energy processing - biology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Last updated 1:29 AM on 5/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
exergonic
change of Gibbs free energy is negative (Δg
2
New cards
endergonic
change of Gibbs free energy is positive (Δg>0)
uses energy, does @@**not**@@ occur spontaneously
3
New cards
anabolic reactions
build molecules and store energy
4
New cards
anabolic pathways
build larger molecules from smaller molecules by creating chemical bonds
endergonic
5
New cards
catabolic reactions
break down molecules and releases energy
6
New cards
catabolic pathways
breaks down larger molecules into smaller molecules by breaking down chemical bonds
exergonic
7
New cards
\-ase
enzyme suffix
8
New cards
enzyme
**biological** catalyst which speeds up chemical reactions in a cell
lowers activation energy (the energy needed to start a chemical reaction)
causes chemical reactions to occur faster
9
New cards
substrate
a molecule that the enzyme binds to cause a reaction to occur
10
New cards
active site
part of the enzyme that fits with the substrate in a *“lock and key manner”*
shaped to ==only be able to bond== with the substrate
11
New cards
why are enzymes specific
enzyme only binds to a specific substrate
can only catalyze one type of reaction
enzymes are specific but reusable *(does not change shape after chemical reaction)*
12
New cards
fixation
a gaseous molecule that is taken from the atmosphere and “fixed” or put into a molecule consumable by plants and animals
*(ex: carbon)*
13
New cards
obligate anaerobe
cells that cannot survive in the presence of oxygen
14
New cards
obligate aerobe
cells that require oxygen
15
New cards
facultative anaerobe
cells that can survive in the presence or absence of oxygen
16
New cards
how do anabolic pathways and catabolic pathways work together
energy released from a catabolic pathway from breaking down chemical bonds is reused as a temporary energy storage molecule otherwise known as ATP, to be used in an anabolic reaction
17
New cards
how does a ATP molecule provide energy
energy stored in the bonds between the phosphate groups is broken down (via hydrolysis) which releases energy
18
New cards
how does an ATP molecule store energy
energy is stored in the bonds between the phosphate groups, built via dehydration hydrolysis
19
New cards
two types of enzyme inhibition
competitive inhibition
non-competitive inhibition
non-competitive inhibition
20
New cards
competitive inhibition
a competitive inhibitor molecule will ^^bind at the active site and block the normal substrate^^ from binding
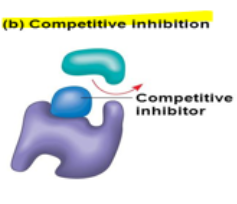
21
New cards
non-competitive inhibition
a non-competitive inhibitor molecule binds at a site that is different from the active site
binding of the inhibitor ^^changes the shape of the active site,^^ making it unable to bind with the substrate
binding of the inhibitor ^^changes the shape of the active site,^^ making it unable to bind with the substrate
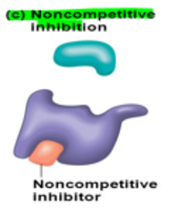
22
New cards
difference between enzyme inhibition and enzyme denaturing
**enzyme inhibition:** certain chemicals work to stop or inhibit the enzymes, thus blocking them from binding with the substrate
**enzyme denaturing:** past optimum temperature/outside optimal pH level enzyme begins to denature -> changes structure and shape of active site -> substrate can no longer bind
enzyme denaturation means an enzyme %%loses its function%% unlike enzyme inhibition
**enzyme denaturing:** past optimum temperature/outside optimal pH level enzyme begins to denature -> changes structure and shape of active site -> substrate can no longer bind
enzyme denaturation means an enzyme %%loses its function%% unlike enzyme inhibition
23
New cards
endergonic reaction graph
goes up
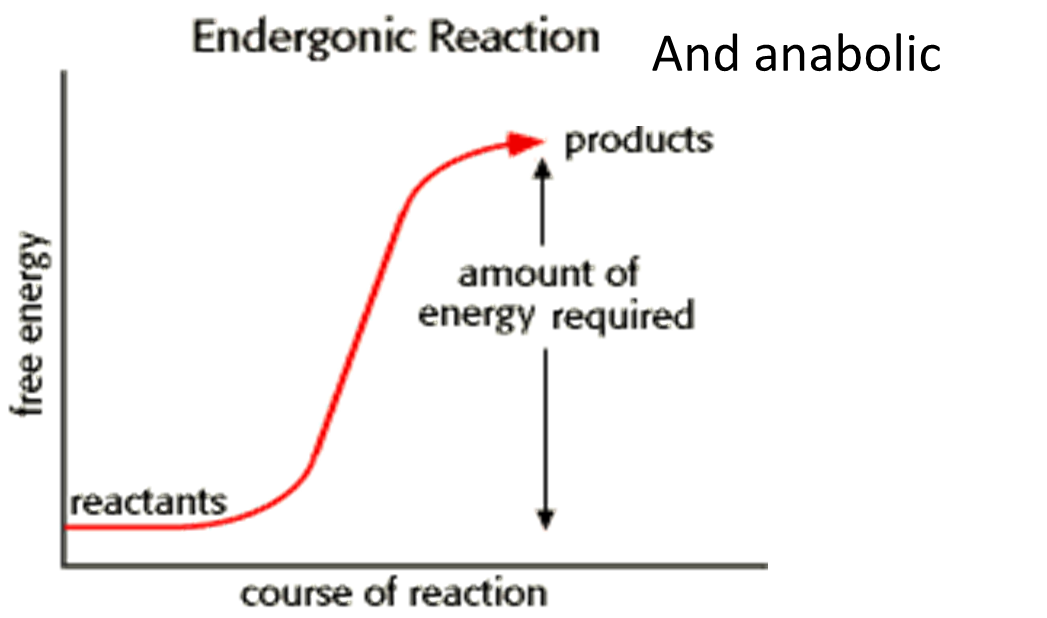
24
New cards
exergonic reaction graph
goes down
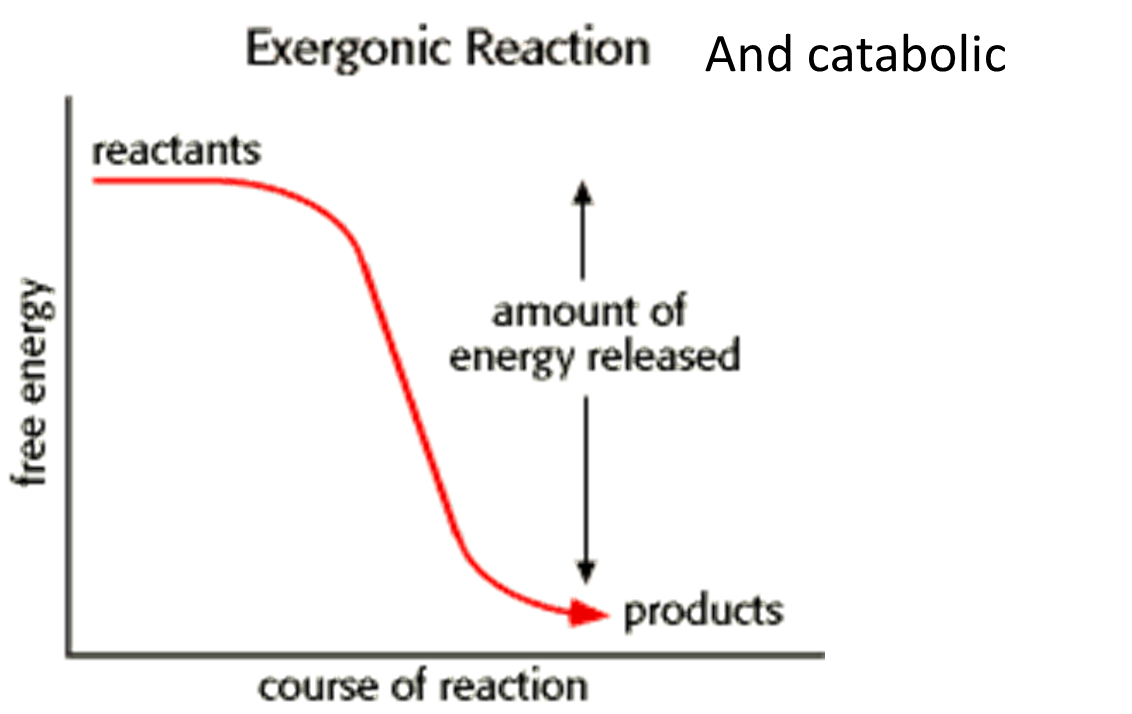
25
New cards
photosynthesis
uses energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into simple sugars through the creation of chemical bonds
anabolic
endergonic
anabolic
endergonic
26
New cards
cellular respiration
breaks down chemical bonds in glucose to release energy (ATP)
catabolic
exergonic
catabolic
exergonic
27
New cards
photosynthesis and cellular respiration work together to carry out metabolism in living things by
photosynthesis produces energy whereas cellular respiration consumes energy
*(metabolism is the chemical reactions that occur within a living organism to maintain life)*
*(metabolism is the chemical reactions that occur within a living organism to maintain life)*
28
New cards
photosynthesis equation
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Light Energy ➜ C6H12O6 + 6O2
29
New cards
cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2➜ 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP
30
New cards
two phases of photosynthesis
light-dependent reactions
light independent reactions (calvin cycle)
light independent reactions (calvin cycle)
31
New cards
light-dependent reactions
requires sunlight
occurs in the %%thylakoid membranes%%
light energy trapped by chlorophyll and temporarily stored in NADPH and ATP molecules
occurs in the %%thylakoid membranes%%
light energy trapped by chlorophyll and temporarily stored in NADPH and ATP molecules
32
New cards
light-dependent reaction equation
^^2 H2O^^ + Light Energy ➜ ==O2== + %%NADPH%% + %%ATP%%
33
New cards
where does carbon fixation occur
in light-independent reactions
34
New cards
carbon fixation
carbon in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere that is “fixed” or put into a molecule of glucose during the Calvin Cycle
cellular respiration breaks down glucose and releases carbon back as gas (**decarboxylation**)
this is called the *carbon cycle*
cellular respiration breaks down glucose and releases carbon back as gas (**decarboxylation**)
this is called the *carbon cycle*
35
New cards
light independent reactions (calvin cycle)
does **NOT** require sunlight
also conducts carbon fixation
occurs in the stroma
CO2 from the environment and ATP + NADPH created during light-dependent reactions used to produce glucose
also conducts carbon fixation
occurs in the stroma
CO2 from the environment and ATP + NADPH created during light-dependent reactions used to produce glucose
36
New cards
light independent reactions equation
==CO2== + %%ATP%% + %%NADPH%% ➜ ^^C6H12O6^^
37
New cards
four phases of cellular respiration
glycolysis
pyruvate decarboxylation
citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle)
oxidative phosphorylation
pyruvate decarboxylation
citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle)
oxidative phosphorylation
38
New cards
glycolysis
occurs in the cytoplasm
glucose is split in half to form two molecules of pyruvate (a 3-carbon molecule)
2 ATP are needed to start glycolysis and 4 ATP are made, forming a %%+2 net ATP%%
***produces 2 ATP***
glucose is split in half to form two molecules of pyruvate (a 3-carbon molecule)
2 ATP are needed to start glycolysis and 4 ATP are made, forming a %%+2 net ATP%%
***produces 2 ATP***
39
New cards
glycolysis equation
==Glucose== + %%2 ATP%% ➜ @@2 Pyruvate@@ + %%4 ATP%%
40
New cards
pyruvate decarboxylation
**MUST** occur because the next cycle (citric acid/Krebs cycle) **CANNOT** process *3 carbon molecules*
removed carbon is given off as 2 CO2 molecules
***produces 0 ATP***
removed carbon is given off as 2 CO2 molecules
***produces 0 ATP***
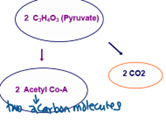
41
New cards
pyruvate decarboxylation equation
^^2 C3H6O3^^ ➜ @@2 Acetyl CoA@@ + ==2 CO2==
42
New cards
citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle)
completes the breakdown of the original glucose molecule
@@one acetyl-CoA can go@@ through the cycle at a time
each produces 1 ATP and releases 2 carbons as 2 CO2 molecules
***produces 2 ATP***
@@one acetyl-CoA can go@@ through the cycle at a time
each produces 1 ATP and releases 2 carbons as 2 CO2 molecules
***produces 2 ATP***
43
New cards
citric acid cycle equation
2 Acetyl CoA ➜ %%2 ATP%% + ^^4 CO2^^
44
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation
produce**s 34 ATP** and **H2O**
oxygen is used and joined with hydrogen to form water
*dehydration synthesis*; anabolic
phosphates are added (phosphorylation) to ADP to produce ATP
oxygen is used and joined with hydrogen to form water
*dehydration synthesis*; anabolic
phosphates are added (phosphorylation) to ADP to produce ATP
45
New cards
why is the yield for oxidative phosphorylation 36-38 ATP molecules
some energy is used to move molecules around and into the mitochondria
46
New cards
photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the carbon cycle
photosynthesis takes *gaseous carbon* in the CO2 out of the atmosphere and *makes it a solid in Glucose*
\
cellular respiration breaks down glucose, releasing the carbon back into the atmosphere *as a gas* in CO2
\
cellular respiration breaks down glucose, releasing the carbon back into the atmosphere *as a gas* in CO2
47
New cards
fermentation
occurs when oxygen is not available
starts at glycolysis
obligate anaerobes and facultative anaerobes can still break down glucose and produce a small amount of ATP
***produces 2 ATP***
starts at glycolysis
obligate anaerobes and facultative anaerobes can still break down glucose and produce a small amount of ATP
***produces 2 ATP***
48
New cards
fermentation equation
^^Glucose^^ + %%2 NAD%% + %%2 ATP%% ➜ ==2 pyruvate== +%%2 NADH%% + %%4 ATP%%
49
New cards
why does fermentation occur
allows glycolysis to continue
*(regeneration of NAD+ so glycolysis can continue)*
\
not really for its ATP production
*(regeneration of NAD+ so glycolysis can continue)*
\
not really for its ATP production
50
New cards
two types of fermentation
lactic acid
ethanol
ethanol
51
New cards
lactic acid fermentation
==pyruvate== ➜ lactic acid + %%NAD+%%
52
New cards
ethanol fermentation
==pyruvate== ➜ @@ethanol@@ + ^^CO2^^ + %%NAD+%%
53
New cards
difference between cellular respiration and fermentation
aerobic cellular respiration yields
36 to 38 ATPs
fermentation yields only
2 ATPs