Rates of Reaction
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Rate of reaction
The change in concentration of any one reactant or product in unit time
Experiment for rate of reaction
When monitoring the production id oxygen gas from the e decomposition of hydrogen peroxide using magnesium oxide as a catalyst the follow receptions occurs
Rate of reaction equation
H202 ———> h20 + ½ O2
Average rate of reaction
Total gas produced/ total time taken by
Instantaneous rate of reaction
Is the rate of a reaction at any one particular time during reaction
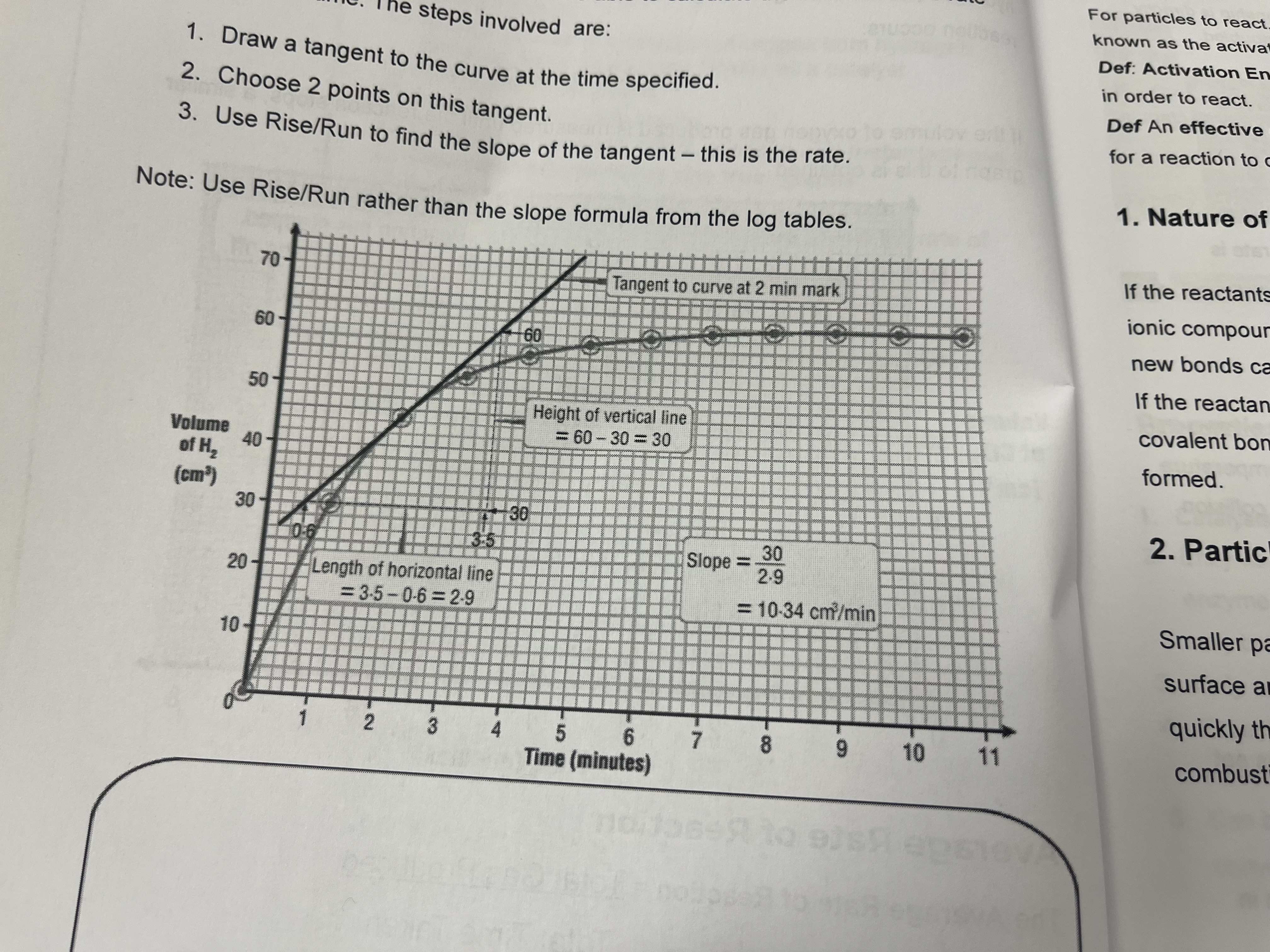
How to calculate the instantaneous rate of a particular time
Draw a tangent to a curve at the time specified
Choose 2 points on this tangent
Use rise over run to find the slope of the tangent. This is the rate.
Factors affecting rate of reaction
For particles to react they need to collide with a certain amount of energy this is known as the activation energy
Nature of reactants
Particle size
Concentration
Presence of catalyst
Temperature
Particle size
smaller particle size means faster reactions because particles have a higher surface area and will collide more often
This is why powered chemicals react more quickly than large chips or the same substance
For example dust explosion needs combustible dust confined area air and a source of ignition