Unit 5: Rotation
4.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/14
Last updated 5:17 AM on 4/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
1
New cards
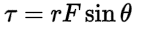
Torque
It is defined as the product of force and the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action of the force.
2
New cards
Newton-meter (Nm) / pound-feet (lb-ft)
unit of torque
3
New cards
moment arm
The perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action of the force and is an important factor in determining torque.
4
New cards
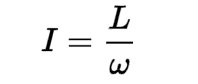
Rotational inertia
the property of an object that determines its resistance to rotational motion. It depends on the mass distribution of the object and the axis of rotation.
5
New cards
Parallel Axis Theorem
It states that the moment of inertia of a body about any axis parallel to its center of mass is equal to the moment of inertia about the center of mass plus the product of the mass of the body and the square of the distance between the two axes.
6
New cards
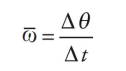
average angular velocity
7
New cards
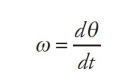
instantaneous angular velocity
8
New cards
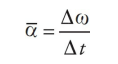
\
average angular acceleration
9
New cards
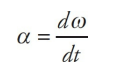
instantaneous angular acceleration
10
New cards
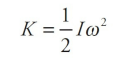
Definition of Rotational Kinetic Energy
11
New cards
rolling motion
For _____ the total kinetic energy is the translational kinetic energy and the rotational kinetic energy
12
New cards
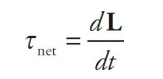
Conservation of Angular Momentum
13
New cards
Equilibrium
____ in rotational motion occurs when an object is not rotating or is rotating at a constant angular velocity.
14
New cards
**Static equilibrium**
This occurs when an object is at rest and the net torque acting on it is zero.
15
New cards
**Dynamic equilibrium**
This occurs when an object is rotating at a constant angular velocity and the net torque acting on it is zero