Cirrhosis
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
how does cirrhosis affect the portal system
Cirrhosis causes a back-up of blood in the portal system (blood can’t go through liver easily; ↑portal pressure
Major liver functions
regulation of glucose cholesterol
metabolism of carbs fats and amino acids
purification, transformation and clearance
storage of glucose fat soluble vitamins
regenerative organ
synthesis and secretion of clotting factors, etc
what is cirrhosis
late stage, impaired liver function caused by formation of scar tissue (fibrosis) due to damage by liver disease
hepatic cirrhosis is also called
liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end- stage liver disease
cirrhosis = kirrhos = yellowish colour of diseased liver
what are associated with cirrhosis
ascites, fibrosis, liver nodules
is cirrhosis reversible
no
what are the major risk factors for cirrhosis
●Excessive alcohol consumption
●Being overweight
●Chronic viral hepatitis
does everyone with chronic hepatitis develops cirrhosis
no
what are the most common causes of cirrhosis
● chronic viral hepatitis (B, C, D)
● chronic alcohol abuse
● non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (fat accumulation in liver)
● drugs and herbals
● metabolic liver disease
hemochromatosis (iron build up in body)
Wilson's disease (copper accumulated in liver)
alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Signs and symptoms of cirrhosis
- early stages asymptomatic
● fatigue, anorexia, weight loss, nausea
● hepatomegaly, splenomegaly
● ascites, edema (legs, ankles), pleural infusion
● easily bleeding or bruising
● pruritus (itchy skin), jaundice, dark urine
● palmar erythema, spider angiomata (spiderlike blood vessels on skin, asterixis
● females: absent or loss of periods
● males: reduced libido (loss of sex drive), gynecomastia (breast enlargement), testicular atrophy
● hepatic encephalopathy (confusion, drowsiness, slurred speech
Is the liver size large or small in cirrhosis?
Liver size can be enlarged, normal, or shrunken in people with cirrhosis. As the disease progresses, liver size typically shrinks due to scar formation
what are the complications of cirrhosis
portal hypertension (↑blood pressure in veins)
swelling in legs and abdomen
enlarged spleen (splenomegaly)
bleeding (enlarged veins in esophagus or stomach, liver not producing enough clotting factors)
jaundice
hepatic encephalopathy
increased risk of liver cancer
infection
acute-on-chronic cirrhosis
ascites
variceal bleeding
spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
Child-Pugh classification system
A means of quantifying the myriad effects of cirrhotic process on laboratory and clinical manifestations
A predictor for patient survival, surgical outcome, and risk of variceal bleeding, severity, and drug dosing adjustments
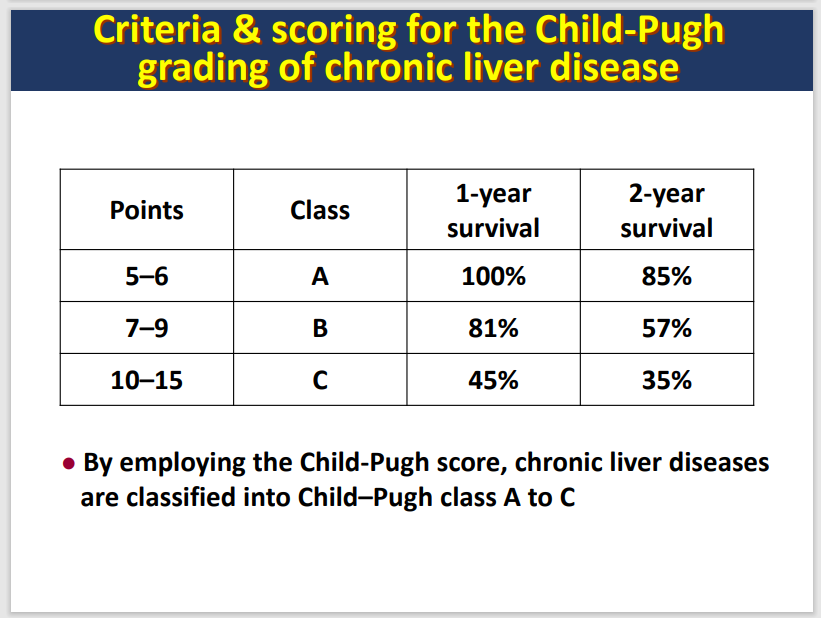
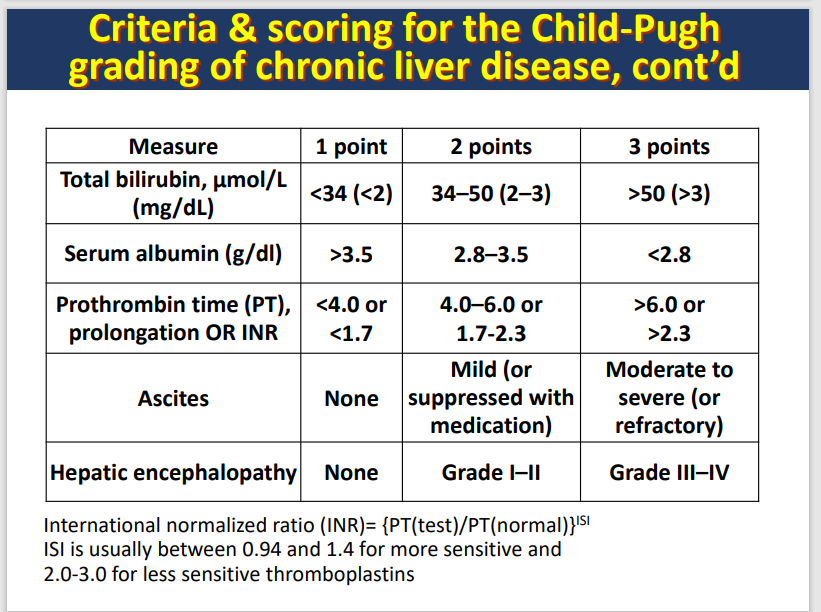
how do you diagnose cirrhosis
blood tests, medical imaging, and liver biopsy (identify severity, extent, and cause of liver damage)
Laboratory tests (assess liver function)
● hypoalbuminemia
● ↑prothrombin time, ↑international normalized ratio (INR)
● thrombocytopenia
● ↑alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
● ↑aspartate transaminase (AST), ↑alanine transaminase (ALT), ↑g-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)
● Patients are also tested for viral hepatitis
is there a specific treatment for cirrhosis
no
Alcohol is recommended in cirrhosis?
AVOID ALCOHOL
when can liver transplantation can be an option
if cirrhosis leads to liver failure
how do you treat ascites
Initial therapeutic paracentesis, sodium restriction and oral diuretics
For refractory ascites: Serial therapeutic paracenteses, Post-paracenteses albumin infusion
Prevention and treatment of variceal bleeding
prevention:
Non-selective β-blockers
EBL (endoscopic band ligation) if intolerance to beta blockers
treatment:
Antibiotic prophylaxis
Vasoactive drugs prior to endoscopy, maintained for 2-5 days
EBL
what is the secondary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding
Nonselective β-blockers, EBL, or both should be used for prevention of recurrent variceal bleeding
Treatment of portal hypertension
Lowering portal pressure with β-adrenergic blockers
Severe cases: a small tube (trans-jugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt ) is placed in vein to reduce liver blood
Treatment of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP)
Ascitic fluid PMN>250 cells/mm3: empiric antibiotic therapy (eg cefotaxime)
Ascitic fluid PMN<250 cells/mm3 & signs of infection: empiric antibiotic therapy while awaiting culture results
Cirrhosis is more common in
adults
is the mechanism of developing cirrhosis and clinical presentations are the same in children and adult?
yes
Causes of developing cirrhosis in kids are more related to
genetic/inherited disease (eg alpha-1 antitrypsin, deficiency, biliary atresia)
Production of clotting factors, bile, and antibodies are three functions of the liver?
no
not the antibodies
Cirrhosis is impaired function of the liver caused by formation of scar tissue and is usually reversible?
irreversible
Chronic viral hepatitis, excessive alcohol consumption, and some of drugs can cause cirrhosis?
yes
Hemochromatosis (buildup of copper in liver) can lead to cirrhosis?
build up of iron
Patients at early stages of liver cirrhosis are typically asymptomatic?
yes
Ascites, edema in legs, and pleural infusion are all signs of cirrhosis?
yes
All patients with cirrhosis have enlarged liver size due to fibrosis?
no
Portal hypertension, hepatic encephalopathy, and variceal bleeding are complications of cirrhosis?
yes
Patients with cirrhosis have hypoalbuminemia and elevated prothrombin time?
yes
Plasma levels of the liver enzymes (ALT, AST, ALP) are reduced in patients with cirrhosis?
increased
Lab tests, imaging, liver biopsy are three diagnostic tools used for cirrhosis?
yes
Paracentesis, sodium restriction, and diuretics are used for treatment of ascites in patients with cirrhosis?
yes