Chapter nine: Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
The STP process
S:
1. establish strategy or objectives
2. use segmentation methods
T:
3. evaluate segment attractiveness
4. select target market
P:
5. identify and develop positioning strategy
Establish the overall strategy or objectives
-articulate the vision or objective of the company's marketing strategy clearly
-must be constant with and derived from mission and objectives as well as its current situation (SWOT)
Use segmentation methods
-use a particular method or combination method to segment market
-develop descriptions of the different segments which helps firms better understand the customer profiles in each segment
-there are 5 segmentation methods (geographic, demographic, psychographic, behavior, and benefit segmentation)
Geographic segmentation
-organizes customers into groups on the basis of where they live (country, region, areas within a region)
-most useful for companies whose products satisfy needs that vary by region
-marketers can make adjustments to meet the needs of smaller geographic groups
Demographic segmentation
groups consumers on the basis of easily measured, objective characteristics such as age, gender, income, and education (you need to know that for the EXAM!!!)
-MOST COMMON FORM OF SEGMENTATION
-easy to identify and easy to reach
-gender is important, but we are becoming more gender neutral
-we must rethink our stereotypes about who is buying what items (ex: not just young people are buying activewear, even old people are)
Psychographic segmentation
segmenting customers based on how they spend time, money, what activities, attitudes, and opinions abt the world
-how consumers describe themselves
Psycographics
studies how people self-select based on characteristics abt how they choose to occupy their time (behavior) and what underlying psychological reasons determine those choices
3 components of peoples psychographic make-up
self-values, self-concept, and lifestyle
self-values
goals for life, not just the goals one wants to accomplish in a day; a component of psychographics that refers to overriding desires that drive how a person lives his or her life
self-concept
people's self-image or the image people ideally have for themselves
-ex: show people laughing and having a great time in a commercial
lifestyle
the way we live
Benefit segmentation
groups consumers on the basis of the benefits hey derive from products or services
Behaviorial Segmentation
divides customers into groups on the basis of how they use the product or service
-two common behavioral measures are occasion and loyalty segmentation
occasion segmentation
segmentation based on when a product or service is purchased or consumed
-ex: snack food
loyalty segmentation
investing in loyalty initiatives to retain the firms profitable customers
-ex: buy 10 sandwiches get the 11th free
Using multiple segmentation methods
-Although all segmentation methods are useful, each has its unique advantages and disadvantages.
-use a combination
-Thus, firms often employ a combination of segmentation methods, using demographics and geography to identify and target marketing communications to their customers, then using benefits or lifestyles to design the product or service and the substance of the marketing message.
-use market basket analysis
-use geographic segmentation or tapestry segmentation system to help retailors find a good location
market basket analysis
A mathematical modeling technique that utilizes millions of customer purchases, often referred to as big data to determine an association between a group of items that customers purchase at the same time and place into their actual or virtual market basket. This analysis enables the firm to classify customers into behaviorally oriented market segments.
Geodemographic segmentation
uses a combination of geographics, demographics, and lifestyle characteristics to classify consumers
-ex: consumers in the same neighborhood tend to buy the same things
Tapestry Segmentation
used for geodemographic marketing
-classifies all U.S. residential neighborhoods into 65 distinct segments based on demographic and lifestyle data and each block is sorted by income, home value, or occupation
Evaluate segment market attractivness
to evaluate the attractiveness of a segment, the marketer must first determine whether the segment is worth pursuing.
-is it identifiable, substantial, reachable, responsive, and profitable?
identifiable
firms must be able to identify who is within their market to be able to design products or services to meet their needs
-must have distinct segments
substantial
needs to measure the size of the target market
-if it is too small, or buying power insignificant it will not generate enough profit
reachable
you need your market to be able to be reachable through persuasive communications and product distribution
-consumers must know that the product exists, what it can do for them, and how they can buy it
Responive
consumers in the segment must react similarly and positively to the firms offering
-firms should not target someone who it cant provide services and products to
profitable
-current and future profits
-keep in mind market growth market competition, and market access
-evaluate the profitability of a segment over the lifetime of one of its types of customers
-focus on how long they will remain loyal , cost of replacing lost customer, whether they will be more or less expensive in the future
Market share calculations
McD's=$300 M share of the market
SB=700 M
7Brew=500 M
Dunkin=500 M
What share of the market does cup of joe have
firms sales/total sales
500/300+700+500+500
=1/4 or 25% of market share (if starbucks has 60% of the market and mcdonalds has 10% of the market, the ratio is 6 to 1)
What is the formula for segment profitability?
Example:
In a segment of children under the age of 15, the segment size if 60 million people, 35% of people are buying, most people make one purchase of $500, the profit margin is 10%, and the fixed cost is $50 million
=(segment size x segment adoption % x purchase behavior x profit margin %)-Fixed costs
=1,000,000,000 (THIS IS POSITIVE SO IT ITS PROFITABLE)
Select a target market
select a target market that you are able to pusue so analyze its own competitors (SW) and the alternatives of the market (OT)
There are 4 targeting strategies:
1. Undifferentiated targeting strategies or mass marketing
2. Differentiated targeting strategy
3.consentrated targeting strategy
4. Micromarketing
Undifferentiated targeting strategy
everyone is a potential customer
-focus on the similarities in the needs of customers
-not that common (used to be in things like sugar but now even those companies are trying to diversify from others
differentiated targeting strategy
target several market segments with a different offering for each
-helps diversify business and has lower risk
-could be more costly for the firm
-helps them have a bigger share of the market
Concentrated targeting strategy
organization selects a single, primary target market and focuses all its energies on providing a product to fit that market's needs
-entrepreneurial startups use this because it allows them to employ their limited resources more efficiently
Mocromarketing
when a firm tailors a product or service to suit an individual customers wants or needs
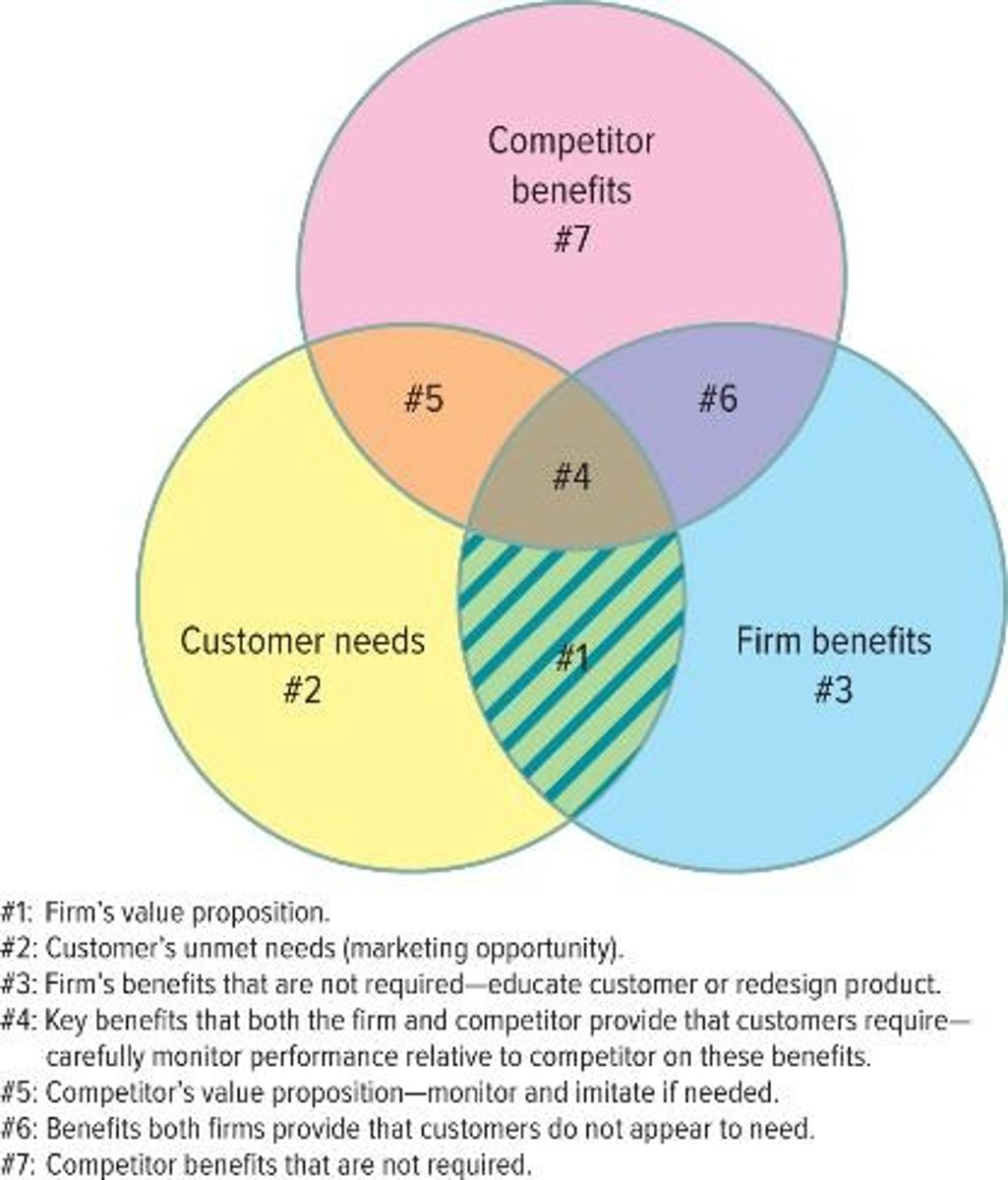
Identify and develop positioning strategy
market positioning and value proposition
marketing positioning
involves the process of defining the marketing mix variables so that target customers have a clear, distinctive, desirable understanding of what the product does or represents in comparison with competing products
Value proposition
the unique value that a product or service provides to its customers and how it is better than and different from those of competitors
4 positioning methods
1. Value
2. Salient Attributes
3. Symbol
4. Competition
value
reflects the relationship of benefits to costs, or what you get for what you give
-but... value is in the eyes of the beholder
Salient attributes
focuses on the product attributes that are most important to the target market
Symbols
well known symbols create a position for the bran that distinguishes it from its competition
competition
choose to position products against a specific competitor or entire product/service classification
-don't want to get too close because you could get a lawsuit
Positioning using perceptual mapping
perceptual map displays two or more dimensions the position of the products or brands in the consumers mind
-the ideal point is the position at which a particular market segment's ideal product would lie on a perceptual map.
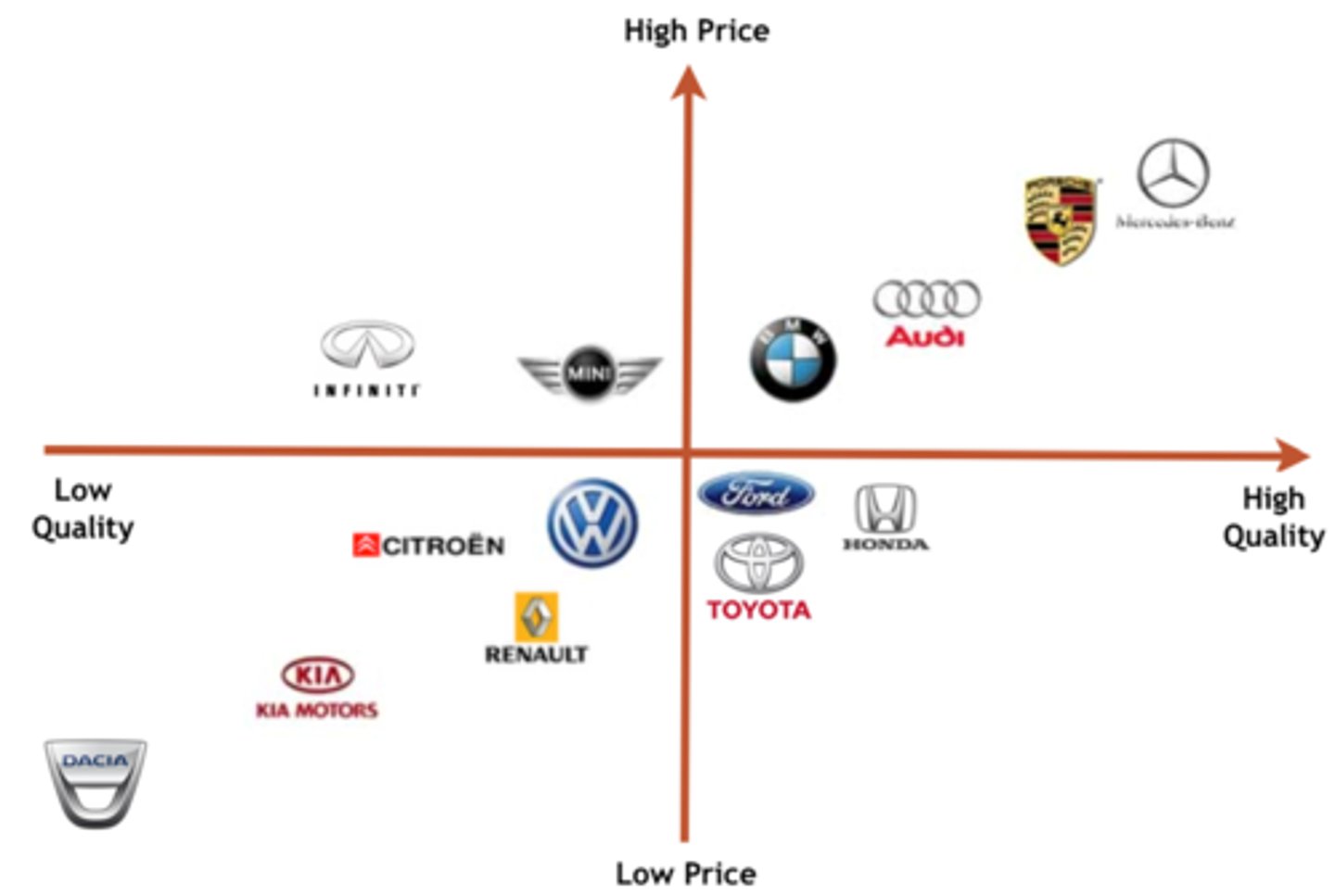
6 steps of perceptual mapping
1. Determine consumers' perceptions and evaluations of the product or service in relation to competitor's product or service (ask questions about from and competitors product why would a consumer choose one over the other)
2. Identify market's ideal point and size (use different size ovals to represent the size of current and potential markets and you want to focus on the larger markets)
3. Identify competitors position (how do competitors position themselves)
4. determine consumer preferences (identify the ideal product or service that appeals to each market)
5. Select the position (could choose to market to people who already like product or develop new product to target market or ignore small market)
6. monitor positioning strategy (consumers tastes shift and competitors react to these shifts. The first three steps should be ongoing and do 4 when needed)