Kinesiology Exam #3 (Hip, Knee, Ankle)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What type of joint is the hip joint?
A ball-and-socket synovial joint.
What are the three degrees of freedom allowed by the hip joint?
Flexion-Extension, Abduction-Adduction, and Medial-Lateral Rotation.
What does the convex-concave rule state in relation to the hip joint?
The femoral head is convex while the acetabulum is concave.
What is an example of an open kinetic chain movement at the hip?
Leg kicks or hip flexion while lying supine.
What is an example of a closed kinetic chain movement at the hip?
Standing, squatting, or walking.
In an open kinetic chain, what is moving?
The femur on the acetabulum.
In a closed kinetic chain, what is moving?
The acetabulum on the femur.
What are the three parts of the pelvis that form the hip joint?
Ilium, Ischium, and Pubis.
What is the anatomical term for the hip joint?
Acetabulofemoral joint.
What is the significance of circumduction in the hip joint?
It is a combination movement that allows for a circular motion.
What anatomical feature is located at the top of the ilium?
Iliac Crest.
Anterior Pelvic Tilt
Pelvis tilts forward; associated with lordosis.
Causes of Anterior Pelvic Tilt
Tight hip flexors, weak glutes and abdominals, poor posture, sedentary lifestyle, pregnancy.
Focus in Rehabilitation for Anterior Pelvic Tilt
Stretch hip flexors, strengthen glutes and hamstrings.
Posterior Pelvic Tilt
Pelvis tilts backwards.
Causes of Posterior Pelvic Tilt
Excessive engagement of glute max, tight hamstrings and glutes, weak hip extensors, poor posture, sedentary lifestyle, slouching.
Focus in Rehabilitation for Posterior Pelvic Tilt
Strengthen abdominal muscles, strengthen glutes.
Anterior vs. Posterior During Movement
Anterior occurs during hip flexion and lumbar extension; posterior occurs during hip extension and lumbar flexion.
Pelvic Drop
One side of pelvic drops lower than the other; caused by weak abductor muscles.
Trendelenburg gait
What is the name of this type of gait? Associated with pelvic drop.
Pelvic Hike
One side of the pelvis is higher than the other; compensation for weakness or tightness of the opposite side.
Ligaments of the Acetabulofemoral Joint
Provide stability, especially in weight-bearing positions.
4 ligaments of the hip
Illiofemoral Ligament, Pubofemoral Ligament, Ischiofemoral Ligament, Ligamentum Teres.
Muscles of the Hip - Flexors
Iliopsoas (psoas major + iliacus), Rectus femoris, Sartorius, Pectineus, Tensor Fascia Latae
Muscles of the Hip - Extensors
Gluteus maximus, Hamstrings (biceps femoris long head, semitendinosus, semimembranosus), Adductor magnus (posterior fibers)
Muscles of the Hip - Abductors
Gluteus medius (primary), Gluteus minimus, Tensor fasciae latae.
Muscles of the Hip - Adductors
Adductor longus, Adductor brevis, Adductor magnus, Gracilis.
Muscles of the Hip - External Rotators
Piriformis, Obturator internus/externus, Gemelli (superior & inferior), Quadratus femoris, Gluteus maximus (posterior fibers).
Muscles of the Hip - Internal Rotators
Gluteus medius (anterior fibers), Gluteus minimus (anterior fibers), Tensor fasciae latae.
What bones make up the knee?
Femur, Tibia, Fibula, and Patella
What are the medial and lateral condyles?
They are parts of the femur that articulate with the tibia.
What is the function of the patella?
Increases the moment arm of the quadriceps, protects the anterior joint, and transmits force efficiently.
What type of bone is the patella?
Seasmoid bone
What is the role of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)?
Prevents anterior translation of the tibia on the femur and limits hyperextension.
What is the role of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)?
Prevents posterior translation of the tibia on the femur and stabilizes the knee during flexion.
What movements occur at the Tibiofemoral Joint?
Flexion/Extension and Internal/External Rotation.
Describe the arthrokinematics of knee extension in an open kinetic chain.
Anterior roll and anterior glide.
Describe the arthrokinematics of knee flexion in an open kinetic chain.
Posterior roll and posterior glide.
What happens during knee extension in a closed kinetic chain?
Anterior roll and posterior glide.
What happens during knee flexion in a closed kinetic chain?
Posterior roll and anterior glide.
What are the patellofemoral joint movements?
Superior glide, inferior glide, lateral glide, and medial glide.
What occurs during a superior glide of the patella?
It occurs during knee extension as the quadriceps contracts, pulling the patella up.
What occurs during an inferior glide of the patella?
It occurs during knee flexion as the patella moves down into the trochlear groove.
What is the significance of the patellofemoral joint?
Improves quadriceps efficiency and reduces friction.
What is the intercondylar notch?
A space in the femur that allows for ligament attachment and movement.
What is the tibial plateau?
The flat top part of the tibia that articulates with the femur.
What is the intercondylar eminence?
A bony prominence between the tibial plateaus that serves as an attachment for ligaments.
What is the function of ligaments in the knee?
They provide stability and limit excessive movement.
What is the primary function of the quadriceps muscle?
To extend the knee.
What are common causes of ACL injuries?
Deceleration combined with valgus and rotation, often when landing from a jump.
How do MCL injuries typically occur?
From a lateral blow to the knee, resulting in valgus stress.
What causes LCL injuries?
From a medial blow to the knee, resulting in varus stress.
What is a common cause of meniscal tears?
Twisting on a flexed knee.
What is patellofemoral pain associated with?
Weak hip abductors or imbalance of the vastus medialis oblique (VMO).
What is the screw home mechanism?
A mechanism that increases joint stability during the final stages of knee extension.
What happens during the last 20° of knee extension in open kinetic chain (OKC)?
The tibia externally rotates.
What occurs during the last 20° of knee extension in closed kinetic chain (CKC)?
The femur internally rotates.
What are the functions of the meniscus?
Shock absorption, stability, load distribution, joint lubrication, proprioception, and attachment for ligaments.
What are the two zones of the meniscus and their characteristics?
Red Zone: outer one third with blood supply; White Zone: inner two thirds, avascular.
What is the role of the popliteus muscle?
It initiates internal rotation of the tibia or external rotation of the femur to unlock the knee.
What muscles are considered knee stabilizers?
Quadriceps (especially VMO), hamstrings, popliteus, and IT band.
What bones are part of the ankle?
Talus, calcaneus, navicular, cuboid, and cuneiforms.
What is a clinical implication of advanced arthritis in the knee?
Loss of cartilage and joint space leading to stiffness and pain.
What is the effect of ligament and cartilage injuries on the screw home mechanism?
They can disrupt the screw home mechanism.
What is the role of proprioceptive exercises in rehabilitation?
To restore the screw home mechanism.
What are the knee flexors (8)?
Biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, popliteus, sartorius, gracilis, gastrocnemius (medial and lateral head), plantaris
What are the knee extensors (4)?
rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius
What are the internal rotators of the knee (5)?
Semitendinosus,semimembranosus,gracilis, sartorius,popliteus
What are the external rotators of the knee
biceps femoris (long and short head)
What membrane connects the tibia and fibula?
interosseous membrane
What are the two main joints of the lower leg?
Proximal and distal tibiofibular joints
What muscles are located in the lateral compartment of the lower leg?
Peroneus Longus and Peroneus Brevis
What are the five joints of the lower leg and ankle?
Tibiofibular joints (proximal & distal), Talocrural joint (ankle joint), Subtalar joint, Transverse tarsal joint (talonavicular & calcaneocuboid)
What type of joint is the Talocrural joint?
A synovial hinge joint
What bones articulate at the Talocrural joint?
Distal tibia and fibula with the talus bone
What is the function of the interosseous membrane?
It binds the tibia to the fibula and provides stability to the distal tibiofibular joint and talocrural joints.
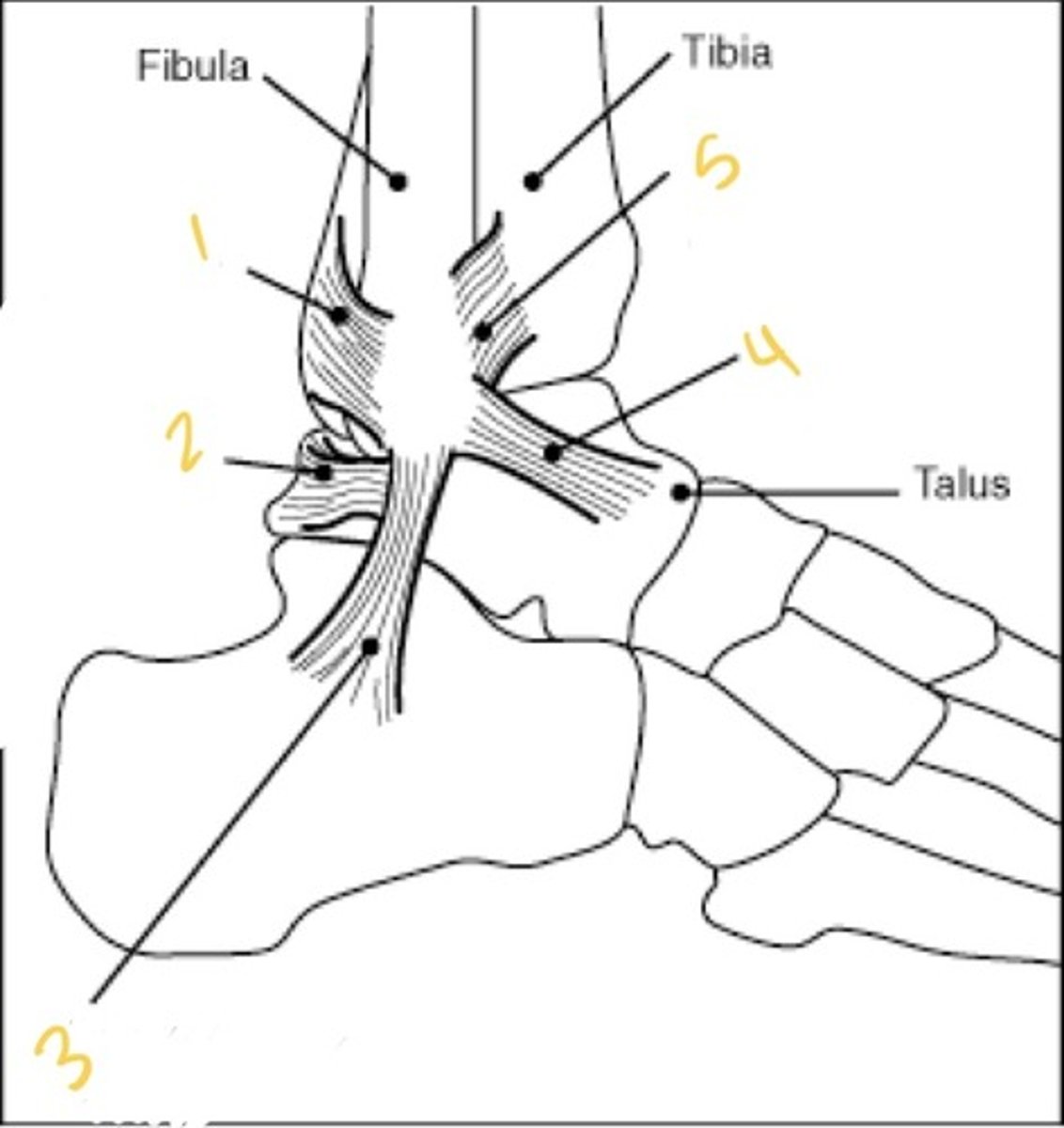
What ligaments improve the stability of the distal tibiofibular joint?
Anterior tibiofibular ligaments and posterior tibiofibular ligaments
What injury is associated with damage to the distal tibiofibular joint?
A high ankle sprain
What ligaments limit inversion at the Talocrural joint?
Anterior Talofibular Ligament, Calcaneofibular Ligament, and Posterior Talofibular Ligament
What movements are allowed at the Talocrural joint?
Dorsiflexion and plantarflexion
What is the rule for open kinetic chain (OKC) movement at the Talocrural joint?
Convex on concave; the talus moves on the tibia and fibula.
What happens during dorsiflexion at the Talocrural joint in OKC?
The talus rolls posteriorly and glides anteriorly.
What is the rule for closed kinetic chain (CKC) movement at the Talocrural joint?
Concave on convex; the tibia and fibula move on the talus.
What is the function of the Subtalar joint?
To adapt to uneven surfaces
What movements are allowed at the Subtalar joint?
Inversion and eversion
What occurs during inversion at the Subtalar joint in OKC?
The talus glides medially and the calcaneus rolls inward and medially.
What is the role of the anterior compartment muscles during gait?
They control foot placement during heel strike and eccentrically decelerate plantarflexion.
What is the primary function of the superficial posterior compartment during gait?
To provide primary propulsion and control forward movement of the tibia.
What is the role of the deep posterior compartment during gait?
To support the medial longitudinal arch and control pronation.
What common issue can arise from weak dorsiflexors?
Foot drop during gait, leading to dragging of the foot.
What effect does tight gastrocnemius-soleus have on movement?
It affects squat depth and gait mechanics.
What is the function of the tibialis posterior and peroneus longus during gait?
They create a 'stirrup' under the foot for medial-lateral stability.
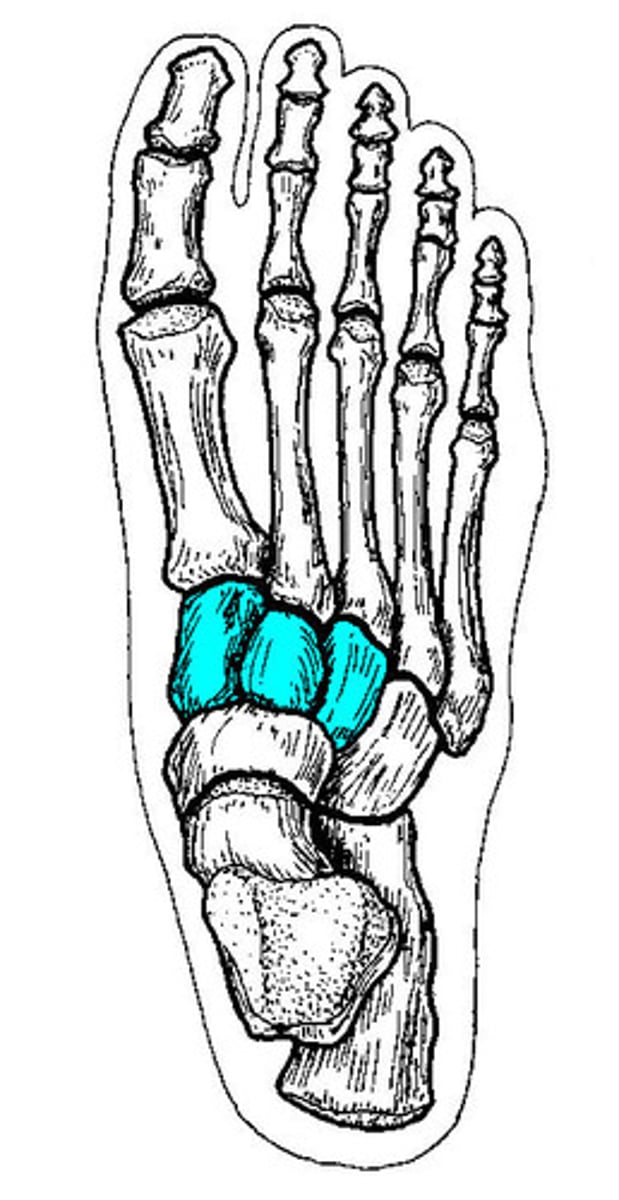
Cuneiforms
What bones are these
Talus
What bone is this
Calcaneus
What bone is this

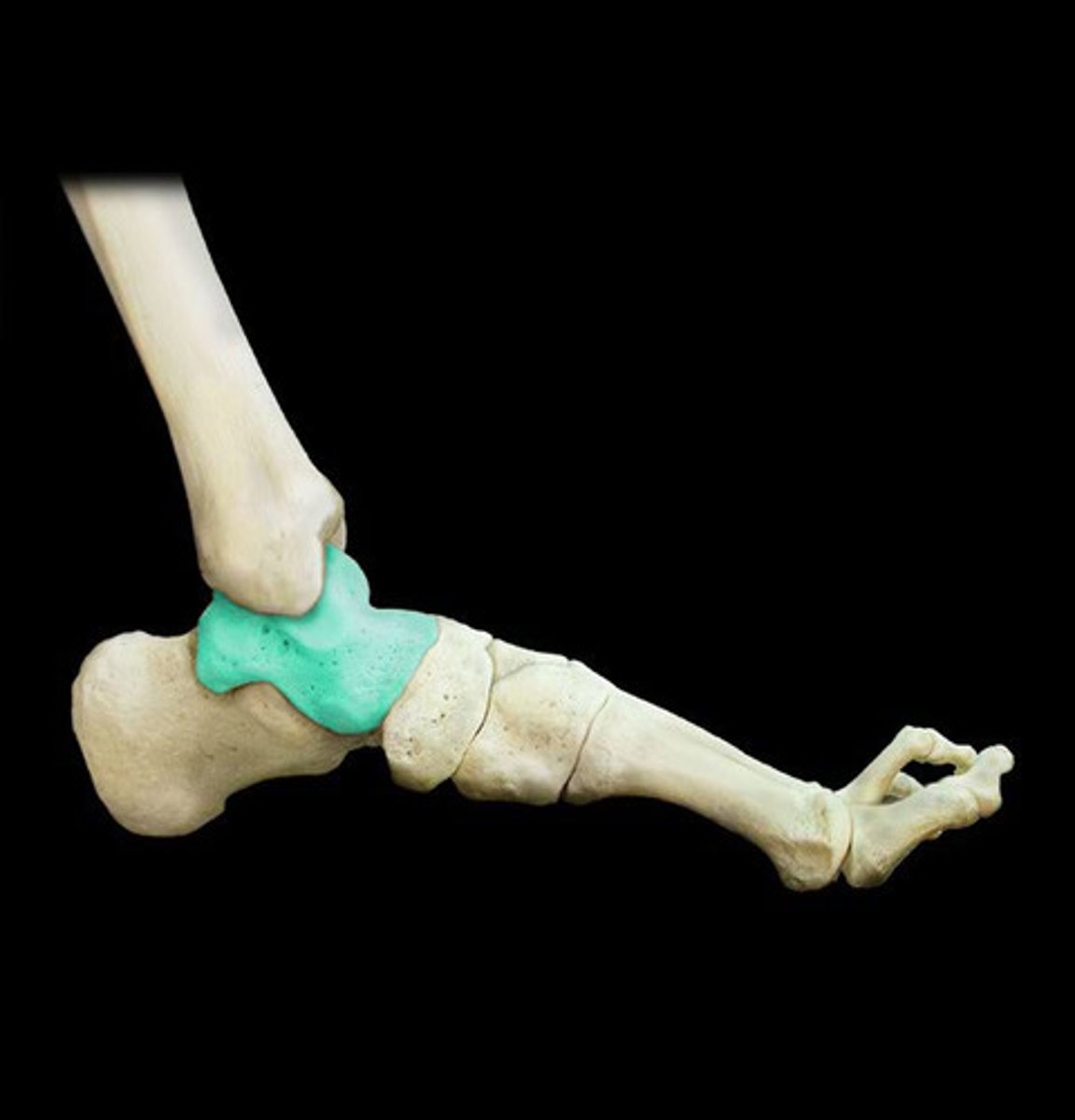
Subtalar joint
What joint is this
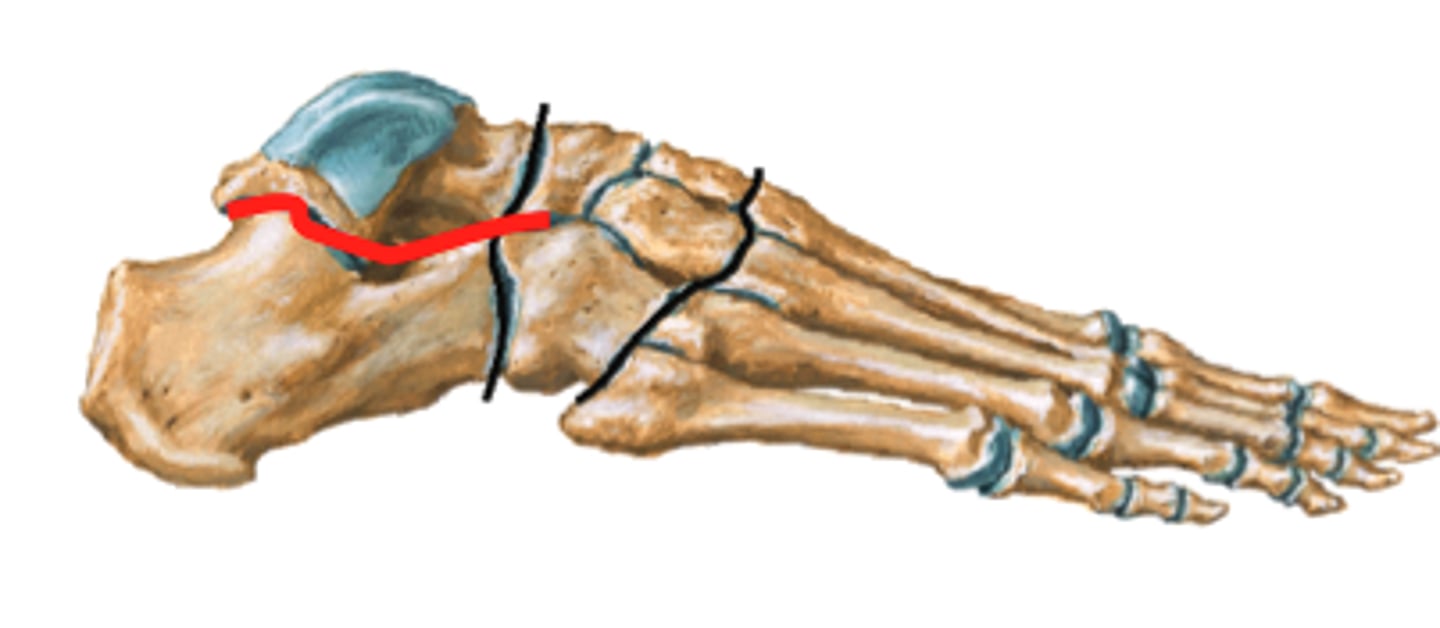
Transverse tarsal joint
What joint is this
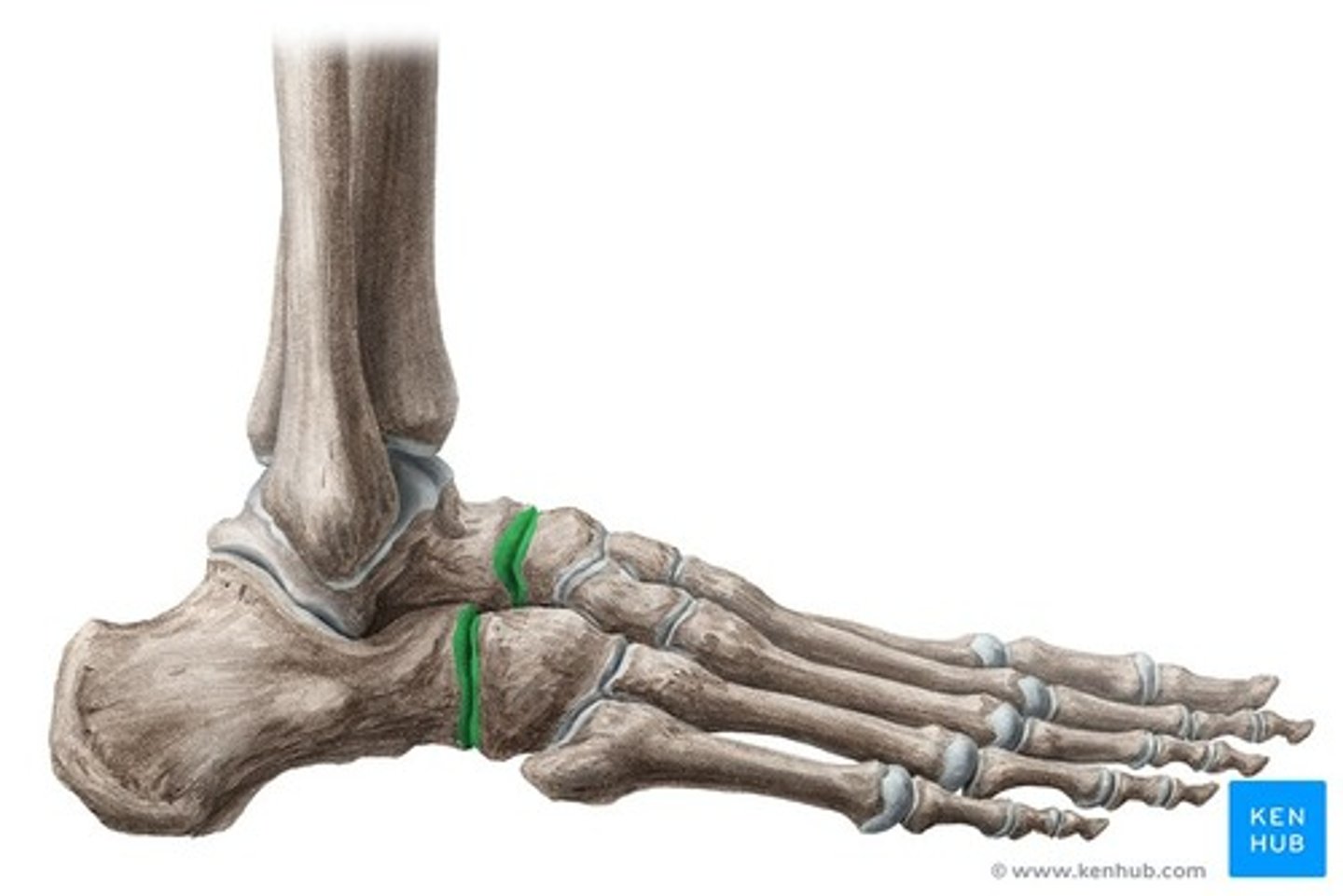
Talocrural joint
What joint is this
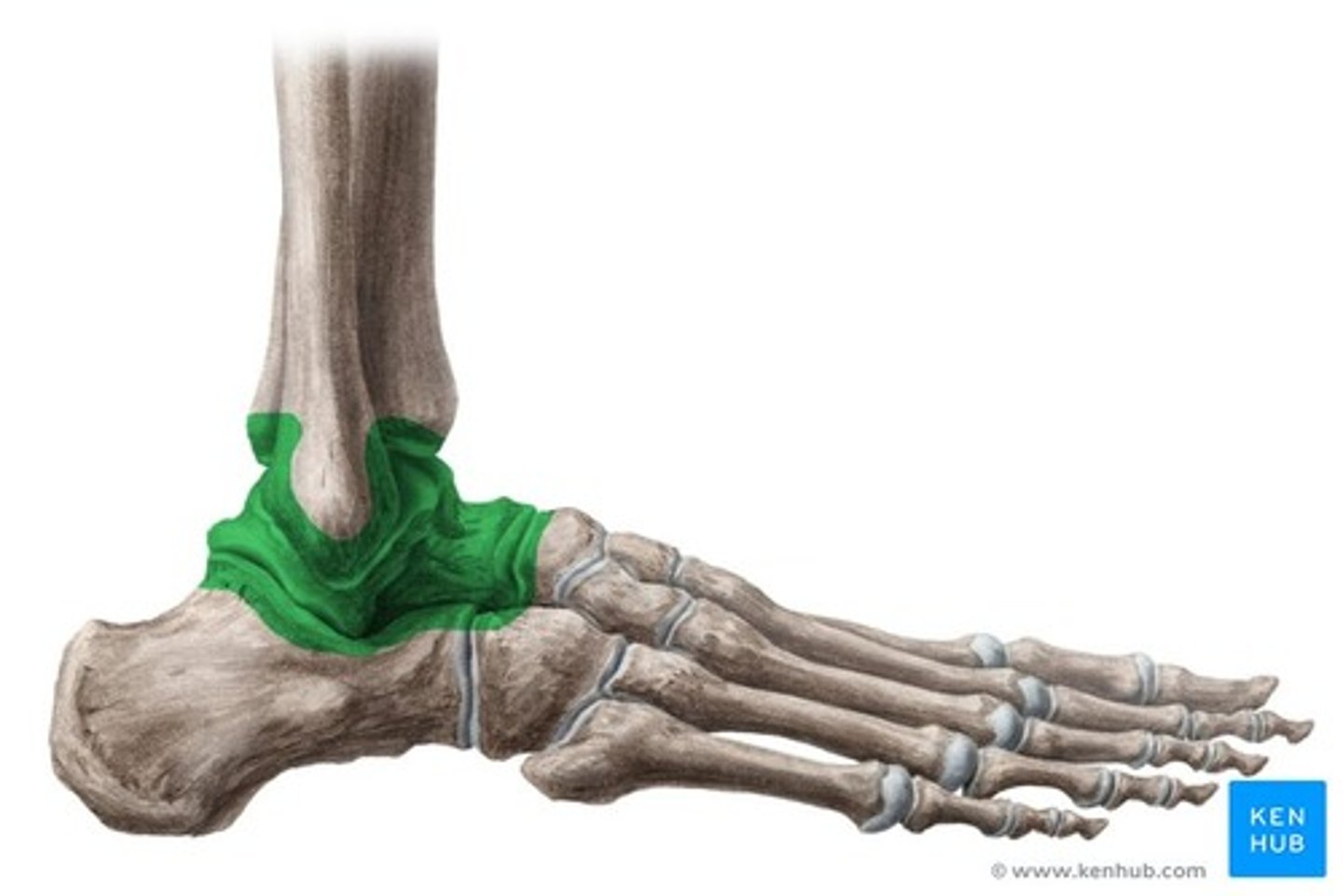
Why is the interosseous membrane important?
Binds the tibia to fibula, provides stability to the distal tibiofibular and talocrural joints, and origin of several muscles in the ankle and foot,
Anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament
What ligament is this (#5)?