Unit 3 - CONSCIOUSNESS & SLEEP CYCLE
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Consciousness (Awareness):
A person’s awareness of everything that is going on around him or her at any given moment, which is used to organize behavior
All the ideas in your immediate awareness, such as your thoughts, feelings, senses
Most people’s time is spent in waking consciousness.
Our thoughts, feelings, and sensations are clear/organized, and we feel alert.
Subconscious
Hidden memories that influence behavior despite no clear memory of them (Backpack of Life)
Unconscious
(Psychoanalytic Perspective) Hidden memories that influence behavior but need intensive therapy to be recovered.
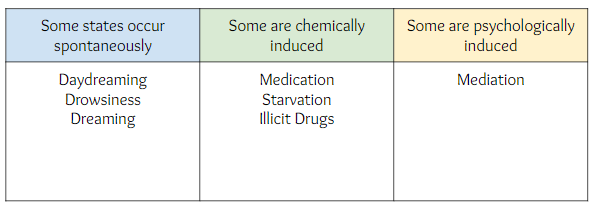
Altered State of Consciousness
State in which there is a shift in the pattern of mental activity as compared to waking consciousness. The person is not aware of their surroundings.
Sleep
The human body’s biological rhythms, natural cycles of activity that the body must go through
Sleep is a unique state of consciousness; it lacks full awareness but the brain is still active
Sleep serves many functions, one of which is to give us a period of mental and physical restoration

The National Sleep Foundation has come up with recommendations
Infants (4-11 months): 12-15 hours
School age children (6-13): 9-11 hours
Teenagers (14-17): 8-10 hours
Young adults (18-25): 7-9 hours
Adults (26-64): 7-9 hours
Older adults (65+): 6-7 hours
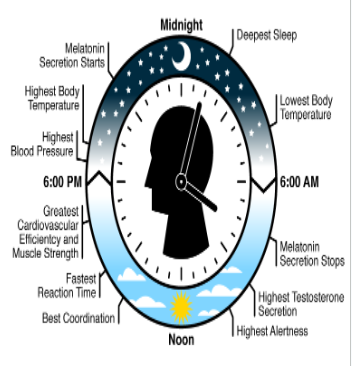
Circadian Rhythm
A cycle of bodily rhythm that occurs over a 24-hour period.
Can be influenced by the amount of daylight to which you are exposed as well as your work and activity schedule
Melatonin- sleep-inducing hormone secreted from the pineal gland. Engages when it’s dark.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
Measures electrical currents of brain wave activity
During a sleep study, electrodes are attached to the scalp to measure the brain’s electrical currents during sleep.
This is how Dr.’s can determine if someone has a sleep disorder and is used for research.
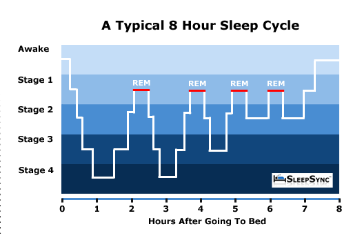
The Wake/Sleep Cycle
Sleep has a biological rhythm, cycle every 90 minutes, four distinct stages
The pattern occurs three the five times per night
Beta Waves
Awake; Full Conscious Awareness
Our brain produces certain “waves” of activity during sleep
Sleep Stages
Sleep is divided into five stages: wake, N1, N2, N3, and REM. The first four stages are non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, and the fifth stage is REM sleep.
Wake
The first stage of sleep, which depends on whether your eyes are open or closed.
N1
The lightest stage of sleep, also known as N1, when you first fall asleep. This stage lasts only a few minutes, and it's easy to wake someone up.
N2
A light sleep stage where your brain slows down, your breathing and heart rate slow, and your body temperature drops.
N3
A deep sleep stage where you're less likely to be disturbed by noise.
REM
A stage where you dream, your eyes move rapidly, and your brain waves are similar to when you're awake. Your body also temporarily becomes paralyzed during REM sleep.
As the night goes on, you spend more time in REM sleep and less time in deep sleep. A typical night's sleep consists of 4–5 sleep cycles, each lasting about 90–120 minutes. During deep sleep and REM sleep, your body repairs and rebuilds cells, secretes hormones for growth, and strengthens your immunity.
“Light Sleep” non-REM Stage 1
Alpha Waves occurs
Transition period between wakefulness and sleep. Hallucinations and body jerks (twitching)occur.
“Medium Sleep” non-REM Stage 2
Theta Waves occurs
Breathing is shallower and irregular. Sleep Talking and Sleep Spindles (Brief spurts of activity)
“Deep Sleep” non-REM Stage 3
Delta Waves Occurs
The most restorative stage of sleep (difficult to be awaken) Hormones released for children to grow, immune system refreshes itself, cells repair and multiply.
“Dream Sleep” REM Sleep
Beta Waves occurs
Rapid eye movements and your muscles become almost paralyzed. Brain waves are active as if we are awake. Your breathing becomes rapid & irregular
Sleep Deprivation
The condition of not having enough sleep; it can be either chronic or acute
REM Sleep Rebound -phenomenon in which there is an increase in REM sleep after a night of little REM sleep.
This helps reset our internal clocks to treat disruption in circadian rhythms, such as insomnia and depression.
Microsleep
When our need for sleep is so great that we are exhausted, a brief shift in brain activity from waking to sleeping brain waves may occur.
This can cause someone to be considered intoxicated.

Circadian Rhythm Disruption
An out-of-sync sleep/wake cycle
Jetlag: Travel across time zones, adjusting to the time change mentally and physically may take you more than a week.
Insomnia
The inability to get to sleep, stay asleep, or get a good quality of sleep
It must be persistent problems in falling or staying asleep
Roughly 10 to 20% of the population suffer from insomnia from time to time or chronically
Relying on sleeping pills—sales of which soared, the person may need increasing doses to get an effect. Then, when the drug is discontinued, the insomnia can worsen. Can cause dependence, sleep walking, sleep driving and sleep eating.
Sleep Apnea
Disorder in which the person stops breathing then gasps for breath
They always feel exhausted and may have high blood pressure
People who are overweight are susceptible because excess fat presses on the airway and cuts off oxygen
Apnea can be treated with a breathing device that helps force air into the lungs through a mask. While the mask may be uncomfortable at first, they are eager to get a good night’s sleep and avoid exhaustion.
Narcolepsy
Sleep disorder in which a person falls immediately into REM sleep during the day without warning
Attacks usually last less than 5 minutes but sometimes occur at the most inopportune times
People diagnosed with narcolepsy can not get a driver's license, unless are are getting treatment
Sleepwalking
Occurring during deep sleep, an episode of moving around or walking around in one’s sleep
Nightmares
Negative dreams occurring during REM sleep (the person usually remembers the nightmare when they wake up.)
Night Terrors
Relatively rare disorder in which the person experiences extreme fear and screams or runs around during deep sleep without waking fully (combined with sleepwalking)
Most common in young children. The person usually does not remember the experience in the morning; Is not the same as nightmare
Dreams
“Hallucinations of the sleeping mind” Include all images, events, sounds, and other sensations experiencing during sleep
We all dream, even if we cannot recall our dreams
The dreams of REM sleep are so vivid we may confuse them with reality
Freud’s Wish Fulfillment:
We dream to...satisfy our own wishes
Book: Interpretation of Dreams
Freud saw dreams as a method for reaching into the unconscious mind and the key to understanding our inner conflicts
Cognitive Development
We dream to...reflect cognitive development
Some dream researchers see dreams as part of brain maturation and cognitive development, their knowledge and understanding
Information-Processing Theory
We dream to...file away memories. Dreams help us sort out the day’s events and consolidate our memories
Brains are active to process new data, consolidate memories, and rewire connections between brain cells
Physiological Function
We dream to...develop & preserve neural pathways
Regular brain stimulation from REM sleep may help develop and preserve neural pathways
If you don’t use it you lose it!
Activation-Synthesis Theory
We dream to...make sense of neural static
Mind’s attempt to make sense of random neural firings in the brain as we sleep
Dreams are meaningless