poll everywhere/kahoot for red/blue/brown lesions
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
all of the following could cause an erythematous tongue w discomfort except:
candidiasis
anemia
chewing trauma
erosive lichen planus
chewing trauma
small red dot lesions on the palate can be due to all of the following except:
coughing
infectious mononucleosis
crest syndrome
anemia
anemia
which of the following exhibits a large (3 cm) bluish mass on the palate
blue nevus
amalgam tattoos
mucocele
mucoepidermoid carcinoma
mucoepidermoid carcinoma
a 36 yr old male w a bluish lesion that appears flat or plaque-like on his palate that has been present for years. which of the following is in the ddx:
melanotic macule and amalgam tattoo
MEC and mucocele
blue nevus and amalgam tattoo
varix and blue nevus
blue nevus and amalgam tattoo
which of the following does not cause intraoral pigmentations
pemphigus vulgaris
lead poisoning
addison’s disease
AZT (zidovudine) medication
pemphigus vulgaris
a 57 yr old women w gingival lesion that is brown to black w irregular borders that has inc in size during the past 3 mo, what would be the best management
incisional biopsy
follow up in a month
excisional biopsy
surgical removal
incisional biopsy
a 45 yr old women presents w a bluish mass on her lower lip. she reports falling a few months ago, after which the lesion appeared. all of the following could be included int he ddx except:
varix
papilloma
mucocele
hemangioma
papilloma
a 44 yr old women w a cell-circumscribed stable brown lesion on her lip since she was young. which of the following would be the most likely dx
melanoma
amalgam tattoo
melanocytic nevus
melanoacanthoma
melanocytic nevus
a 10 yr old male pt has multiple brown pigmented lesion on the skin. all of the following are in the ddx except:
peutz jehgers syndrome
neurofibromatosis type 1
sturge weber syndrome
mccune albright syndrome
sturge weber syndrome
which of the following characteristics is correctly associated w its syndrome/condition:
Peutz-Jegher's shows maxillary freckles
NF 1 shows freckle-like pigmentations on the lip
McCune Albright shows small cafe au lait spots crossing the midline
Sturge weber shows unilateral red/purple birthmark on skin
Sturge weber shows unilateral red/purple birthmark on skin
an asymptomatic small red-purple nodule on the inner aspect of the lower lip has been present for several months w no change. what is the most likely dx:
Neurofibroma
Hemagnioma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Mucocele
Hemagnioma
which of the following is not associated w a syndrome
fibrous dysplasia
neurofibroma
varix
telangiectasia
varix
which of the following about blue nevus is true
Most common intraoral pigmented lesion
Malignant nevus lesion
Hard palate is a common location
Blanch during pressure
Hard palate is a common location
which of the following medications is most appropriate as first-line therapy for erosive oral lichen planus
Oral prednisolone tablets
Tacrolimus 0.1% topical ointment
Clobetasol propionate 0.05% topical gel
Nystatin oral suspension
Clobetasol propionate 0.05% topical gel
which of the following statements about brown pigmentation is true:
Melanoacanthoma grows slowly over years
Melanotic macule is usually a rapidly enlarging lesion
Smokeless melanosis is cancerous
The ABCDE criteria help assess if a brown lesion is malignant
The ABCDE criteria help assess if a brown lesion is malignant
which of the following statements about a mucocele is false:
Commonly occurs on the lower lip
Mucoceles are true cysts lined by epithelium
Typically painless swellings
Trauma to minor salivary glands often causes mucocele
Mucoceles are true cysts lined by epithelium
which of the following syndromes can present w telangiectasia
CREST syndrome
Gorlin syndrome
Gardner syndrome
McCune Albright syndrome
CREST syndrome
which of the following statements about oral varix is true
Painful and rapidly enlarging
Due to trauma to minor salivary gland
Are common in children
Most commonly found on the ventral surface of the tongue
Most commonly found on the ventral surface of the tongue
which of the following statements of intra-oral nevus is true
Incisional biopsy maybe needed for a diagnosis
A vascular lesion
Due to UV light
Common location is lower lip
Incisional biopsy maybe needed for a diagnosis
all of the following statements about intraoral melanoma are true except
Commonly occurs on the palate and maxillary gingiva
Aggressive with poor prognosis
Usually asymptomatic in early stages
Arises frequently from pre-existing benign nevus
Arises frequently from pre-existing benign nevus
all of the following are characteristic features of neurofibromatosis type 1 except
Fibrous dysplasia
Café-au-lait spots
Lisch nodules (iris hamartomas)
Cutaneous neurofibromas
fibrous dysplasia
all of the following are characteristic features of peutz jehgers syndrome except
Gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyps
Café-au-lait spots
Increased risk of certain malignancies
Multiple oral and perioral pigmented macules
Café-au-lait spots
which of the following statements about erythroplakia is true
Commonly found on the lower lip and is always benign
Resolves spontaneously without treatment
Painless and appears as a red, velvety patch in the oral cavity
Caused by fungal infections
Painless and appears as a red, velvety patch in the oral cavity
which of the following is true about hemangioma
Due to spilled blood in tissue
Occurs with McCune Albright syndrome
Benign vascular tumor that may blanch on pressure
Least likely to occur in children
Benign vascular tumor that may blanch on pressure
which of the following statements regarding gingival cyst of adults is true
An extraosseous lesion derived from remnants of dental lamina
Commonly occurs in children and is associated with unerupted teeth
Usually presents as a painful swelling
Radiographs typically show a well-defined radiolucency
An extraosseous lesion derived from remnants of dental lamina
which of the following statements regarding amalgam tattoo is false
Radiograph may reveal fine radiopaque particles
Usually asymptomatic and remains stable over time
No treatment is required once the diagnosis is confirmed
Due to increased melanin production
Due to increased melanin production
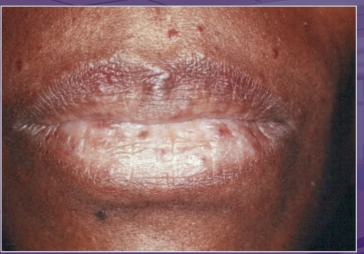
what is the dx of these dilated blood vessels
ecchymosis
telangiectasia
petechia
hematoma
telangiectasia
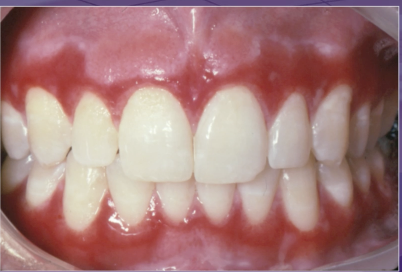
what is NOT part of the differential dx
lichen planus
pemphigus vulgaris
erythema multiforme
mucous membrane pemphigoid
erythema multiforme
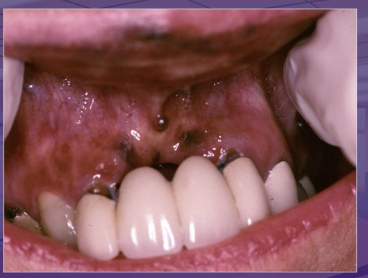
what is the dx
amalgam tattoo
melanotic macule
melanoma
melanocytic nevus
melanoma
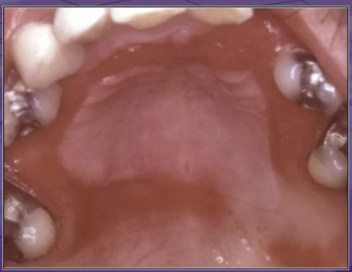
what is the cause of this lesion
wearing denture all the time
trauma
bacterial infection
unknown
wearing denture all the time
hemangioma is associated w which type of syndrome
lichen planus
CREST
sturge weber
systemic lupus
sturge weber
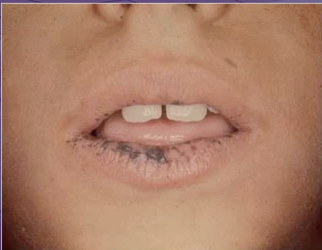
which of the following features is not a characteristic of this condition
intestinal polyps
supernumerary teeth
autosomal dominant
increased risk for cancer
supernumerary teeth
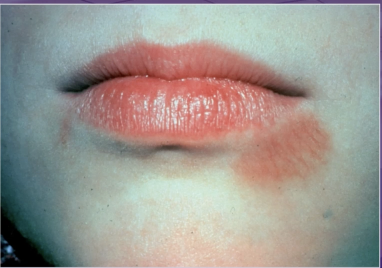
what is the cause of this lesion
primary herpes
herpangina
licking lower lip
erythema multiforme
licking lower lip
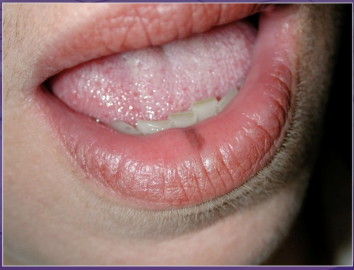
dx
varix
melanotic macule
melanoma
hemagioma
melanotic macule
cafe au lat spot are associated w
peutz jegher syndrome
gorlin syndrome
neurofibromatosis type 1
ectodermal dysplasia
neurofibromatosis type 1
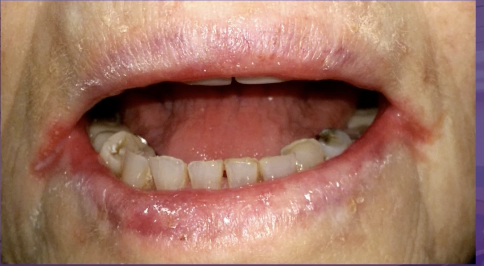
what would be the management
mycelex troches
nystatin ointment
topical clobetasol
prednisone tablet
nystatin ointment