neurones
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
neurone
specialised cells that carries electrical impulses around the body [nervous system is made up of neurones]
types of neurones and their role
sensory neurones
-carry nerve impulses from receptors to the CNS (central nervous system)
relay neurones
-carry impulses within the CNS
-carry nerve impulses between the sensory and motor neurones
motor neurones
-Carry impulses from the CNS to effectors
relay neurones are also called…
where is it found?
-intermediate neurones
-found within CNS
CNS (2)
brain or spinal cord
common features for all neurones
- have a cell body with a nucleus
- have an axon
- have dendrites
what does cell body contain?
- nucleus
-cytoplasm
-organelles→ mitochondria, ribosomes, RER, golgi apparatus etc
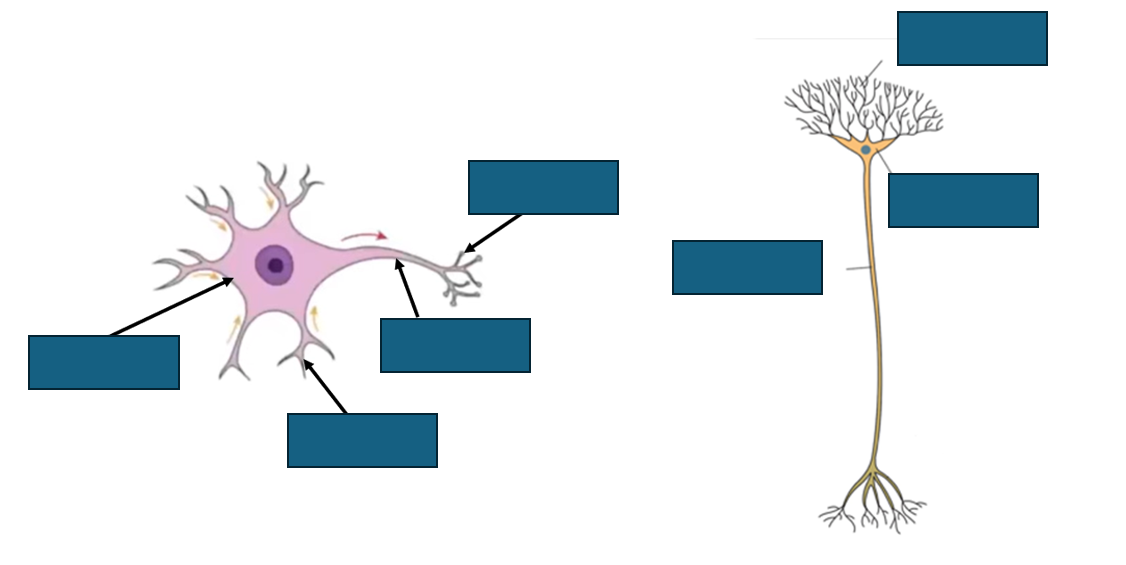
structure of sensory neurone
[- cell body branches off to the side in the middle of neurone]
![<p>[- cell body branches off to the side in the middle of neurone]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bc421a19-17c4-4971-9eeb-054a36e57e35.png)
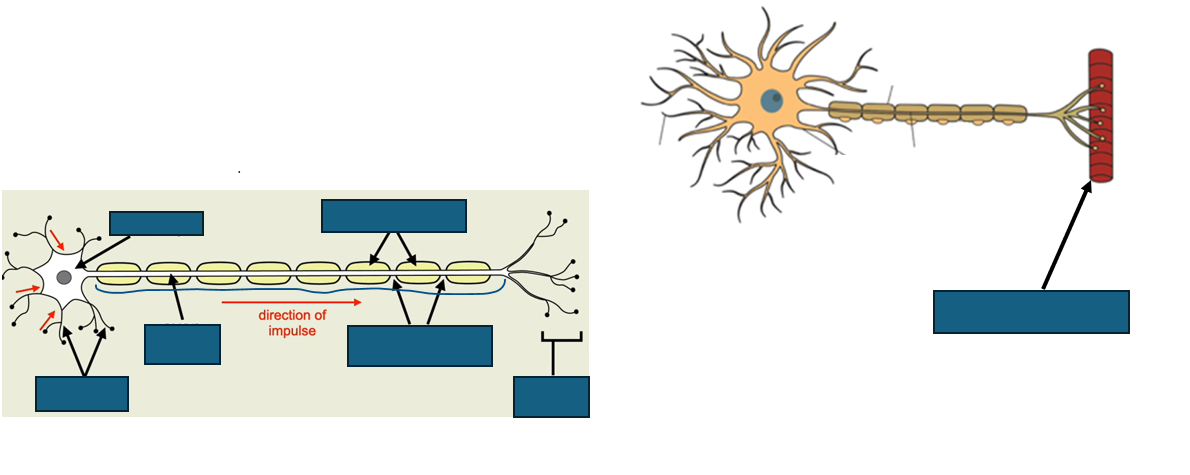
structure of relay neurone
[short axon and dendrites]
![<p>[short axon and dendrites]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f294a771-f956-48a3-805a-2a77b373e3d1.png)
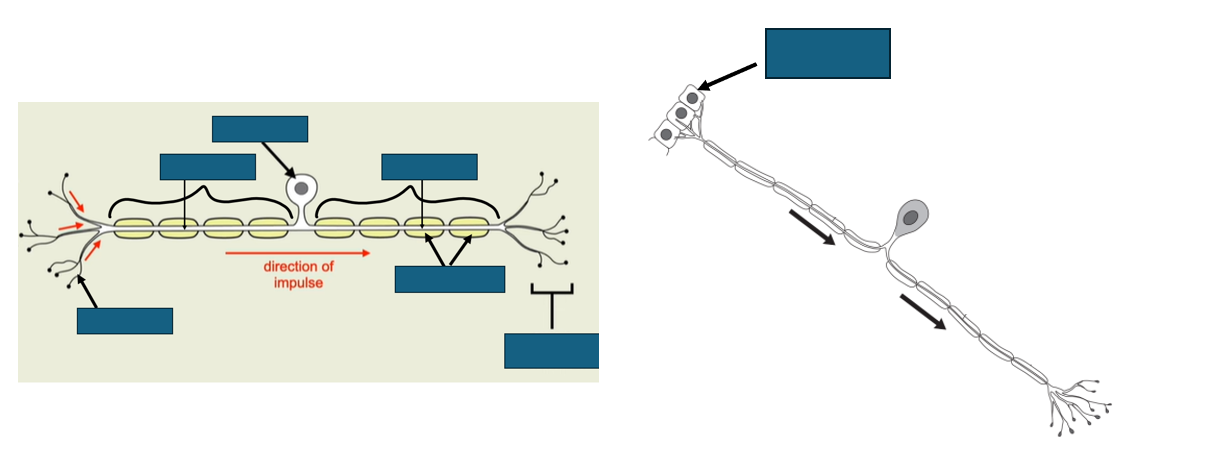
structure of motor neurone
[long axon]
![<p>[long axon]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/58b23726-b808-4fbe-bbf0-3e5f5a66d61a.png)
role of:
-dendron
-cell body
-axon
-dendron→ carry nerve impulses to the cell body
-cell body→ produce neurotransmitters
-axon→ carry nerve impulses away from the cell body
difference in structure of motor and sensory neurones (4)
-the cell body is at the end motor neurone. The cell body is in the middle of sensory neurone
-motor neurone has a longer axon
-motor neurone has no dendron
-cell body of motor neurone is in CNS. the cell body of sensory neurone is not in CNS
myelinated neurones
non-myelinated neurones
-have a myelin sheath wrapped around the axon
-they are not surrounded by myelin sheath
what is the myelin sheath made up of?
Schwann cells
what are the gaps in between the Schwann cells called?
nodes of Ranvier
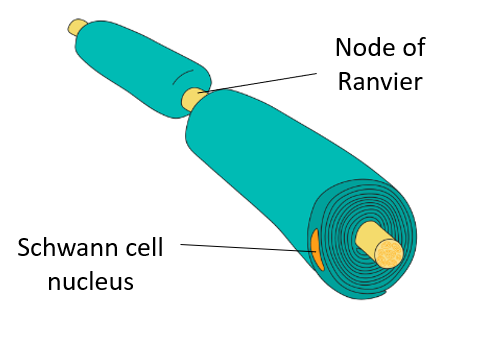
role of the myelin sheath (3)
-acts as an electrical insulator and speeds up conduction of action potentials
-prevents depolarisation (prevents movement of ions into and out of neurone)
how do Schwann cells produce myelin?
they wrap themselves around the axon multiple times
is conduction faster in myelinated or non-myelinated neurones
conduction is faster in myelinated neurone
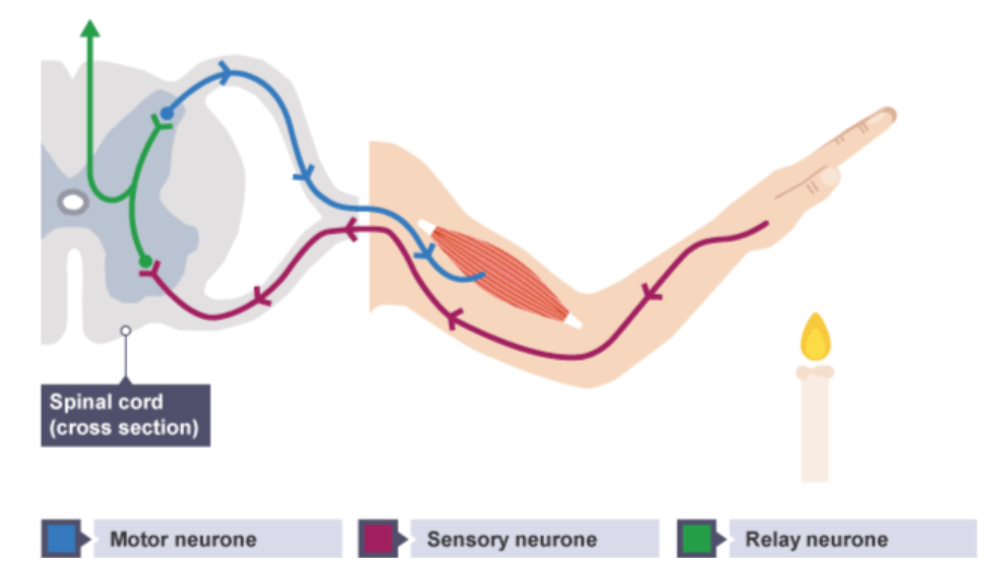
pathway of nervous communication
stimulus→ receptors→sensory neurone → relay neurone → motor neurone → effector
[receptor cells detect a stimuli. Sensory neurones carry nerve impulses from the receptors to the CNS. The CNS processes the info and sends impulses along motor neurones to effectors. Effectors carry out a response]
![<p><strong>stimulus→ receptors→<span>sensory neurone → relay neurone → motor neurone → effector</span></strong></p><p><span>[receptor cells detect a stimuli. Sensory neurones carry nerve impulses from the receptors to the CNS. The CNS processes the info and sends impulses along motor neurones to effectors. Effectors carry out a response]</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d1975105-6022-4a71-b265-40db7413ea2d.png)