DNA structure and replication
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
DNA
Type of nitrogen base
Type of sugur used
Shape
A,T,C,G
deoxyribose
Double helix
RNA
type of nitrogen bases
Type of sugur used
Shape
A,U,C,G
Ribose
Single strand
Explain the base pairing rules of DNA and provide a example of DNA strand with its complementary strand
A always pairs with T
C always pairs with G
Example
ATGCCG
complentary strand is TACGGC
Draw the Structure of a nucleotide (make sure to label)
Sugur
Phosphate
Nitorgenous base
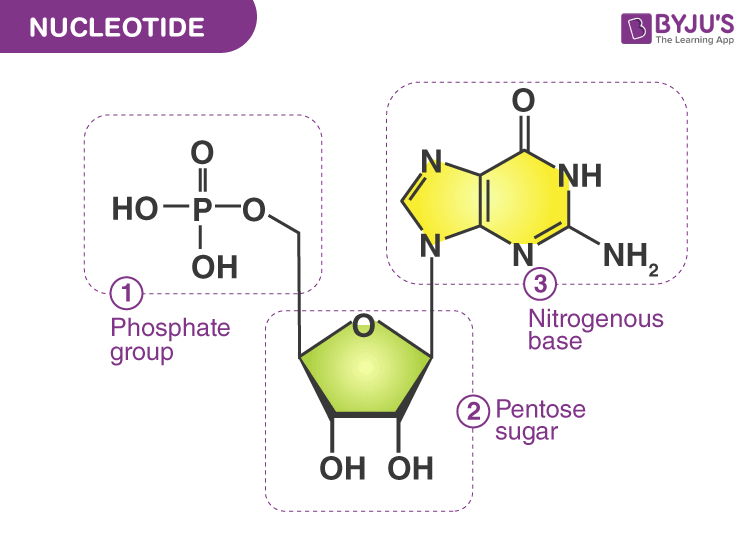
Tell the difference between purines and pyrimidines, including which nitrogen bases are which
Purines, larger bases with two rings
A and G are purines
Pyrimidines, smaller bases with one ring
C,T,U are pyrimidines
Explain in detail the structure of DNA molecule
Double helix, two strands of nucleotides twisted into a spiral
Backbone, sugur and phoshate
Bases, A,G,C,T
Anti parallel strand, the strands run in a opposite or anti parallel direction
Summerize the process of DNA replication, include the enzymes involved, and explain then importance of the process
Start, enzyme helicase unwinds the DNA double helix
Elongation
DNA polymerase, adds new nucleotides complementary to each original strand
Leading strand, synthesized continuously
Lagging stand, synthesized in short segments called okazai fragments
RNA primer, starts DNA synthesis
Termination, enzymes seal nicks resulting into identical DNA molecules
Importance, ensures genetic information is accurately copied for cell division
The difference between the leading strand and lagging strand
Leading strand, Synthesize continuously in the 5 to 3 direction toward the replicating fork
Lagging strand, synthesized discontinously in short segments the okazaki fragments away from the replication fork
Explain why DNA replication is considered to be semi conversative
Each new DNA molecule made consist of one original strand and one new strand, perserving half of the original molecule in each new copy
Be able to identify DNA and RNA
DNA, double stranded, contains T, deoxyribose sugur
RNA, single stranded, contains U, ribose sugur
What's a consequence for an error made during DNA replication
Malfuciton, genetic disorder, disease, mutations