Bio AT2 2023
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/180
Last updated 8:39 AM on 3/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
1
New cards
Purines
Adenine and guanine, 2 fused rings
2
New cards
Pyrimidines
Thymine and Cytosine, 1 fused ring
3
New cards
5’ (5 prime)
Phosphate linked to 5th carbon in sugar
4
New cards
3’ (3 prime)
OH group linked to 3rd carbon in sugar
5
New cards
DNA replication step 2 (after unzipping)
Binding proteins attach to the exposed ends of each strand to prevent them from coming back together
6
New cards
What end is primer added to in DNA replication?
3’ end
7
New cards
What removes the RNA primers?
exonuclease
8
New cards
What is different about RNA’s sugar
Ribose, extra oxygen
9
New cards
What is different about the nucleotide bases of RNA?
Uracil instead of thymine
10
New cards
What does RNA polymerase bind to during transcription?
Promoter
11
New cards
What causes introns to form loops?
Small nuclear ribonucleic particles (snRPS)
12
New cards
What excises the introns?
Splicosomes
13
New cards
What sticks exons back together?
RNA ligase
14
New cards
Functions of proteins (6)
Development and repair
energy
hormones
enzymes
transport and storage
antibodies
energy
hormones
enzymes
transport and storage
antibodies
15
New cards
What are prokaryotes’ version of histones?
Nucleoid-associated proteins
16
New cards
DNA methylation
A methyl group is added to the DNA which stops some genes from being expressed
17
New cards
Histone modification
Acetyl group is added, which loosens the DNA from being too tight around the histones, activates the gene
18
New cards
Order of the steps in mitosis / meiosis
Interphase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
19
New cards
Mitosis interphase
The centrosomes and DNA duplicate
20
New cards
Mitosis Prophase
Centrosomes migrate to opposite poles, spindle fibres form
21
New cards
Mitosis metaphase
The spindle fibres align the sister chromatids along the equator of the cell
22
New cards
Mitosis Anaphase
The sister chromatids are separated, and brought to opposite poles
23
New cards
Mitosis telophase
A new nuclear membrane forms around the two groups of chromosomes
24
New cards
Mitosis cytokinesis
Cytoplasm is divided
25
New cards
Meiosis Interphase
DNA and centrosomes replicate
26
New cards
Meiosis prophase 1
Homologous pairs arrange themselves in tetrads, crossing over occurs, centrosomes migrate to either pole
27
New cards
Meiosis metaphase 1
The tetrads are arranged along the equator
28
New cards
Meiosis Anaphase 1
The HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES are separated and brought to opposite poles
29
New cards
Meiosis telophase 1
new nuclear membrane forms around groups of sister chromatids, then CYTOKINESIS
30
New cards
Meiosis prophase 2
nuclear membrane disintegrates
31
New cards
Meiosis metaphase 2
Sister chromatids are arranged along equator of cell perpendicular to how they were in meiosis 1
32
New cards
Meiosis Anaphase 2
Sister chromatids are separated and pulled to either pole
33
New cards
Meiosis telophase 2
new nuclear membrane forms, then CYTOKINESIS
34
New cards
Random segregation
It is random which cells get maternal vs. paternal chromosomes (alleles) during meiosis
35
New cards
Independent assortment
Its random whether the maternal goes on top of the paternal or the paternal goes on top of the maternal when they’re arranged in tetrads
36
New cards
Crossing over
When homologous chromosomes are arranged in tetrads, parts of them can form a chiasma, where sections of the chromosomes are exchanged
37
New cards
Recombitant chromatids
Due to crossing over they contain both maternal AND paternal alleles
38
New cards
What does SNP stand for?
Single nucleotide polymorphism
39
New cards
What is a SNP?
single nucleotide substitution
40
New cards
>1% of population = ?
SNP
41
New cards
Mutation
42
New cards
What must the environment ensure for fertilisation? (4)
Gametes can meet
Moisture
Food + shelter
Dispersal of young
Moisture
Food + shelter
Dispersal of young
43
New cards
Process of producing gametes
Gametogenesis
44
New cards
To sexually reproduce, organisms must be able to find a mate, therefore ? (2)
Must be a difference between species and between sexes
45
New cards
What environment uses external fertilisation
aquatic environments
46
New cards
How does the embryo receive nutrients in external fertilisation?
Direct diffusion between the water and the cell
47
New cards
Why are large numbers of gametes produced in external fertilisation?
Low chance of gametes meeting
48
New cards
How are chances of gametes meeting increased in external fertilisation? (3)
Cyclical reproductive behaviour
Synchronised gamete release
Mating behaviour
Synchronised gamete release
Mating behaviour
49
New cards
Drying out of gametes
dessication
50
New cards
What does more parental care result in?
Greater offspring survival chance, which means less offspring need to be produced at once
51
New cards
What do the leaves of bulbs store?
food
52
New cards
What does the terminal bud of a bulb do?
Produce a flower
53
New cards
What does the lateral bud of a bulb do?
Produce a new plant
54
New cards
What do rhizomes look like / where are they located?
Horizontal, underground
55
New cards
What does the terminal bud of a rhizome do?
Makes a flower
56
New cards
What does the lateral bud of a rhizome do?
Makes more rhizomes
57
New cards
What does a runner look like / where is it located?
Horizontal above ground
58
New cards
What do the terminal buds of a runner do once they touch the ground?
Make a new plant
59
New cards
What is unique about gymnosperms?
Their seeds are not housed in ovaries
60
New cards
What do the leaves of gymnosperms form?
Cones - can be male or female
61
New cards
What does the male cone of a gymnosperm produce?
Large amounts of pollen
62
New cards
What does a gymnosperm rely on for pollination?
Wind
63
New cards
Angiosperms
flowering plants
64
New cards
Function of petals
Advertise to pollinators
65
New cards
Function of sepals
Protect flower bud
66
New cards
Stamen structure
Filament tipped by anther x
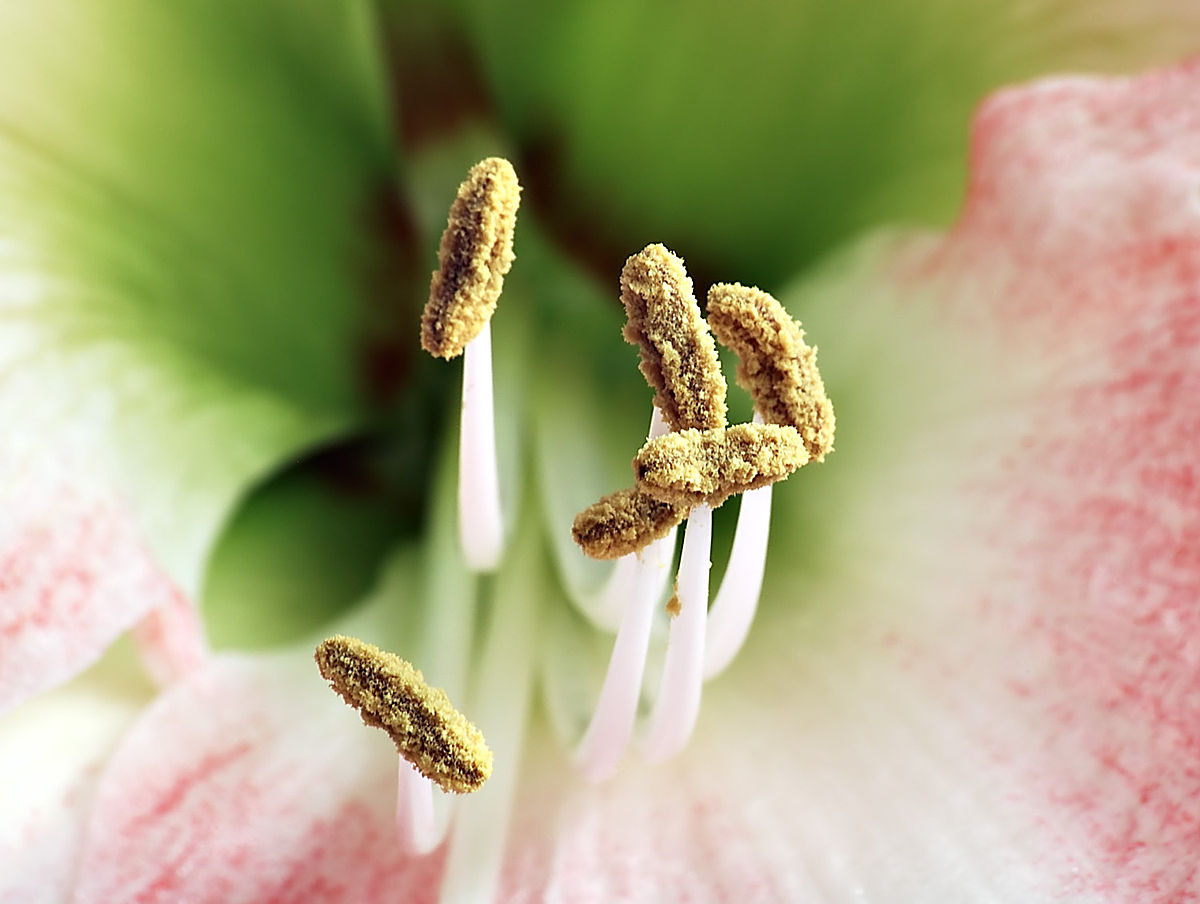

67
New cards
What happens within the anther?
Sacs produce pollen via meiosis
68
New cards
What do pollen grains house?
Cells that develop into sperm
69
New cards
Carpal structure
Style with stigma
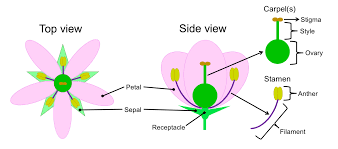
70
New cards
What is at the base of the carpal
The ovary
71
New cards
What is inside the ovary (flower)?
Ovules
72
New cards
What do ovules house?
Developing ova and supporting cells
73
New cards
Pistil
Single carpal or group of fused carpals
74
New cards
How are the male gametes of angiosperms produced?
Cells inside pollen sacs undergo mitosis
75
New cards
Pollination
Pollen moves from an anther to a stigma
76
New cards
What happens after pollen grain lands on the stigma?
A tube grows from the grain to an ovule. 2 male gametes go down the tube, one of them fertilises the ovum.
77
New cards
What does a fertilised ovule become?
Seed
78
New cards
What does the ovary become after fertilisation?
Fruit
79
New cards
Development of an angiosperm zygote stops until there are favourable environmental conditions, then ?
The seed germinates
80
New cards
Fungi vs plant
Cell wall but no chloroplasts or chlorophyll
81
New cards
Fungi structure
Hyphae
Mycelium
Sporangium
Mycelium
Sporangium
82
New cards
Hyphae
Long thin threads, make up fungi
83
New cards
Mycelium
Tangled web of hyphae
84
New cards
Sporangium
Capsule where spores are made
85
New cards
What division process makes spores?
Mitosis
86
New cards
Budding process
Outgrowth off parent organism, the parent nucleus divides and one of the nuclei move to the bud. The bud breaks off and becomes the new organism
87
New cards
Why would fungi choose to reproduce sexually?
Adverse environmental conditions
88
New cards
How do bacteria reproduce
Binary fission - cell forms DUMBBELL shape when doing this
89
New cards
Protists structure
unicellular or unicellular-colonial
90
New cards
How do protists reproduce?
Most by binary fission, some by budding
91
New cards
Ionising radiation energy
high
92
New cards
How can ionising radiation cause a mutation? (2)
If it hits DNA directly, it can break the covalent bonds between nucleotides causing the backbone to break. As DNA repair enzymes put the DNA back together, they may reassemble it in the wrong order
\
It can also knock electrons out of orbit of nearby molecules, causing them to ionise. They are now called FREE RADICALS. These free radicals can react with nearby DNA, and may prevent transcription or translation, resulting in loss of control of the cell cycle
\
It can also knock electrons out of orbit of nearby molecules, causing them to ionise. They are now called FREE RADICALS. These free radicals can react with nearby DNA, and may prevent transcription or translation, resulting in loss of control of the cell cycle
93
New cards
Non-ionising radiation energy
Low, only UVC can do any damage (UVA and UVB stopped by ozone)
94
New cards
How can UV radiation cause a mutation? (1)
It can cause adjacent thymine or cytosine bases on the same DNA strand to link together to form a dimer. These dimers cause structural kinks in the DNA, preventing transcription and translation and resulting in loss of control of the cell cycle.
95
New cards
How can chemical mutagens cause a mutation? (general)
Can be put into DNA instead of a nitrogenous base (because they are chemically similar)
96
New cards
How do deanimating agents cause mutations?
They can change one base to another one
97
New cards
How do viruses cause mutations?
They insert their DNA into the host genome to reproduce. If they insert their DNA in the vicinity of a gene, this can cause a mutation.
98
New cards
How does a retrovirus turn its RNA into DNA?
Reverse transcriptase
99
New cards
What is radon?
A radioactive gas
100
New cards
What does radon release to cause mutations?
Ionising radiation