BSCI 222 St Leger Exam 2
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
Line of Regression
Made by Galton, line of best fit
Regression Coefficient
b, change in y per unit change in x
b=0.35 most parent v children traits
Linkage
genes located on the same chromosome
can only produce certain gametes ie. PpLl can only produce PL & pl
Recombinant Configurations
different from parents
non-parental
1 crossing over effects 2/4 chromatids
Cis Configuration
Heterozygous alleles of 2 linked genes
(coupling)
PL/pl
like dominance alleles on same gene
Trans Configuration
Heterozygous alleles of 2 linked genes
(repulsion)
Pl/pL
different dominance alleles on same gene
Alfred Sturtevant
* student of Thomas Hunt Morgan
* proved linkage & proposed recombination is powered by crossing over
* measured gene length to determine recombination frequency
* 3 point testcross
Recombination Frequency (RF)
# recombinants/ total # offspring x 100
can't exceed frequency expected for independent assortment
0.5 or 50% means that the genes are unlinked or too far apart
* consider each gene pair separately (the first 2 then the last 2 for 3 point cross)
ie. if the parentals are VPB & vpb then the number of recombinants would be vPB & Vpb & VpB & vPb
Map Unit (m.u.)
RF/100
CentiMorgan (cM)
m.u. x 100
3 Gene Double Crossover
* the middle gene is the odd one out
ie. ABC, abc -> ABc abC, C is the middle gene. AcB & aCb
Tester
genes homozygous recessive in test cross, because it allows non-tester alleles to fully determine phenotype of offspring
Coefficient Of Coincidence (C.O.C)
#observed double crossovers/ # expected double crossovers
* anything less than 1 has interference
Expected double crossovers
(fraction of crossovers at location1)(location2)(total #offspring)
Interference
1-C.O.C
expected but not observed
Gene Order of 3-Point Cross
1) Non-recombinant offspring (2 highest #)
2) Double Recombinant offspring (2 lowest #)
3) Determine which one differs between the 2 & that is the middle
FISH
Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
*identifies gene locations on chromosome by fluorescent probes
*easy to detect segmental deletions & translocations
Central Dogma
DNA Replication > DNA > Transcription > RNA > Translation > Amino Acid > Polypeptide > Protein
Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (AIS)
XY fetuses unresponsive to androgens / male hormones
*externally female, genetically male
*undersized vagina and hidden testicles
Amino Acids
Amine Group- NH2
Carboxyl Group- COOH
R Group- side chain, 20 options
Protein Folding Structures
Primary- Amino Acid Sequence, determines how the other structures fold up
Secondary- fold to spiral
Tertiary- fold to glob
Quaternary- 2+ polypeptide chains globbing up
AlphaFold3
AI developed by DeepMind that predicts 3D models of protein sequences accurately
Polypeptide
long chain of Amino Acids joined by peptide bonds
The Big Scientists behind DNA Structure
Linus Pauling- wrote the book on bonds, thought DNA was triple helix, missed his flight so didn't see photo 51
James Watson- put together the model of DNA from Franklin's photo 51
Francis Crick- also put together the model of DNA from the photo 51
Rosalind Franklin- fact checked Watson & Crick, took the photo 51of DNA
Maurice Wilkins- also took the photo 51 of DNA
It has not escaped our notice
Genetic Material Key Characteristics
*have complex info
*compact
*stable
*replicate (copy) accurately
*changeable
*quick easy retrieval
Paleogenetics
extracting DNA from tissues of ancient remains and analyzing
Archeological Genetics
studying genetics & proteins in preserved ancient bones
eDNA
eDNA is DNA detected in environmental samples such as water or soil that is used to confirm the presence of the species that produced it.
Nucleotide
Pentose Sugar- Ribose: has 3 OH Deoxyribose: has 2 OH
Phosphate Groups
Nitrogenous Bases- Purines (2 rings): Guanine, Adenine
Pyrimidines (1 ring): Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil
Adenine
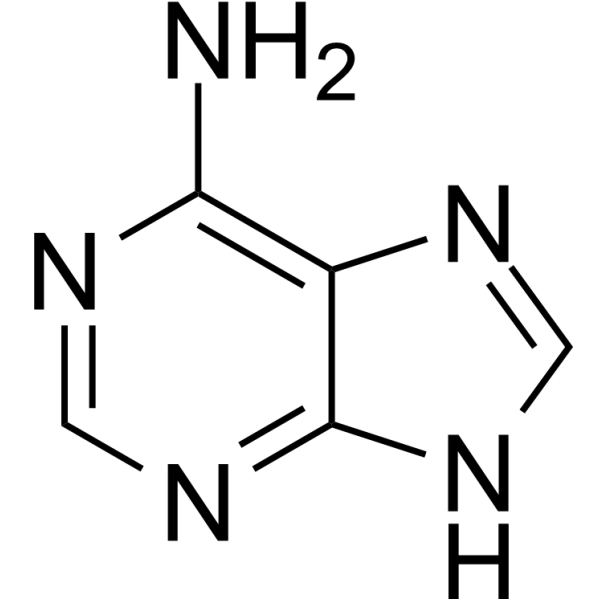
Thymine
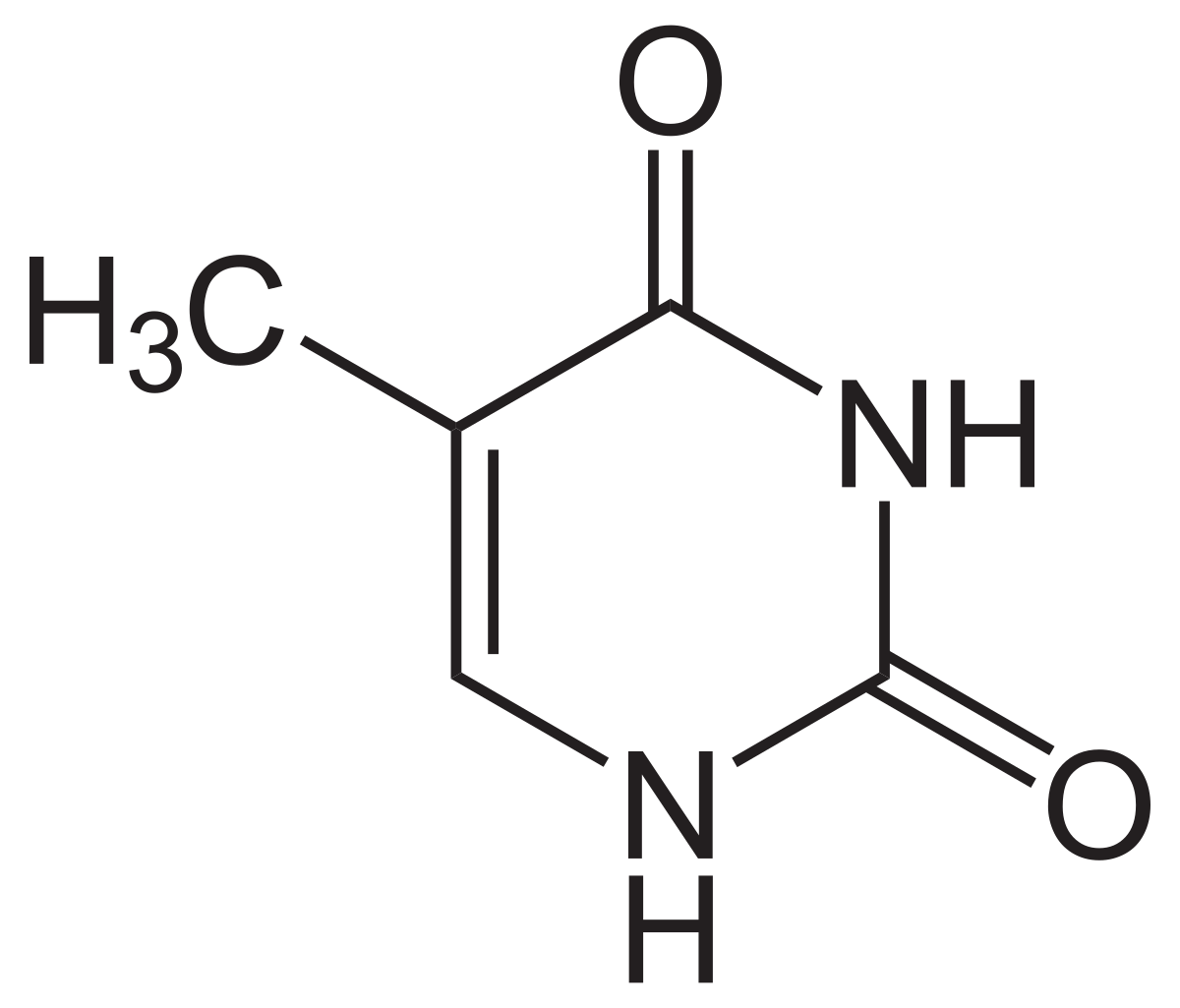
Guanine
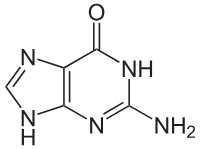
Cytosine
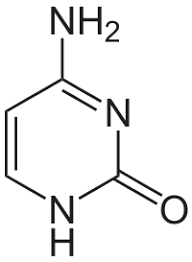
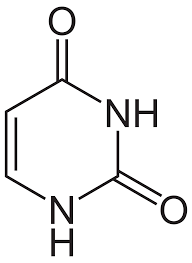
Uracil
Chargaff's Rule
#A=#T=#U (2H bonds) #G=#C (3H bonds)
Erwin Chargaff
Secondary DNA Structure
*double helix
*phosphodiester bond backbone- always link 3' (sugar) to 5' (phosphate) ends of the nucleotides, covalent bonds to be strong
*hydrogen bond & base pairing
*antiparallel complementary DNA strands
Melting Temperature of DNA (Tm)
Temp where 50% is double & 50% single stranded
2(A+T)+4(C+G) rule 2º & 4º
Right handed DNA
clockwise spiral
B-DNA- looser, predominates in cells
A-DNA- tighter
diameter of 2.0nm
1 rotation is 10 base pairs & 3.5nm long
Left handed DNA
Z-DNA
most loosely wound
sometimes present in active genes
Advantages of 2 stranded DNA
*thin for tight packing
*hydrophobic inside & stability to protect sequence
*prevents tangling up on itself of the base pairs
Hairpin Structure
sequence of nucleotides are inverted complements of at least 5 bases for the stem
Ribosymes
RNA molecules that function as enzymes
Supercoiling
overwinding (positive) or under winding (negative) DNA
Topoisomerase I
cuts a single strand of double helix, relaxes the coil, and rebinds the cut (reanneal)
Eukaryotic Chromatin
1/3 Histones, 1/3 DNA, 1/3 nonhistone proteins
Polytene Chromosome
repeated rounds of DNA replication w/ no division
Chromosomal Puffs
regions of relaxed euchromatin where active transcription is taking place
Euchromatin v Heterochromatin
E) less condensed, on chromosome arms, unique sequence many genes, replicated through S phase, transcription often, crossing over common
H) more condensed, on centromeres & telomeres, repeated sequences, few genes, replicated late S phase, transcription infrequent, crossing over uncommon
Histones
DNA wraps around it to coil tighter, H1 clamps to keep DNA wrapped
Each nucleosome has 2 copies of H4
Condensin
5-unit protein complex that folds chromatin
Protein Kinases
transfers phosphates fr/ ATP to protein, Phosphotases do the opposite
Topoisomerase II
untangles pair of DNA strands by cutting 1 & passing the other through, and then rebinding the cut
Transcription Factories
specialized sites where transcription occurs
loops of other chromosome territories may overlap
C-value Paradox
C-Value) haploid DNA content per nucleus
for eukaryotes there is no correlation bt/ genome size & complexity of a species
Satelite DNA
repeated pattern of sequences unrelated to transposons
Nucleolus Organizer Regions (NORs)
chromosomal regions that consist of tandemly repeated sequences coding for 18S, 5.8S, & 28S rRNA
Telomeres
caps of repeated DNA to protect the ends of the chromosomes
G (3') rich is longer than C (5') rich strand & G folds over to form the t-loop
Shelterin
binds to telomeres to protect them from degradation & the ends of chromosomes being joined by DNA repair systems
Centromere
binding site of spindle fibers, many satelite DNA
Microsatellites
Short tandem repeats (STRs), up to 8bp variable number of copies of repeat sequences possessed by many organisms
DNA Fingerprinting
1986, helpful for crime scenes, any biological fluids can be sequenced
CODIS
Combined DNA Index System, panel of 13 STRs, homozygous 1 tall peak, heterozygous 2 small peaks
Transposons
terminal inverted repeats
enzyme transposase cuts them & the target site
segments of DNA that can move from one region of DNA to another
rapid macroevolutionary change
Barbara McClintock
DNA transposons (class II)
move DNA directly, cut & paste
Insertion sequences- carries only genetic info for transposition
Composite transposons- 2 copies of an insertion sequence that may itself transpose, can trigger duplication & deletion of DNA
Retrotransposons (class I)
use RNA intermediaries, copy & paste
plasmid
small extrachromosomal DNA molecule w/in a cell that is physically separated fr/ the chromosomal DNA & can replicate independently
Conjugation
genes that can transfer to other bacteria
R-plasmids
MRSA
methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
RAG genes
cut & paste transposases
VDJ- variability, diversity, joining segments
Humam Endogenous Retrovirus (HERVs)
retrovirus gets into germline viral DNA
amylase (breaks down carbohydrates) derived fr/ ERVs
Syncytiotrophoblast
outer covering of trophoblast villous trees
comes in contact w/ maternal blood
Selfish DNA
parasitic DNA that exists because it is good at getting itself replicated
Long Interspersed Nuclear Elements (LINEs)
Replisome
large complex of enzymes that are required for replication
Origins of Replication
specific site where replication begins, recognized by sequence
Theta Replication
replication of circular DNA
initiated by the unwinding of the two nucleotide strands, producing a replication bubble
Unwinding continues at both ends of the bubble, making it progressively larger & separating the DNA into 2 bubbles
DNA replication on both of the template strands is simultaneous with unwinding until the two replication forks meet.
Linera DNA Replication
Each chromosome has multiple bubbles that eventually meet up and fuse till their is 2 separate strands of double stranded DNA
Helicase
moves replication fork forward by unwinding the DNA (breaking Hydrogen bonds bt bps)
DNA Gyrase
"relaxer"
prevents DNA fr being too tightly wound as DNA opens up ahead of replication fork
Single Stranded Binging Proteins (SSBs)
coat the separated strands of DNA to keep them from coming back together into double helix
DNA Polymerase III
"the builder"
add nucleotides to growing DNA 3' existing chain
*require a primer from RNA Primase in order to start from scratch adding 5'-3' & reading 3'-5'
Deoxyribonucleoside Triphosphates (dNTPs)
new DNA is synthesized from them
complementary & antiparallel
Leading Strand
new strand 5' to 3' towards replication fork, reads off of old 3' to 5', made continuously
Lagging Strand
new strand adds 3' to 5' but reads off of old 5' to 3', made in Okazaki fragments, & needs a primer for each fragment
Exonuclease
removes RNA primers & removes nucleotides
DNA Ligase
seals backbone after primers are removed
End Replication Problem
last primer on lagging strand leaves a gap bc there is no 3' end for DNA polymerase to bind to
Progerias
premature aging from short telomeres
Amatin
toxin that inhibits RNA polymerase 2 if ingested
RNA Polymerase I, RNA Polymerase II, and RNA Polymerase III
makes rRNA, makes mRNA, makes tRNA
Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP)
growth factor, bone growth primarily
Adaptive Radiation
single ancestral form diversifies to fill available roles in environment
Transcription Requirements
*DNA Template
*promoter
*RNA-coding sequence
*Terminator
Initiation, Elongation, Termination
Motif
simple structure that fits into the major groove of DNA & usually recognizes a specific sequence
helix-turn-helix, zinc-finger, steroid receptor, leucine-zipper, helix-loop-helix, homeodomain
Initiation Site
+1 site
site where first RNA nucleotide is transcribed
upstream is before this site & downstream after
Consensus Sequences
short stretches of most common bases in sequences on promoters
Y=pyrimidine
R=purine
N=none
/=both equally common
sigma factor
controls the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter
holoenzyme
apoenzyme + cofactor
capable of binding to a promoter & initiating transcription
Rho-independent Termination
Formation of a hairpin loop C&G rich with tail of U that stalls the RNA polymerase and transcription terminates
Causal Emergence
complex systems can exhibit stronger causal effects at macro than at micro level
Chromatin Remodeling Factors
A protein that disrupts chromatin structure by breaking bonds between DNA and histones.