HE 12-13 : Vertical Product Differentiation and Airline Classes-Karteikarten | Quizlet
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Vertical product differentiation states ?
• Level or degree of superiority
• Quality provision: low quality vs high quality
How to describe and analyse a product ?
• A set of utility-bearing attributes
• For any attribute, we can assess low or high value
• An attribute having a high value is superior to the same attribute having a low value, other things being equal
Parameters of duopoly in vertical product differentiation ?
• 𝐹1 and 𝐹2 compete by choosing quality
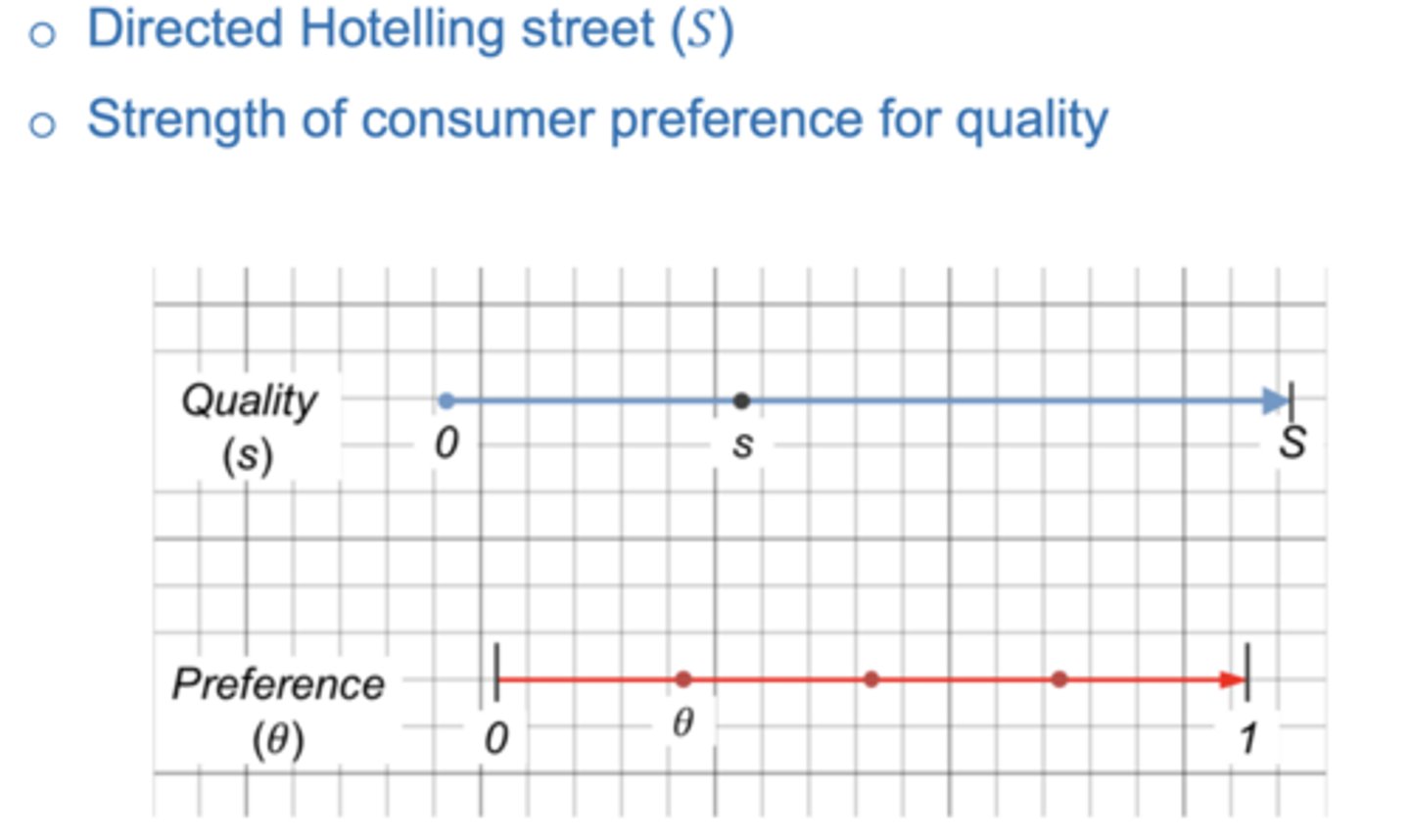
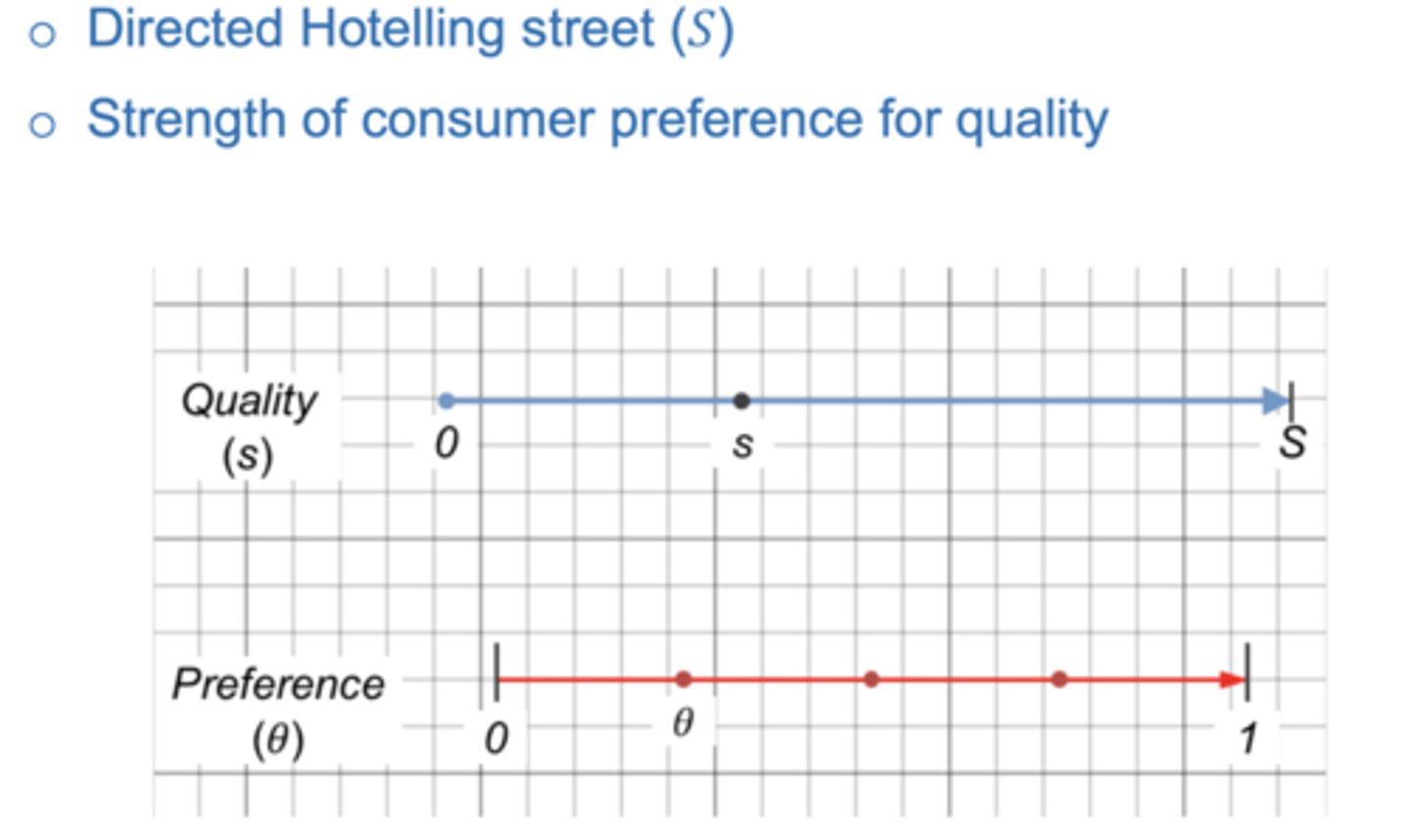
• 𝑆-mile-long directed street (𝑆 > 0 )
• 𝑠 measures quality level: 𝑠 = 0, 𝑠 = 1, 𝑠 = 2, ..., 𝑠 = S
How is the supply side ?
• Same product with various quality (one attribute)
• No production constraints
• Same marginal cost: 𝑐1 = 𝑐2 = 𝑐 = 0 (quality independence)
How is the demand side ?
• Consumer preference for quality uniformly distributed
• To what extent a consumer values quality: 𝜃(0 ≤ 𝜃 ≤ 1): value attached to a given quality
• Each consumer has the same willingness to pay: r
• Utility of the consumer: 𝑟 − 𝑝 + 𝜃 ∙ 𝑠
What do firm decisions consist of ?
Quality choice and price choice (s, p)
What price if s1 = s2 ?
regardless of what level, no product differentiation
Firms have no market power: 𝑝1 = 𝑝2 = �
What price if p1 = p2 ?
all consumers will only buy high quality
Firms will only choose high quality, 𝑠1 = 𝑠2 = 𝑆, still no product differentiation
What are the optimal qualities and prices ?
• Determine quality and price at the same time
• Competition
How to identify equilibrium condition ?
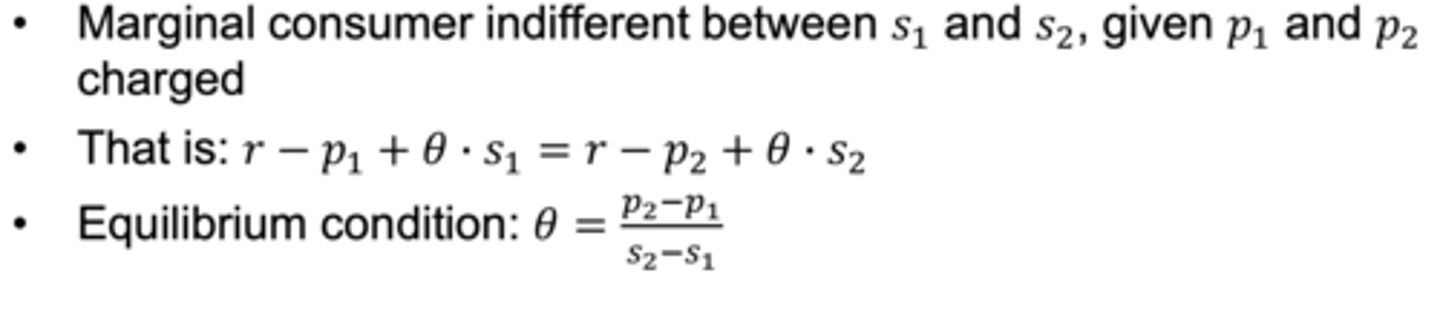
Demands and profits at equilibrium ?
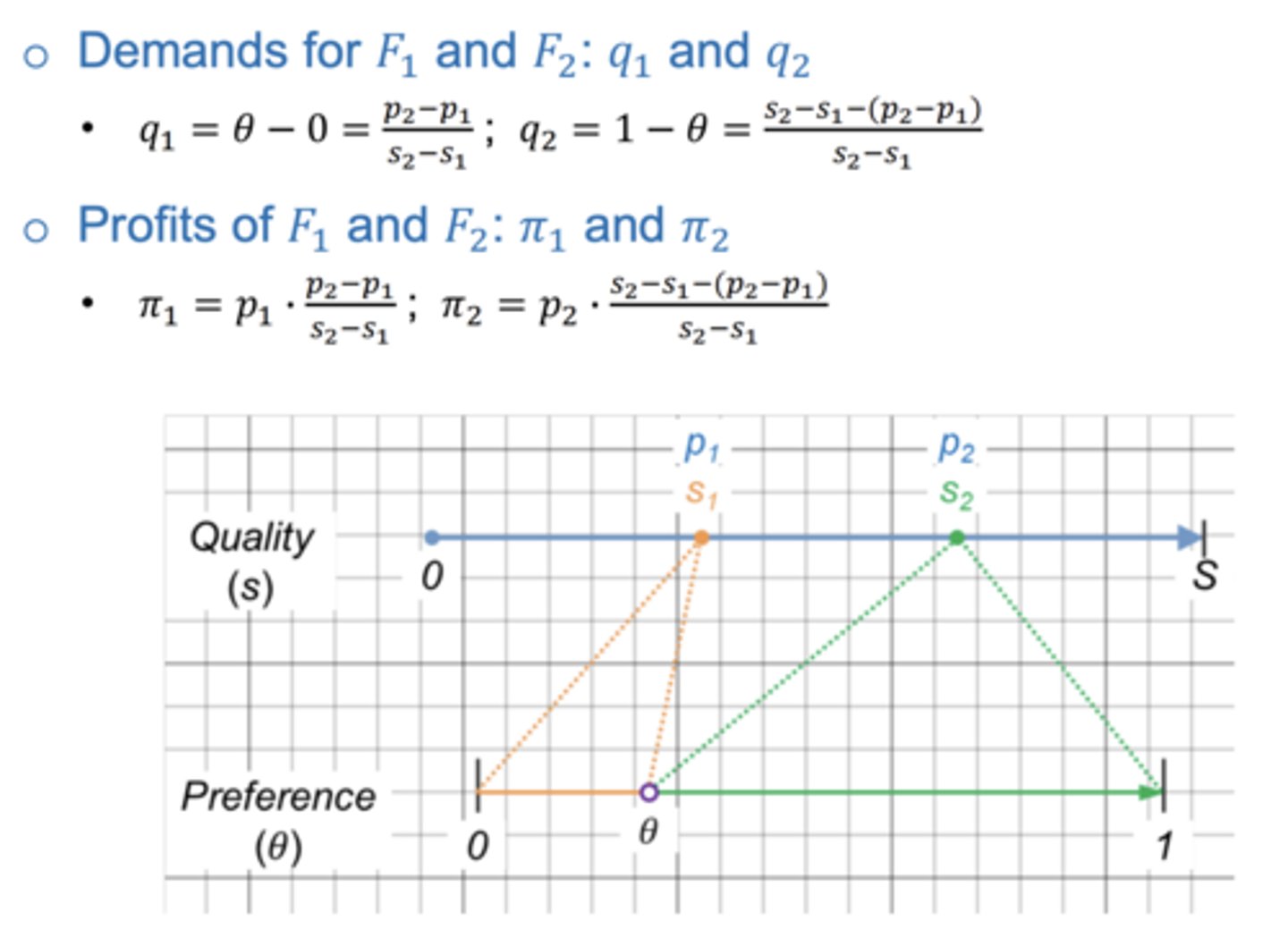
How to find the maximum profit for F1 and F2 ?
Set the marginal profit to 0
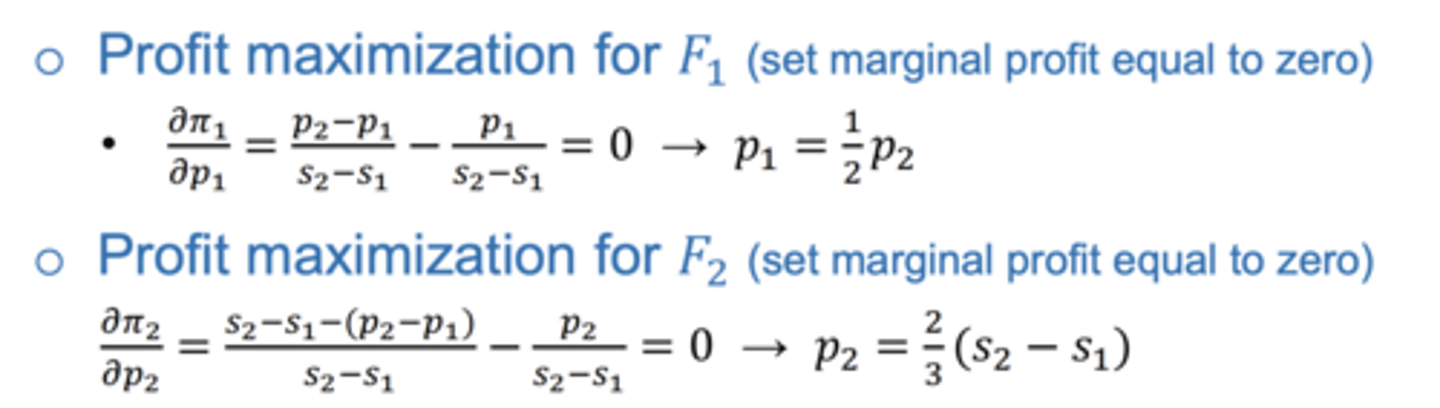
What are therefore the optimal prices ?
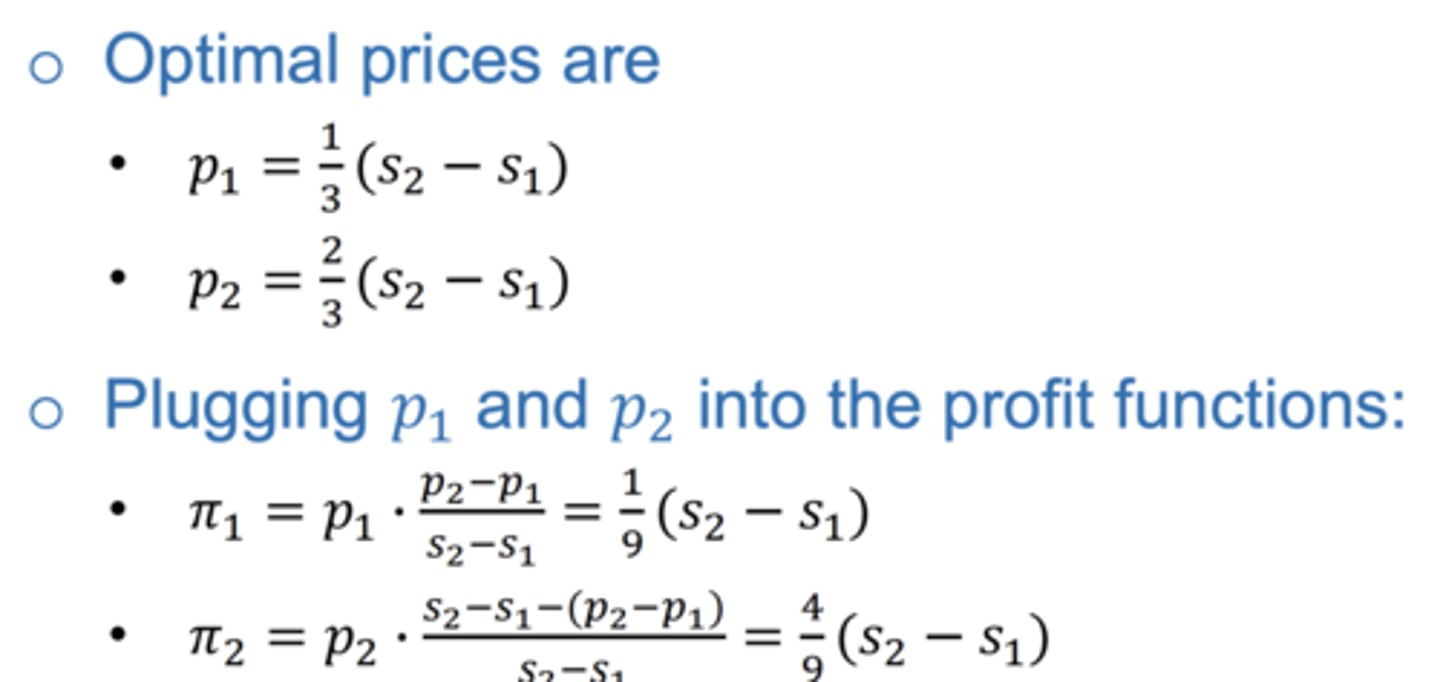
When do you maximise profit ? Equilibrium ?
When S2 - S1 is maxed
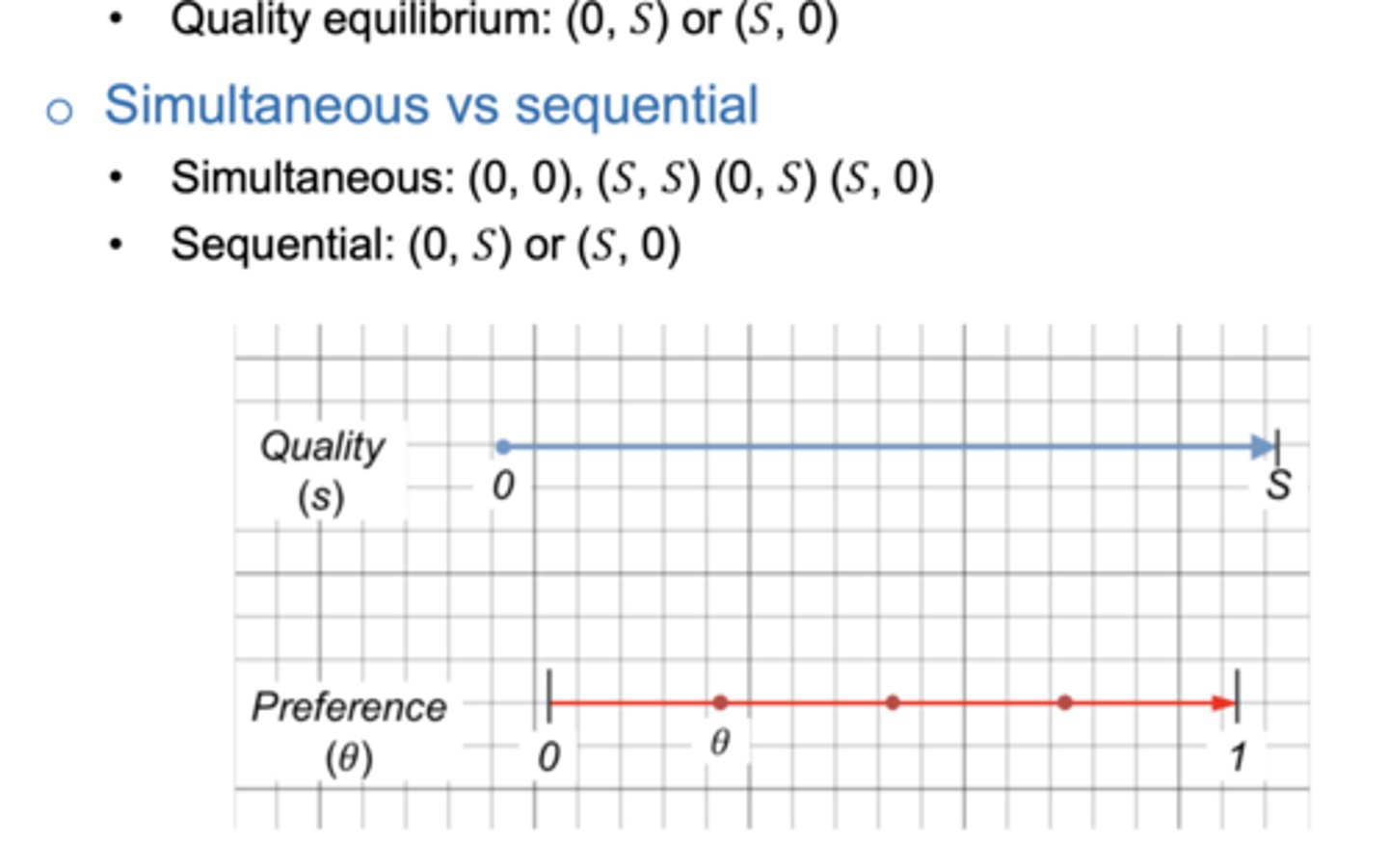
Where is the marginal consumer ?
at (S;0) or (0;S) monopolist