Amino acids
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
How different amino acids are there?
20
How many sub-groups of amino acids are there?
6
Name all sub-groups of amino acids
Aliphatic, Aromatic, Basic, Acidic, Other, Polar
Properties of aliphatic amino acids
hydrophobic/non-polar
Variable length and carbon branching
Exception is methionine which includes a sulphur
What is physiological pH?
7.40
Name all amino acids in aliphatic group
Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine
Properties of aromatic group
larger
mostly hydrophobic
tyrosine has hydroxyl group - forms hydrogen bonds
tryptophan has an indole ring - forms hydrogen bonds
pi stacking occurs (benzene rings stack)
Name the amino acids in the aromatic group
Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan
Properties of charged amino acids
Ionisable sidechains - charged in cellular environment
basic have +ve charge
acidic have -ve charge
histidine is partially charged
Name amino acids in basic group
Histidine, Lysine, Arginine
Name amino acids in acidic group
Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid
Properties of polar group
hydrophillic (interact with water outside the protein or each other through H bonds)
histidine cam also be polar
cysteine can form disulphide bonds
Properties of other group
glycine R-group is a H atom so is has conformational flexibility
proline R-group is also bonded to amine group to create 5-membered ring so rigid
How can protein concentration be determined using aromatic amino acids?
Use Beer-Lambert law where:
Absorbance = extinction coefficient x concentration x path length

If an acid is strong will it have a low or high pKa?
Low - higher degree of ionisation so donates protons more readily than a weaker acid
What is the henderson-hasselbach equation?
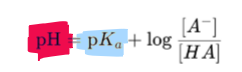
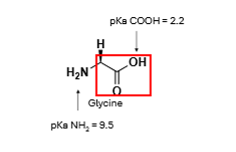
Looking at the amine group, which way will the equilibrium shift when the pH is 7.4?
To the left, protonation will take place, +ve charge
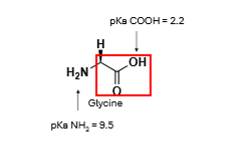
Looking at the carbonyl group, which way will the equilibrium shift at pH 10?
To the right, deprotonation will take place, -ve charge
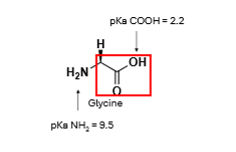
At pH 7.4 what is the net charge of the molecule? What is the name of this ion?
Net charge is 0, but there is both a +ve and -ve charge so it is called a Zwitterion
What is the isoelectric point (pl)?
The pH at which a particular molecule carries no net charge, unique to each.
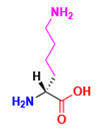
Is this an L or D amino acid?
D (Lysine)
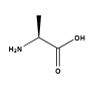
Is this L or D alanine?
L-alanine
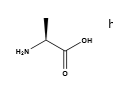
Is L-alanine R or S?
S
Are all L-amino acids S?
L-cysteine is the only natural amino acid that is R, this is due to the Sulphur group
What is the approximate pKa value of NH2 group and carboxyl group on amino acids?
9 and 2 respectively
What is the Phi angle?
Nitrogen and carbon
What is the Psi angle?
Carbon to carbonyl (C to C)