Comprehensive Nutrition, Digestion, and Healthcare System Overview
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
What is digestion?
The act of the body breaking down food into simple substances that are absorbed as nutrients or eliminated as waste.
What initiates the process of digestion?
Saliva.
What organs are involved in the human digestive system?
Mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
What is the role of the esophagus in digestion?
It connects the mouth to the stomach and propels food down using muscular contractions.
What functions does the liver perform in digestion?
Filters toxins from the blood and produces bile to break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
What is the function of the gallbladder?
Stores bile produced by the liver and releases it when needed.
What does the pancreas produce and what is its role?
Produces insulin, which regulates the metabolism of sugars.
What happens in the small intestine during digestion?
Food is broken down further and nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream.
What is the function of the large intestine?
Removes water and electrolytes from food particles and converts the rest into feces.
What common digestive issues can disrupt the digestive system?
Diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, gas, and bloating.
What are the basics of healthy eating patterns?
Maintaining a balanced diet, watching caloric intake, and consuming necessary nutrients.
What is the recommended dietary intake for adults?
2 cups of fruit, 2 ½ cups of vegetables, 6 ounces of grains, 5 ½ ounces of protein, and 3 cups of dairy.
What is the significance of fiber in a diet?
Helps control weight and hunger by allowing fewer calories to be eaten.
What is a healthy weight loss plan?
Losing 1-2 pounds per week through lifestyle and dietary changes along with exercise.
What are macronutrients?
Nutrients required in large amounts, including protein, carbohydrates, and fats.
What are micronutrients?
Vitamins and minerals required in small amounts for optimal growth and body function.
What is the role of protein in the body?
Provides amino acids necessary for structure, function, and repair of body tissues.
What are sources of protein?
beans, soy, nuts, meats, eggs, and fish
What are healthy sources of carbohydrates?
Vegetables, fruits, milk, nuts, grains, legumes, and seeds.
What is the glycemic index?
A measure of how carbohydrate-containing food affects blood glucose levels.
What types of fats should be limited or avoided?
Trans and saturated fats.
What are trans fats and why are they harmful?
Partially hydrogenated oils found in processed foods that raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL cholesterol.
What is the recommended daily protein intake for adults?
Between 2 and 6 ½ ounces, depending on activity level, age, and gender.
What is the role of carbohydrates in the body?
Provide energy and make up 45-65% of total daily calories.
What is the difference between simple and complex carbohydrates?
Simple carbohydrates are sugars, while complex carbohydrates include starch and fiber.
What should be prioritized in a healthy diet?
Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and low-fat proteins while limiting unhealthy fats and salt.
What type of fats are found in full-fat dairy products?
Saturated fats
How can a diet high in saturated fat affect health?
It can increase the risk of heart disease and raise total blood cholesterol levels.
What are monounsaturated fats primarily sourced from?
Foods such as avocados, various nuts and their oils, and olives and olive oil.
What role do vitamins play in the body?
They promote health, ward off disease, and support bodily functions.
Why must vitamins be derived from diet?
Because they are not produced in the body.
What are water-soluble vitamins?
Vitamins that dissolve in water, such as vitamin C and B complex, and are not stored in the body.
What are fat-soluble vitamins, and where are they stored?
Vitamins that dissolve in fats and are stored in the liver and fatty tissues for later use.
What are primary minerals and name a few examples?
Noncarbon, inorganic nutrients with specific functions, such as calcium, iron, and potassium.
What is the function of calcium in the body?
It helps build and maintain bones and teeth, and assists with muscle function, nerve signaling, and blood clotting.
What is the role of zinc in the body?
It supports immune function, helps heal wounds, and is critical for growth and development.
What does iron do in the body?
It transports oxygen via hemoglobin cells, helps maintain energy levels, and supports the immune system.
What is the significance of water as a nutrient?
It makes up more than half of body weight and is essential for proper bodily functions.
What are the recommended daily water intake amounts for men and women?
(F) 2.7 to 3 L; (M) 3.5 to 3.7 L.
How can adequate nutrition be assessed?
By evaluating physical appearance, weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
What BMI range is considered normal/healthy?
A BMI of 18.5 to 24.9.
What are the potential health risks associated with obesity?
Diabetes, high blood pressure, certain cancers, osteoarthritis, and elevated cholesterol levels.
What dietary recommendations can help combat obesity?
Adopt a healthy eating plan, increase physical activity, and consume more micronutrients and vitamins.
What are antioxidants and where are they found?
Substances that protect cells from free radicals, commonly found in plant-based foods.
What is the role of proteins in the body?
They form the structure of bones, cartilage, muscles, blood, and skin, and constitute enzymes, hormones, and vitamins.
How can nutritional status be indicated through physical appearance?
By assessing the condition of hair and skin.
What are signs of inadequate nutrition?
Low body weight, weakness, fatigue, dry skin, brittle hair, and frequent infections.
What can a diet low in vitamin C lead to?
Irritation in the gums.
What dietary changes can improve oral health?
Increasing vitamin C intake through foods like tomatoes, leafy greens, and strawberries.
What vitamins are important for skin health?
Vitamins A, C, D, and E.
What dietary components support brain health?
Adequate omega-3 fatty acids.
What are omega-3 fatty acids important for?
They support brain health and can help prevent fatigue, memory loss, and concentration issues.
Name three food sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
Flax seed, walnuts, and fish oil.
What diets have been shown to reduce changes to white and gray matter in the brain?
The Mediterranean diet, DASH diet, and MIND diet.
What types of foods, besides omega-3 sources, are recommended for brain health?
Berries (like blueberries, strawberries, blackberries) and whole grains.
What is the relationship between fiber intake and chronic disease?
Adequate fiber intake can decrease overall rates of chronic disease.
What are some health benefits of a high-fiber diet?
Lower cholesterol, improved blood glucose control, and reduced risk of colorectal cancer.
List some food sources of dietary fiber.
Legumes, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
What is the first step to reduce inflammation through diet?
Eliminating dietary items known to provoke inflammation.
What types of foods should be avoided to reduce inflammation?
Processed foods with extensive ingredient lists, especially those high in sugar, salt, or unhealthy oils.
What are some examples of whole foods recommended for an anti-inflammatory diet?
Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, poultry, fish, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
What improvements might individuals notice on an anti-inflammatory diet?
Clearer skin, reduced discomfort, better digestive health, and lower blood pressure.
What is included in a nutritional assessment?
Reviewing dietary habits, performing a 24-hour recall, and using food frequency questionnaires.
What is the purpose of a 24-hour recall in nutritional assessments?
To see what the client has consumed in the last 24 hours, including foods and portion sizes.
What does a food frequency questionnaire aim to determine?
The client's typical food consumption based on a list of foods.
What is an NPO diet?
A diet that restricts the client from eating or drinking anything until the diet is advanced.
Why might a client be placed on an NPO diet?
Due to inability to safely eat, scheduled surgery, or diagnostic tests requiring fasting.
What is a regular diet?
A healthy, varied diet with foods from all food groups without significant health concerns.
What characterizes a soft diet?
Foods that are soft, easy to digest, low in fiber, and easy to swallow.
What is a pureed diet?
A diet of soft and smooth foods that do not require chewing.
What is a full liquid diet?
A diet consisting of liquids and foods that are considered liquids at room temperature.
What is a clear liquid diet?
A diet consisting of clear liquids that offer little daily calories and nutrients.
What is the purpose of a clear liquid diet?
To decrease strain on the digestive system while keeping the body adequately hydrated.
What should be avoided in clear liquid diets for colon procedures?
Liquids or gelatins with red coloring to prevent confusion with bleeding.
What are the risks associated with aspiration?
Aspiration occurs when food, liquid, or other materials enter the lungs, which can happen due to difficulty swallowing.
What medical conditions increase the risk of aspiration?
Stroke, acid reflux, mouth sores, and dental issues.
What are the symptoms of overt aspiration?
Coughing, wheezing, trouble breathing, congestion, heartburn, throat clearing, or chest discomfort.
What is silent aspiration?
Aspiration that occurs without obvious symptoms.
How can diet modification help prevent aspiration?
By thickening liquids to reduce the risk of aspiration in clients with dysphagia.
What are the different consistencies of thickened liquids?
Mildly thick (nectar), moderately thick (honey), and extremely thick (pudding).
What should be done to verify the thickness of thickened liquids?
Stir the liquid after adding thickener and tilt the spoon to see how fast the liquid flows off.
What are some examples of liquids that can be thickened?
Milk, tea, water, coffee, soup, juice, and nutritional supplements.
What is the role of nurses in assisting clients with eating?
To assess clients' ability to safely swallow and provide nutritional support.
What should be done before a meal arrives for a client?
Position the client upright, check if they need to use the restroom, and ensure necessary items are within reach.
What is glucose and its significance in the body?
Glucose is the primary sugar in the blood and the body's major source of energy.
When should blood glucose monitoring be performed?
Before/after meals or exercise, prior to bed, during illness, with new medications, or when routines change.
What is considered a fasting blood glucose level?
A blood glucose level taken after being NPO for at least 8 hours.
What is the expected reference range for fasting blood glucose in clients without diabetes?
70 to 110 mg/dL.
What is hypoglycemia?
A condition where blood glucose levels drop below 70 mg/dL.
How should hypoglycemia be treated?
Provide 15g of carbohydrates and recheck glucose levels after 15 minutes.
What is insulin and its function?
A hormone made in the pancreas that helps lower blood glucose by using or storing sugar.
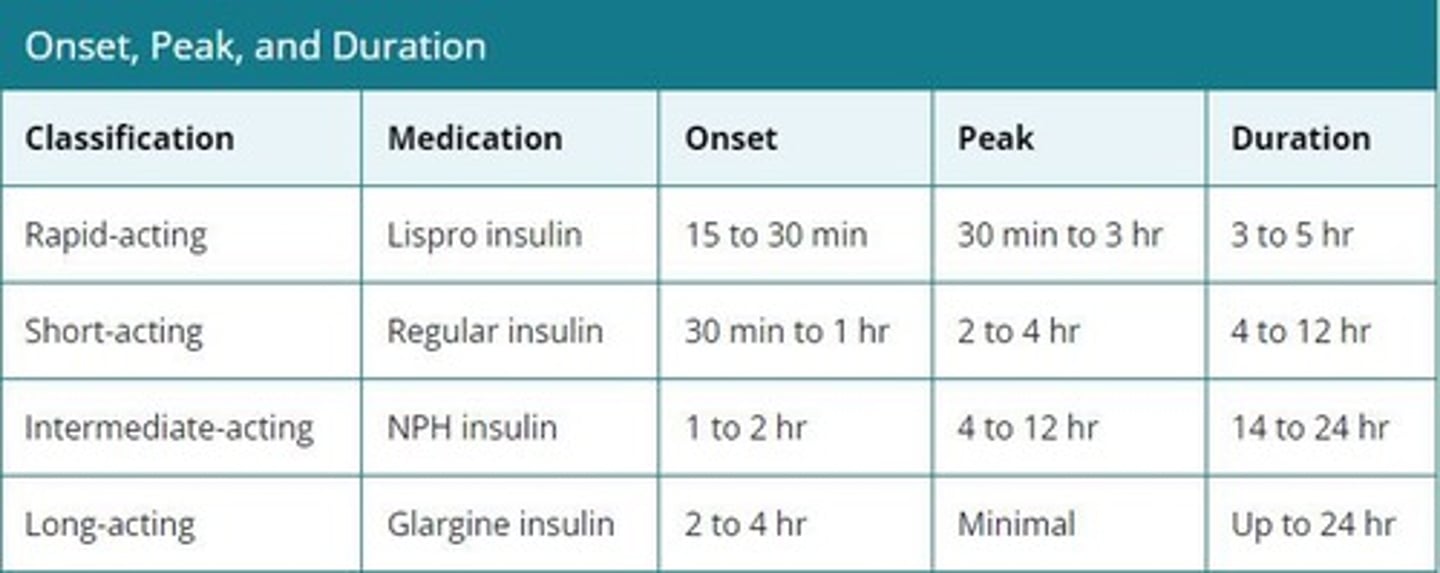
What are the common methods for administering insulin?
Injected into fatty tissue under the skin, typically at a 90° angle.
What is a gastrostomy tube (G-tube)?
A tube that delivers nutrition directly into the stomach for clients unable to consume enough nutrition.
What are the three methods for G-tube insertion?
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG), laparoscopic technique, and open surgery technique.
What is the most common method for G-tube insertion?
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG).
What is the purpose of monitoring for aspiration in tube feeding?
To prevent complications such as difficulty breathing or pneumonia.
What signs indicate a client may have aspirated during tube feeding?
Coughing, choking, gagging, or vomiting.
What should be done if signs of tube feeding aspiration occur?
Stop tube feeding and immediately notify the provider.
What is a nasogastric (NG) tube?
A thin plastic tube inserted into the nostril and down the esophagus, ending in the stomach, used to administer nourishment or remove substances.
What is the primary use of a nasoduodenal tube?
Used primarily for long-term enteral feedings for clients who cannot tolerate gastric feeding.