all ANOVA
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is ANOVA used for?
To compare two or more means and test the null hypothesis.
What does the p-value in ANOVA indicate?
How likely the observed results would occur if the null hypothesis were true.
What type of variables does ANOVA require?
Categorical independent variable (IV) and continuous dependent variable (DV).
What does ANOVA measure?
How much variance in the DV is explained by the IV.
What is the F ratio?
Ratio of model variance to error variance (how good the model is vs. error).
What is an omnibus test?
Tells if there is a difference among groups but not where → hence why you need follow ups; reduces Type I error (false positive)
How many IVs and groups in one-way ANOVA?
One IV (with multiple levels), 2+ groups with no overlapping members.
What are the assumptions of ANOVA? (INCH)
Independent sampling
Normal distribution
Continuous DV (interval or ratio)
Homogeneity of variance (Levene’s test should be non-significant)
Why do we need post hoc tests?
ANOVA tells if there is an effect but not where; post hoc compares all levels.
What is the risk with post hoc tests?
Inflates Type I error; use corrections like Bonferroni.
planned contrast reduce the type 1 error
What are planned contrasts and which one is simple, repeated, helmert and deviation
Hypothesis-driven comparisons:
Simple: Each level vs first/last
Repeated: Stepwise comparisons
Helmert: Each level vs all previous
Deviation: Each level vs overall effect
What is ANCOVA?
ANOVA with a covariate to control for additional variance in DV.
What does ANCOVA test?
After accounting for covariate, how much variance in DV is explained by IV.
Assumptions of ANCOVA?
Covariate is continuous
Covariate independent of IV
Homogeneity of regression slopes (relationship CV-DV same across IV levels
how to check the assumptions of ANCOVA
covariate independence: non sig = independence (run GLM with covariate as DV)
how to check linearity: scatterplot → should be linear
homogeneity of regression slopes: Add interaction in model → non sig is assumption met
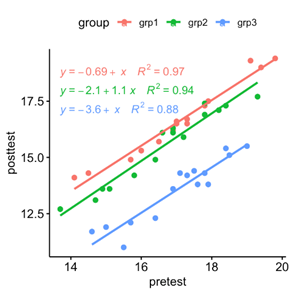
What does effect size measure?
Magnitude of difference between groups; not affected by sample size.
what is difference between eta squared and partial eta squared
Eta sqaured = if there’s only one effect - proportion of total variance explained by the effect
Partial eta squared = if ore than one effect → proportion of variance explained by effect, which is not explained by other variables
Formula for partial eta squared?

What benchmarks are used for interpreting effect size?
Small ≈ 0.01
Medium ≈ 0.06
Large ≈ 0.14
What is a one-way repeated measures ANOVA used for?
It is used when there is one group measured under multiple conditions or time points, allowing comparison of means across these conditions.
How is the F-ratio in repeated measures ANOVA different from independent groups ANOVA?
It tells us how much better our model fits compared to the null model, but is calculated differently because repeated measures remove variance due to individual differences.
Why does repeated measures ANOVA have more statistical power than independent groups ANOVA?
Because the denominator of the F-ratio is smaller after removing variance due to individual differences (same participants in all conditions).
What are the assumptions of one-way repeated measures ANOVA?
DV is on a continuous scale (interval or ratio)
Data are normally distributed
Sphericity (equal variances and covariances across levels)
What is sphericity and how is it tested?
Sphericity means equal variance within each level of the IV and equal covariance between pairs of levels. Tested using Mauchly’s test, required only if there are 3 or more levels.
don’t use homogeneity of variance for this ANOVA
What happens if Mauchly’s test is significant?
Sphericity is violated; apply corrections:
Greenhouse-Geisser (conservative)
Huynh-Feldt (liberal, used if epsilon > .75)
Safest option: Greenhouse-Geisser.
What is a factorial (mixed) ANOVA?
An ANOVA with two or more IVs, which can be any combination of within-subjects and between-subjects factors. It tests main effects and interactions.
What is a 2×2 ANOVA?
An ANOVA with two IVs, each having two levels, resulting in four conditions.
What does an interaction mean in factorial ANOVA?
The effect of one IV on the DV changes depending on the level of the other IV.
What are the assumptions for factorial ANOVA?
DV is continuous and normally distributed
Sphericity for within-subject factors
Homogeneity of variance for between-subject factors
How do you interpret plots in factorial ANOVA?
If lines are not parallel, there is an interaction.
what does nesting mean
which of the IV is a higher priority based on the independent variable we want to test
when looking at plots how can you tell if there was an interaction
if there is any difference in the lines
What are confidence intervals?
Confidence intervals give a range around a sample mean that is likely to contain the true population mean.
How do you calculate a confidence interval?
CI = sample mean ± (Z × StE); StE = SD / √n
How can confidence intervals be interpreted?
A 95% CI means 95% of CIs from repeated samples would contain the population mean; non-overlapping CIs suggest a likely meaningful difference.
How should variables be nested in ANOVA?
Nest the high‑priority variable within the lower‑priority variable conceptually when forming or testing hypotheses.
What should you do if your data violate sphericity?
Apply Greenhouse–Geisser or Huynh–Feldt corrections to adjust degrees of freedom.
How should variables be plotted to best see an interaction?
Use a line graph with the lower‑priority variable on the x‑axis and the other variable shown as separate lines.
What relationship between lines suggests an interaction?
Non‑parallel lines, indicating the effect of one variable depends on the level of the other.
Which analyses follow up a significant interaction in a 3×2 ANOVA?
Run planned contrasts for the repeated‑measures factor and simple main effects to test the effect of one variable at each level of the other.
What should you do if the interaction isn’t significant?
Do not run follow‑up interaction tests; interpret only the main effects.
What is meant by a three-way interaction?
A three-way interaction occurs when the two-way interaction between two variables changes depending on the level of a third variable.
How many two-way interactions and main effects are in a three-way ANOVA?
A three-way ANOVA has three main effects (one for each IV) and three two-way interactions, plus one three-way interaction.
when looking at a plots for a three way interaction what do they look like if they are sig interaction
they will look different from each other in the 2nd level
What should you do if a three-way interaction is not significant?
Move down the hierarchy: interpret the two-way interactions, and if those are not significant, interpret the main effects.
What are the limitations of ANOVA in psychological research?
Assumptions are often violated (normality, homogeneity, sphericity); sensitive to outliers, skew, measurement error; - - NHST (Null hypothesis significance testing ) logic is limited and can be unintuitive.
how can you overcome the limitations of an ANOVA
non parametric tests or robust ANOVA
What steps are taken in a robust ANOVA?
Use trimmed means to reduce influence of extreme values (remove data from each end of the distribution)
run bootstrapping procedures to estimate parameters across many resampled datasets.
treat sample like mini population
take a random sample from within the sample
run analysis on mini sample
take average of parameter estimate
What are limitations of null hypothesis significance testing (NHST)?
p-values depend heavily on sample size; p>.05 does not confirm the null; p<.05 does not prove the alternative; the threshold is arbitrary and often misleading.
you only assume that you haven’t found evidence of it not being there- not the same as it actually existing
What is Bayesian inference and how does it differ from NHST?
entirely different from ANOVA
beliefs about the effect prior to collecting the data and then adjust the beliefs
testing the alternative hypothesis
the bayes factor is a ration of support for null hypothesis vs alternative hypothesis (need to do 1/B for actual value)
