AICE Marine biology 4.1-4.3
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Binomial nonmenclature
Universally recognized two-word name for a particular species
Genus
First part of binomial nonmenclature given the capital letter
Species
Second part of binomial nonmenclature given the lowercase letter
Levels of classification
Domain — different kingdoms
Kingdom — different phylum
Phylum — different classes
Class — similar orders
Order — similar families
Family — one of more similar genus
Genus — one of more closely related species
Species — unique to each organism within a genus
Dichotomous key
System used to identify organisms
Made up of pairs of contrasting descriptions
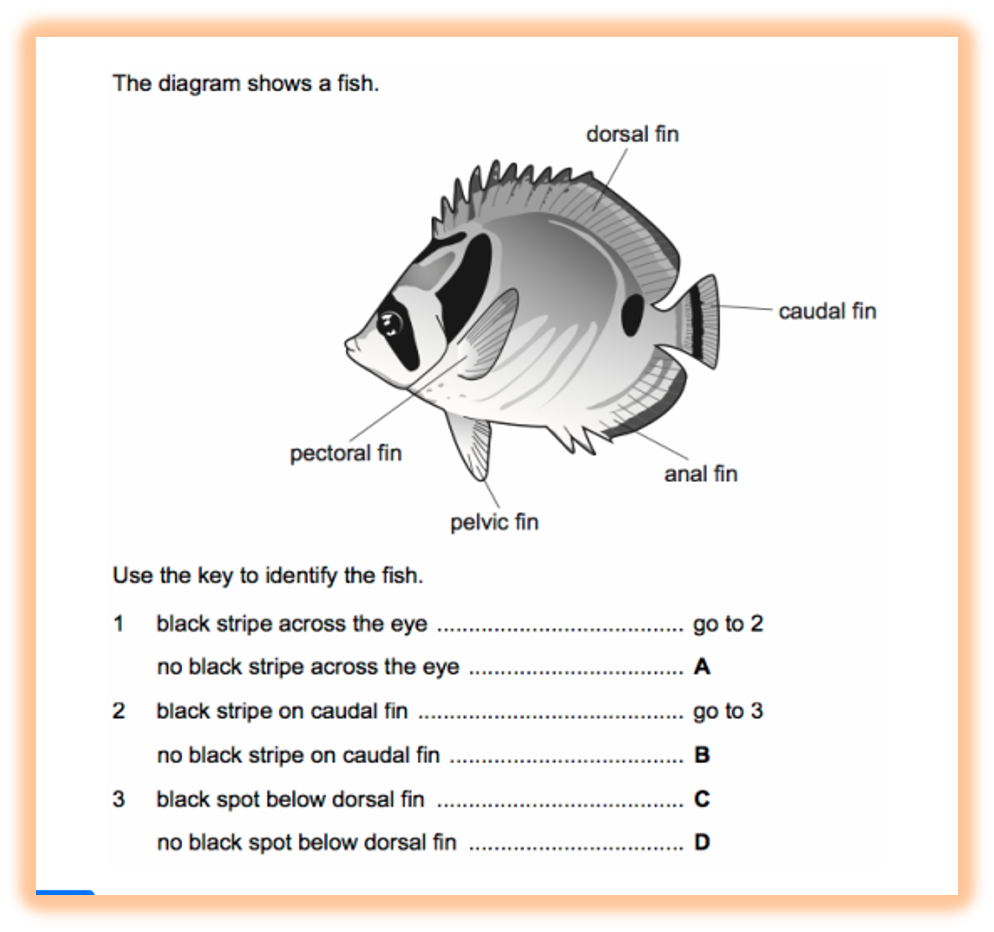
What are the 8 groups of marine organisms
Phytoplankton
Zooplankton
Echinoderms
Crustaceans
Bony fish
Cartilaginous fish
Macroalgae
Marine grasses
Plankton
Diverse collection of microscopic organisms that have limited mobility and drift in water currents
Why are plankton considered keystone species
They are indicative of the health of an ecosystem
Two groups plankton is divided in to
Phytoplankton (producers) and zooplankton (consumers)
Main types of phytoplankton
Diatoms and dinoflaggellates
Diatoms
Unicellular
Cell walls with silica
Found in surface waters, reproduce rapidly
Represent base of food web
Consumed by krill
Dinoflagellates
Unicellular
No silica cell walls
Found in surface water, reproduce rapidly
Some produce toxins that can poison fish and accumulate in shellfish poisoning humans and other organisms
Zooplankton
Consumers (including larvae, copepods, jellyfish)
Migrate vertically in the water column each day to feed on phytoplankton
Sensitive to environmental changes (pullution, microplastics, acidification, etc)
Larvae
Planktonic stage of fish and invertebrates like sea star (adapted to life floating in the ocean)
Copepods
Most abundant and diverse group of zooplankton
Are crustaceans, herbivores,, feed on diatoms
Bodies are divided (head, thorax, abdomen, two antennae, 2-4 pairs of appendices extend thorax)
Exoskelton made of calcium carbonate and have spikes for protection and better floatation
Jellyfish
Found in every part of the ocean, belong to cnidaria group
Body with two parts: medusa (transparent bell) and tentacles with stinging cells
Krill
Shrimp like organisms
Feed on zooplankton and phytoplankton
Important source of food for birds, fish, seals, whales
Echinoderms
Phylum including invertebrates like sea-stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, sea lilies and brittle stars
Body has thin layer of skin over a hard calcium carbonate skelton
Have planktonic larvae
Have pentaradial symmetry (five arms radiating around a central body cavity)
Movement through a system of eater filled tubes whuch increase of decrease the water pressure in tube feet
Main uses of tube feet
Open shells of oysters and clams
Act as suction cups to help adhere to the seafloor
Help in gaseous exchange for respiration (takes in O2 and releases CO2)
Ecological importance of Crown-of -thorns starfish
Support colonization of slow growing coral
Increase biodiversity of the reef
Ecological importance of sea urchins
If sea urchins are overharvested → increase in kelp population
If sea otters are removed or decline → Sea urchins population increase → decrease of kelp population → unbalance
Ecological importance of sea cucumbers
Borrow in sand and provide oxygen to other organisms living there
Produce nitrogenous waste → important nutrient
Economic importance of echnioderms
Sea cucumbers and sea urchins can be a source of income (using in agriculture, fishing, food delicacy in Chinese cuisine, medicine to treat fatigue, constipation, frequent urination)
COTS can damage the ecotourism industry if destroy the coral reefs
Crustaceans
Can be found in salt, brackish, freshwater
Including crabs, crayfish, lobsters, krill, shrimp, prawns, barnacles, copepods, etc
Have hard exoskeleton made of calcium and chitin
Outside of exoskeleton offers protection against predators and water loss
Inner part of exoskeleton to support the attachment muscles
Ecological importance of Crustaceans
Detrivores, break down the organic matter → help recycle the mineral nutrients
Krill is a target for commerical fishing, overfishing krill can lead to decline in population of them and then phytoplankton bloom → harmful toxins
Economic importance of Crusteceans
Large crustaceans = food for us
Small crustaceans = food for the larger crustacean
Krill is eaten in certain countries like Japan
Used as bait in aquariums, aquaculture, fishing, pharmaceutical industry
Bony fish external and internal features
Lateral line
Operculum
Gills
Swim bladder
Scale
Bony skeleton
Lateral line
Extremely visible
Contains sense organs that can detect changes in electric field as well as vibrations in water
Assists in shoaling behavior, navigation, finding prey
Operculum
Bony flap covering and protecting the gills
Gills
Supported by bony gills arches
Used for gas exchange
Swim bladder
Buoyancy organ
Scale
Made of bone, overlapping, flexible
Covered by skin and mucus
Used for protection, drag reduction
Ecological importance of bony fish (5)
Excretion → nutrients (nitrates and phosphates) used by producers
Link aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems
Example: salmon to trees
Economic importance of bony fish (10)
Important source of protein and 5 amino acids we cant synthesize
Cod liver: rich in iodin, vitamin A and D
Scales: jewelry
Cartilaginous fish features (11)
Skelton and jaws made of cartilage only (less calcium, softer, more flexible than bone)
Spiracle
Denticles
Dorsal fin
Not extremely visible lateral line (under the skin)
Caudal fin (heteroceral)
Anal fin
Pelvic fin
Pectoral fin
5-7 pairs of gil slits
No swim bladder (must keep swimming to keep buoyant)
Ecological importance of cartilaginous fish
Sharks play ecological role in marine food webs: keep prey population in check= keystone species
Sharks also control the population of invasive species (lionfish)
Economic importance of cartilaginous fish (6)
Fins are a culinary delicacy in China
Shark liver oil is a source of vitamin A, used in preserving leather and wood, in cosmetics for treating arthritis and cancer
Denticles: used in Japan to cover sword hilts
Shark leather: boots, belts, wallets
In Greenland Inuits make rope from shark skin
Ecotourism: diving with sharks and rays bring important revenue
What phylum to bony and cartilaginous fish belong to
Phylum Chordata
Chordates common features
Notochord
Dorsal neural tube
Pharyngeal slits
Post anal tail
Notochord
Flexible, rod-shaped organ, extends the length of the body and allows body to bend during muscle contractions
Dorsal neural tube
Tube-shaped organ, extends the length of the body
During development anterior part becomes the brain and posterior part becomes the spinal cord
Pharyngeal slits
Links mouth cavity and digestive system
In bony and cartilaginous fish it develops into gill arches to support ventilation across the gills
Post anal tail
Located at the rear of the fish, used for swimming
Macroalgae
Large marine producers, photoautotrophs, found in shallow areas
Examples: kelp and seaweed
Body is called a thallus
Macroalgae features
Holdfast
Stipe
Blades
Gas bladders
Holdfast
Strong, root like structure
Anchor the kelp to the seabed (no function in absorbing minerals)
Stipe
Long, tough vertical stalk
Connects to holdfast to the blades
Blades
Leaflike structure, absorb light and minerals
Gas bladders
Found underneath the blades
Act as floatation acid and contain accessory pigments to absorb traditional wavelengths of light
Ecological importance of macroalgae (2)
Kelp forests serve as habitat for a diverse range of fauna
Generates large quantities of nutrients/detritus
Economic importance of macroalgae
Cooking: wrapping suishi rolls, sea weed is rich in vitamins and minerals and low in fat
Food industry: used as additive in many foods
Cosmetics and herbal medicine: skin creams, herbal remedies, etc
Marine plants/sea grasses
Are flowering plants
Have rots and rhizome (thick, horizontal) in seabed
Leaf structure — epidermis layer with chloroplast, no stomata, and very thin waxy cuticle
Plants can reproduce sexually and asexually
Marine plants ecological and economical importance
Base of food webs
Provides food, nutrients, detritus, habitat
Nursery ground for marine invertebrates
Sustain biodiversity → ecotourism, recreational fishing, snorkeling
Types of biodiversity
Species diversity
Genetic diversity
Ecological diversity
Species diversity
Measure of abundance and richness of a species in each place at one time
Species abundance = number of individuals per species
Species richness = number of species in an area
Genetic diversity
The variety of forms of gene’s alleles within a species
Measure of allele frequency/gene (less alleles = population less able to adapt to changes in environment
Ecological diveristy
Variation of ecosystems/habitats on a regional or global level at one time
Hard to measure since ecosystems merge into the ecosystems around them
Unstable and extreme environments with low biodiversity
Hydrothermal vents — extreme conditions because the abiotic conditions are out of zone of tolerance (like temp, pH, pressure, toxins) not a lot of organisms live here = low biodiversity
Reef slopes — steep walls/slope at the front of reef, sandy substrate constantly changing due to exposure to wave currents, wind erosion
Stable, non extreme environments with high biodiversity
Coral reefs — abiotic conditions close to optimum for producers → long food chains
Rocky shores — good substrate for attachment, protective habitats (rock pools, crevices) → great biodiversity
Benefits of marine biodiversity (4)
Protection of the physical environment (coral reefs protect coastlines)
Climate control (phytoplankton absorb CO2 and release O2)
Providing food resources (algae, crustaceans, and fish)
Sources of medicine (anticancer drugs such as keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH))