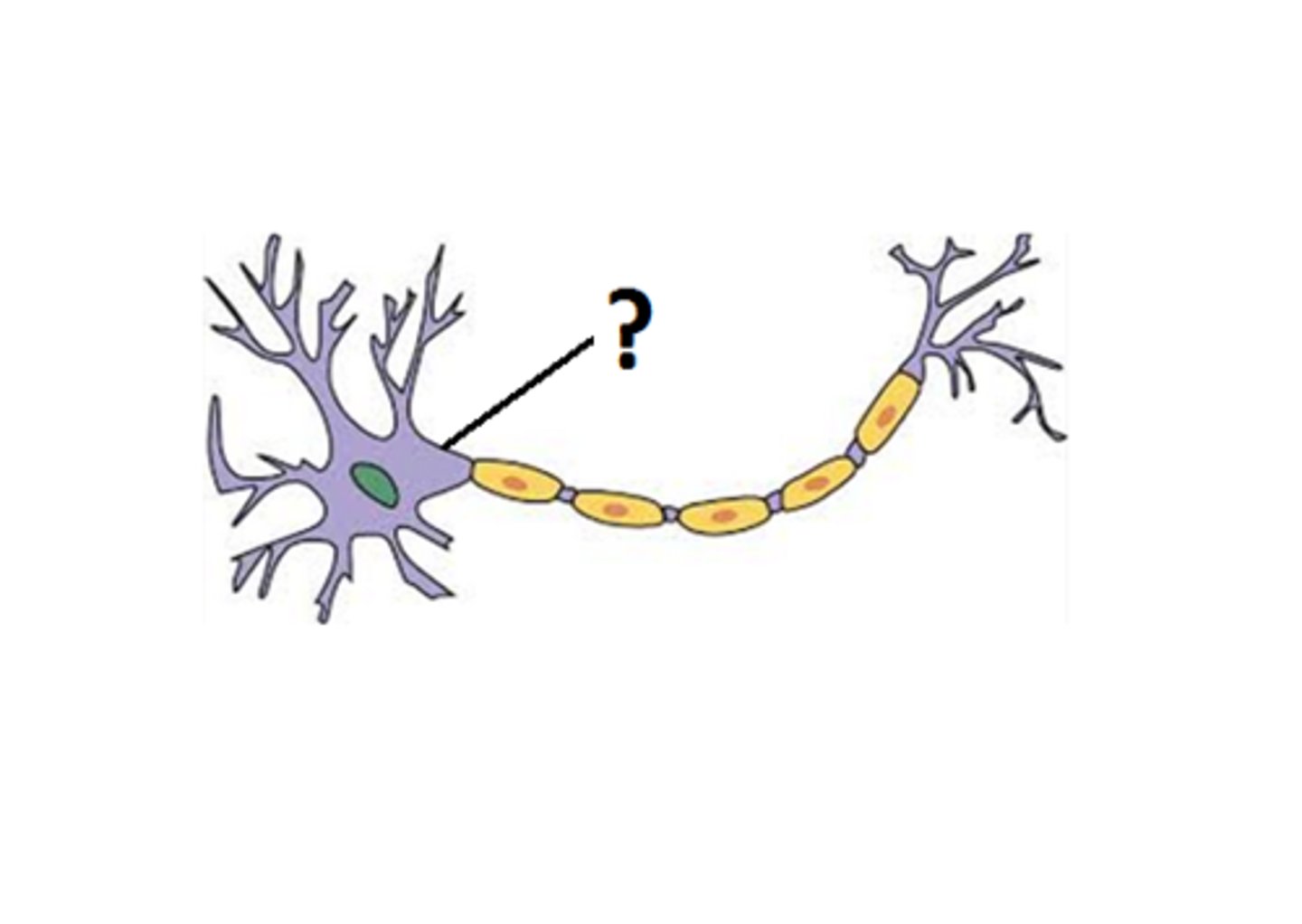
cell body
contains nucleus and organelles
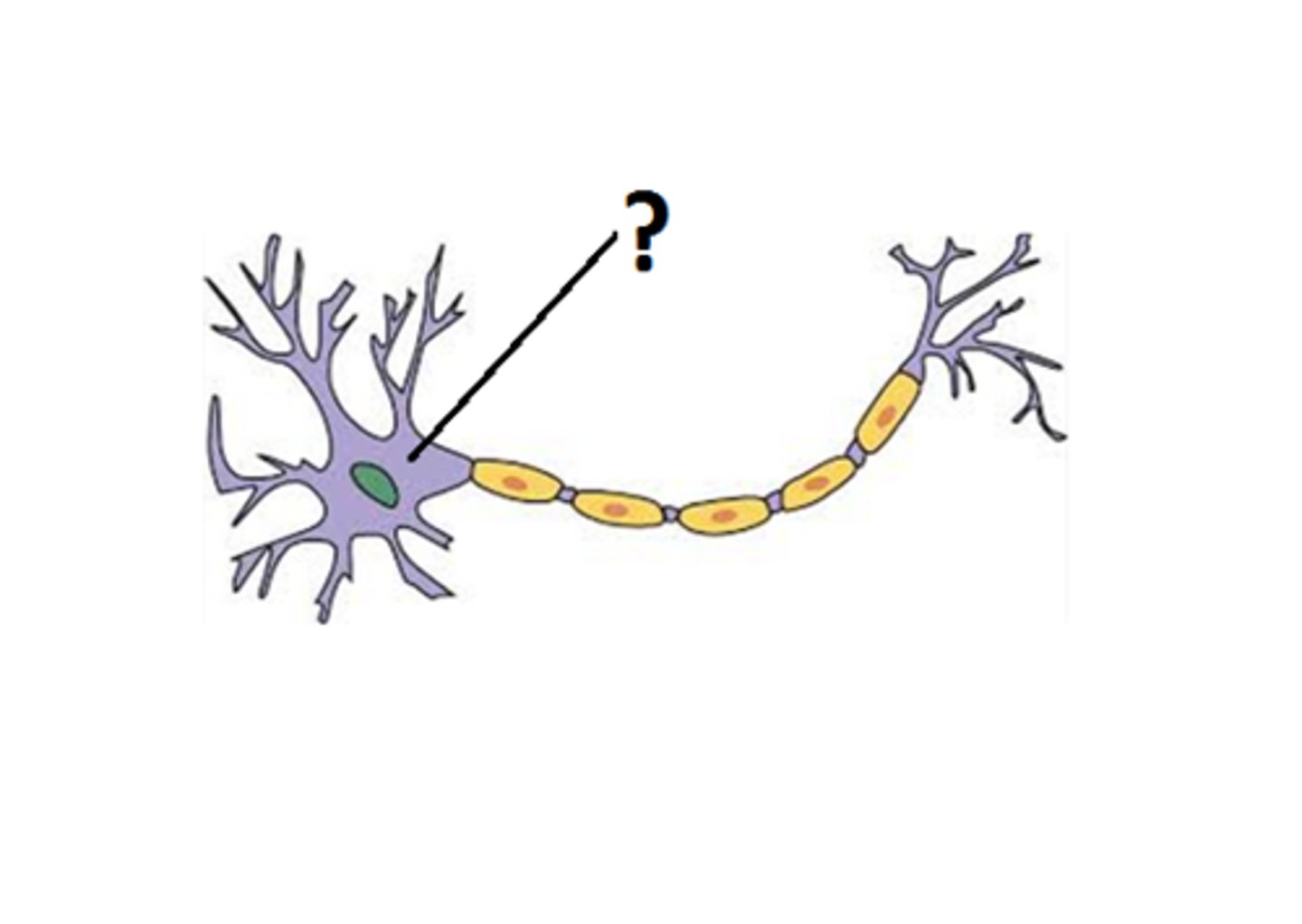
dendrites
Branch-like structures that receive signals from other neurons.
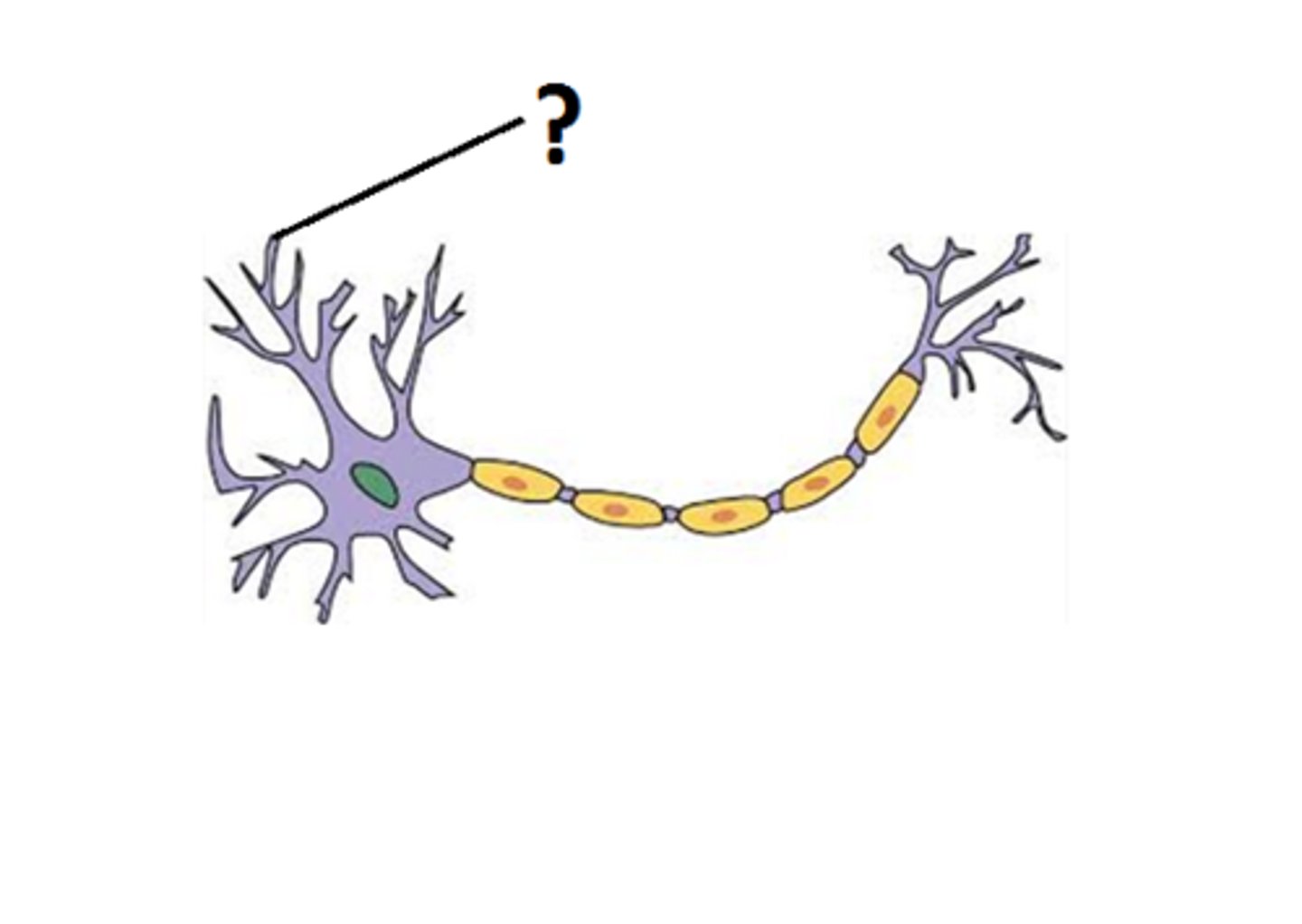
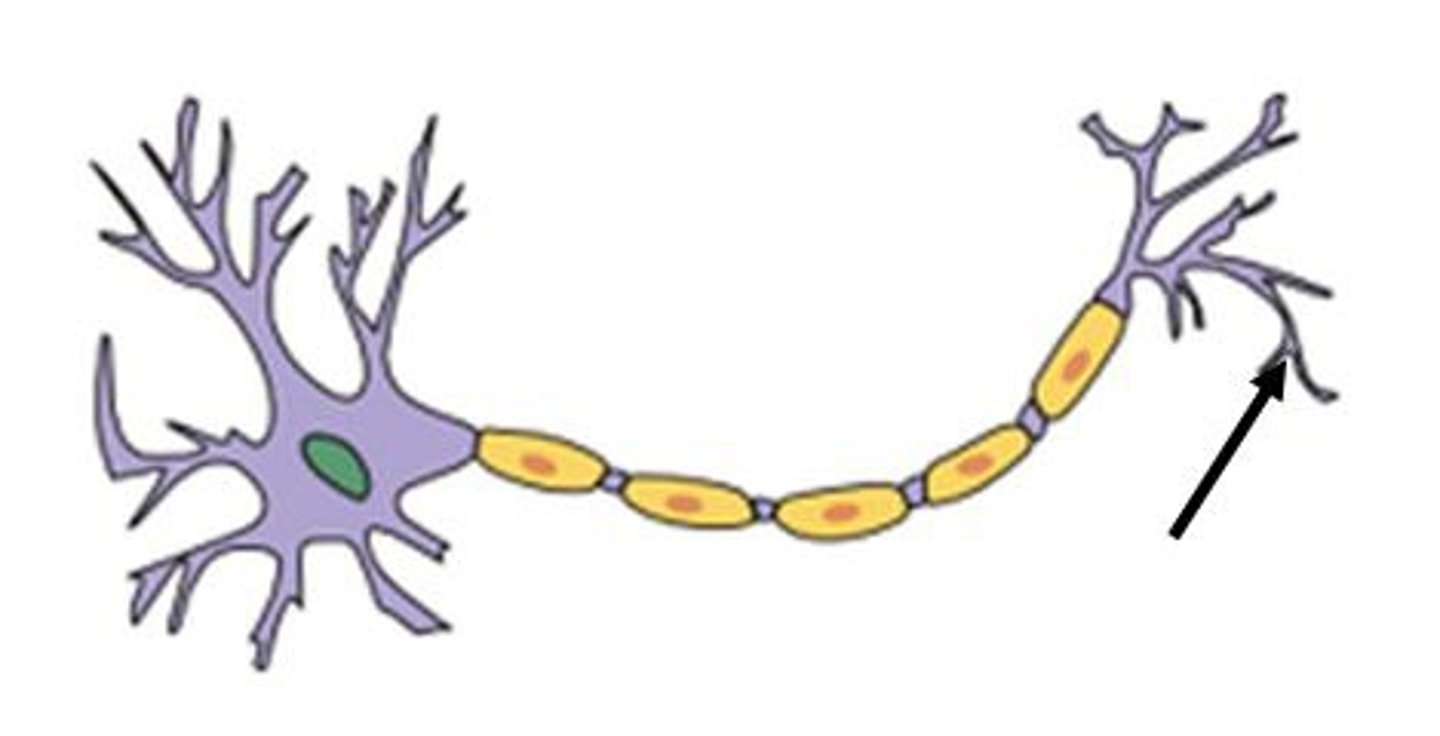
axon terminals
messenger stations that deliver signals to the next cell
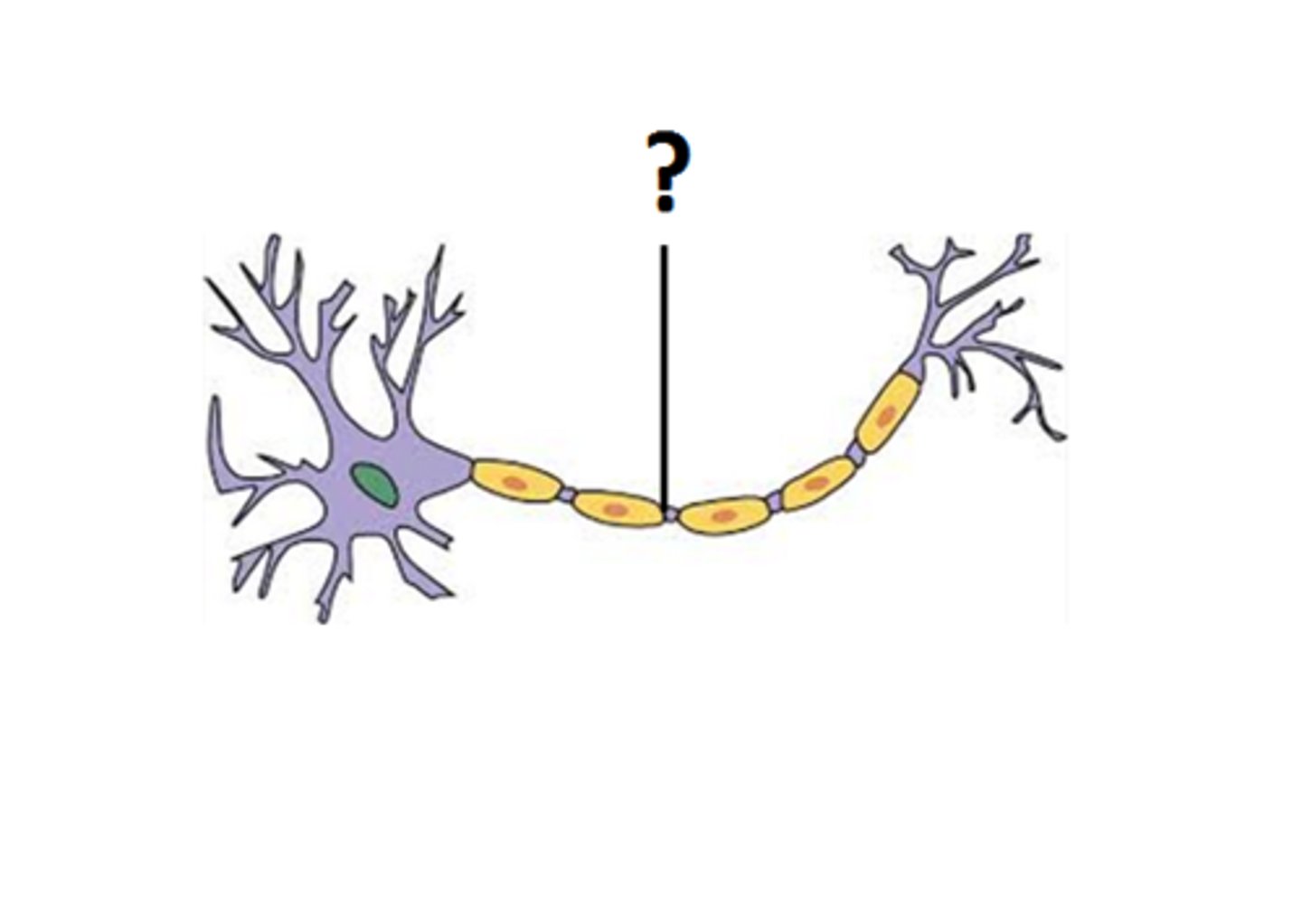
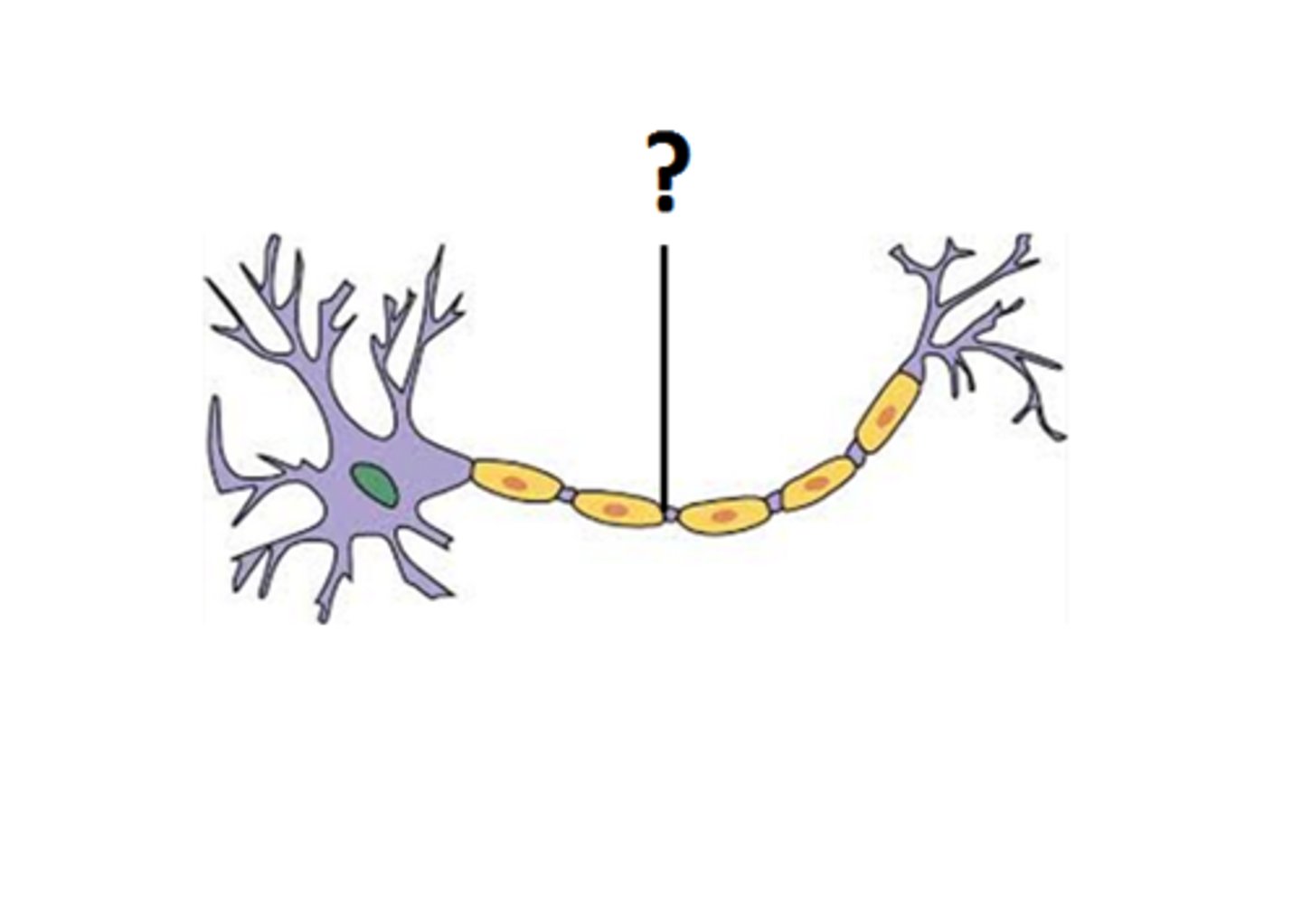
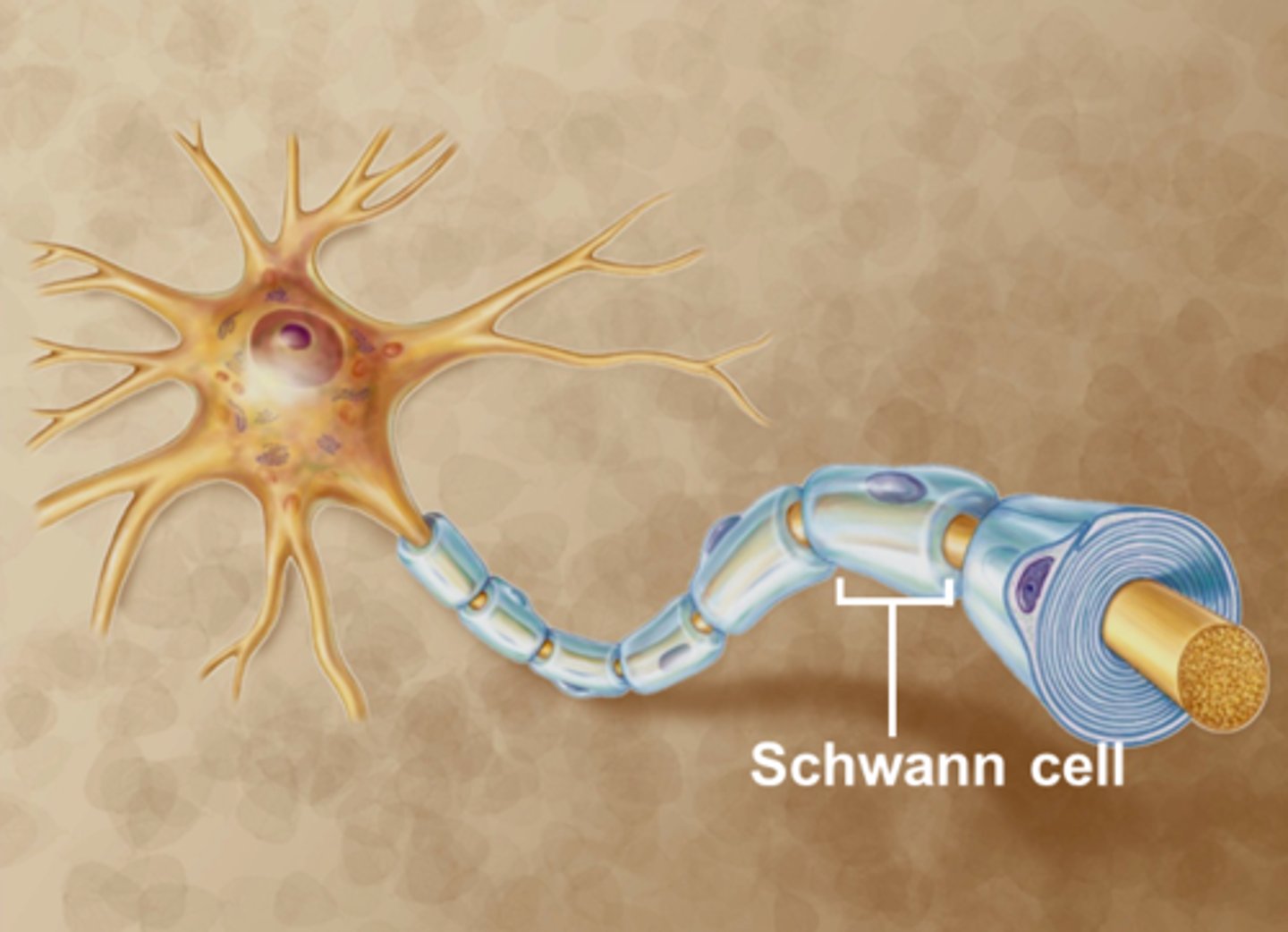
schwann cell
wrap around axons of neurons and form a protective coating called the myelin sheath.
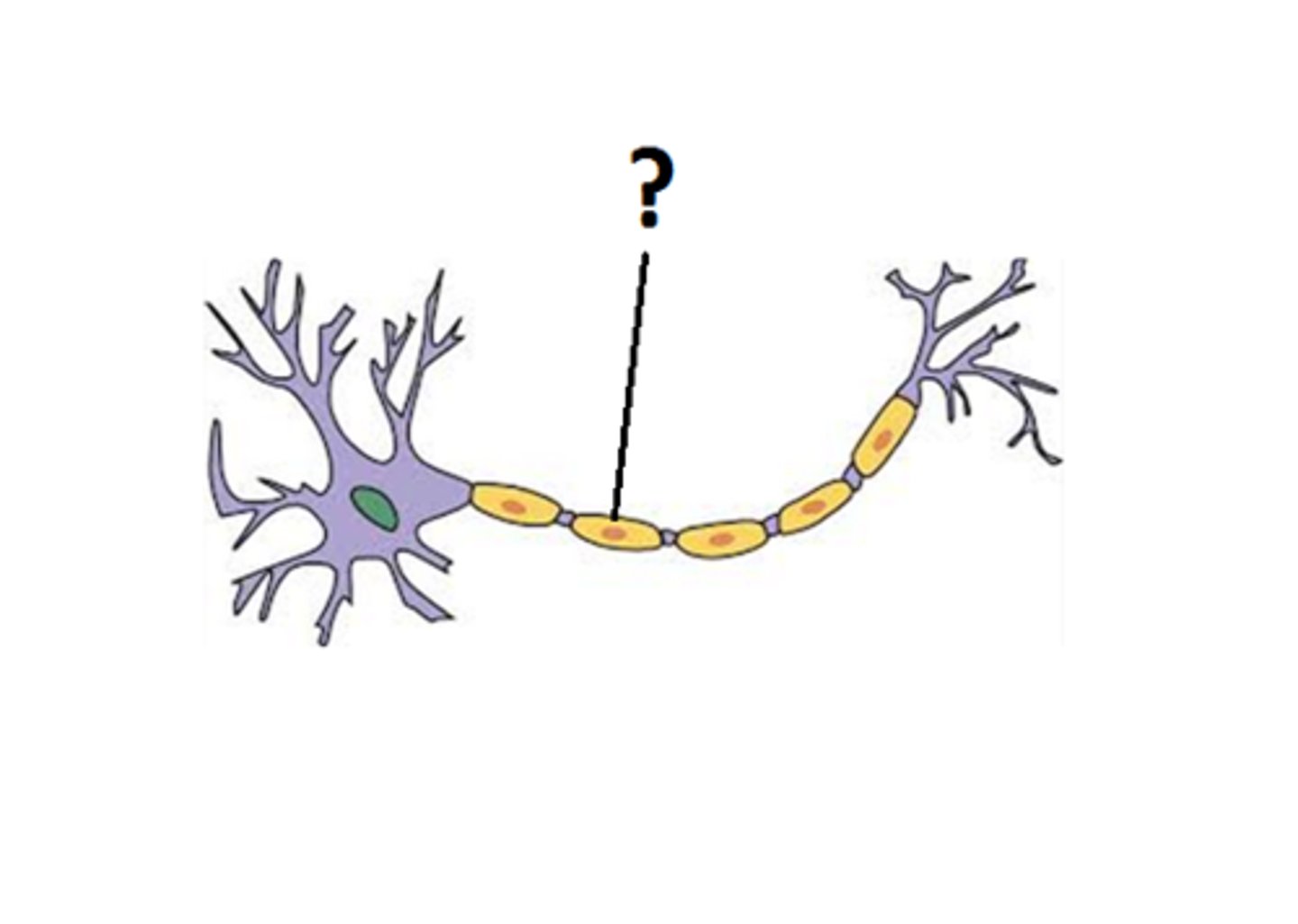
myelin
insulate the axon and help electrical signals travel faster and more efficiently along the nerve cells.
made by: shwann cells and oligodendrocytes
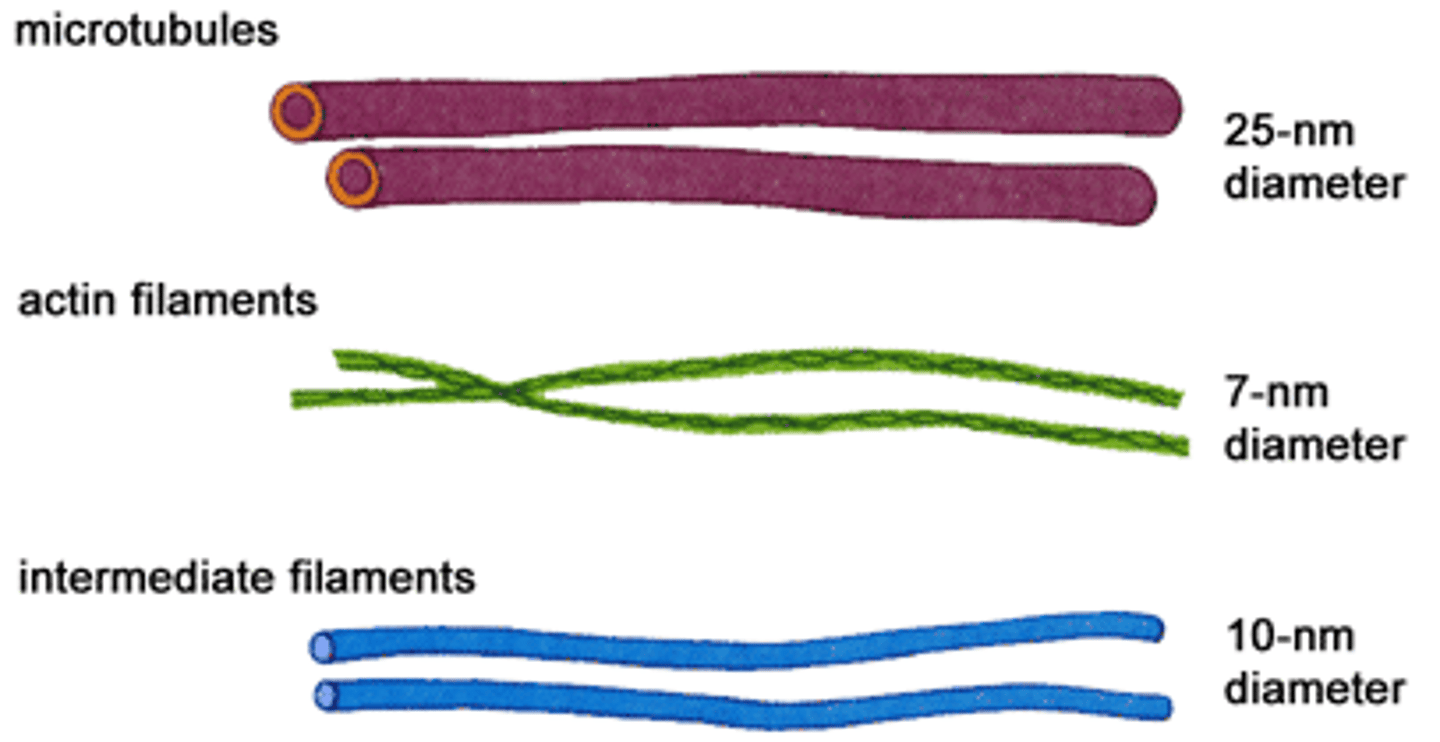
actin filaments
thin, thread-like protein fibers that are part of the cytoskeleton inside cells
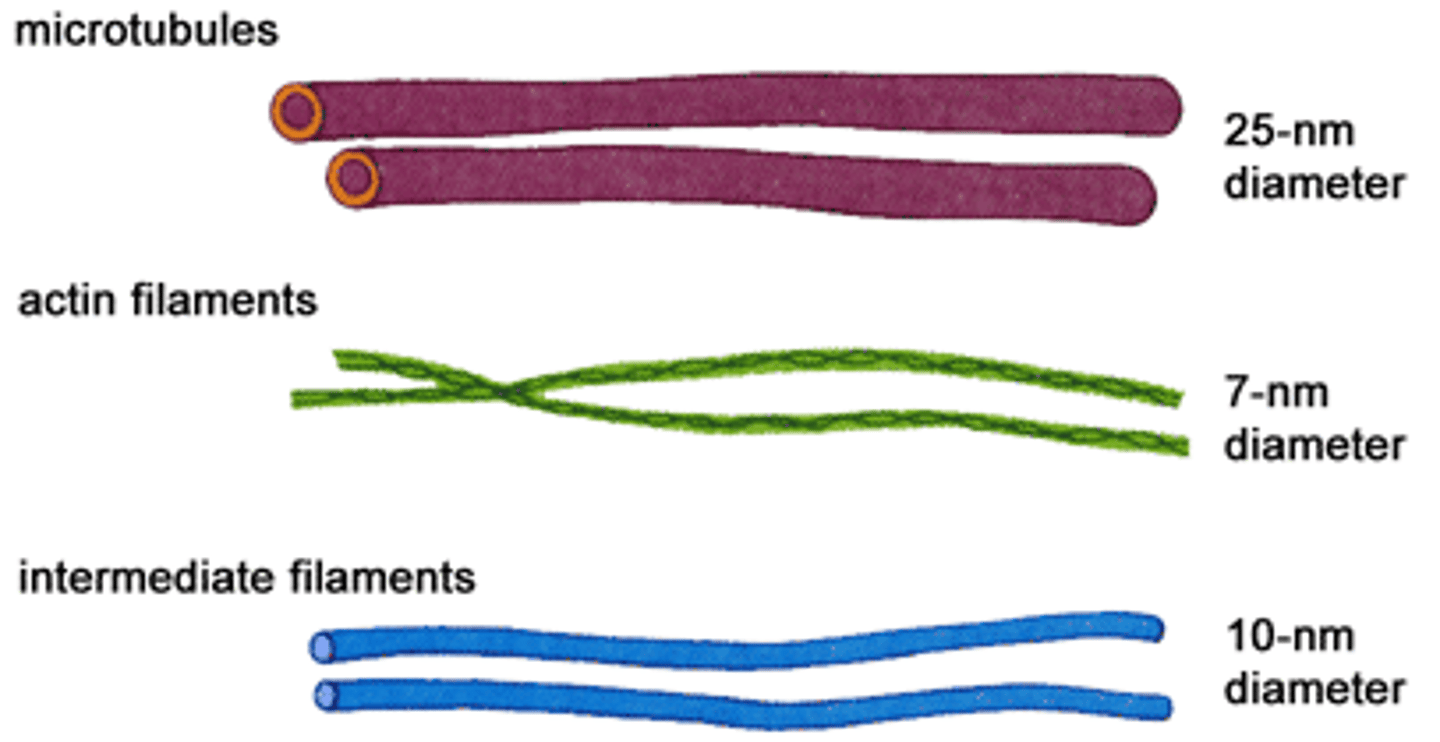
intermediate filaments
strong, rope-like protein fibers that are part of the cytoskeleton inside cells.
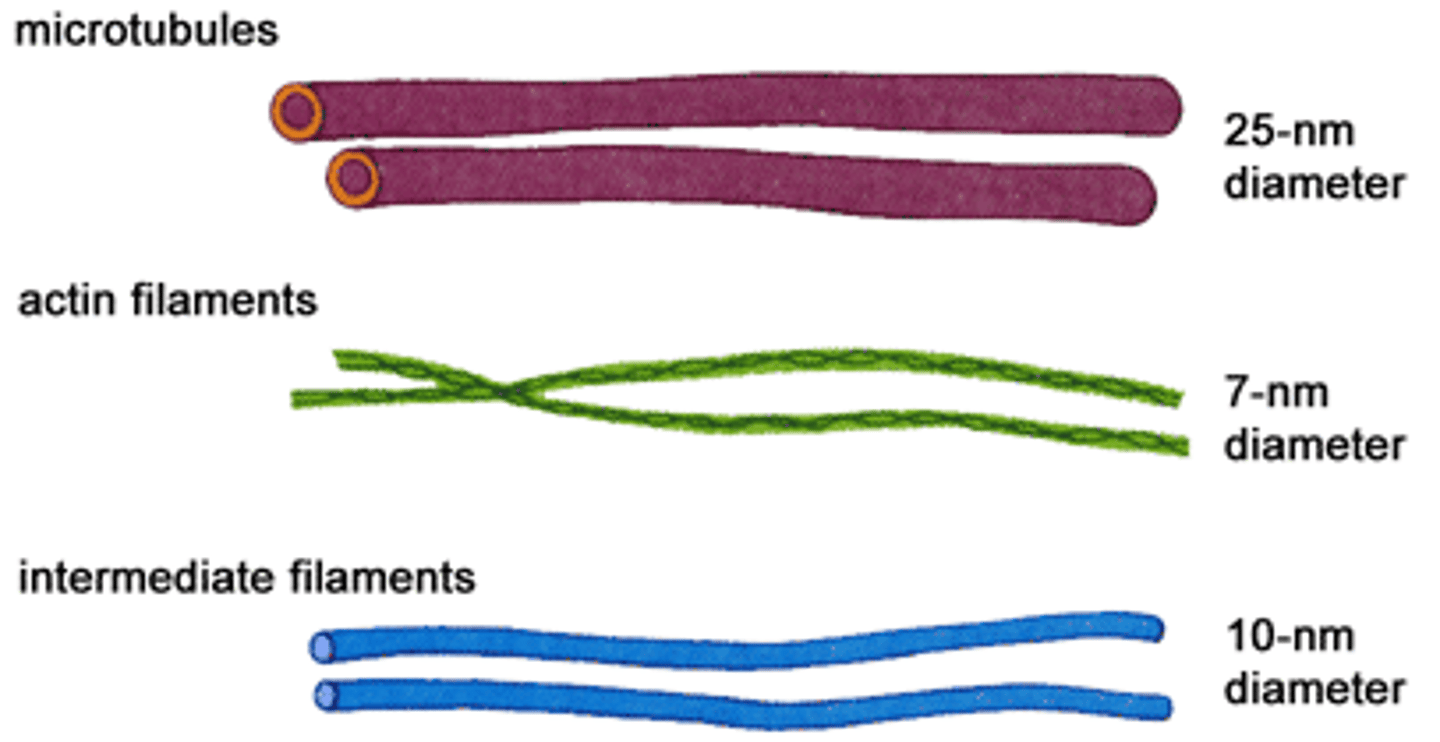
microtubules
Spiral strands of protein molecules that form a tube-like structure
Which information is correct regarding interneurons? Interneurons:
transmit impulses between neurons in the same part of the nervous system
glia are in the ______ and _______
CNS + PNS
CNS glia
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells
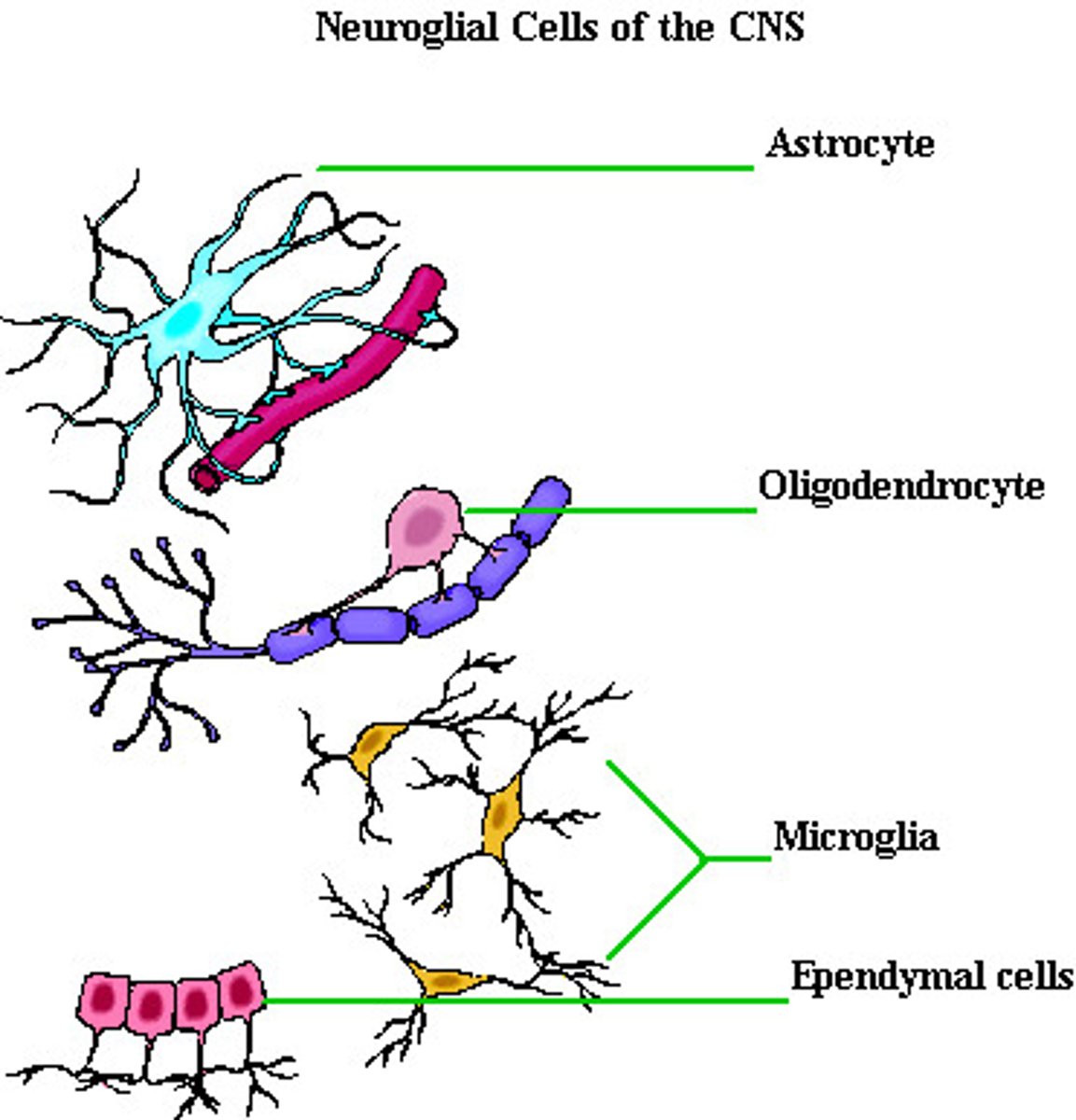
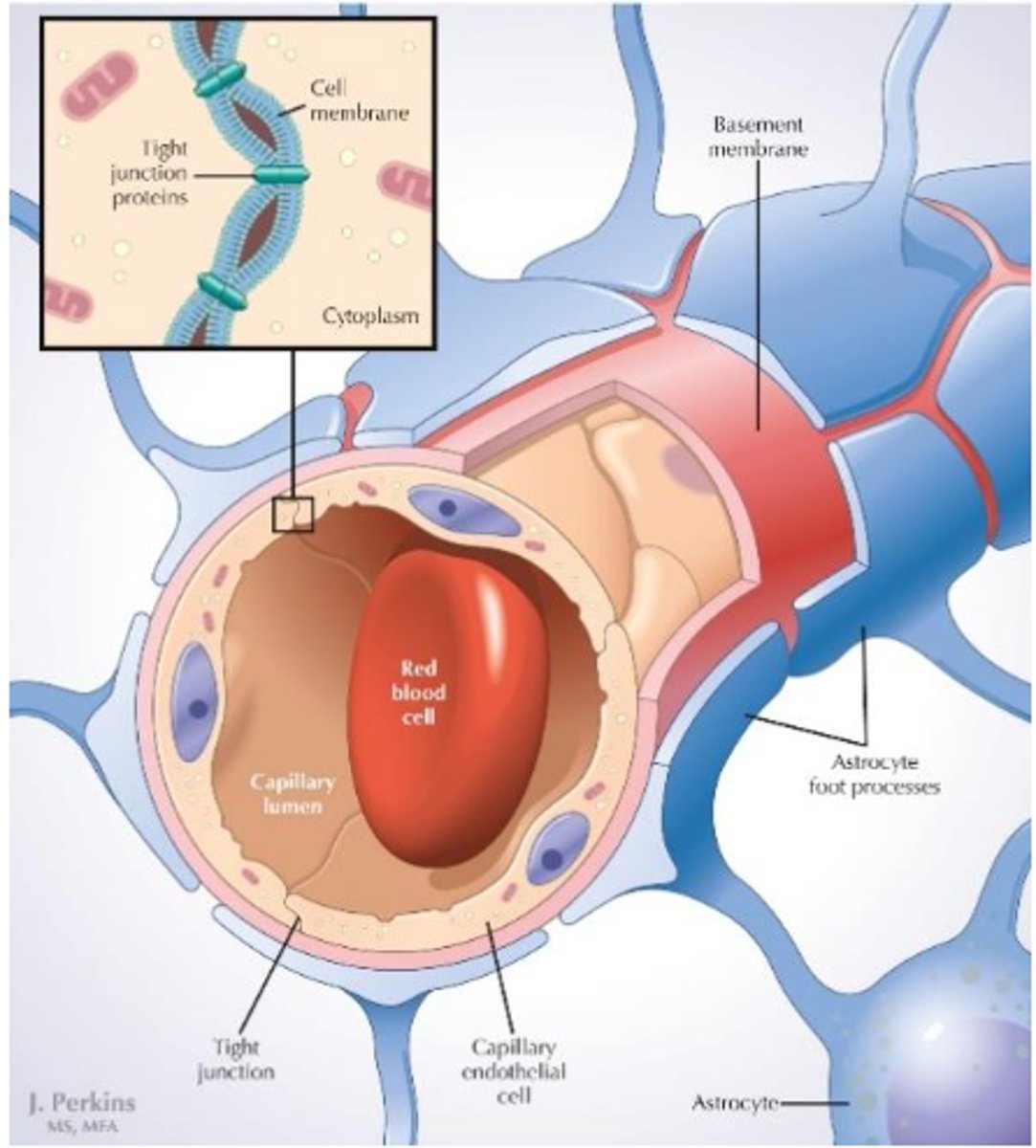
astrocytes
Provide structural and metabolic support for neurons.
form blood brain barrier
macroglia (bigger cells)
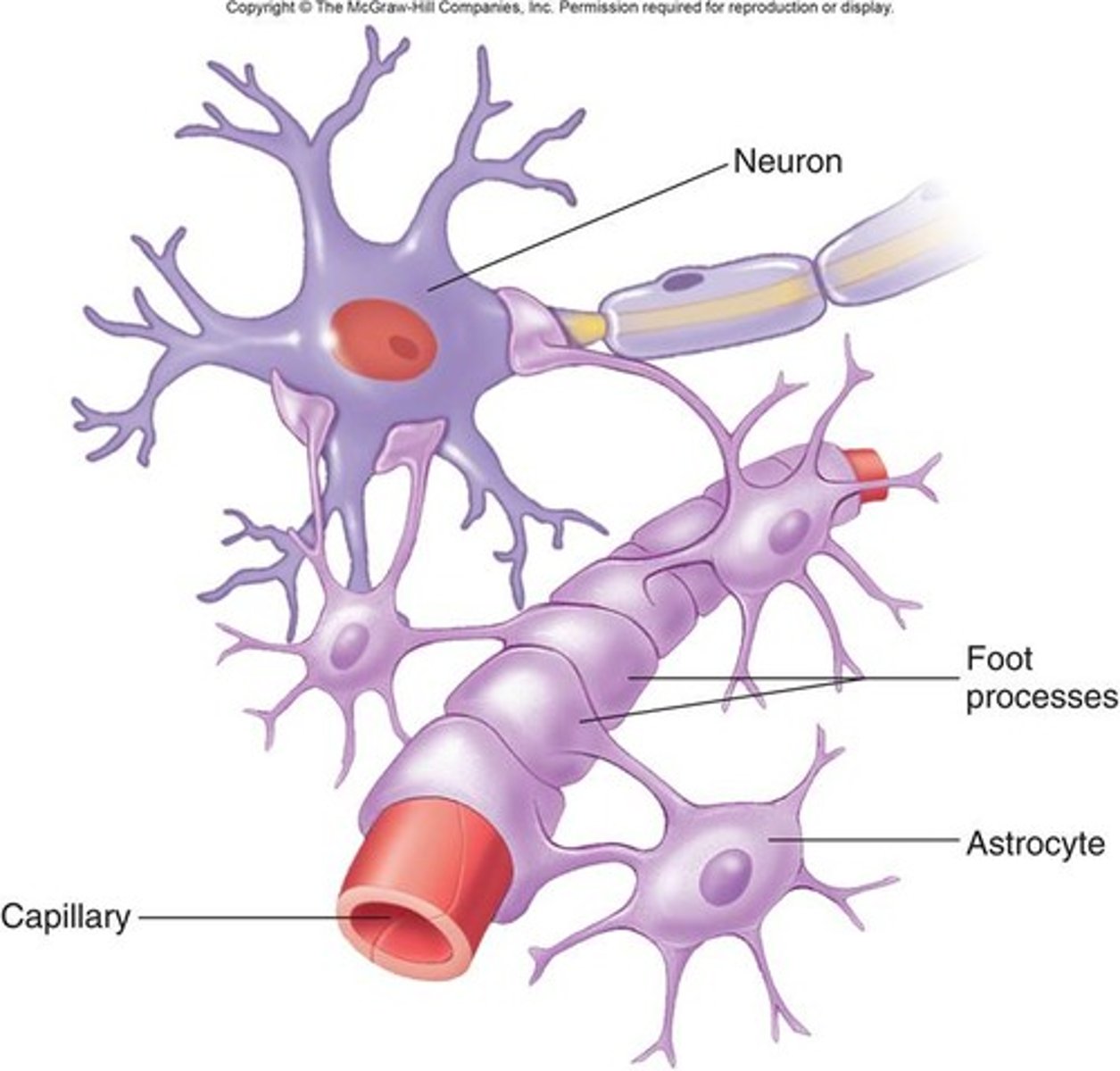
astrocyte end feet
cover capillaries and help control what substances can pass from the blood into the brain, keeping out harmful molecules.
if they didn't, body would attack our own neurons.
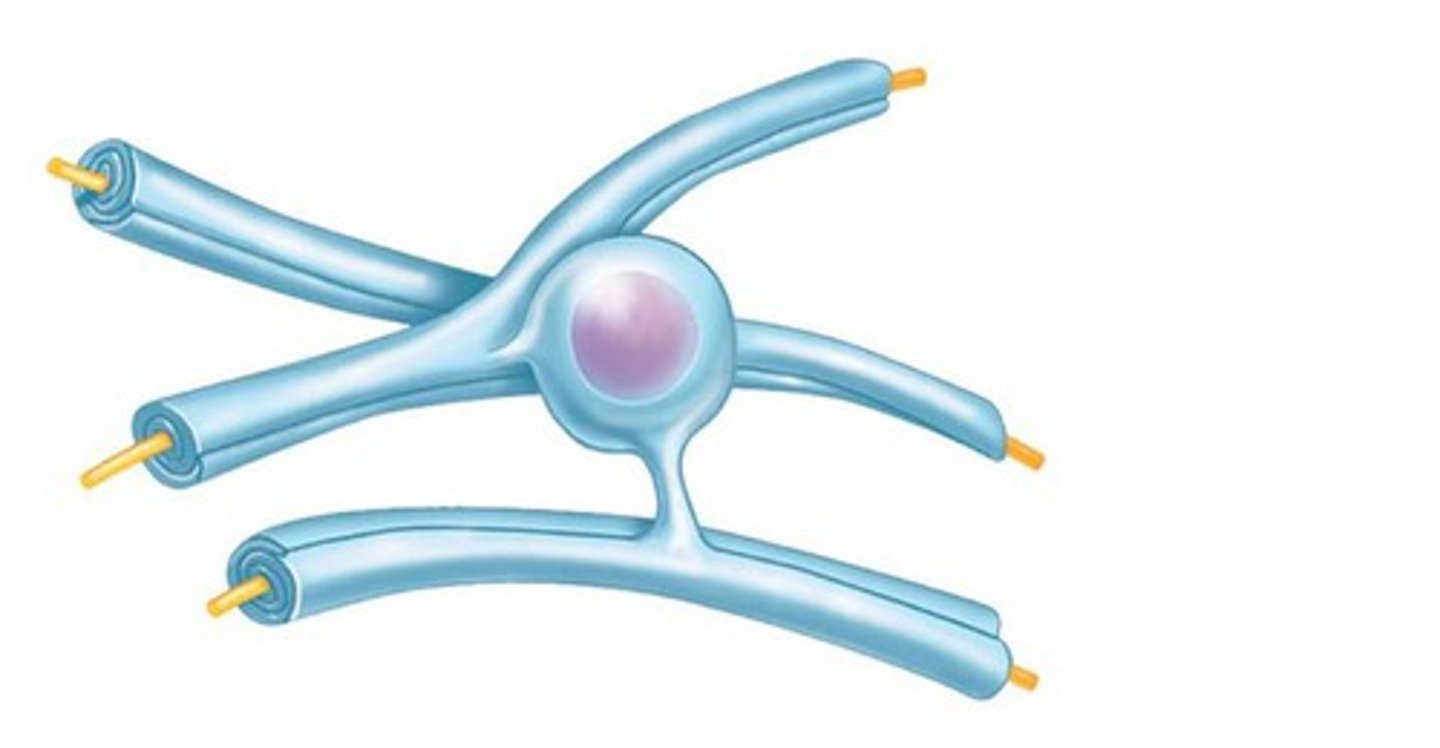
oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheath in CNS
macroglia (bigger cells)
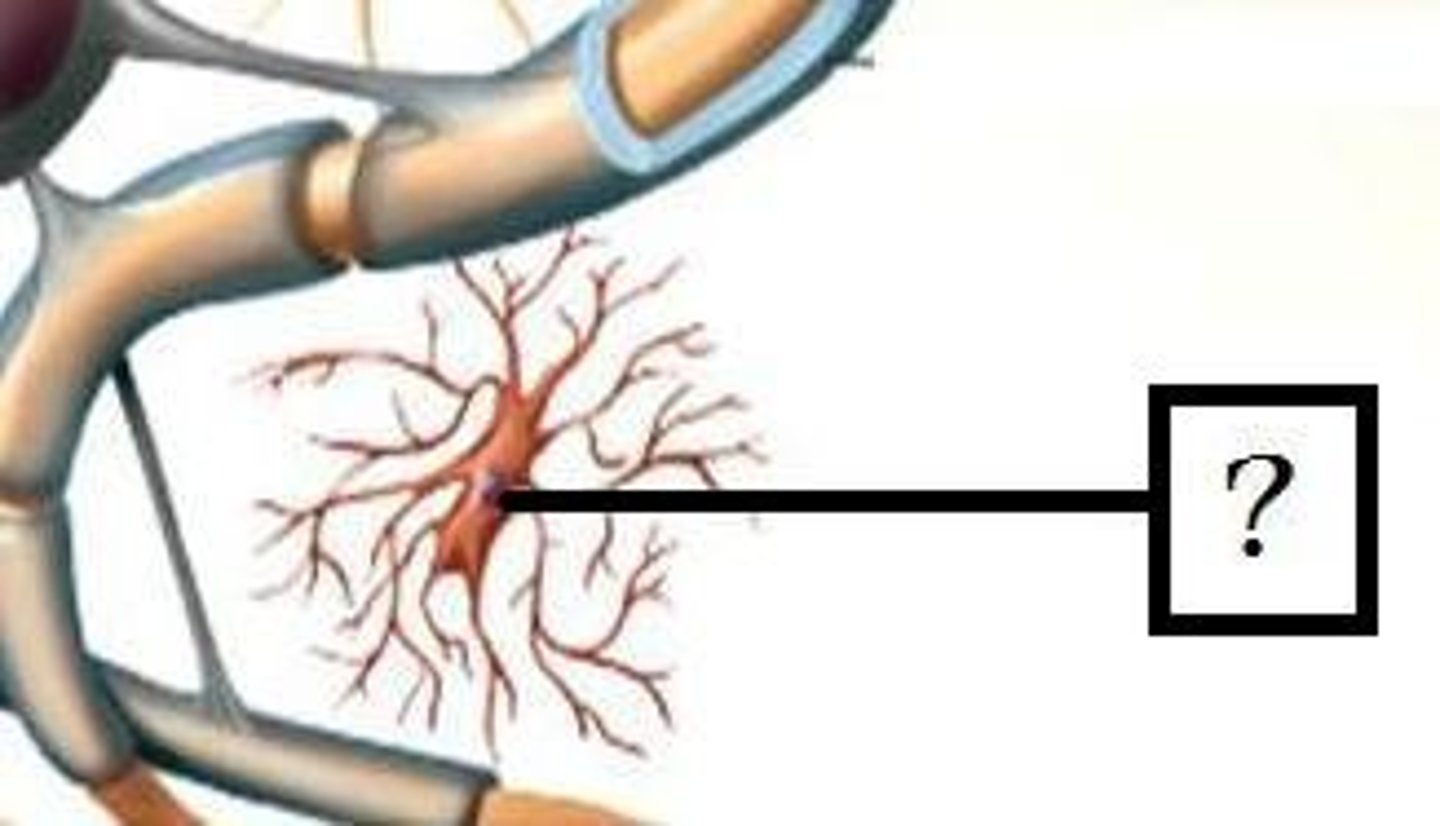
microglia
phagocytes
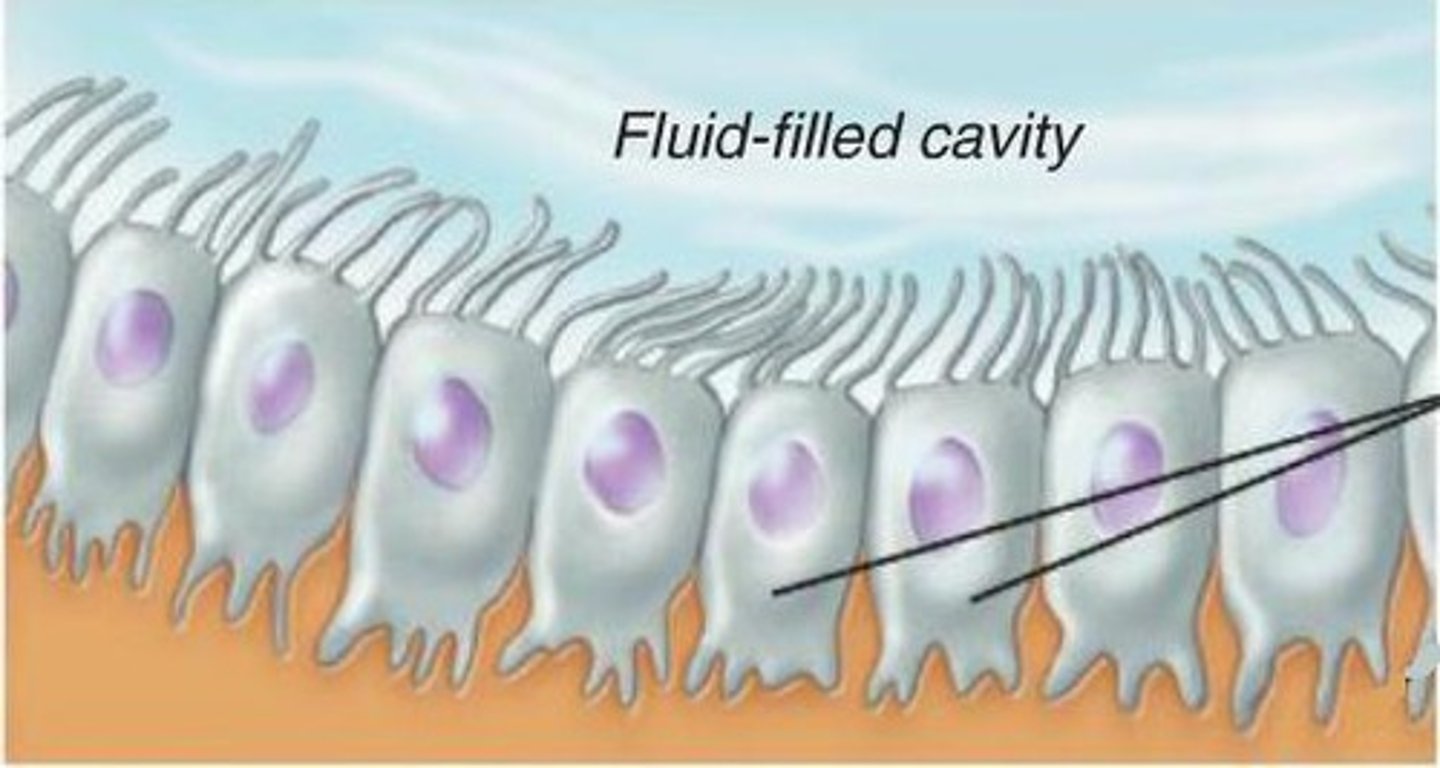
ependymal cells
lines ventricles + produce cerebrospinal fluid
PNS glia
Schwann cells and satellite cells
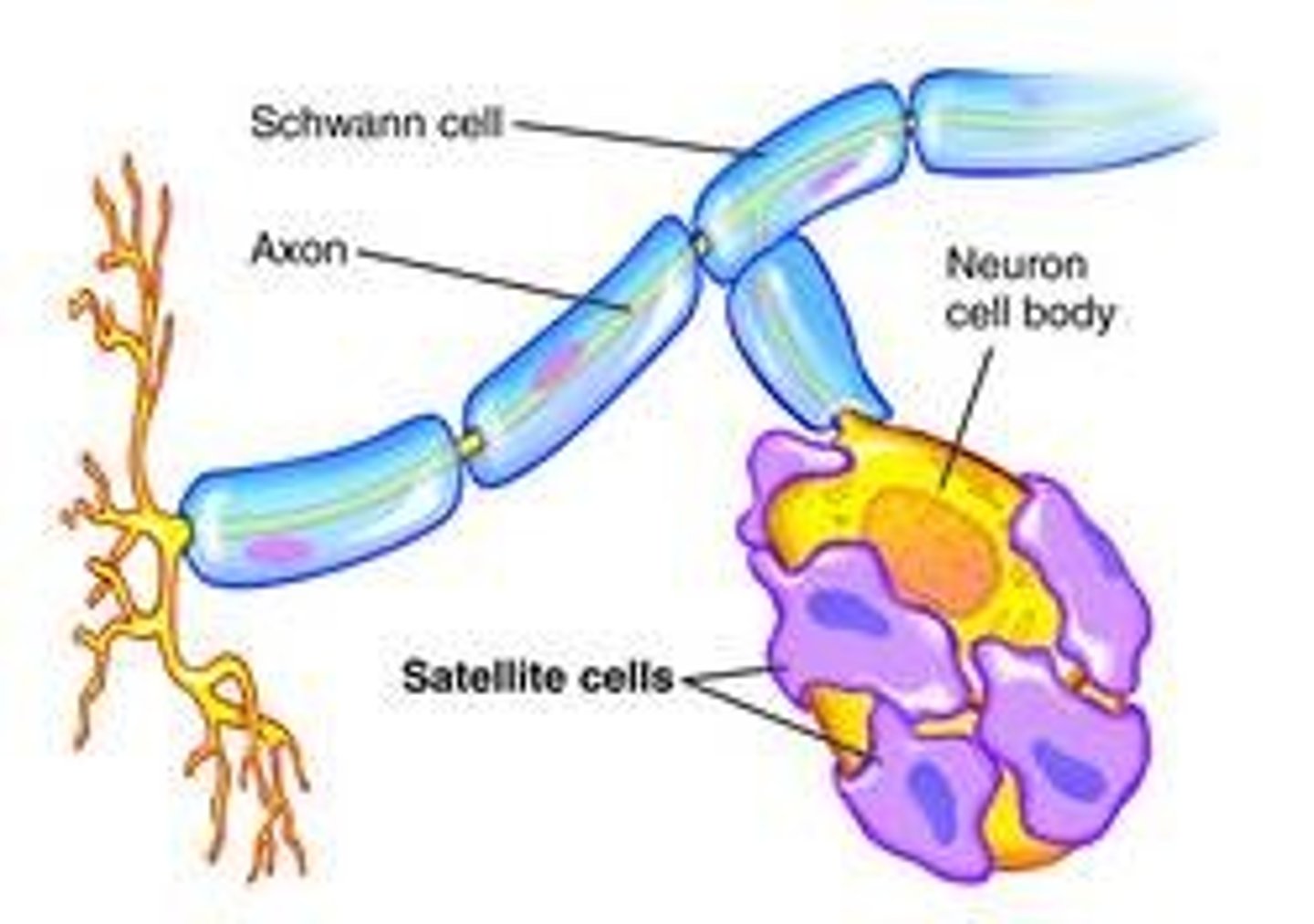
satelite cells
surround neuron cell bodies for support and fluid exchange
can form new neurons
they act like nurses
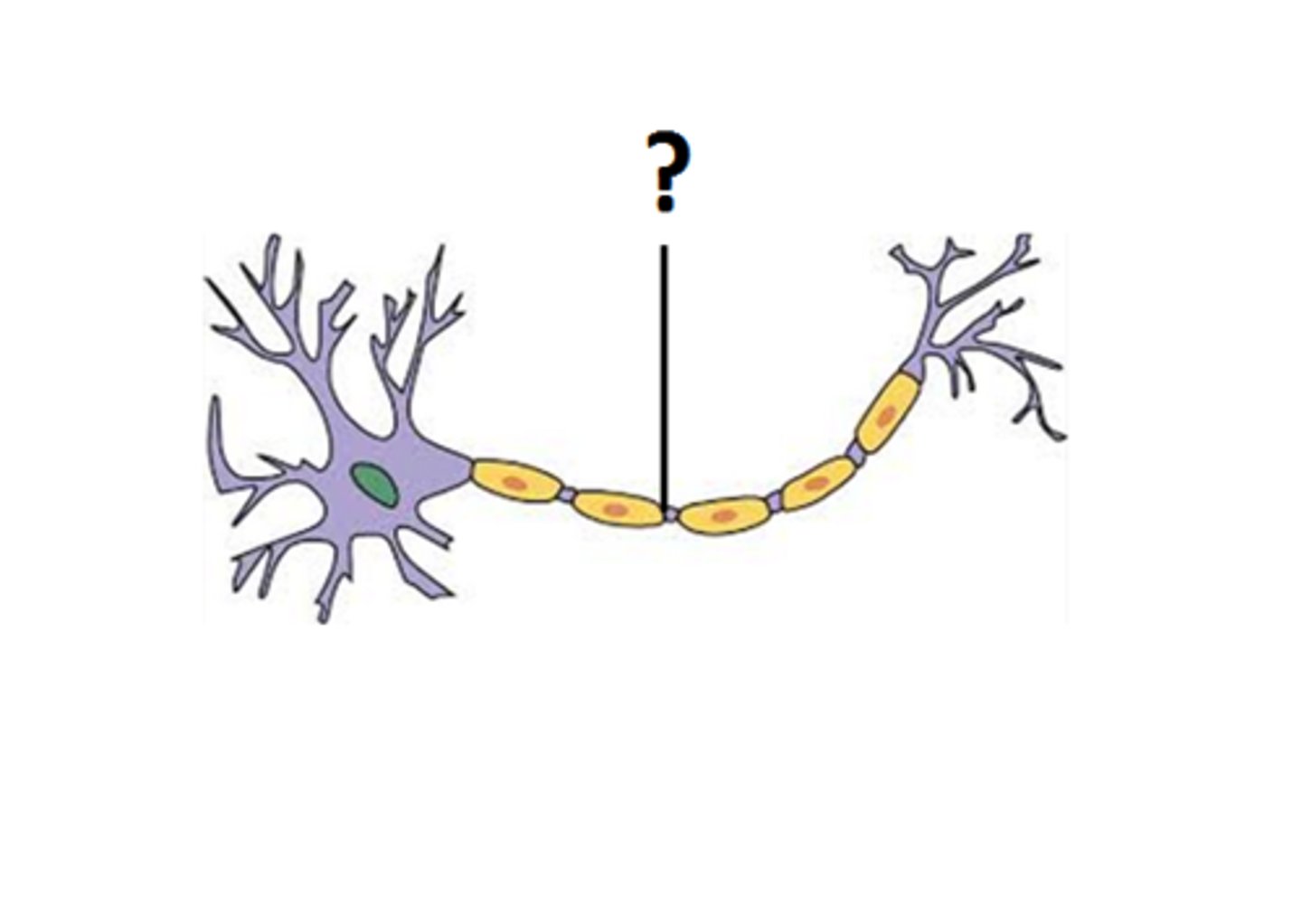
node of ranvier
small gap between the myelin sheath segments that cover an axon. These gaps are not insulated and are rich in ion channels.
Wallerian degeneration
degeneration of the distal portion of the axon and myelin sheath

distal changes
distal axon degrades
schwann cells induced to proliferate

proximal changes
sprouting (trying to recover by regenerating its axon)

regeneration of axons
ONLY in PNS
ONLY if lesion is small
if damage is close to cell body, more likely it is to die
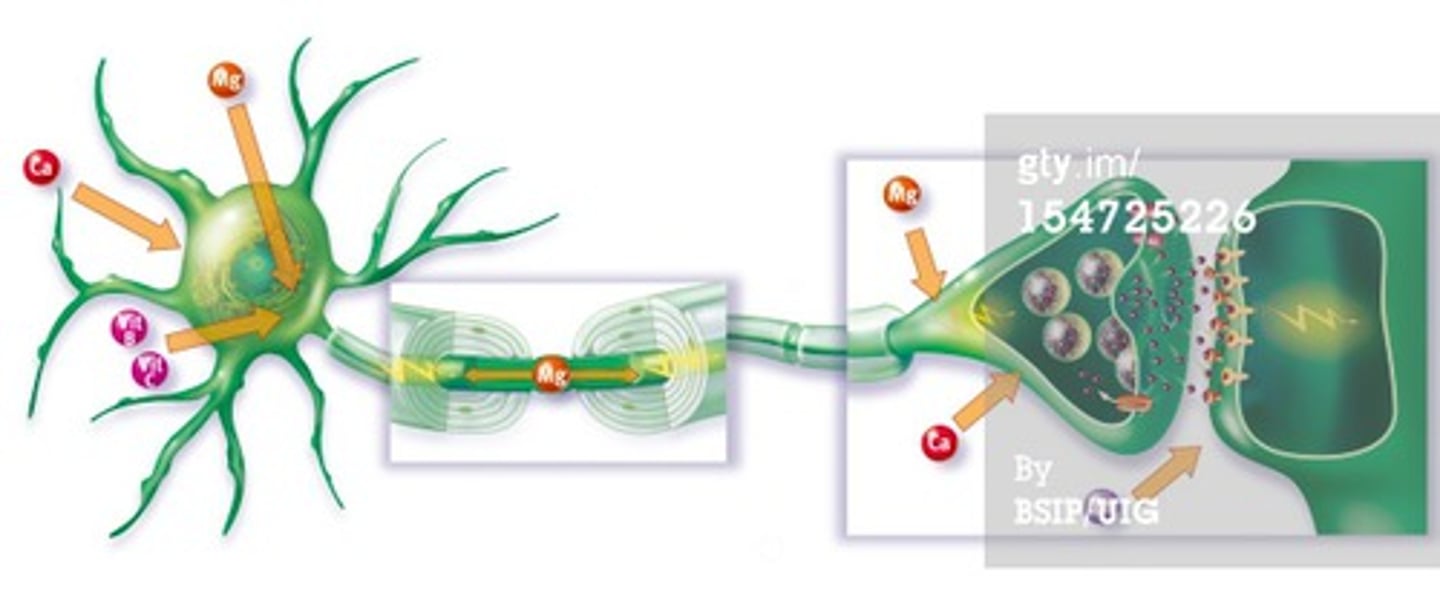
nerve impulse (neurocommunication)
involves changes from the resting membrane potential (electrical) followed by release of a neurotransmitter that binds to receptors on target cell. target cell response depends on the neurotransmitter that is released.
two types of changes in nerve impulses
local change
generation of action potential
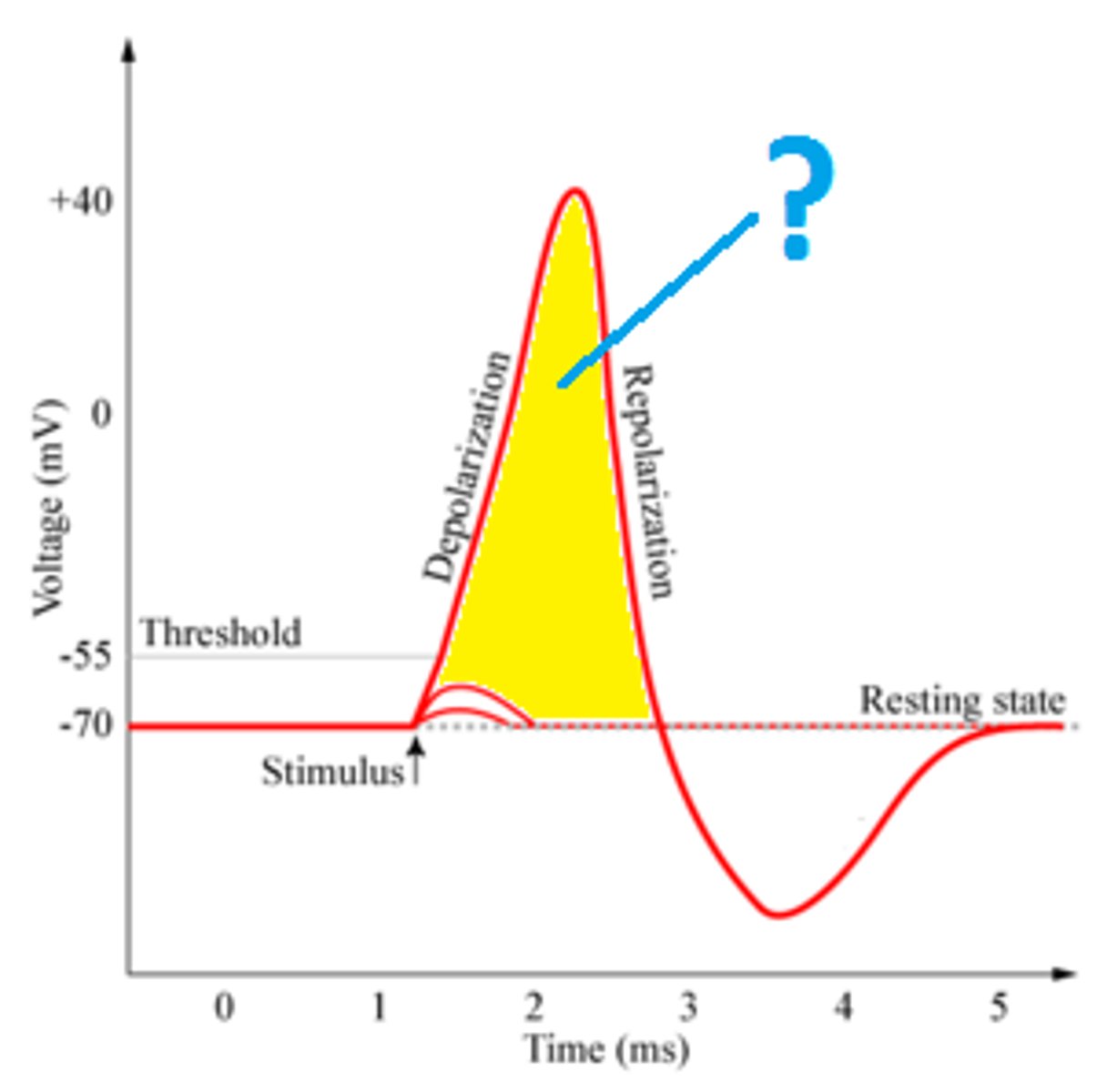
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
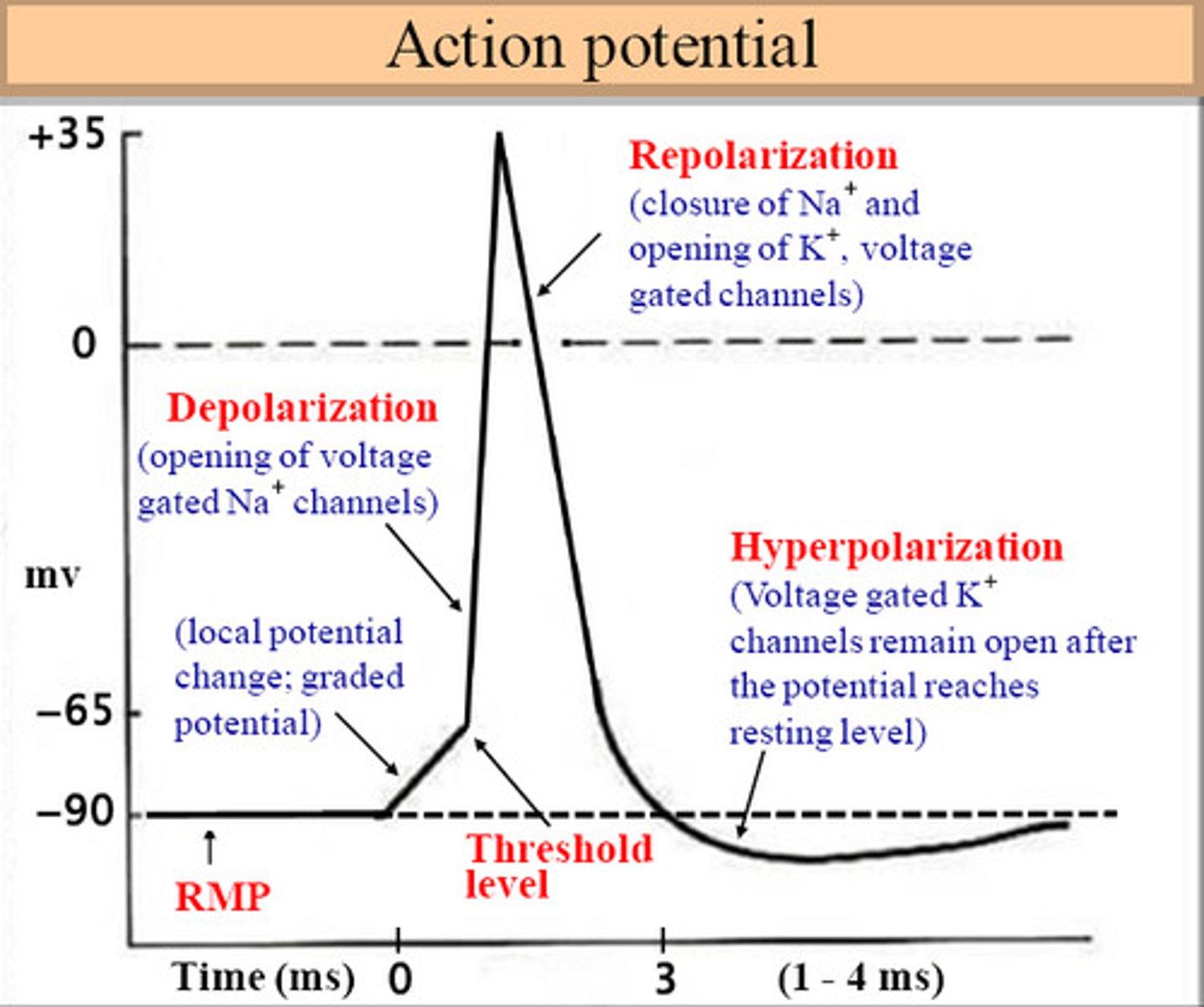
nerve impulse: resting stage
"polarization"
the neuron is at rest with a negative charge inside and a positive charge outside
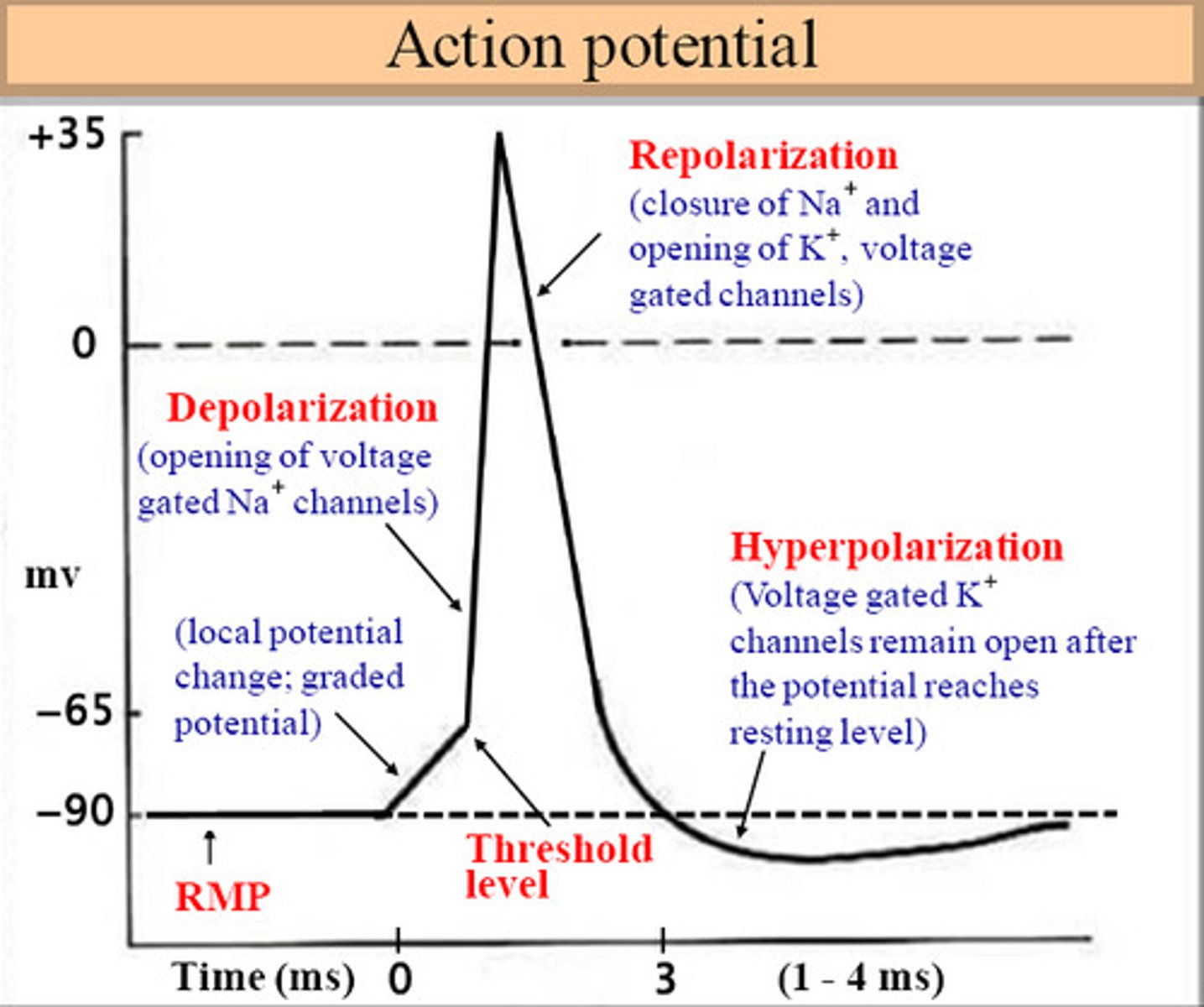
nerve impulse: triggering the impulse
"depolarization"
When a neuron gets stimulated (by a chemical signal, for example), sodium channels open.
Na⁺ ions rush in, making the inside more positive.
This change in charge creates an action potential (the actual nerve impulse).
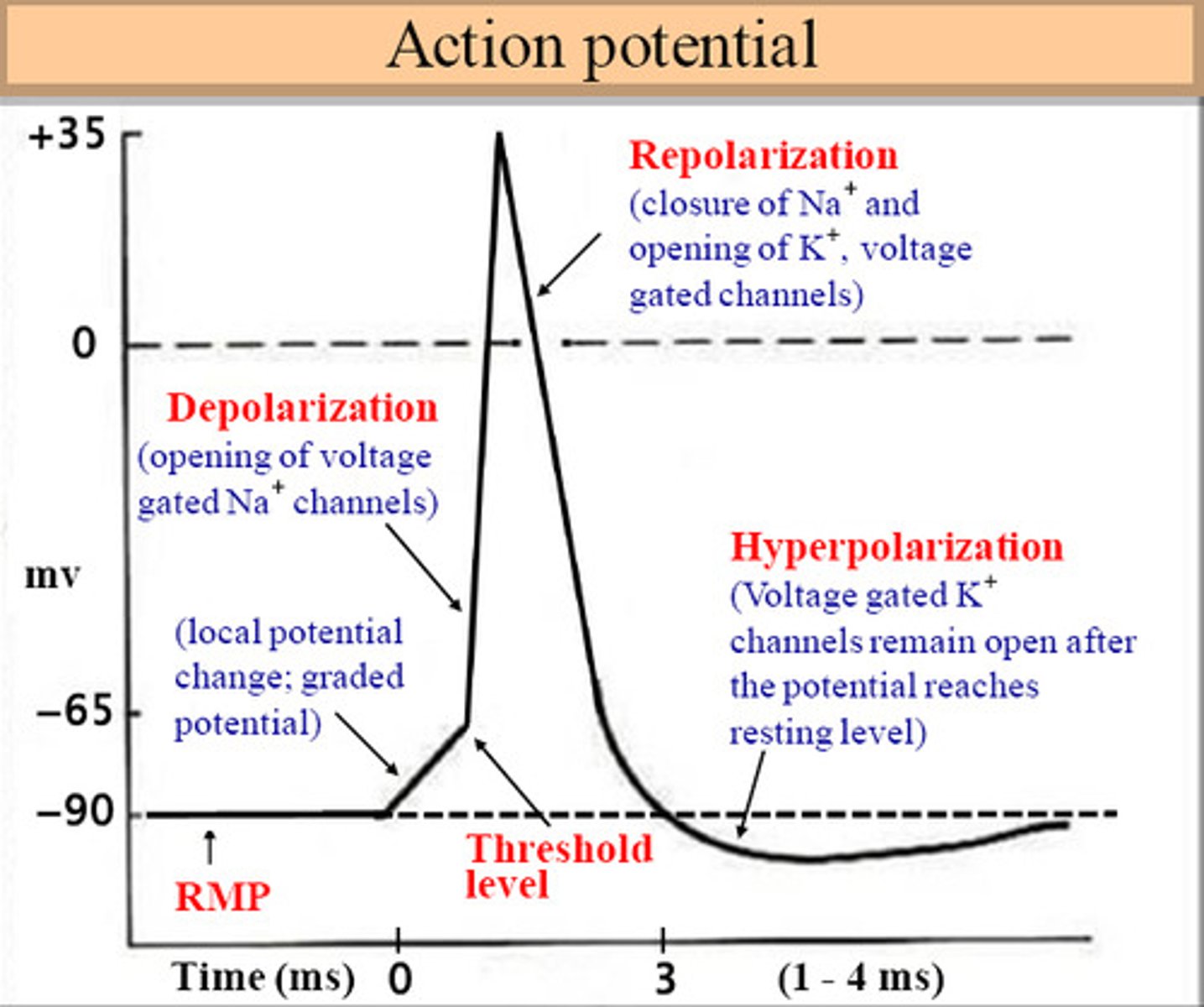
nerve impulse: resetting the neuron
"repolarization"
To return to its resting state, potassium channels open and K⁺ ions flow out, making the inside negative again.
The sodium-potassium pump restores the original balance of ions.
nerve impulse: passing the message
"synaptic transmission"
When the impulse reaches the axon terminals, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters into the synapse (the gap between neurons).
Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the next neuron, triggering a new impulse if the signal is strong enough.
postsynaptic neuron
neuron that receives the signal
presynaptic neuron
conducts impulses toward the synapse
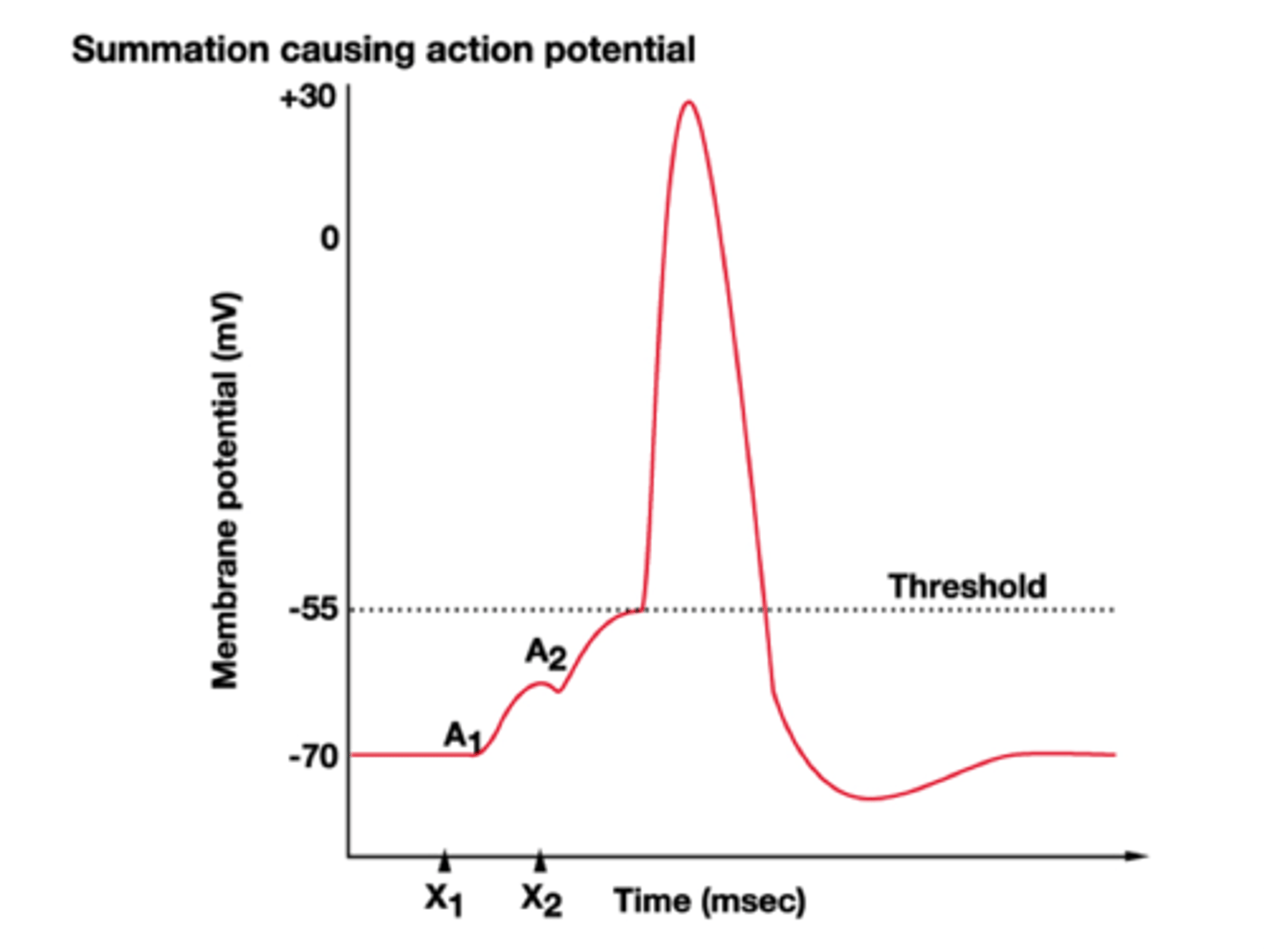
temporal summation
process in which multiple nerve impulses from the same presynaptic neuron are sent one after another in quick succession to a single postsynaptic neuron. These rapid signals add up (or summate) over time to reach the threshold needed to trigger an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron.
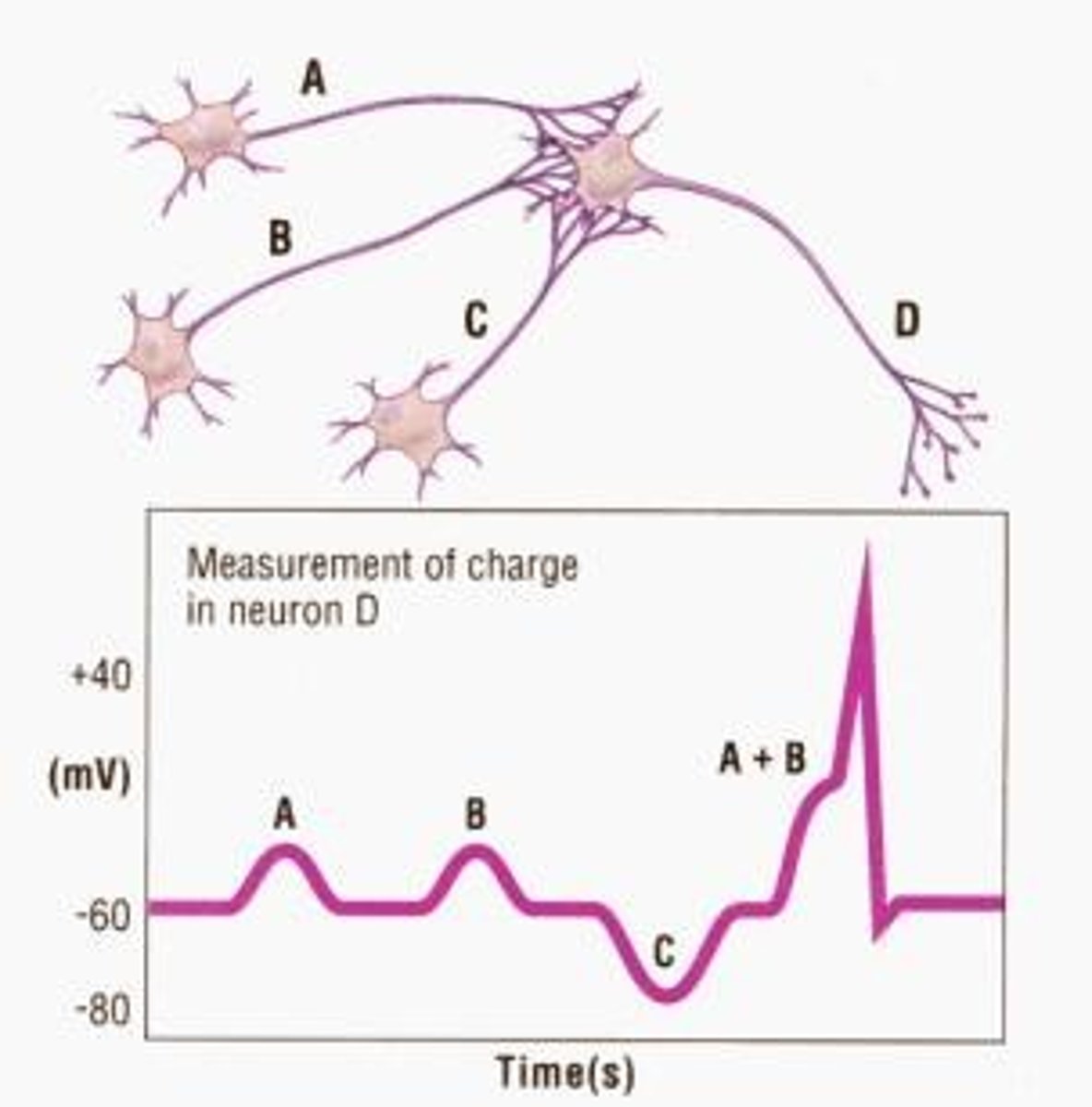
spatial summation
multiple presynaptic neurons send signals at the same time to a single postsynaptic neuron. These signals add up (or summate) across different locations on the postsynaptic membrane. If the combined effect is strong enough to reach the threshold, it triggers an action potential (nerve impulse) in the postsynaptic neuron.
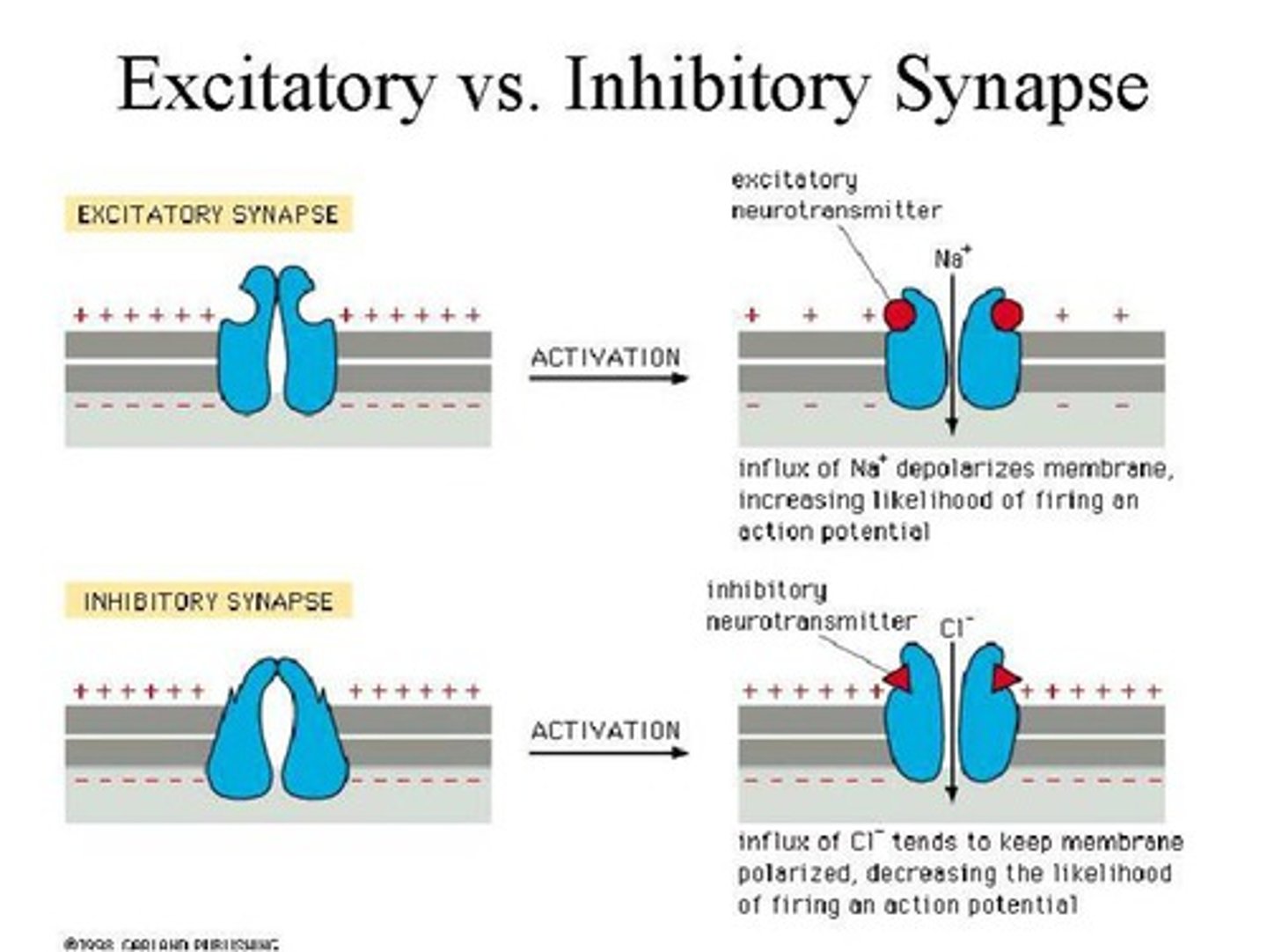
excitatory neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that increase the likelihood that a nerve impulse (or action potential) will be triggered in the postsynaptic neuron.
They do this by binding to receptors on the postsynaptic cell and causing positive ions (like sodium, Na⁺) to flow in, making the inside of the neuron more positive (a process called depolarization)
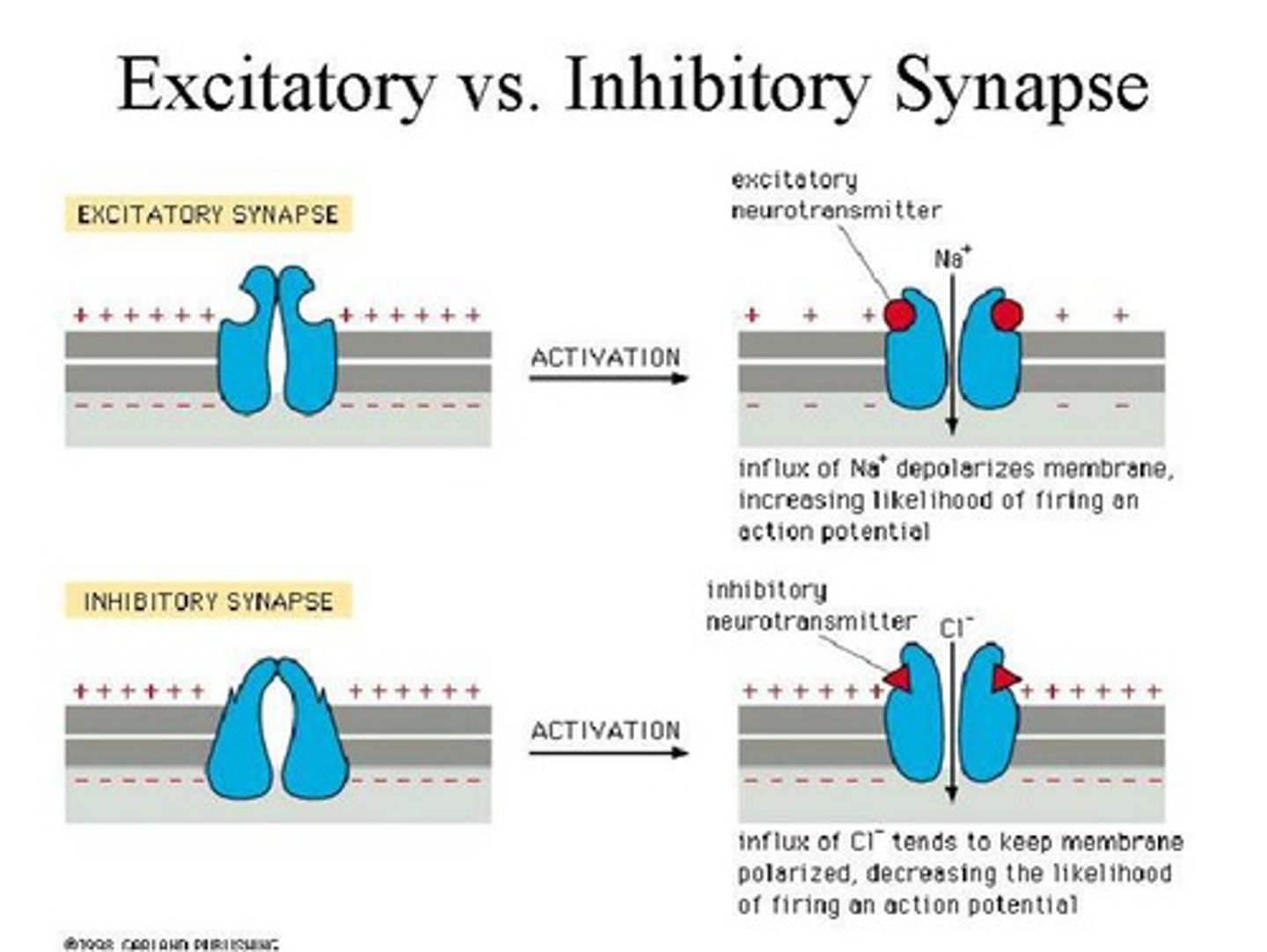
inhibitory neurotransmitters
decrease the likelihood that a nerve impulse (or action potential) will be triggered in the postsynaptic neuron.
They do this by binding to receptors on the postsynaptic cell and causing negative ions (like chloride, Cl⁻) to flow in or positive ions (like potassium, K⁺) to flow out.
This makes the inside of the neuron more negative (a process called hyperpolarization), moving it farther from the threshold needed to fire an action potential.
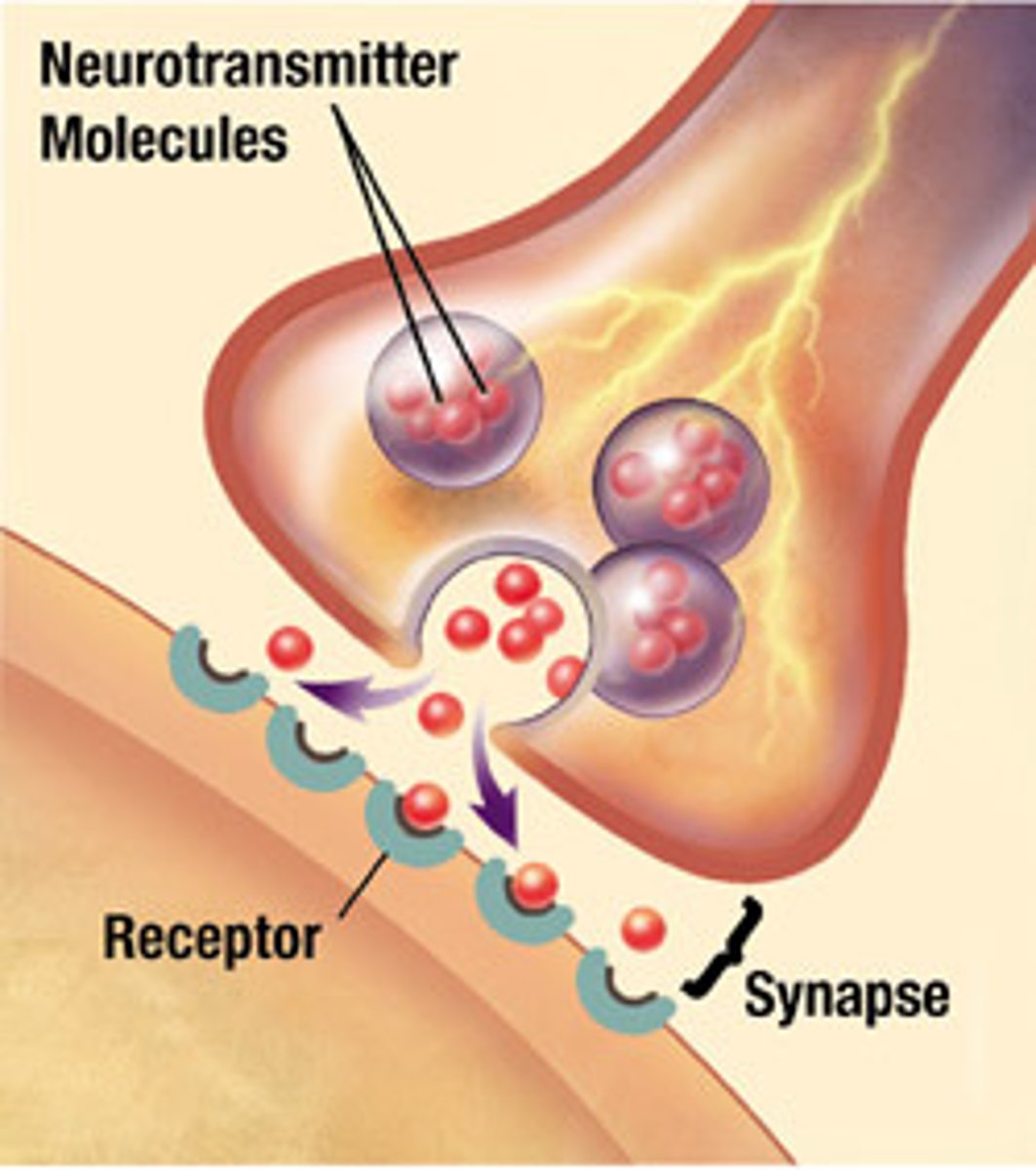
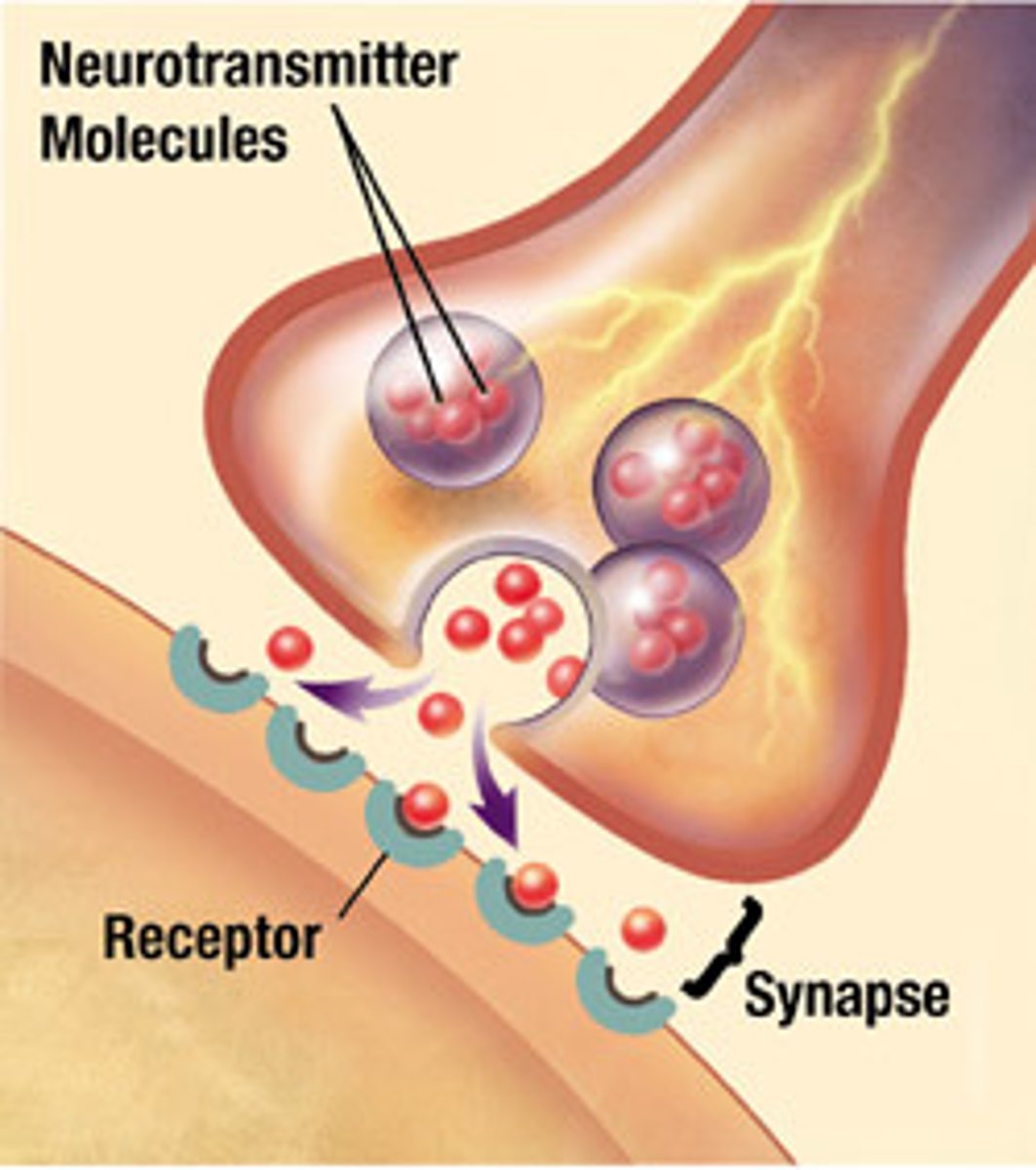
synapses
chemical
tiny gap between two neurons (or between a neuron and another cell, like a muscle cell) where nerve signals are passed from one cell to the next.
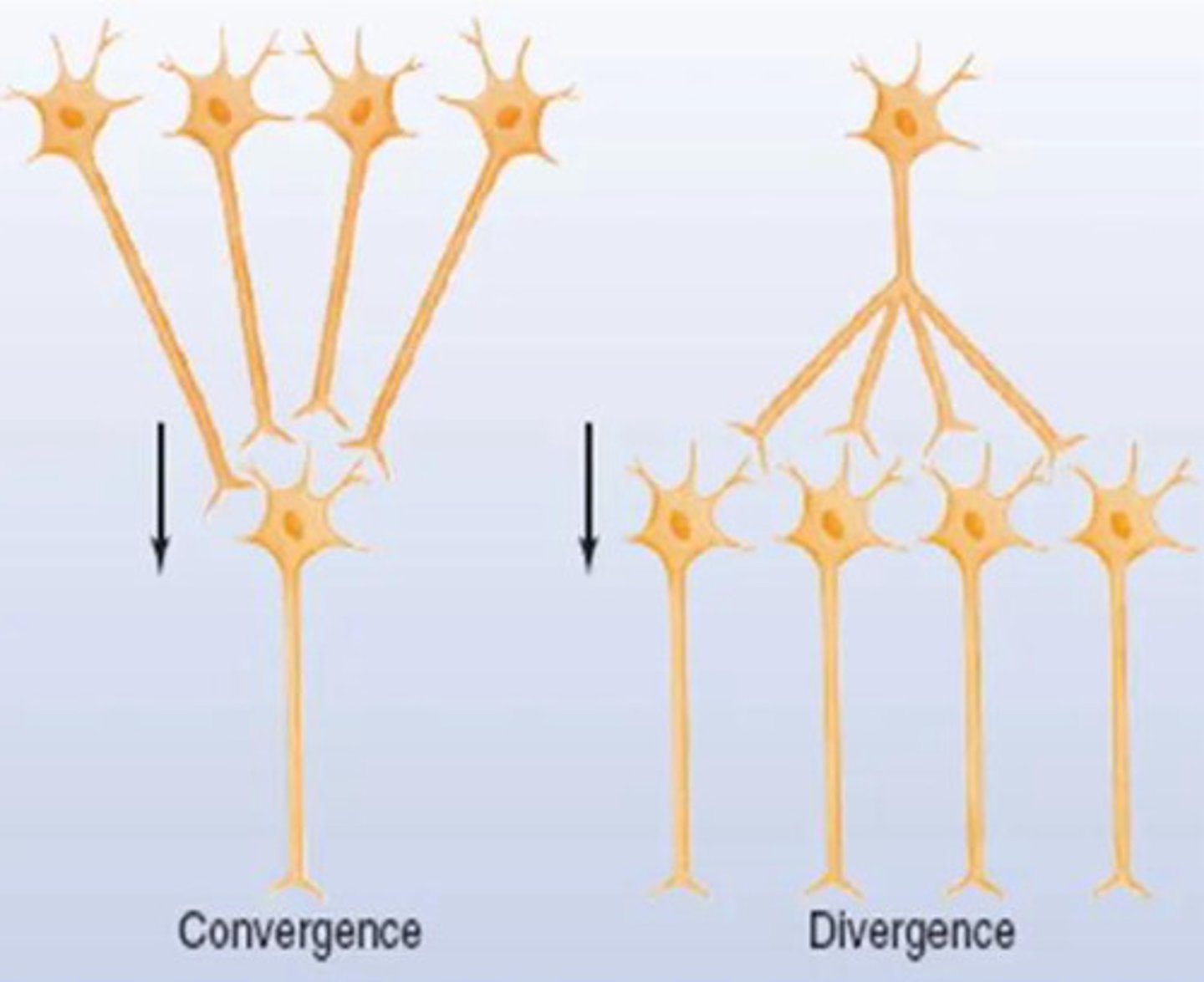
convergent signaling
when multiple neurons send signals to one single neuron
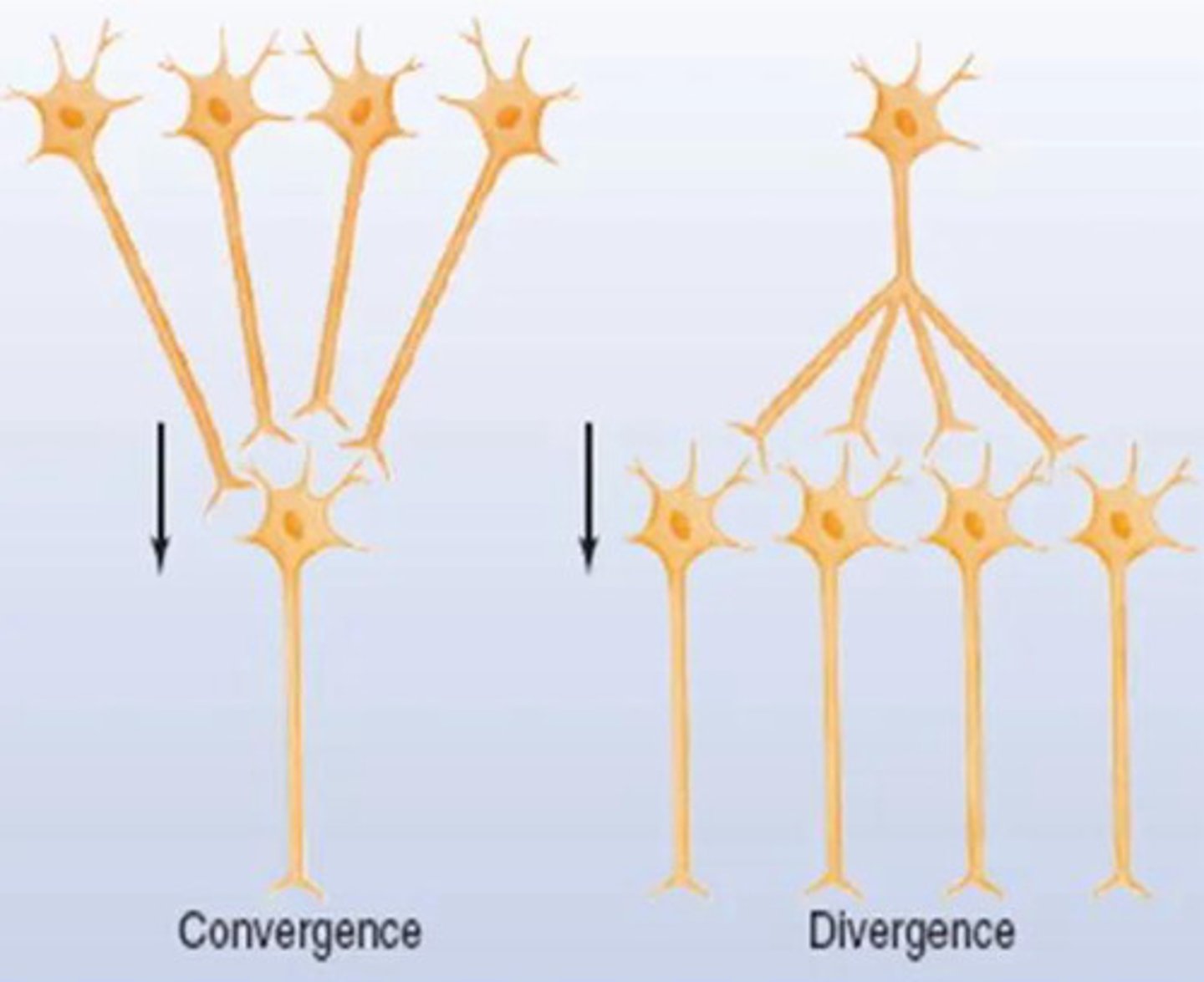
divergent signaling
one presynaptic neuron signals to multiple post-synaptic neurons
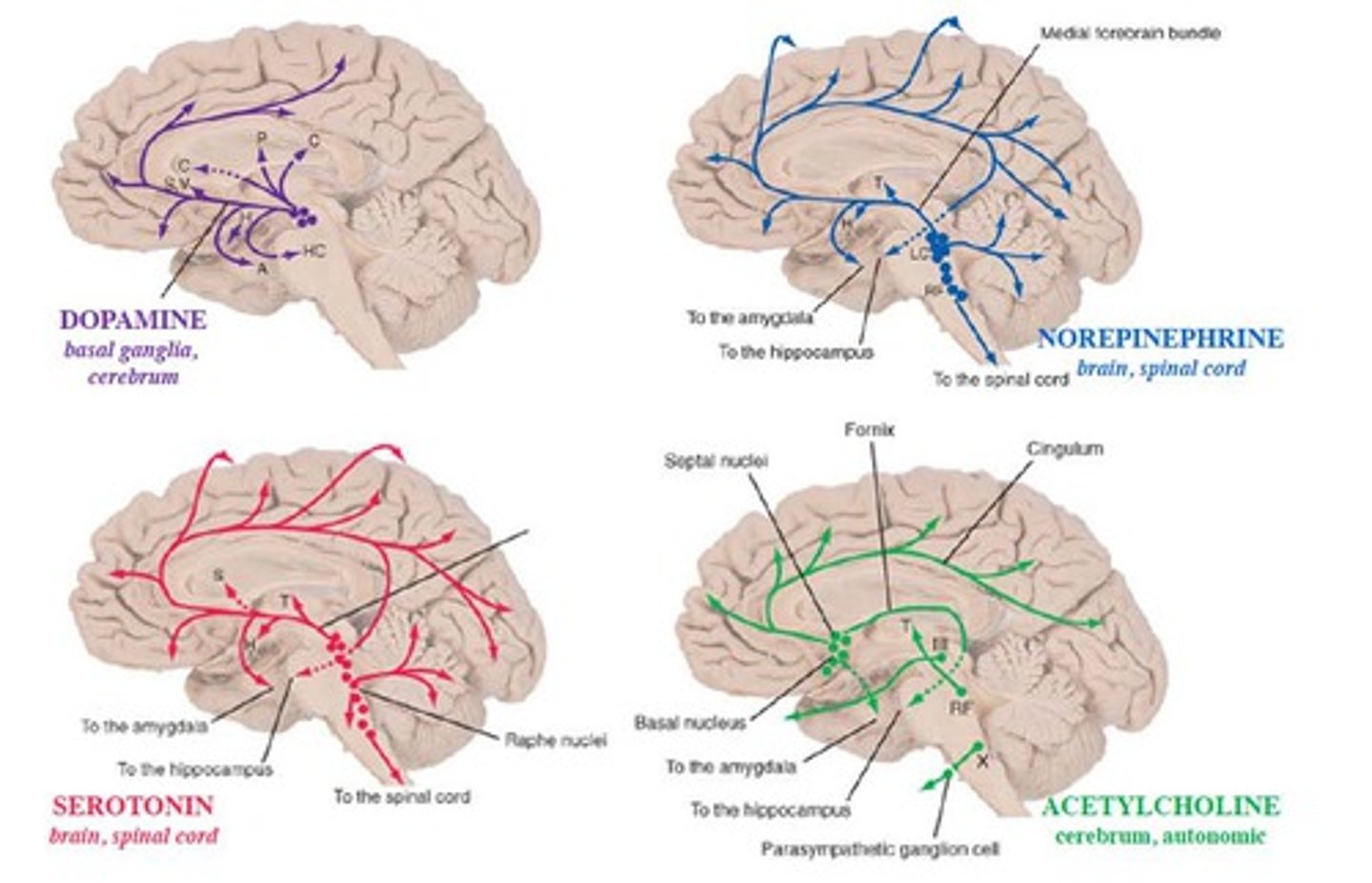
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that carry signals between neurons by crossing the synapse (the gap between neurons). They can either excite or inhibit the next neuron, helping control everything from muscle movements to mood and memory.
common types of neurotransmitters
Monoamines - serotonin
Nucleotides/nucleosides - adenosine
Amino acids
Acetylcholine - in neuromuscular junctions
Neuropeptides
neuromodulation
activate receptor that is not an ion channel
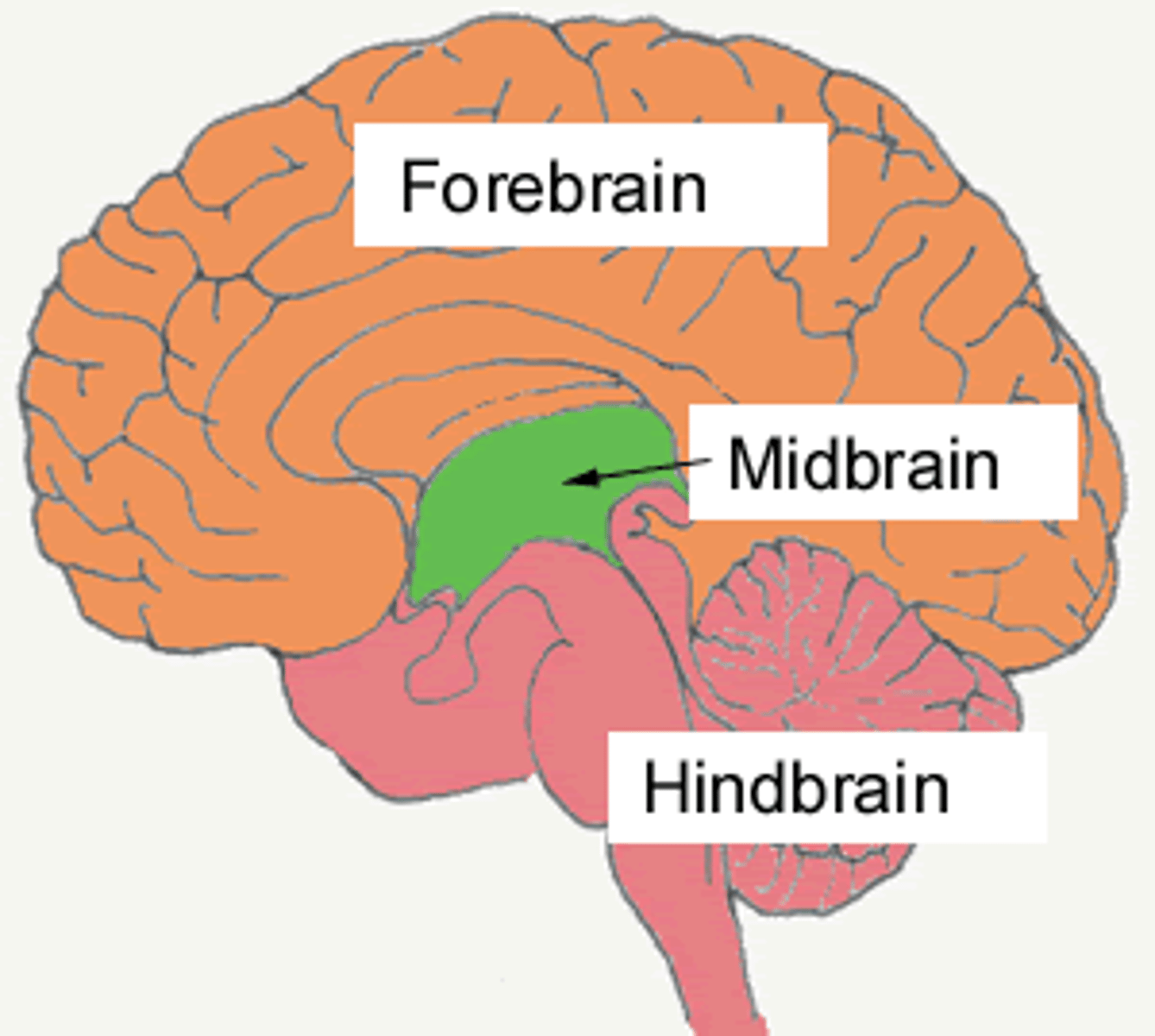
3 major divisions of the brain
forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
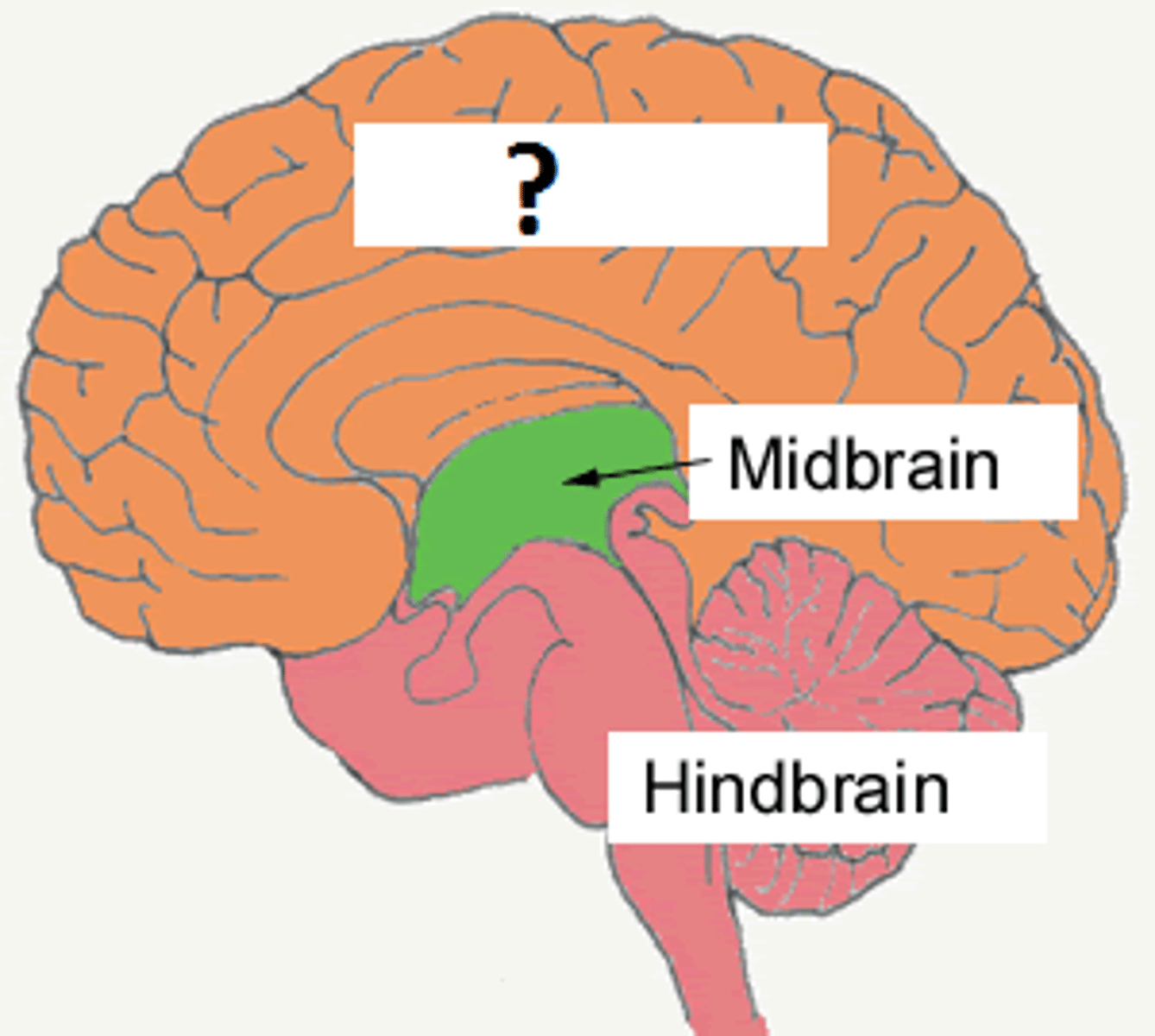
forebrain
telencephalon and diencephalon
telencephalon
cerebral hemispheres
diencephalon
thalamus and thalamus named structures
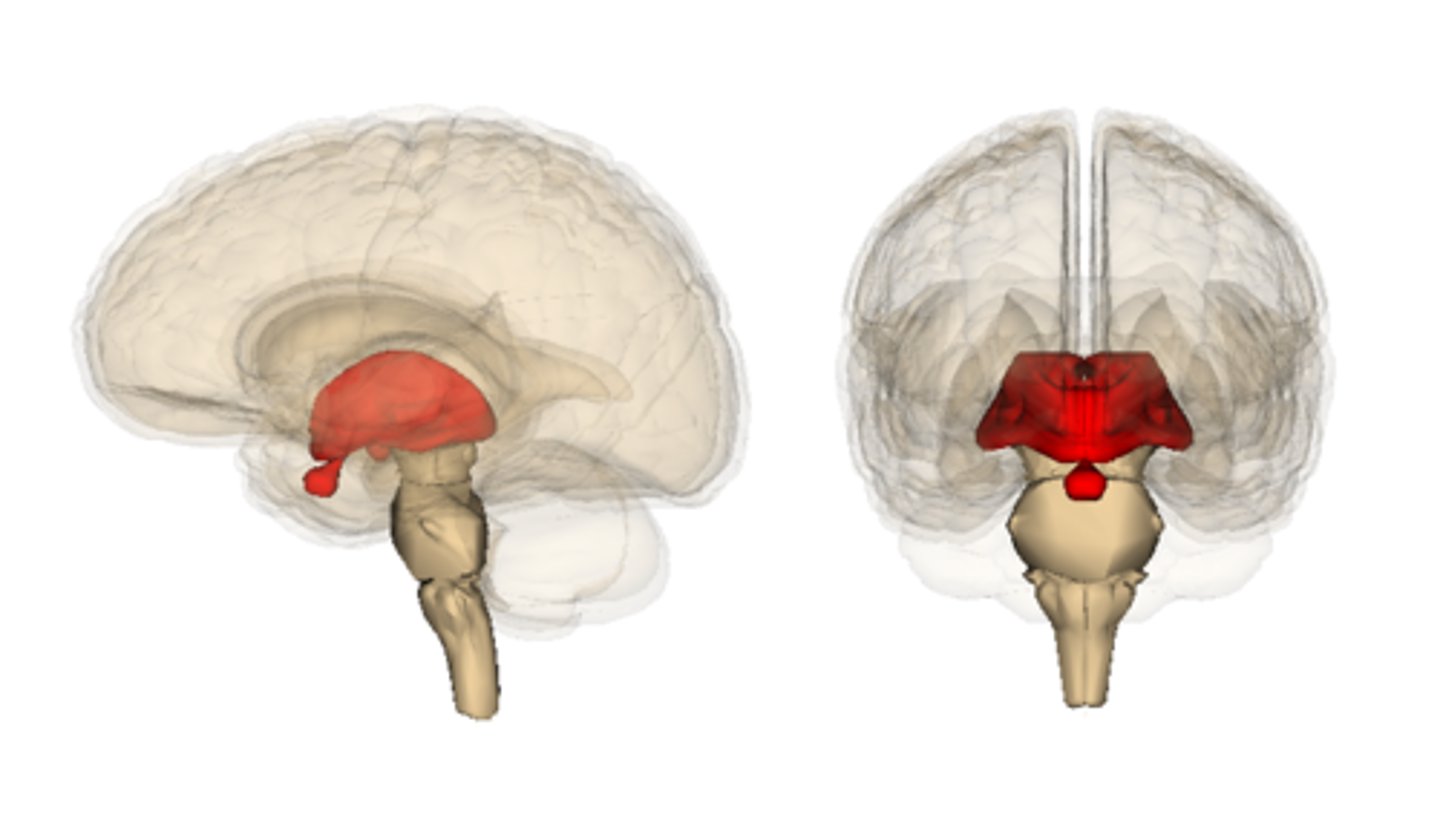
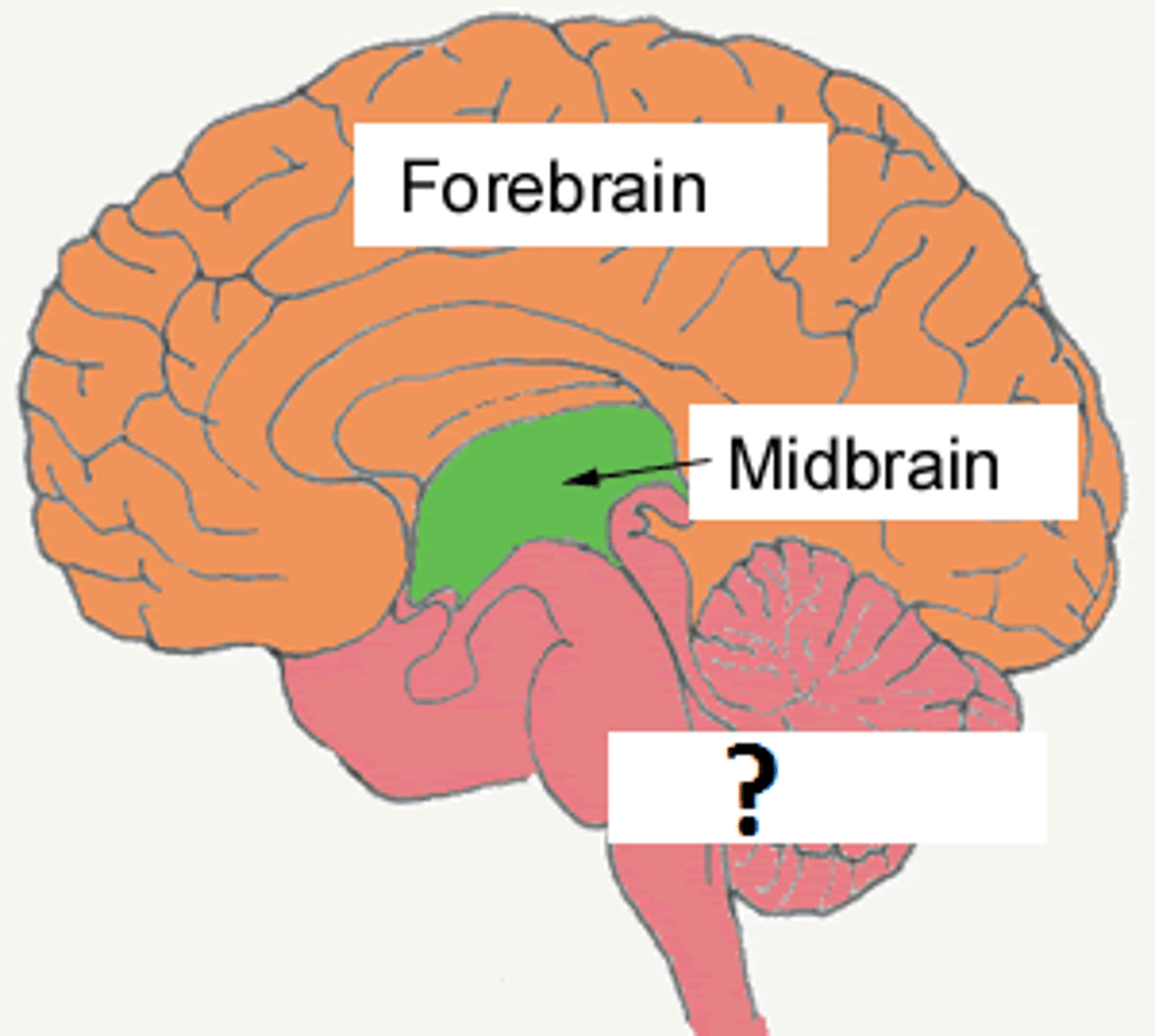
midbrain
the mesencephalon; the central of the three major divisions of the brain
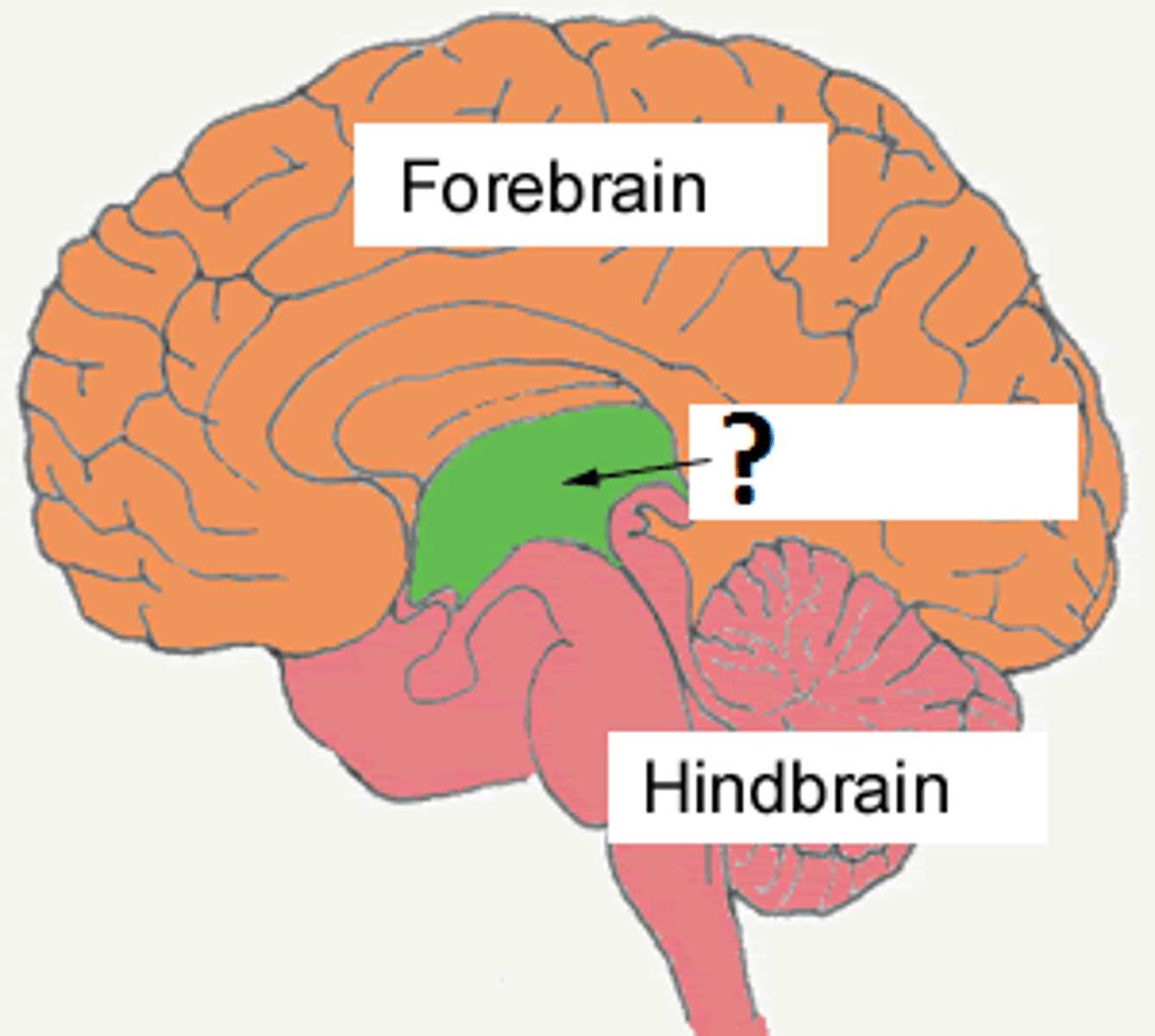
hindbrain
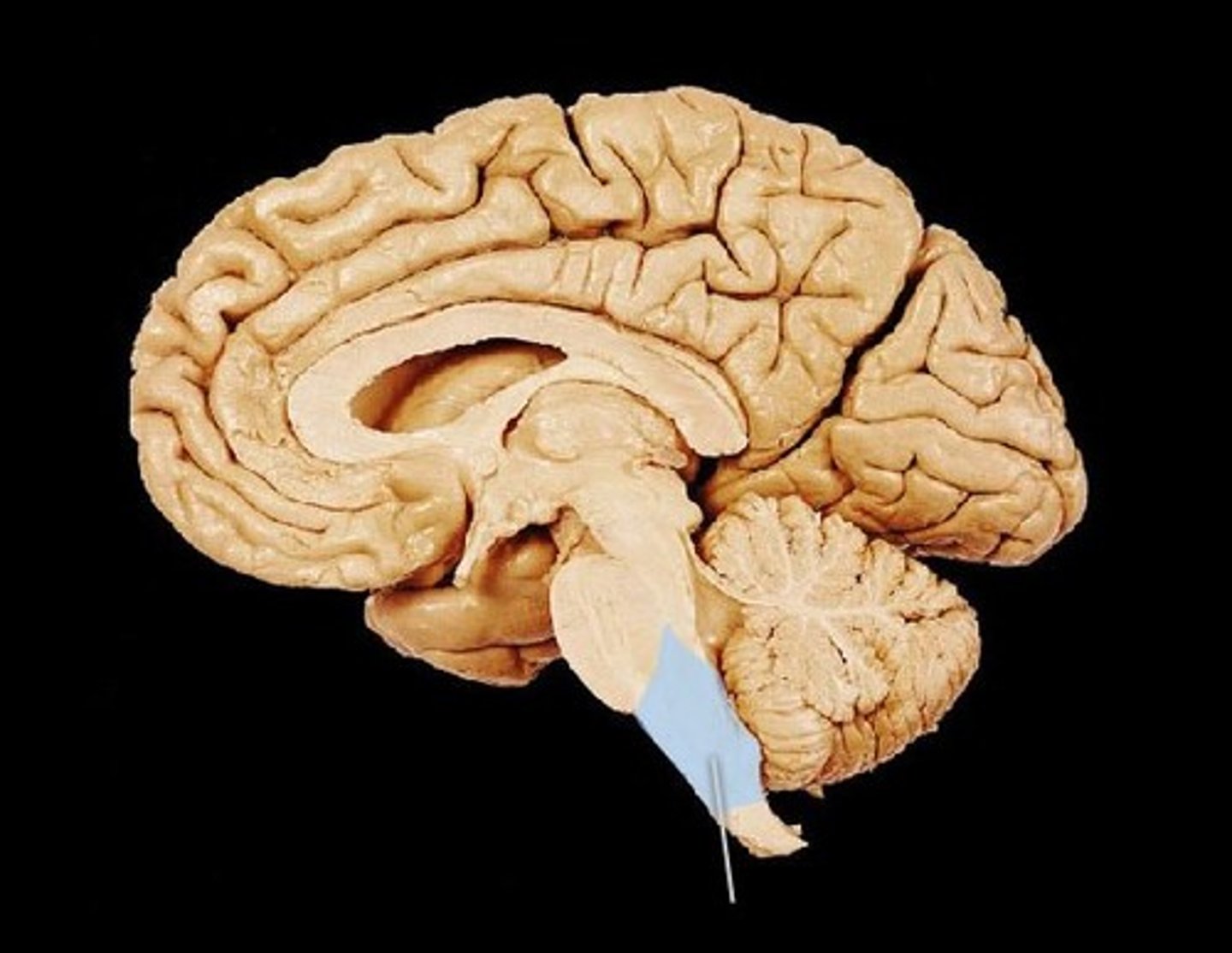
medulla, pons, cerebellum
back of the brain
metencephalon + myelencephalon
Metencephalon
pons and cerebellum
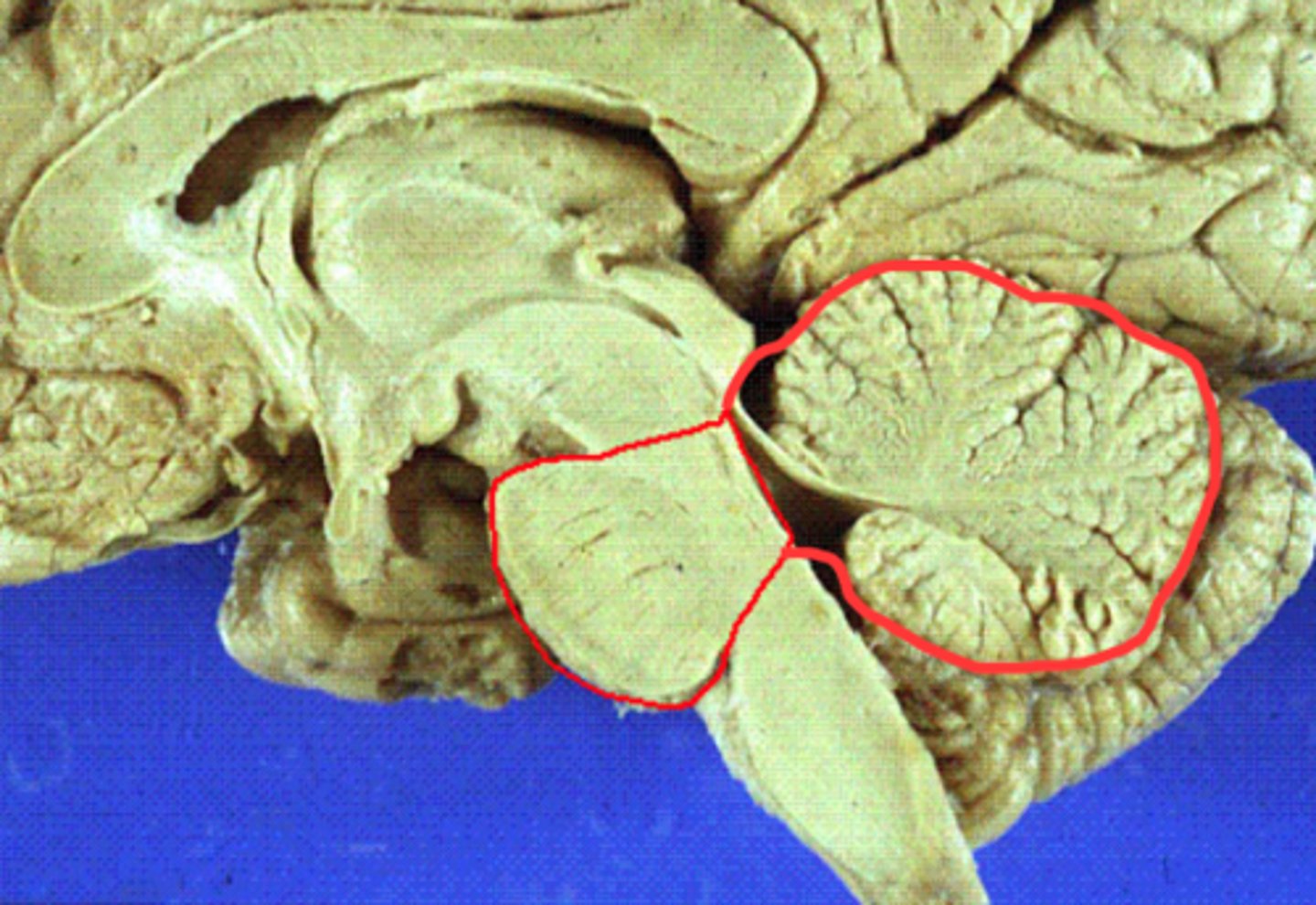
myelencephalon
medulla
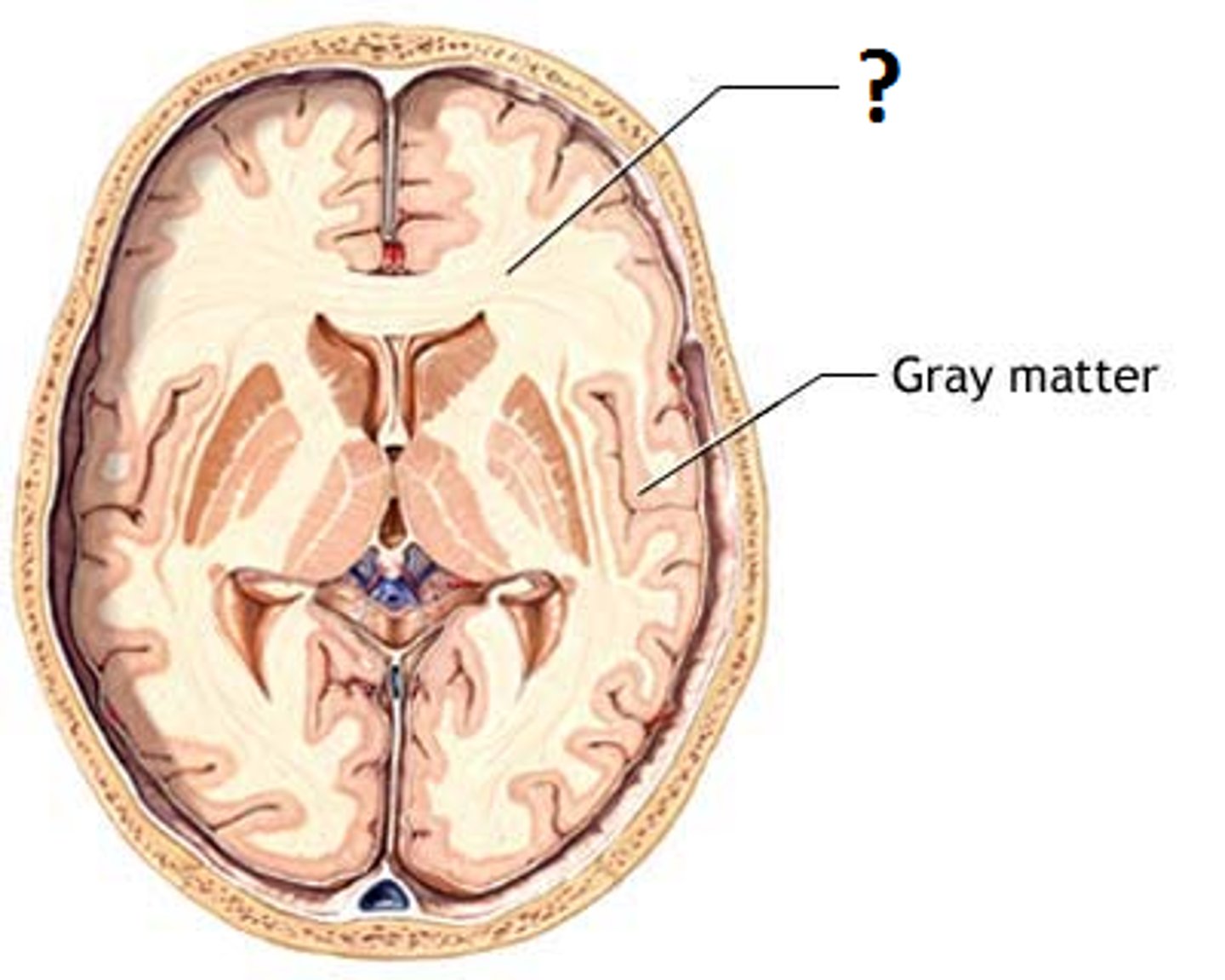
nuclei
clusters of cell bodies in the CNS (gray matter)
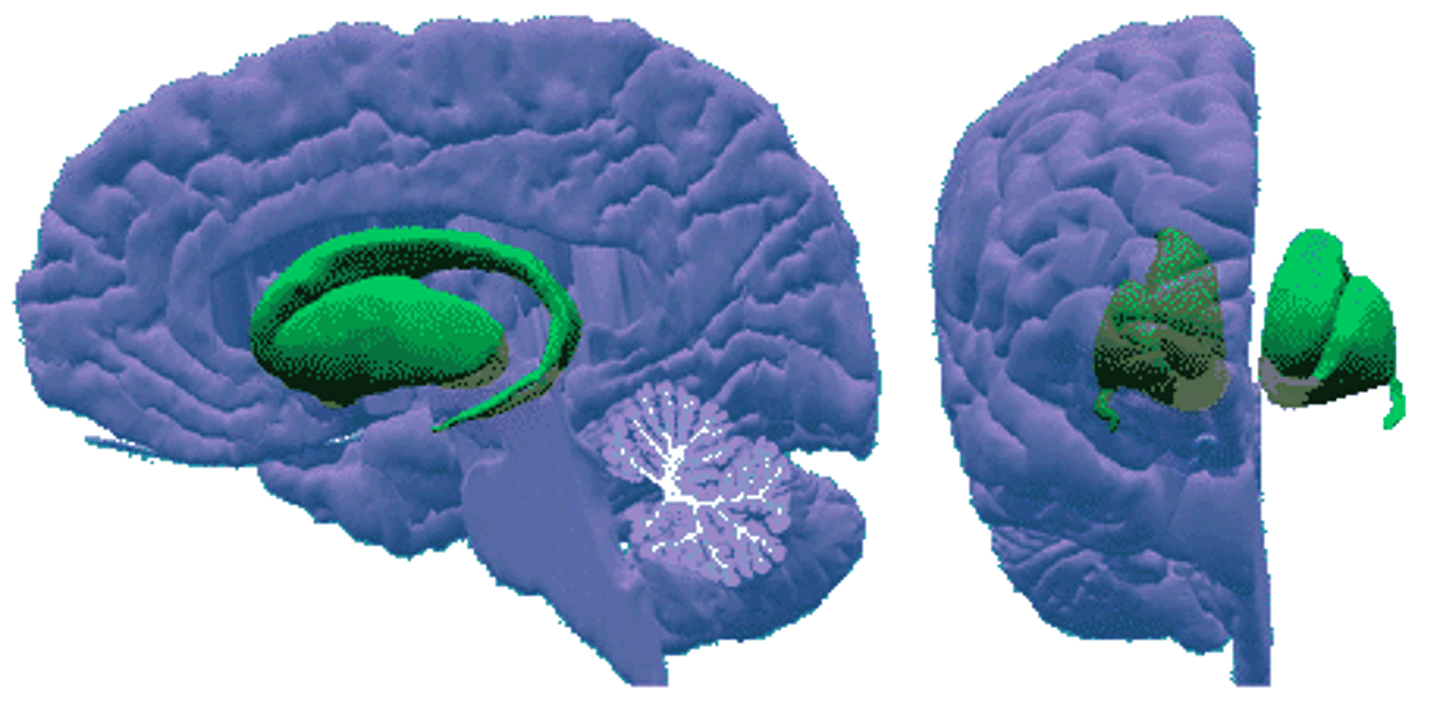
fibers/tracts
axon bundles in CNS (white matter)
it is white due to myelin from axons
function of cerebral hemisphere
sensory motor processing
- info coming from senses and how we form an action
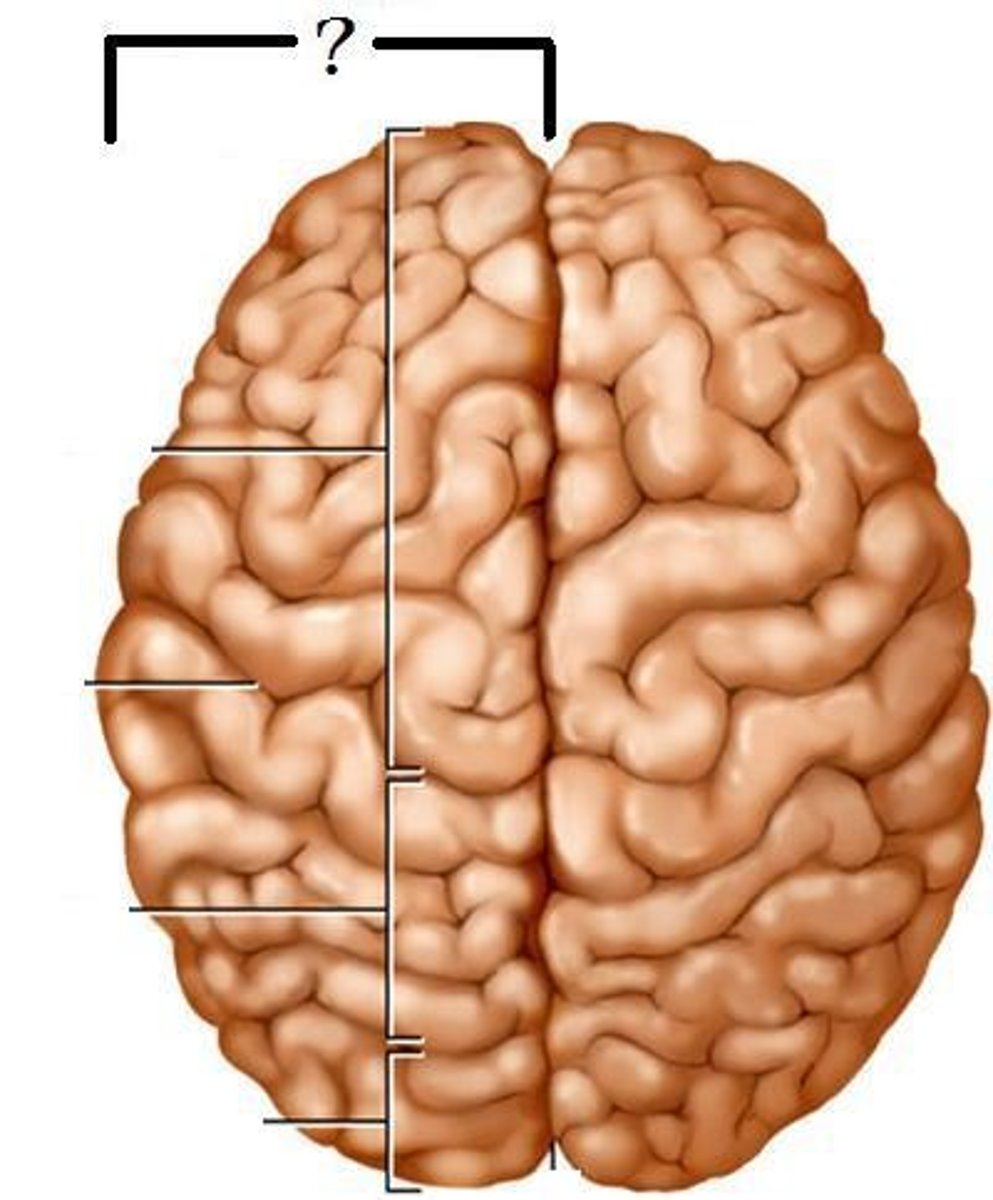
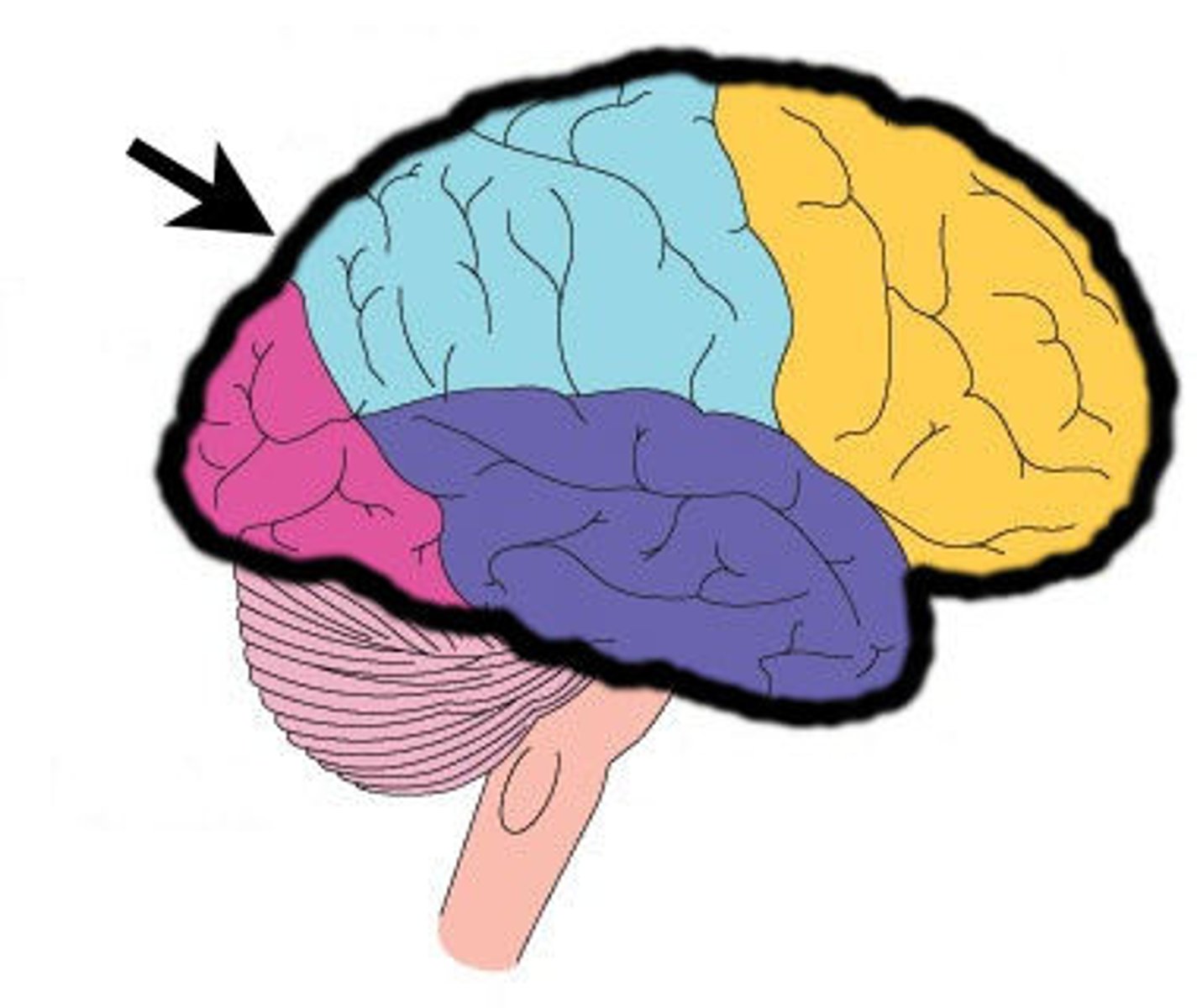
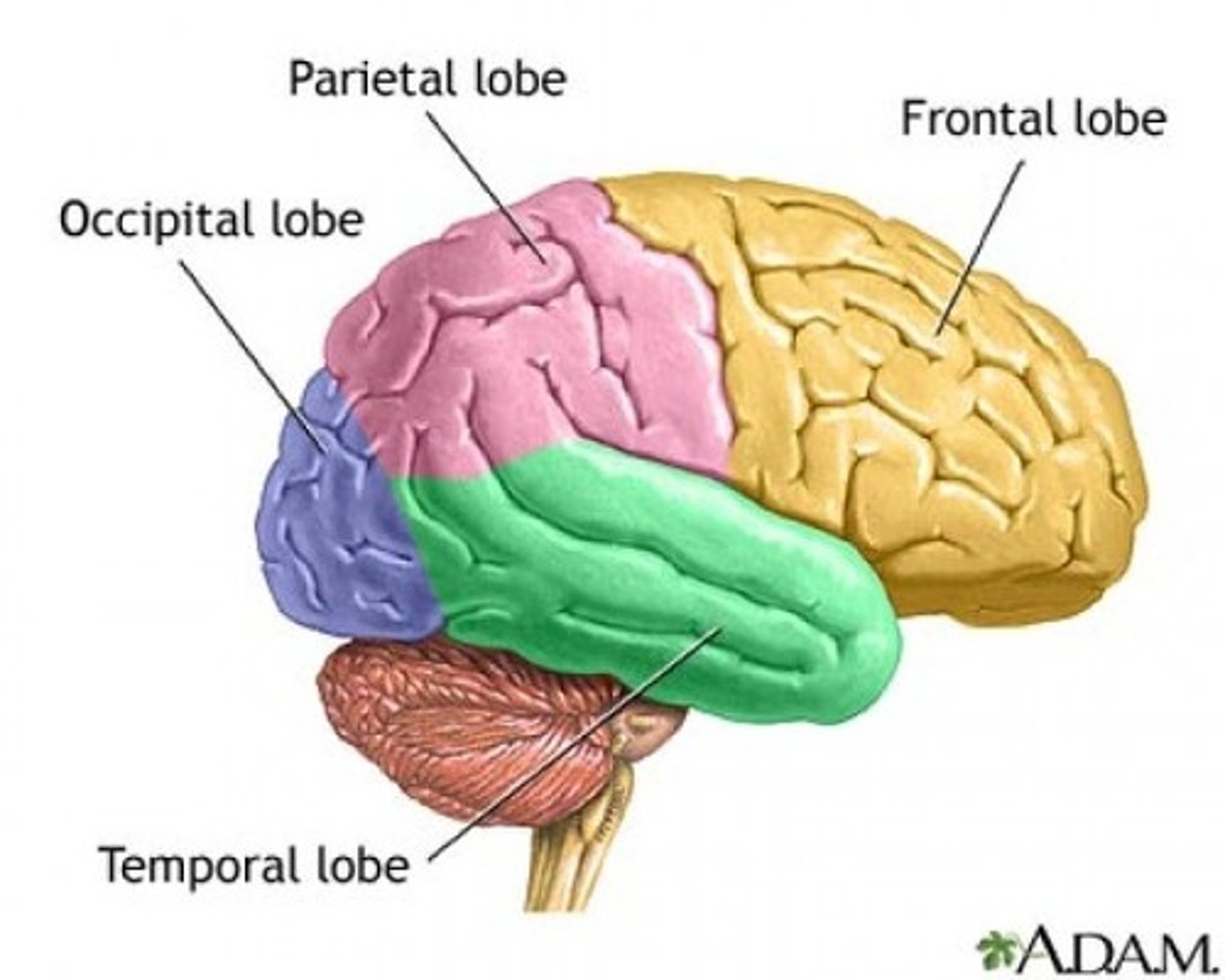
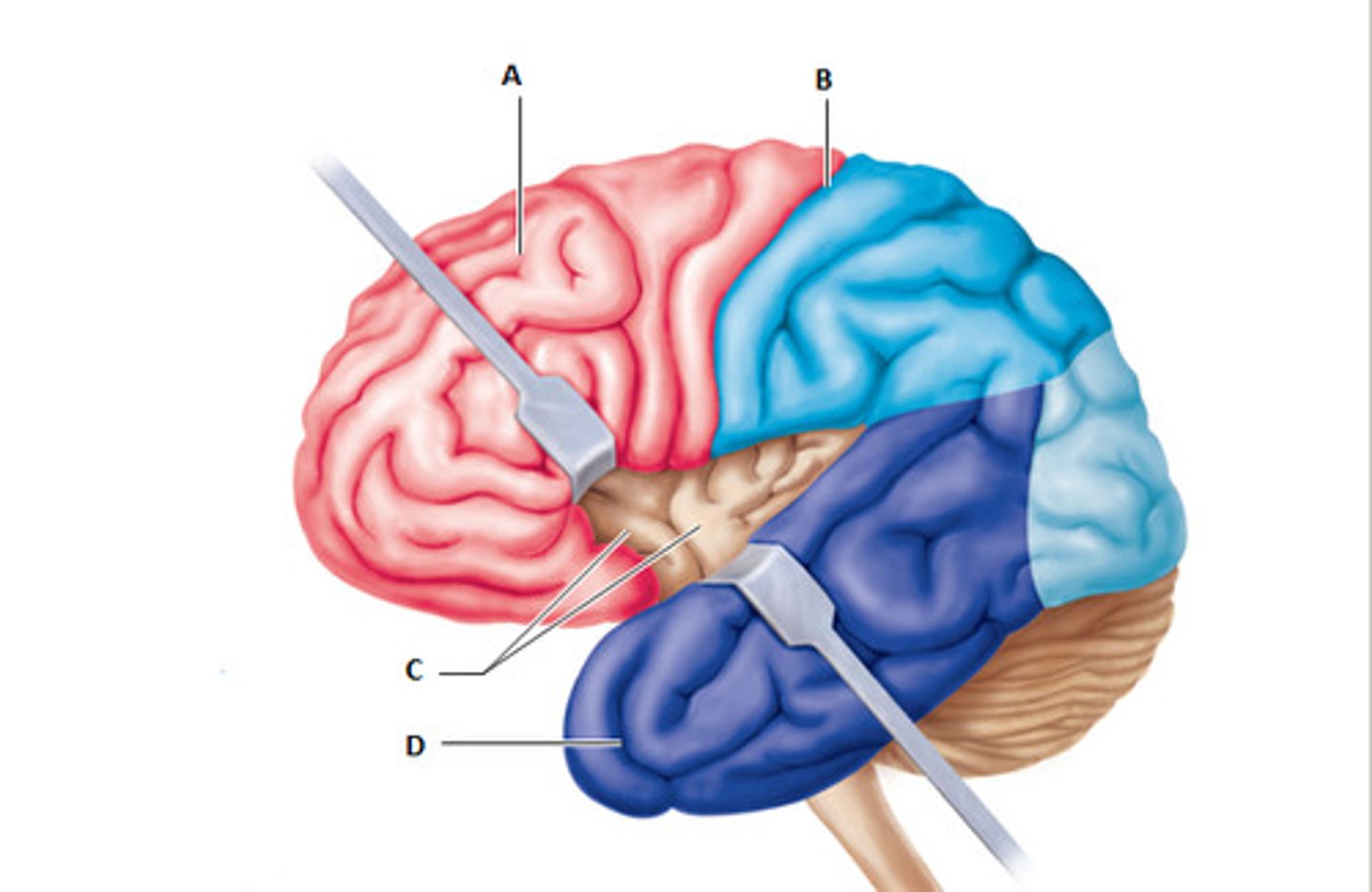
5 lobes of the cerebrum
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, insula
sensory input leads to
motor response
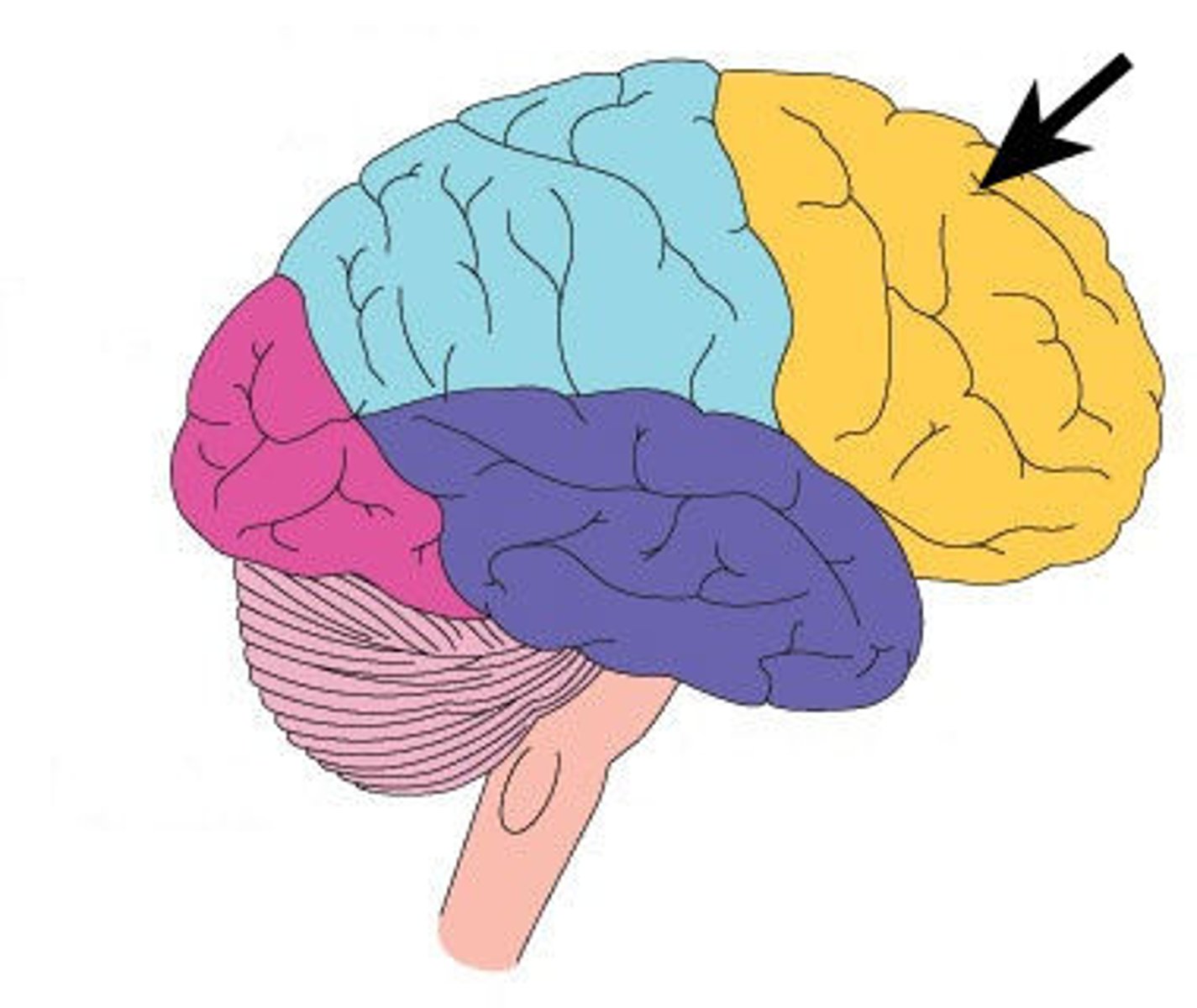
frontal lobe
The lobe at the front of the brain associated with movement, speech, and impulsive behavior.
the frontal lobe contains
Prefrontal cortex
Premotor/supplementary motor cortex
Primary motor cortex
Broca's area

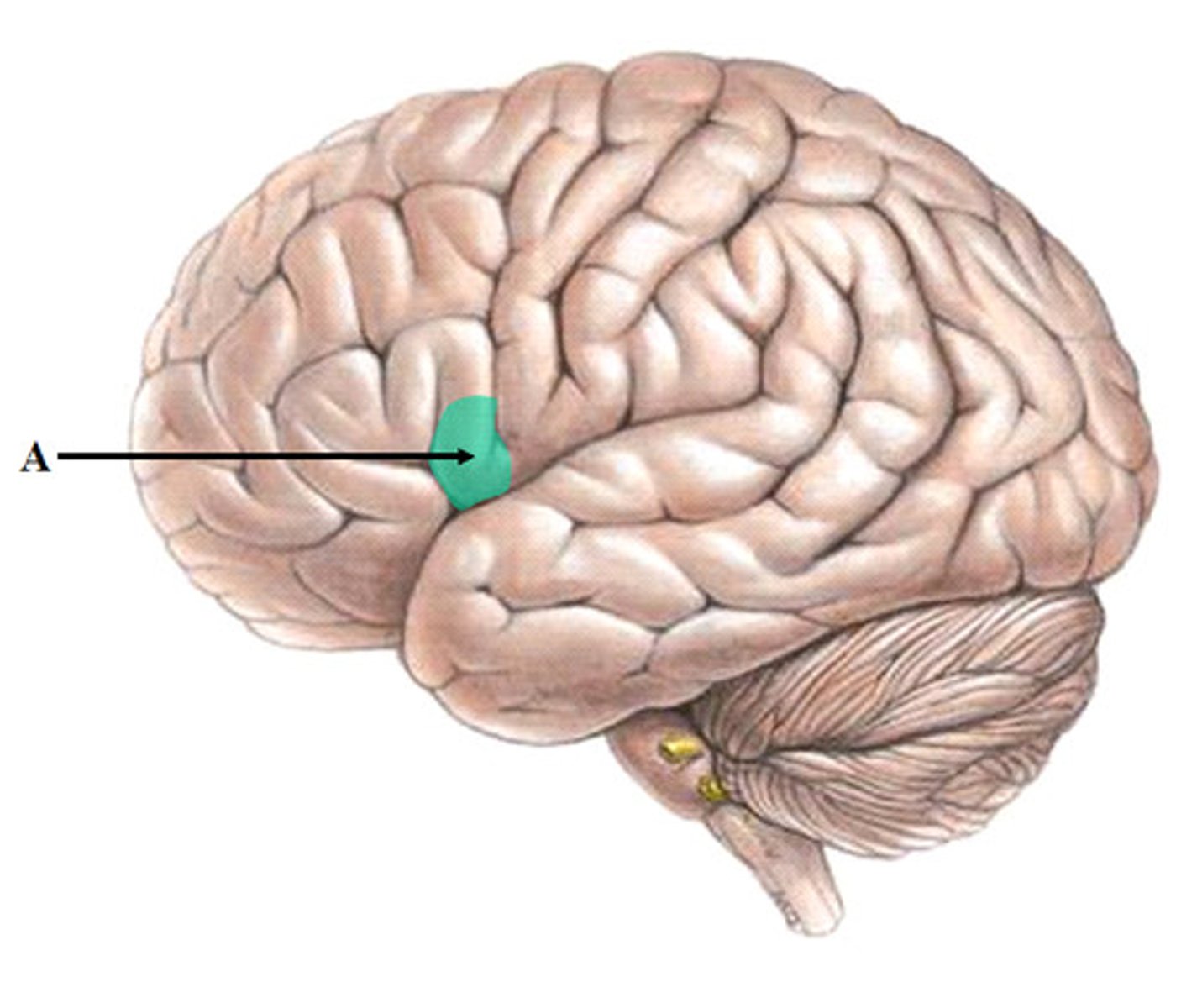
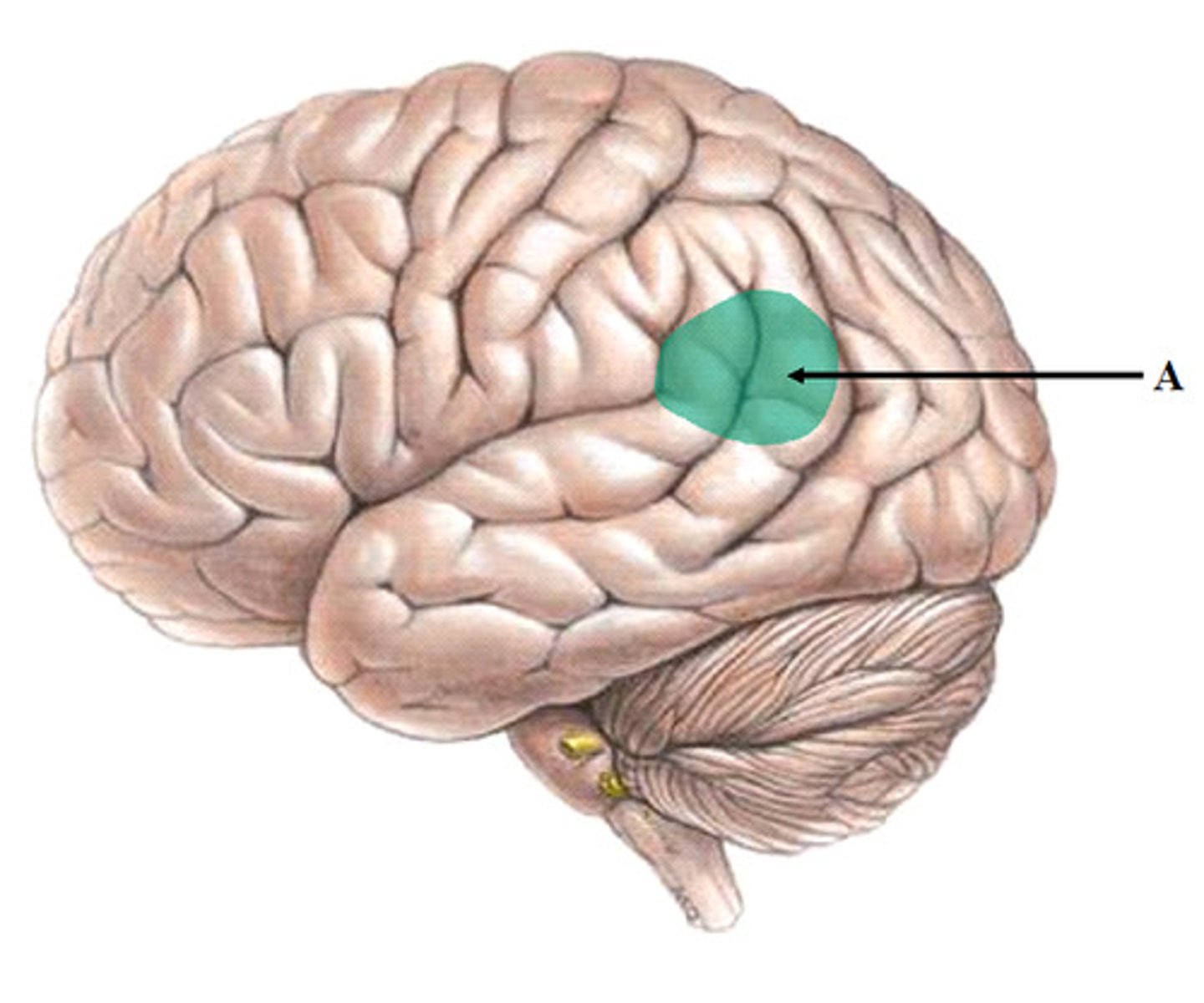
broca's area
speech production
You know that the premotor area (Brodmann area 6) is
involved in programming motor movements.

parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
- problem solving
- Wernicke area
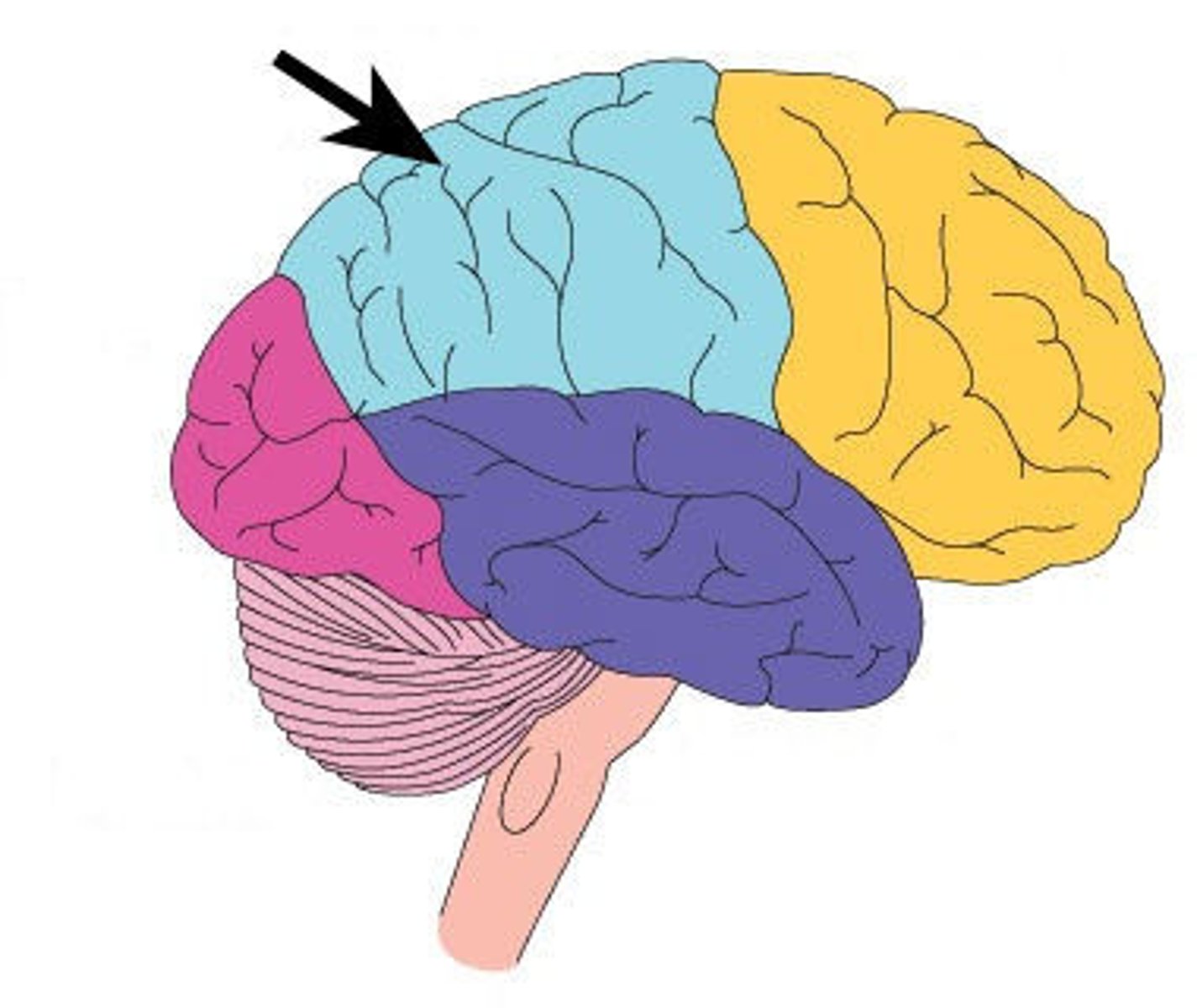
Wernicke's area
language comprehension
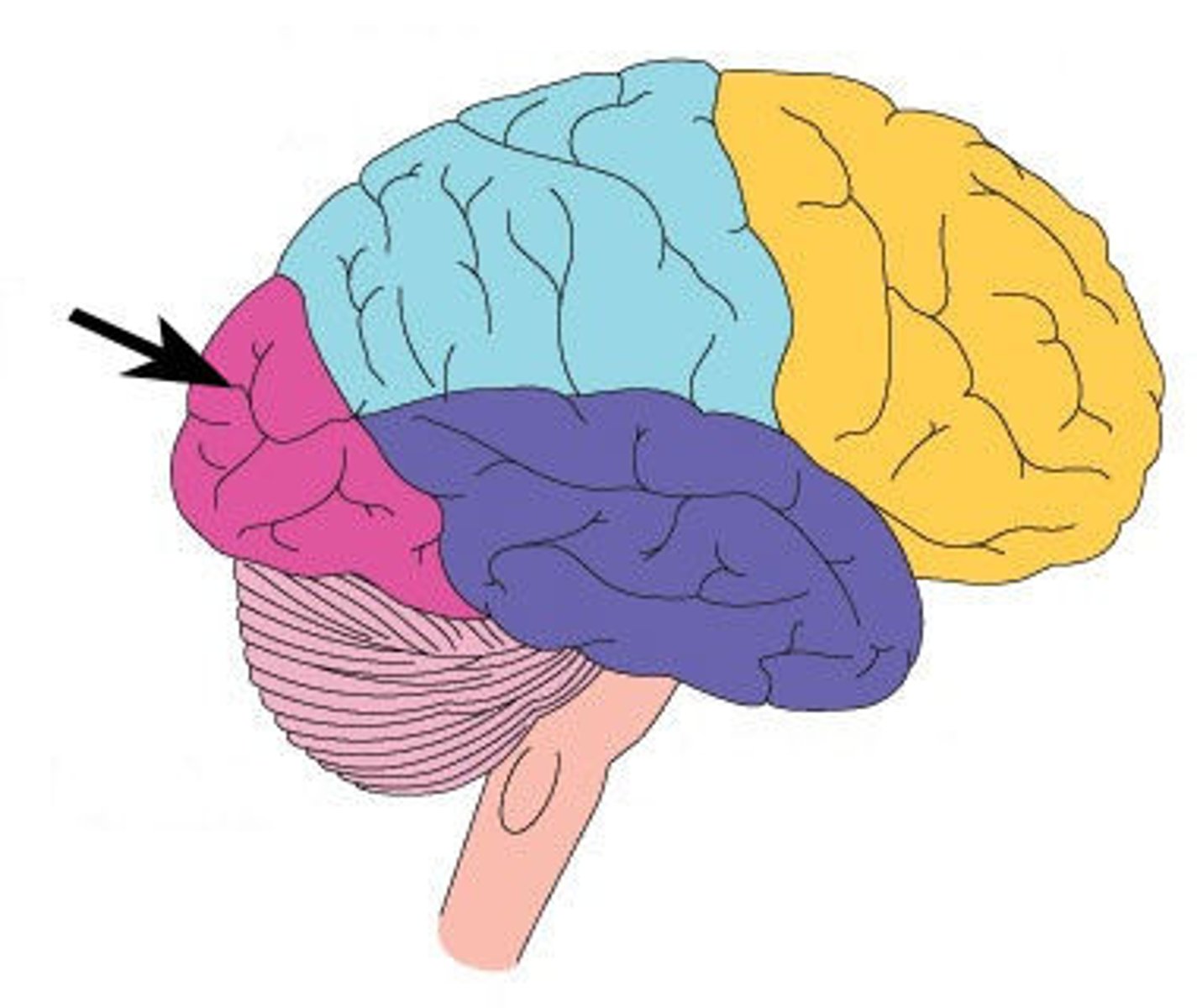
occipital lobe
visual processing
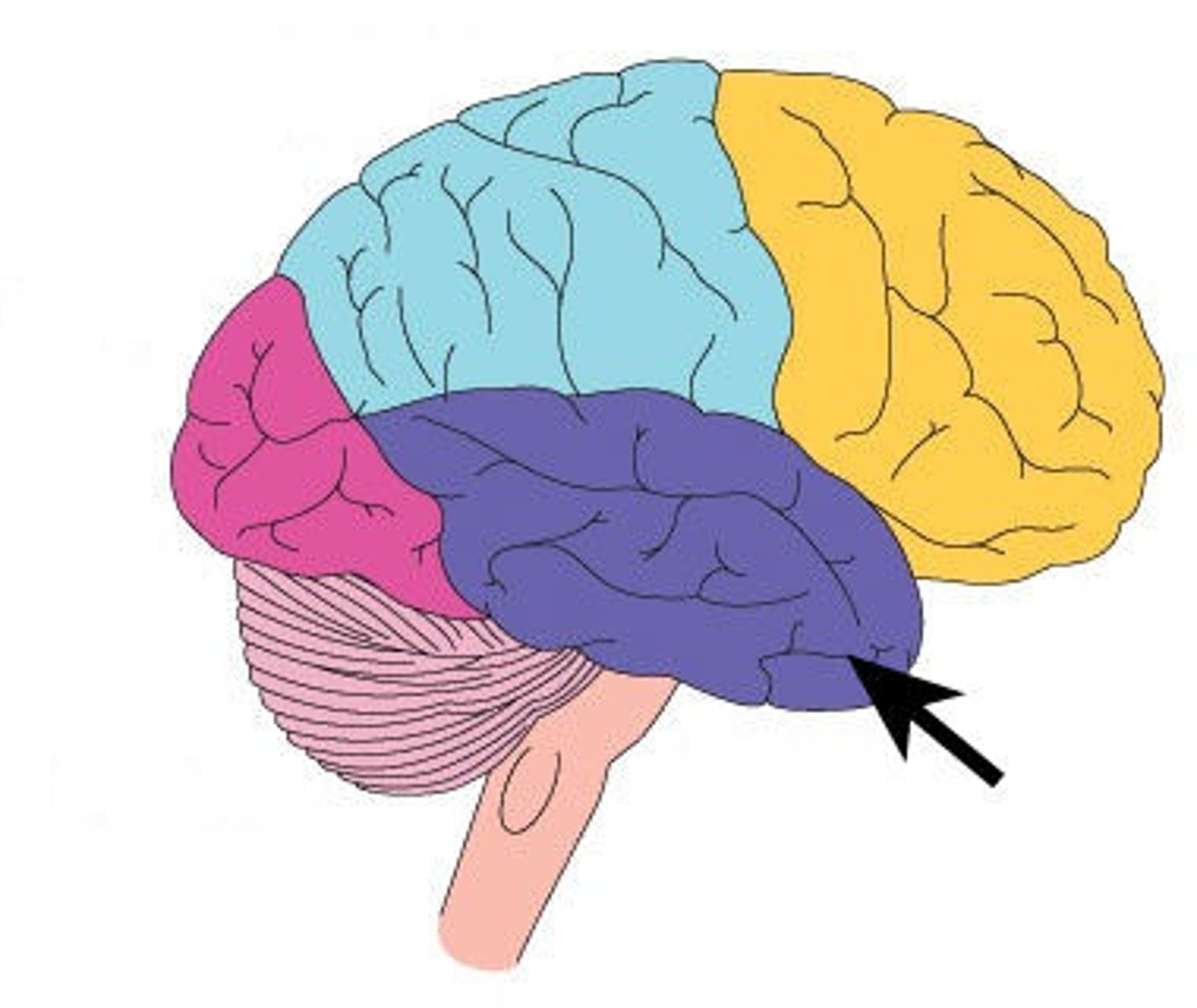
temporal lobe
hearing
second vision area
olfactory (smell)
insular lobe
emotions, perception, self-awareness, and bodily sensations like pain, temperature, and taste. It also helps with empathy, decision-making.
limbic system
involved in emotions, memory, motivation, and behavior. It connects the higher-thinking parts of the brain with the emotional and survival-related areas.
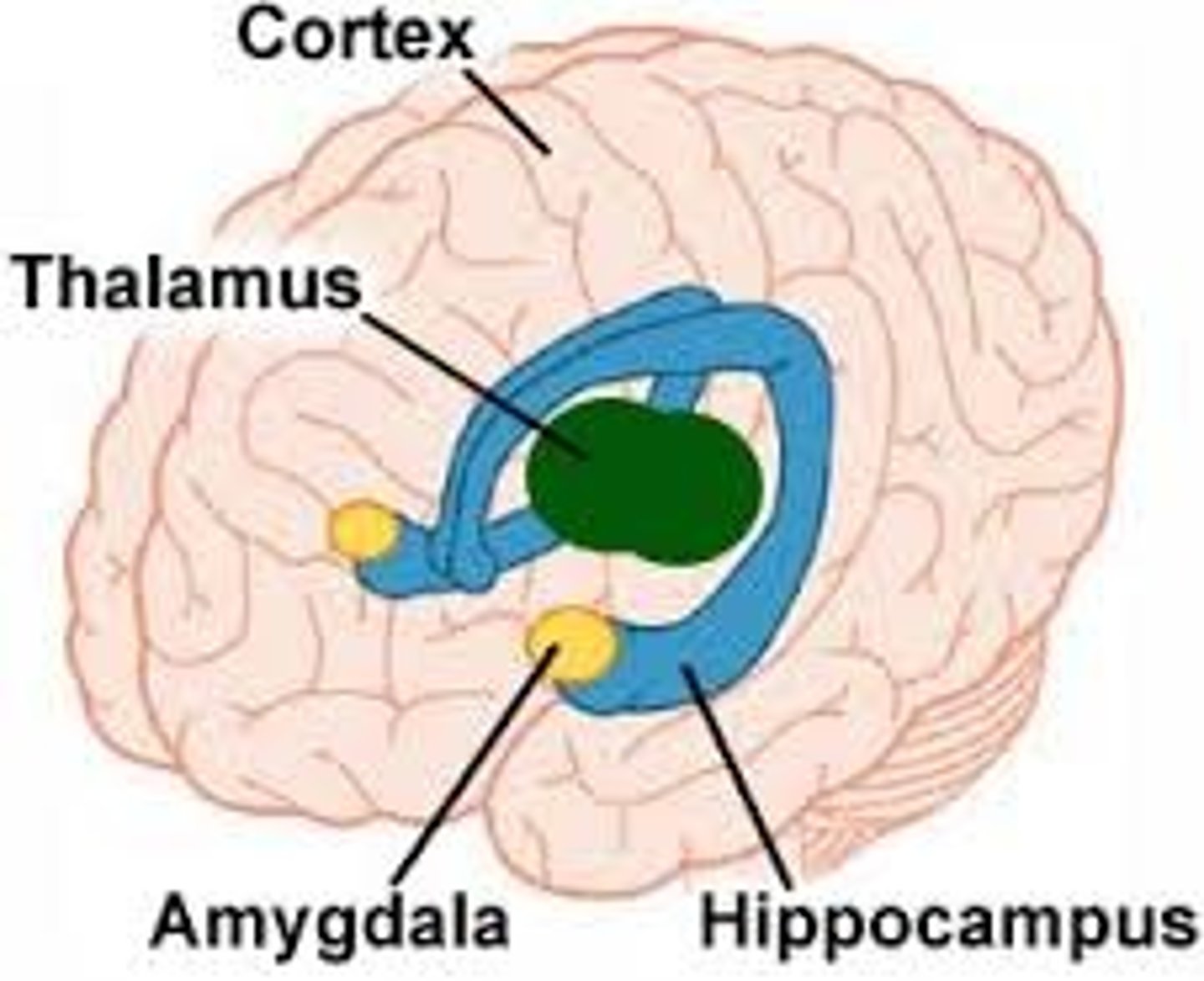
hippocampus
memory

amygdala
fear and aggression

cingulate gyrus
plays role in expressing emotions via gestures and resolves mental conflict

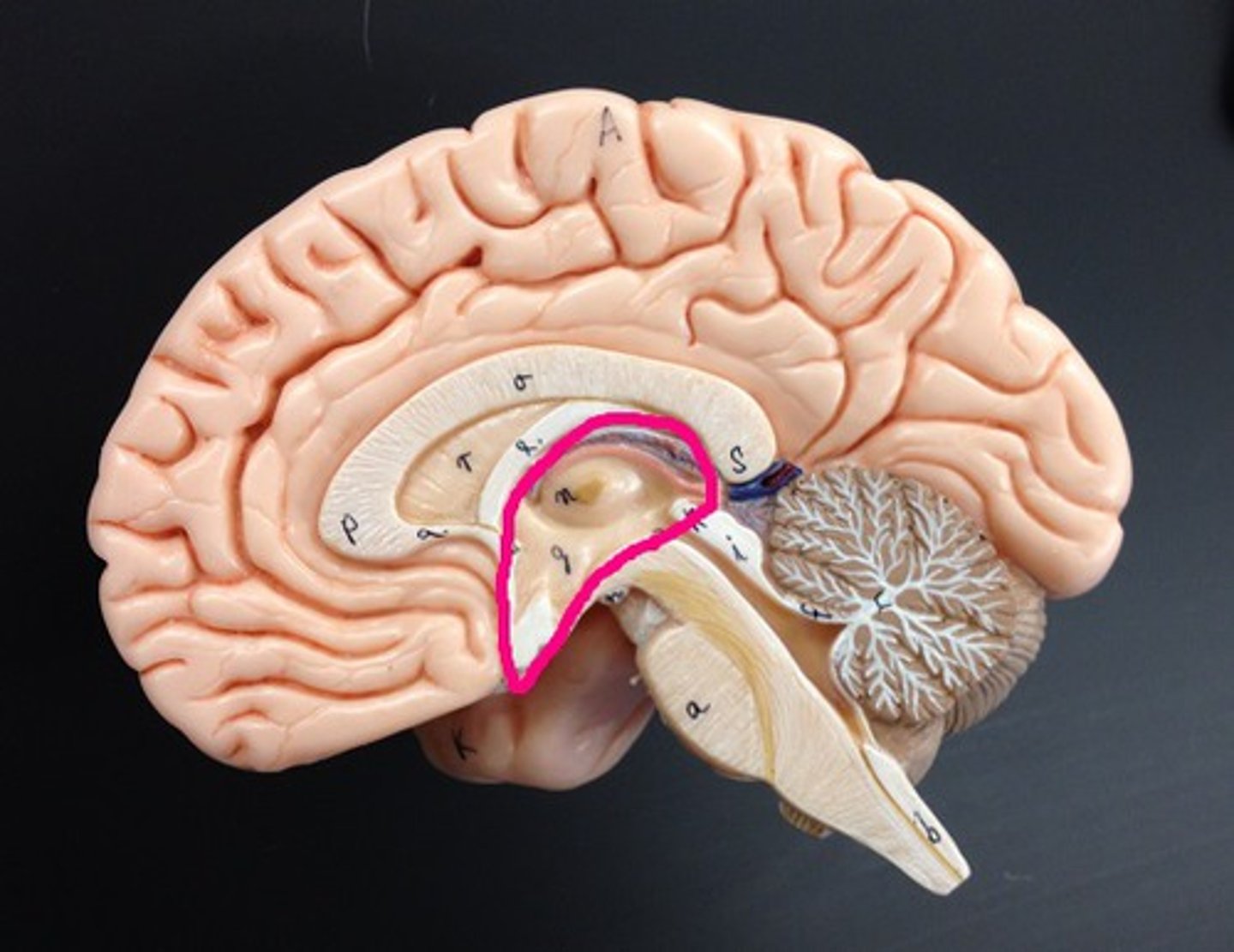
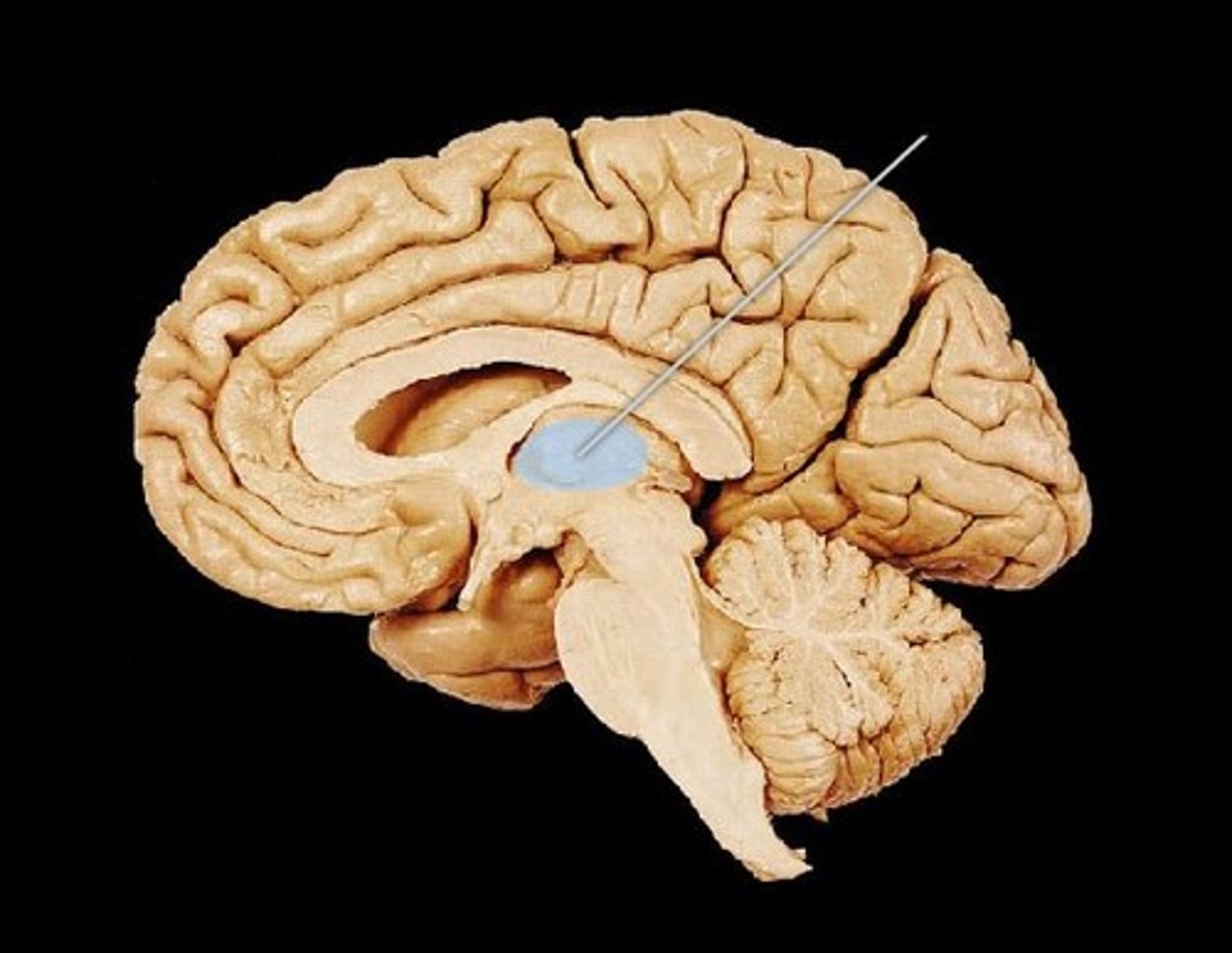
diencephalon contains
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, subthalamus
thalamus
the brain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
epithalamus
Contains pineal body. Involved in olfactory senses and sleep/wake cycle
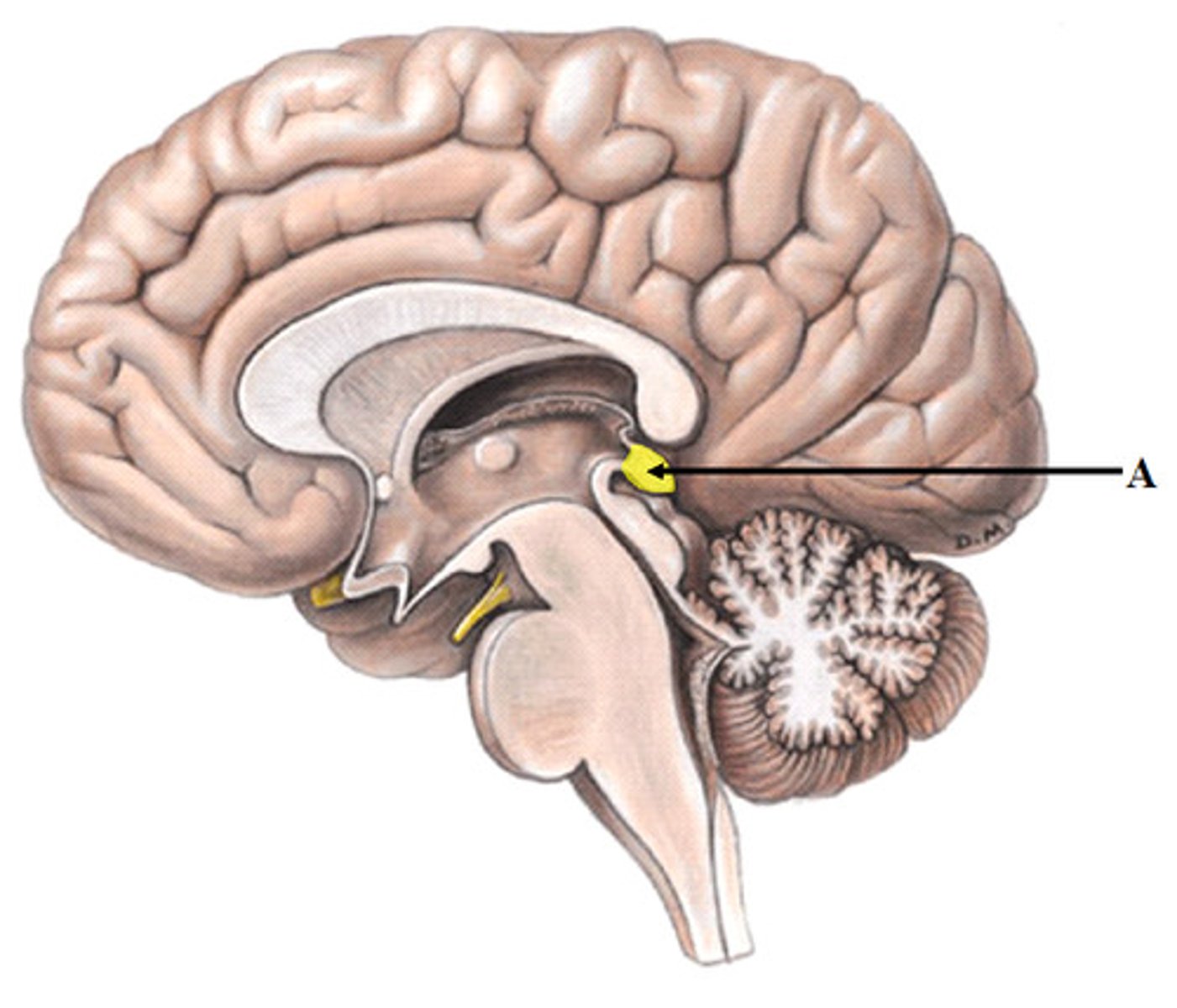
hypothalamus
brain region controlling the pituitary gland
hormones
subthalamus
works with basal ganglia for motor control
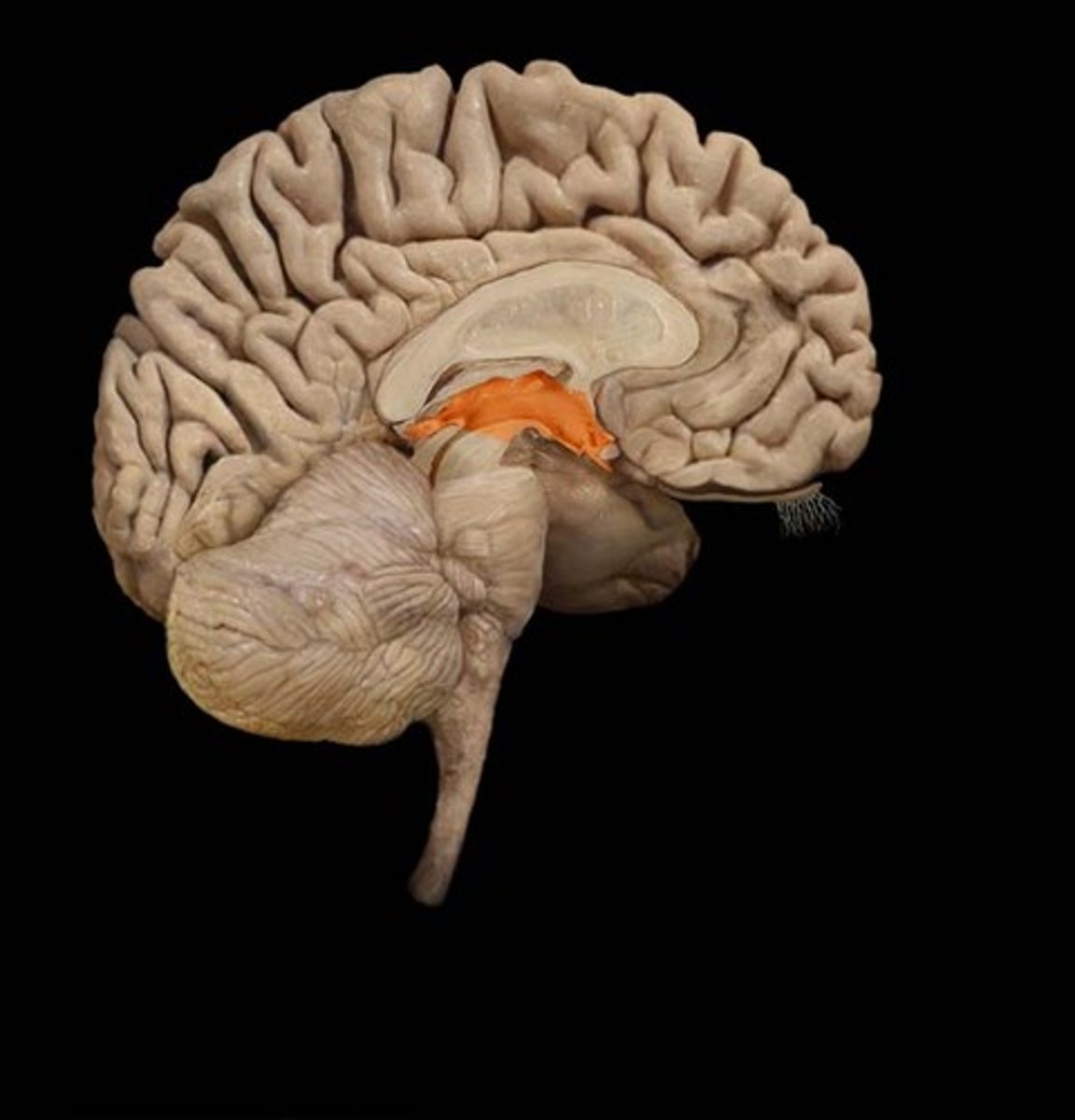
Mesencephalon contains
tectum and tegmentum
cerebral peduncles and aqueduct
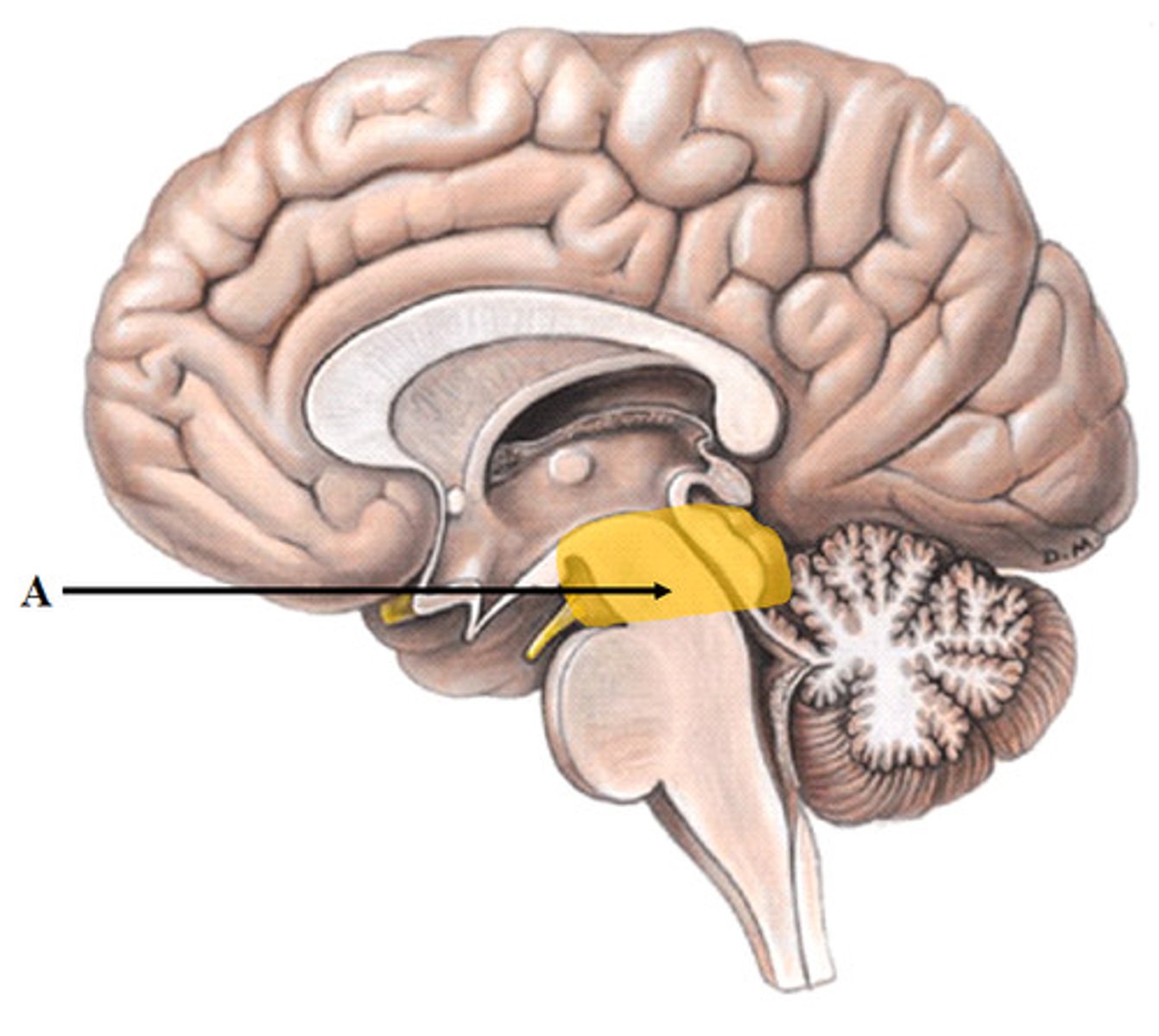
mesencephalon function
vision, hearing, movement, and reflexes
pons
relays signals, controls breathing, aids in movement, regulates sleep
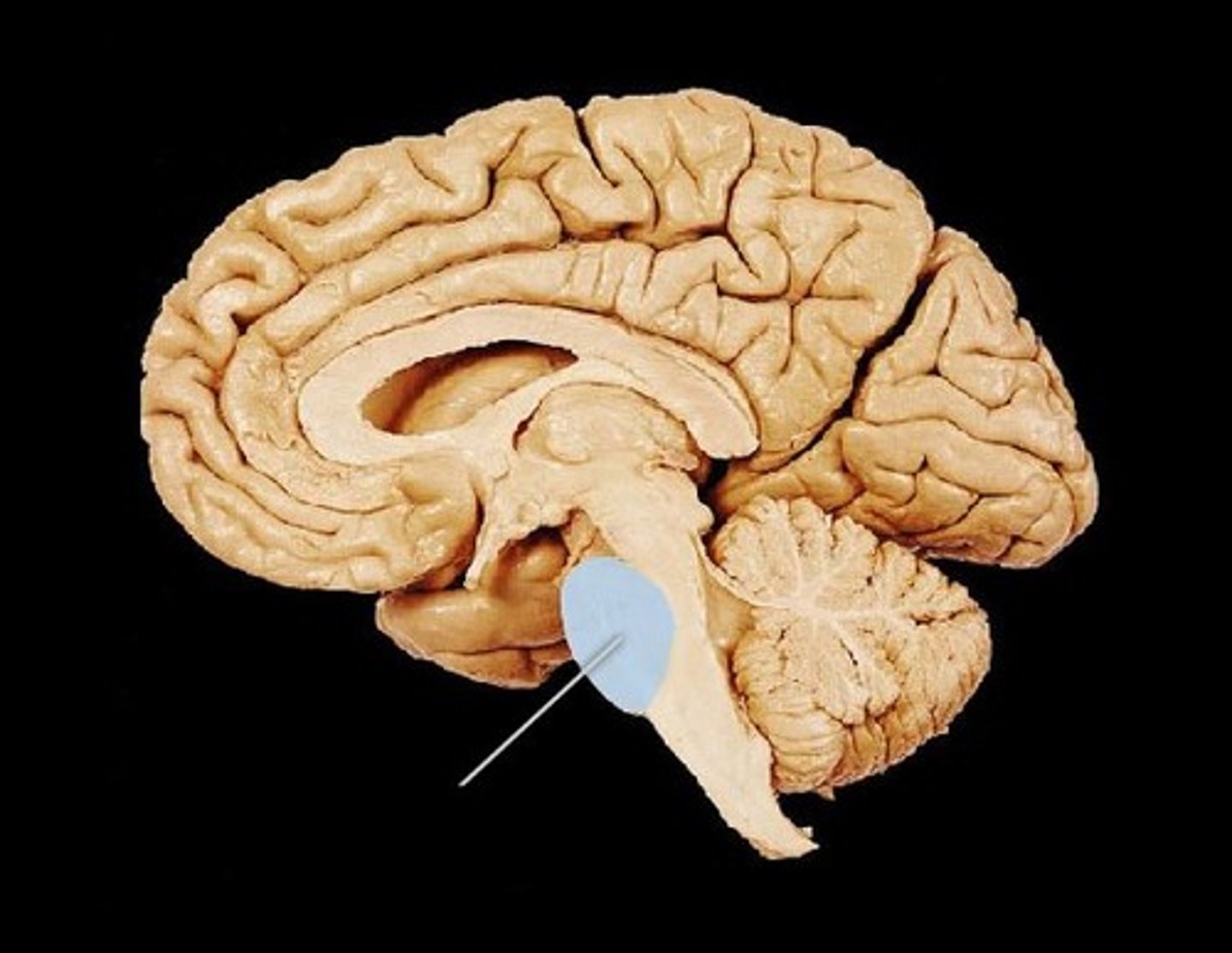
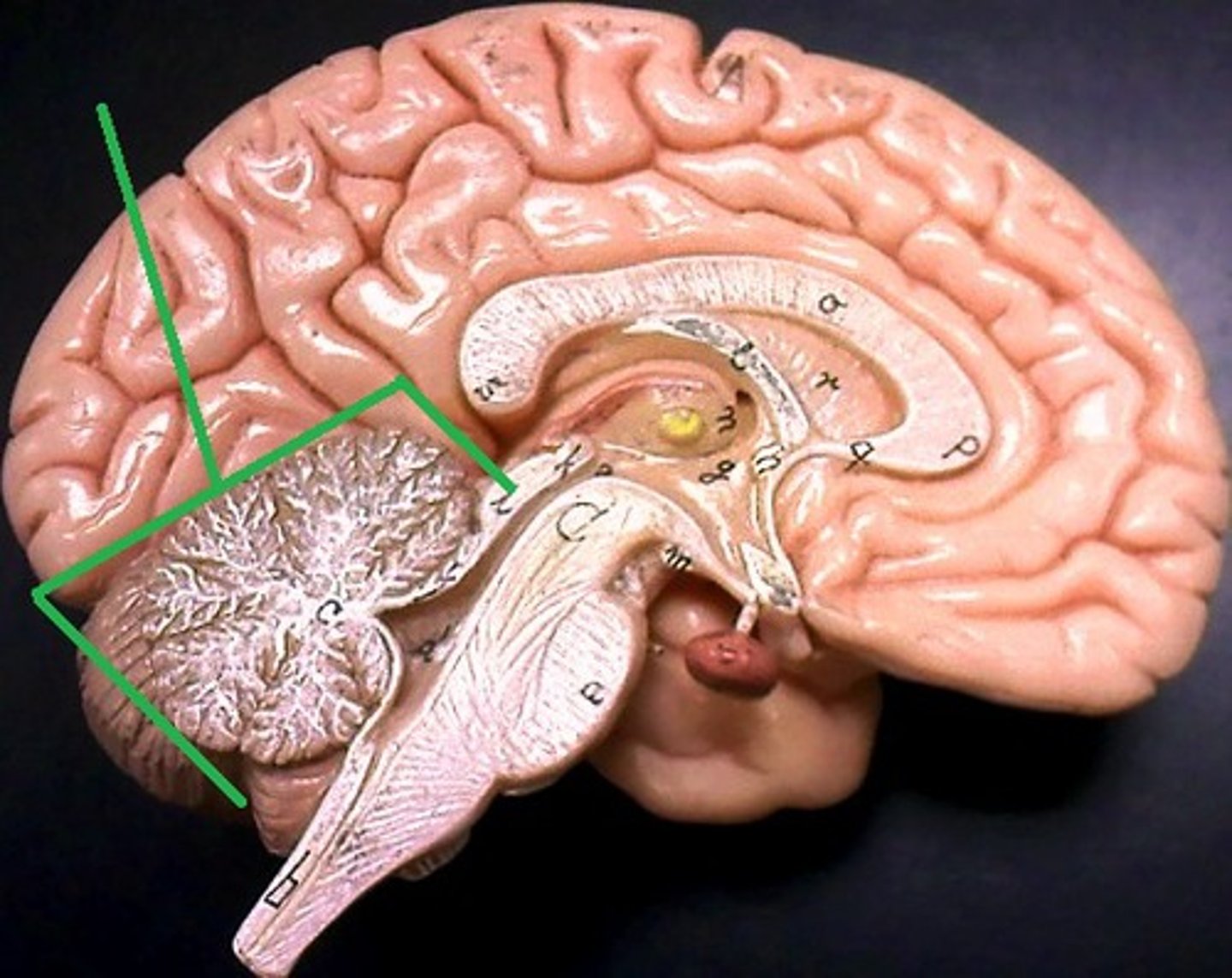
cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance
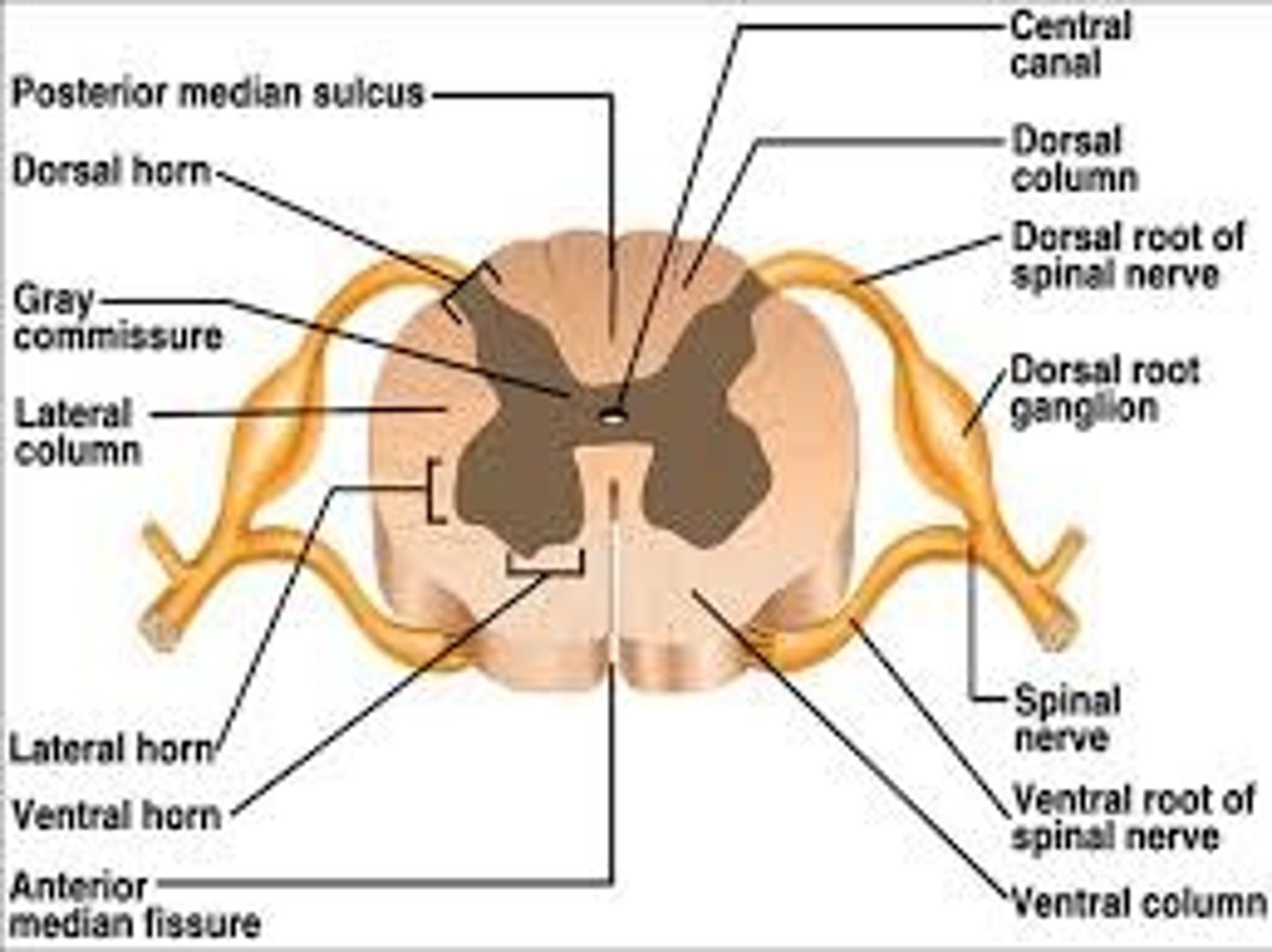
spinal cord
white matter is on the outside
gray matter on the inside