A&P (Sr.) Final
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
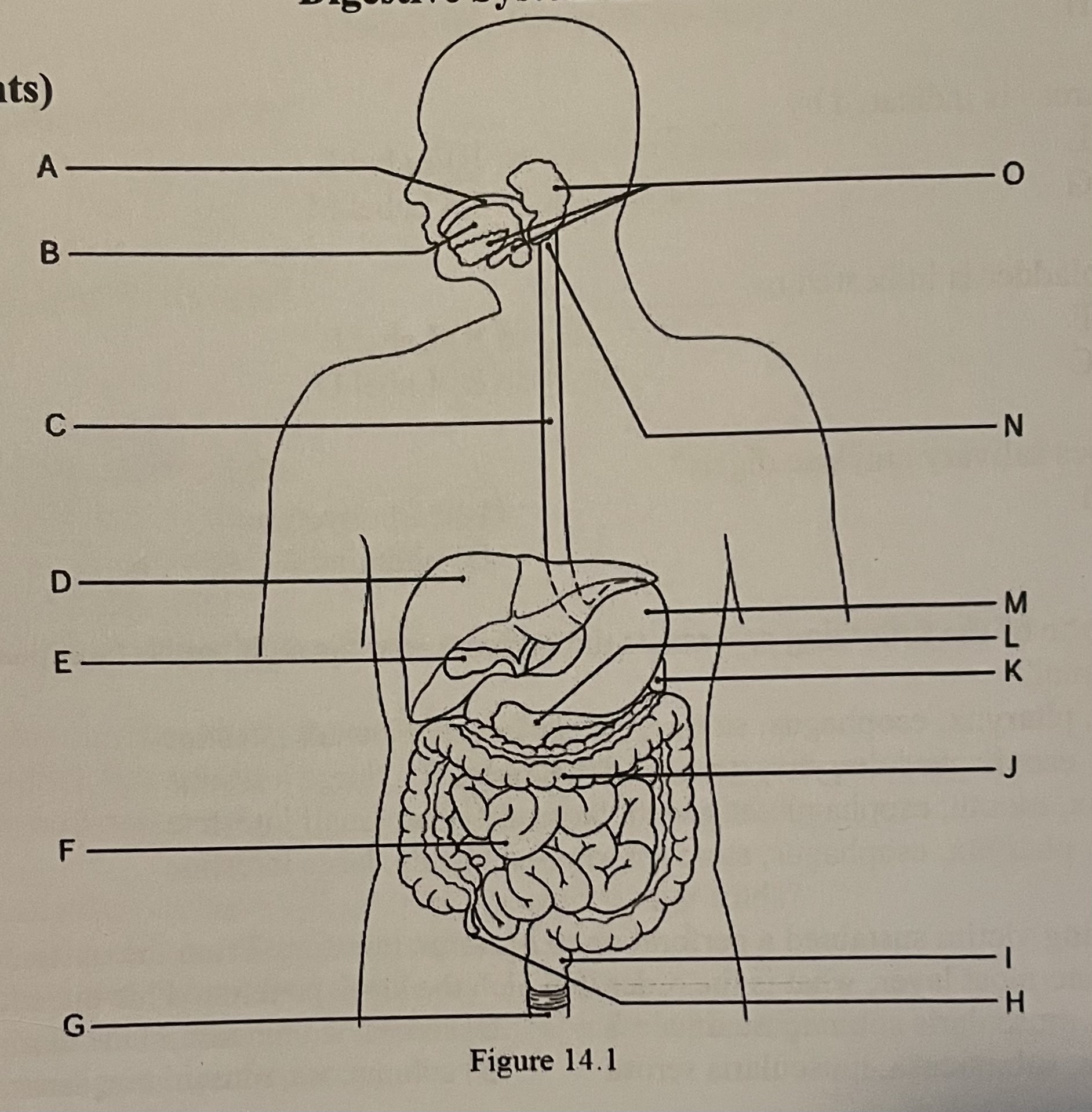
DIAGRAM The large intestine is indicated by ___
Label J, Label L, Label K, Label M
Label J
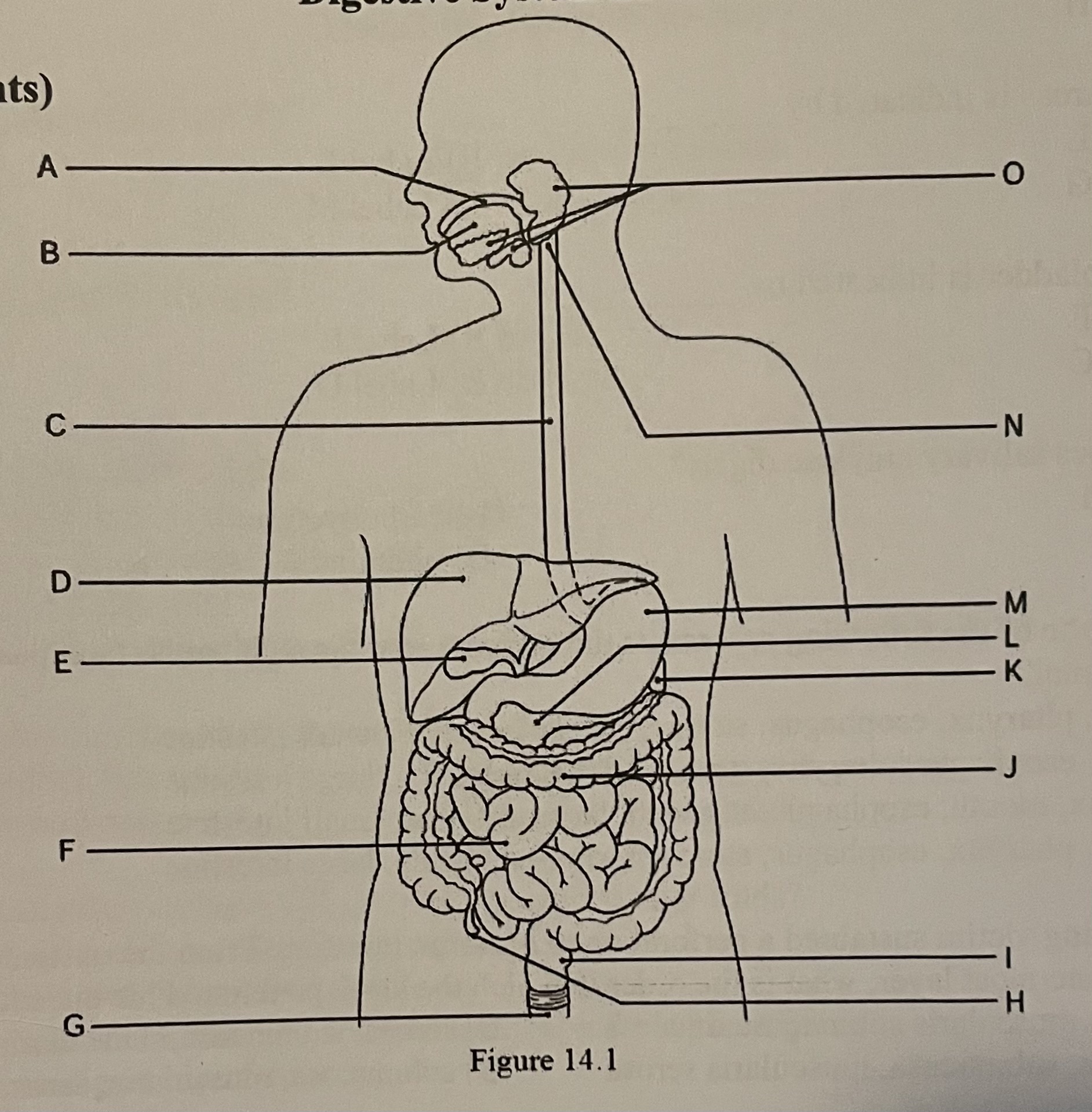
DIAGRAM The salivary glands are indicated by ___
Label J, Label M, Label N, Label O
Label O
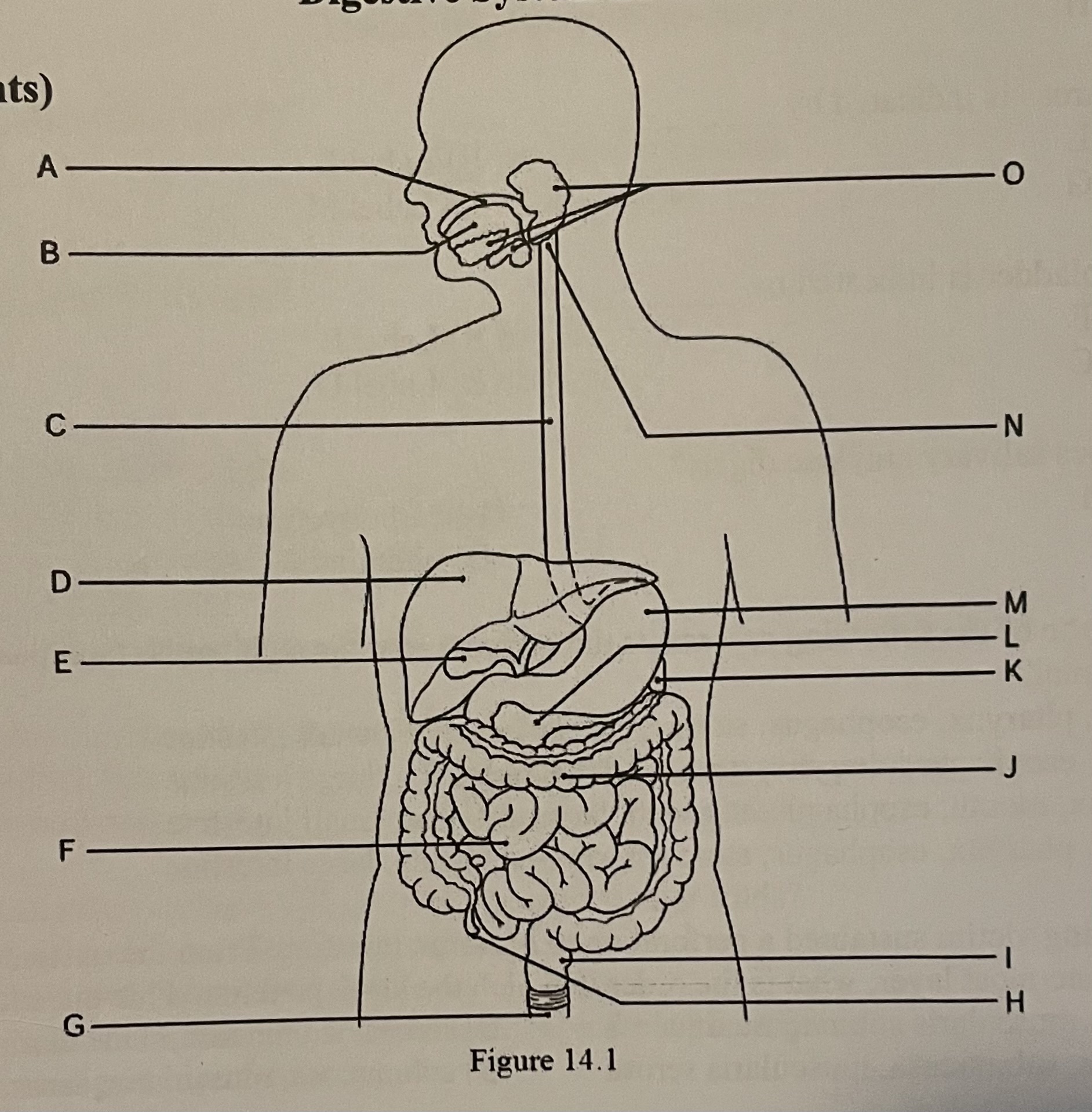
DIAGRAM The small intestine is indicated by ___
Label H, Label J, Label F, Label D
Label F
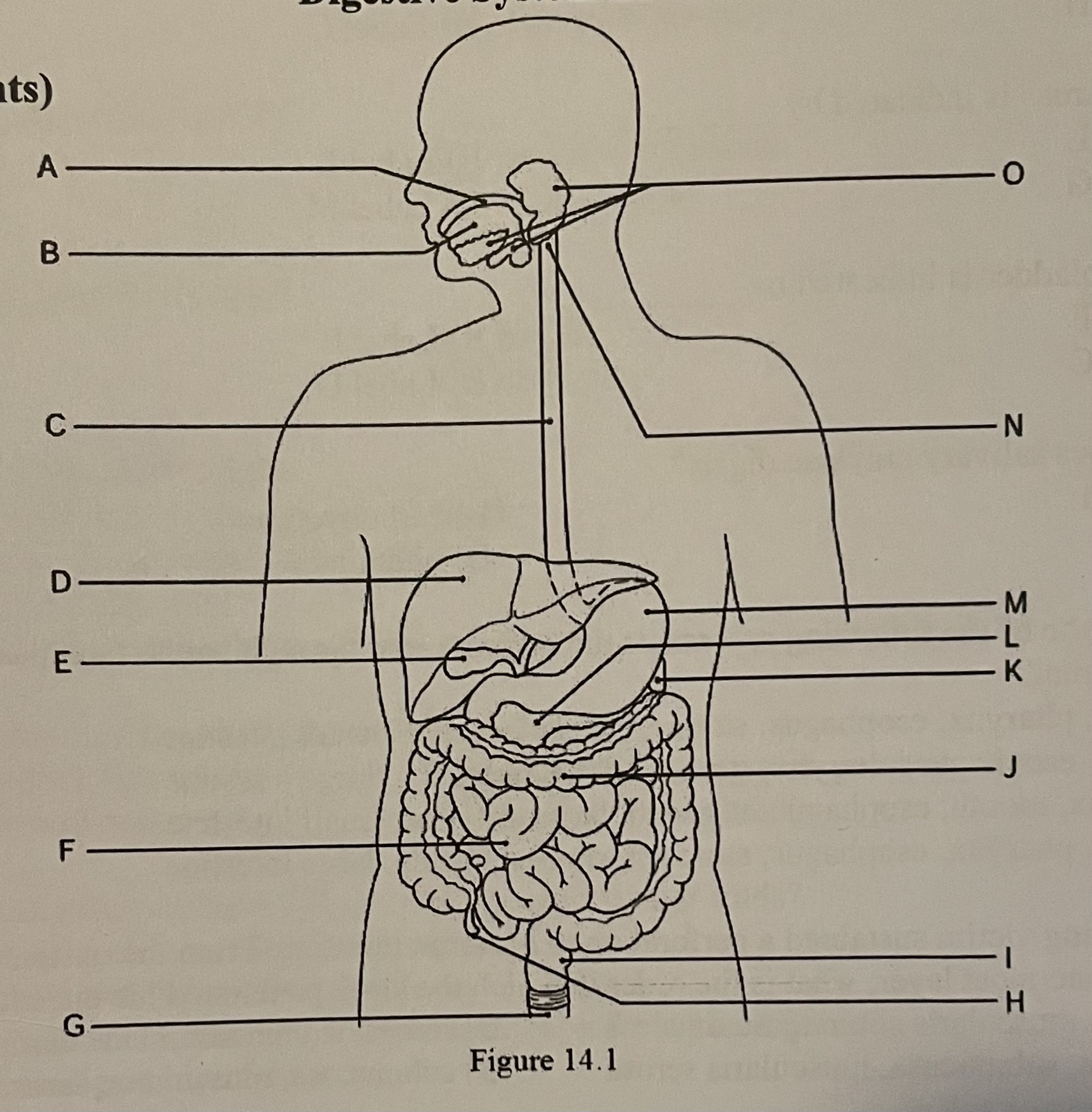
DIAGRAM The liver is indicated by ___
Label F, Label G, Label E, Label D
Label D
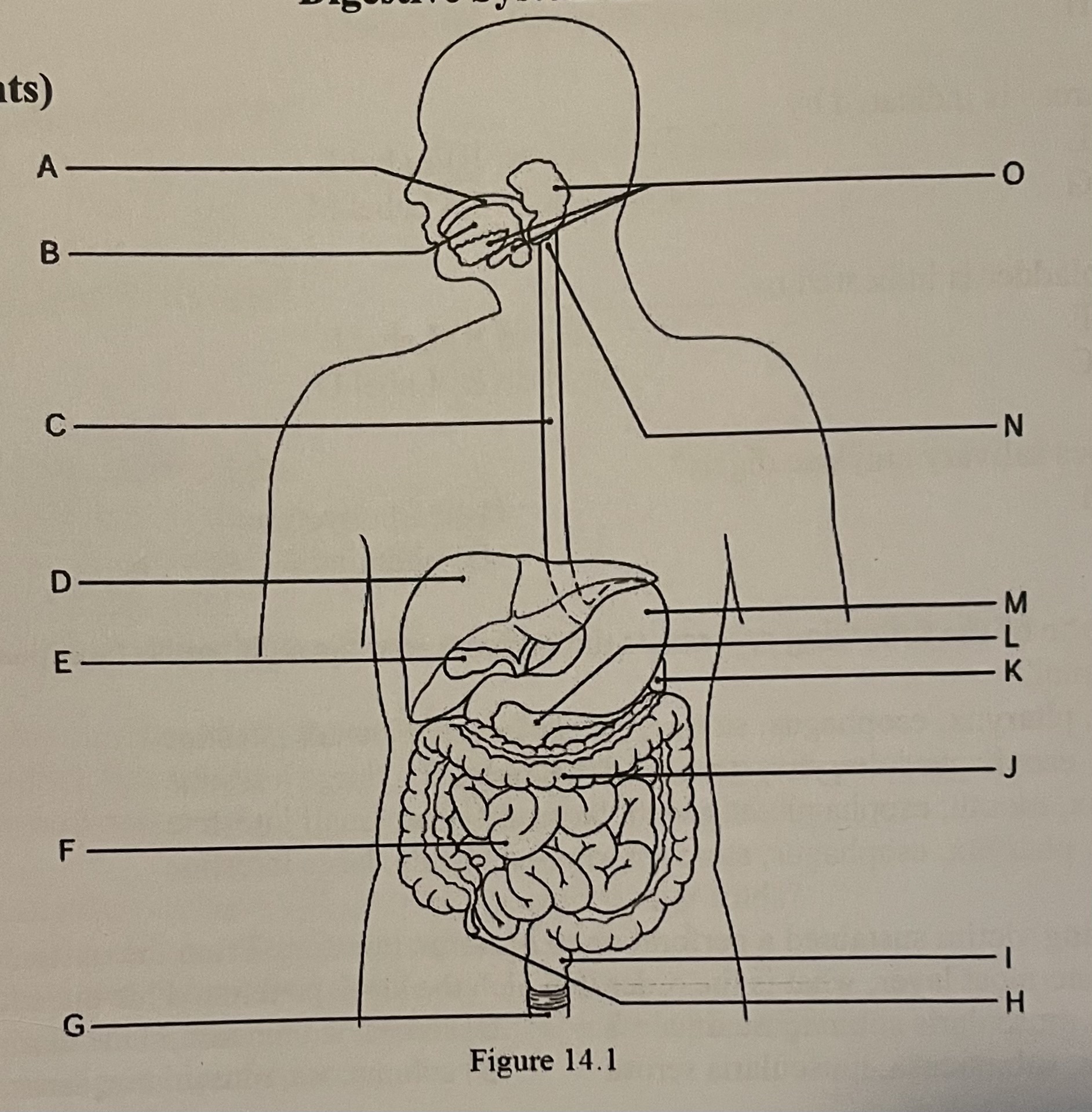
DIAGRAM The esophagus is indicated by ___
Label A, Label E, Label C, Label D
Label C
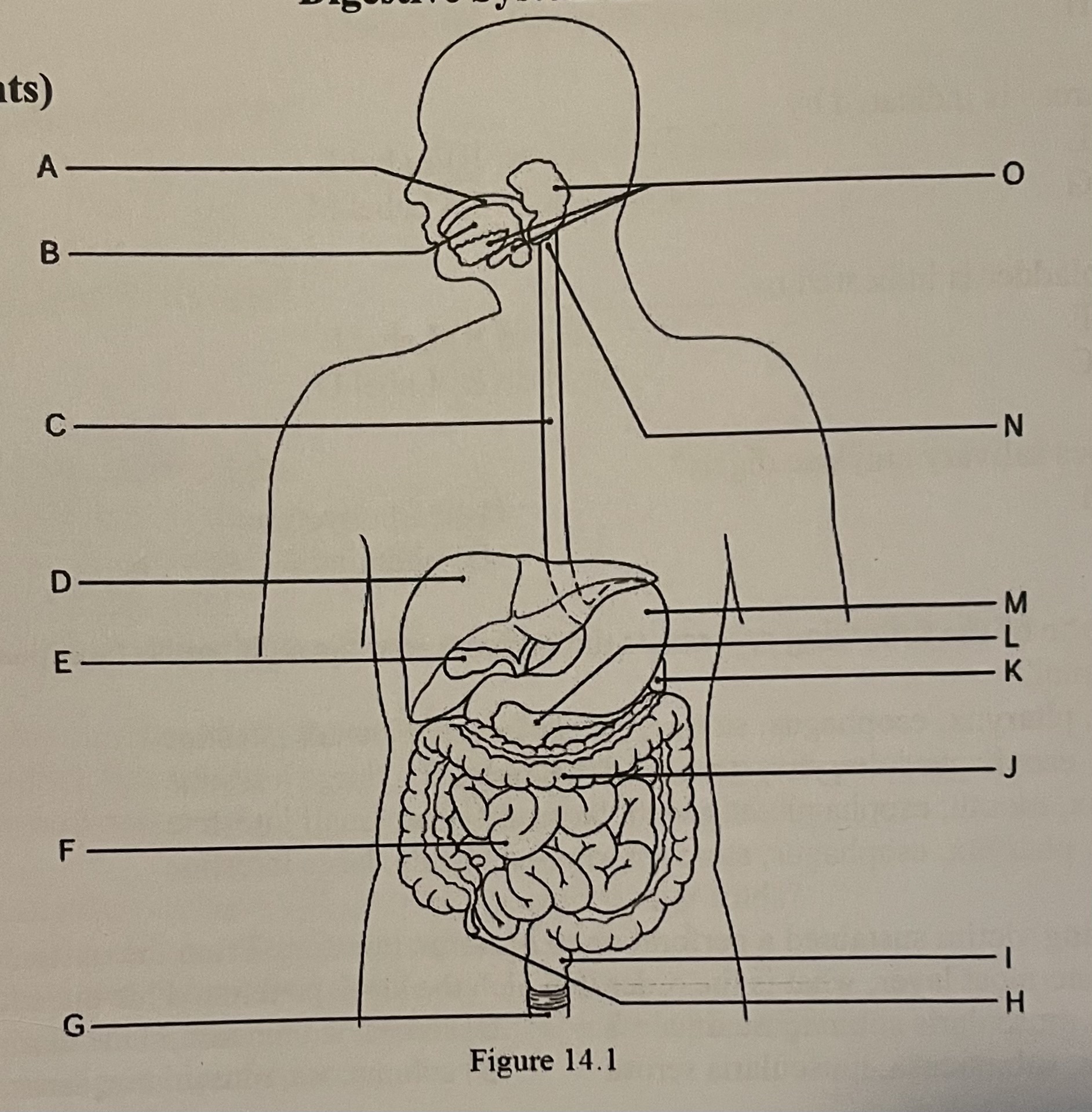
DIAGRAM The appendix is indicated by ___
Label I, Label F, Label H, Label G
Label H
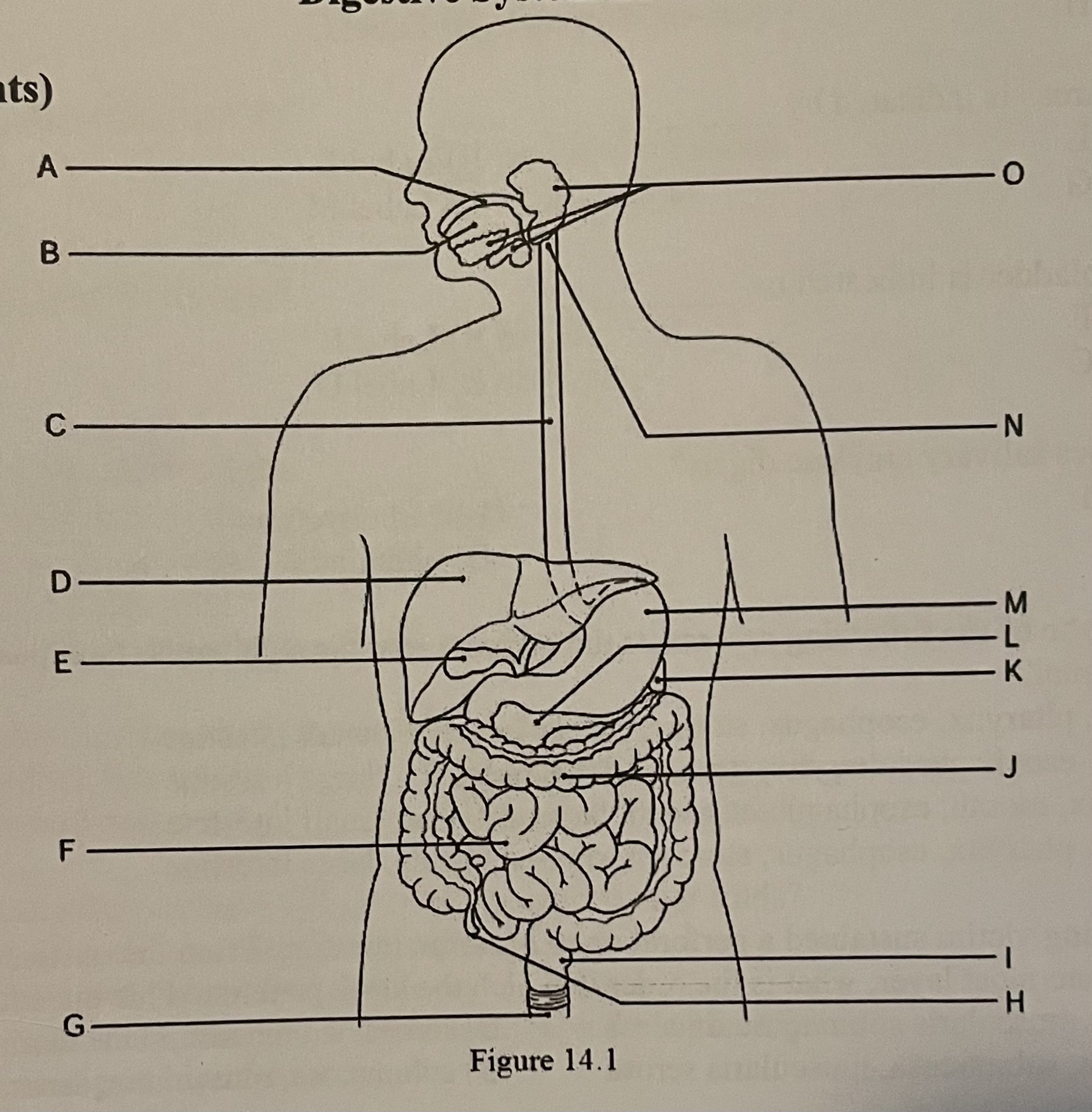
DIAGRAM The pancreas is indicated by ___
Label L, Label E, Label G, Label M
Label L
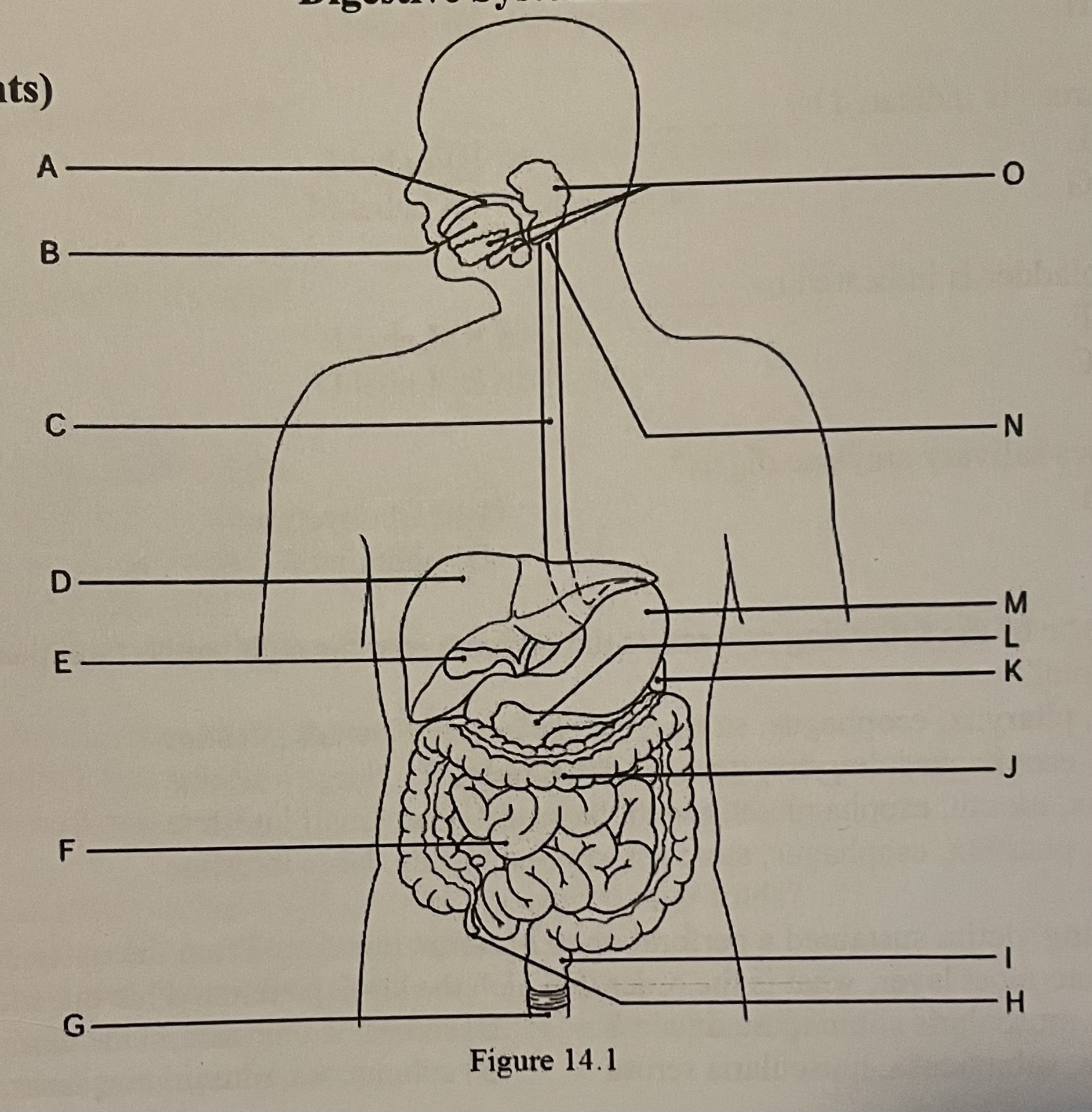
DIAGRAM The gallbladder is indicated by ___
Label F, Label E, Label C, Label D
Label E
What does salivary amylase digest?
protein, carbohydrate, fat, or vitamins
Carbohydrate
Which one of the following represents the correct order through which food passes in the alimentary canal?
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, large intestine, small intestine (A)
mouth, esophagus, pharynx, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (B)
pharynx, mouth, esophagus, stomach, large intestine, small intestine (C)
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (D)
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (D)
A stabbing victim sustained a perforation to his large intestine. From the outermost layer to the innermost layer what is the order in which the knife penetrated his intestine?
A. serosa, muscularis submucosa, mucosa
B. serosa,submucosa, muscularis mucosa
C. mucosa, submucosa, muscularis serosa
D. submuscosa, muscularis, serosa, mucosa
A. serosa, muscularis submucosa, mucosa
What are the three subdivisions of the small intestine?
A. cecum, colon, rectum
B. duodenum, jejunum, ileum
C. cardiac, body pylorus
D. ileum, cecum, rectum
B. duodenum, jejunum, ileum
Which one of the following alimentary segments has NO digestive function?
A. stomach
B. mouth
C. esophagus
D. duodenum
C. esophagus
Hydrochloric acid is necessary in the stomach for the conversion of pepsinogen to _____
A. acid
B. rennin
C. pepsin
D. gastrin
C. pepsin
Bile is formed by the ____ and stored in the ____
A. spleen; liver
B. liver; gallbladder
C. gallbladder; liver
D. pancreas; gallbladder
B. liver; gallbladder
How does the structure of the alimentary canal different in the stomach from the esophagus?
A. the esophagus has villi and microvilli
B. the stomach has an additional layer of muscle
C. the esophagus only has 3 layers
D. the stomach has a submucosa layer
B. the stomach has an additional layer of muscle
What is one of the main functions of the small intestine?
A. absorption of nutrients
B. absorption of water
C. waste secretion
D. vitamin conversion
A. absorption of nutrients
Where is the vomiting center located?
A. medullary cavity
B. medulla oblongata
C. spinal cord
D. frontal cortex
B. medulla oblongata
Where does protein digestion begin?
pancreas, mouth, large intestine, or stomach
stomach
The small intestine extends from the ___
A. cardioesophgeal sphincter to the pyloric sphincter
B. pyloric sphincter to the ileocecal valve
C. ileocecal valve to the appendix
D. gastroesophageal sphincter to ileocecal valve
B. pyloric sphincter to the ileocecal valve
What organs release secretions into the small intestine?
A. pancreas, gallbladder and spleen
B. appendix and Peyer’s patches
C. liver, gallbladder and pancreas
D. cecum and appendix
C. liver, gallbladder and pancreas
Why does the small intestine have villi, microvilli, and circular folds?
A. to increase surface area for absorption of nutrients
B. to increase surface area of water absorptions
C. to increase the number of places to secrete intestinal juice with enzymes
D. to produce bile to digest high fat meals
A. to increase surface area for absorption of nutrients
Which organ is responsible for drying out indigestible food residue through water absorption and the elimination of feces?
stomach, large intestine, small intestine, or pancreas
large intestine
Where does starch (CHO) digestion begin?
mouth, pancreas, large intestine, small intestine
mouth
We do NOT have the enzymes to digest ___
cellulose, sucrose, lactose, maltose
cellulose
TRUE or FALSE: The pancreas makes an alkaline fluid that neutralizes the acidic chyme entering the small intestine from the stomach.
TRUE
During vomiting, the ____ raises up to close off the nasal cavity.
soft palate, epiglottis, hard palate, or esophagus
soft palate
Which of the following does NOT contribute to the digestion of proteins?
trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase, or amylase
amylase
Bacteria in the large intestine serve what purpose?
synthesize vitamins, absorb water, make enzymes, or destroy red blood cells
synthesize vitamins
Where do bile and pancreatic juice enter the alimentary canal?
stomach, duodenum, cecum, ilium
duodenum
Enzyme-rich pancreatic juice contains all the following EXCEPT _____
amylase, trypsin, pepsin, or lipase
pepsin
Which of the following is a function of saliva?
A. dissolve chemicals so they can be tasted
B. start the breakdown of carbohydrate
C. moisten and bind food together
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
Which of the following is NOT a function/activity of the large intestine?
A. digestive enzyme production
B. water absorption
C. vitamin synthesis by bacteria
D. gas production by bacteria
A. digestive enzyme production
Which of the following is a good source of carbohydrates?
A. meats
B. fruits and vegetables
C. nuts, seeds and vegetable oil
D. eggs
B. fruits and vegetables
Which of the following is a good source of vitamins?
A. fruits and veggies
B. milk and meat products
C. egg yolk
D. nuts
A. fruits and veggies
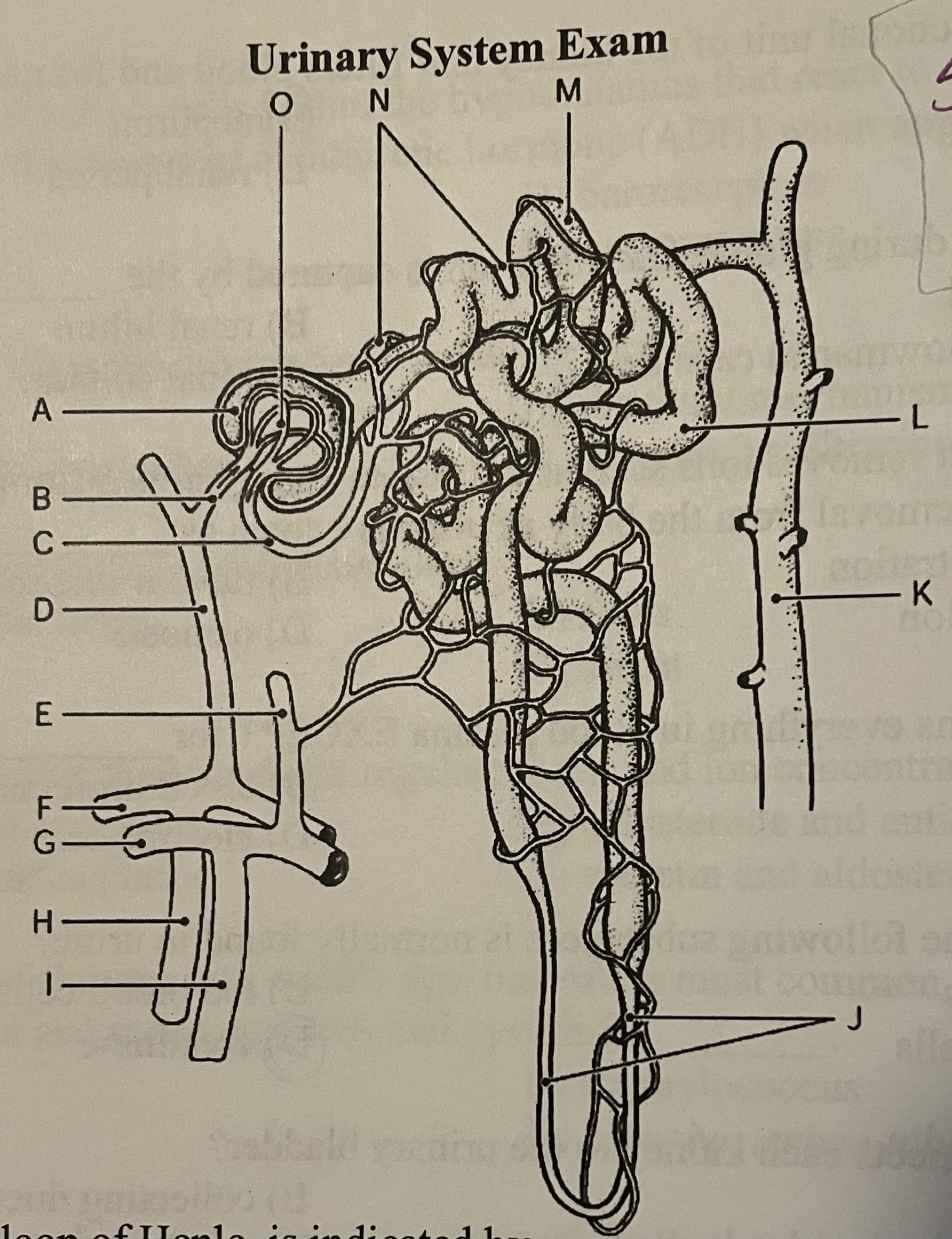
DIAGRAM The nephron loop, or loop of Henle, is indicated by ___
Label I, Label J, Label K, Label M
Label J
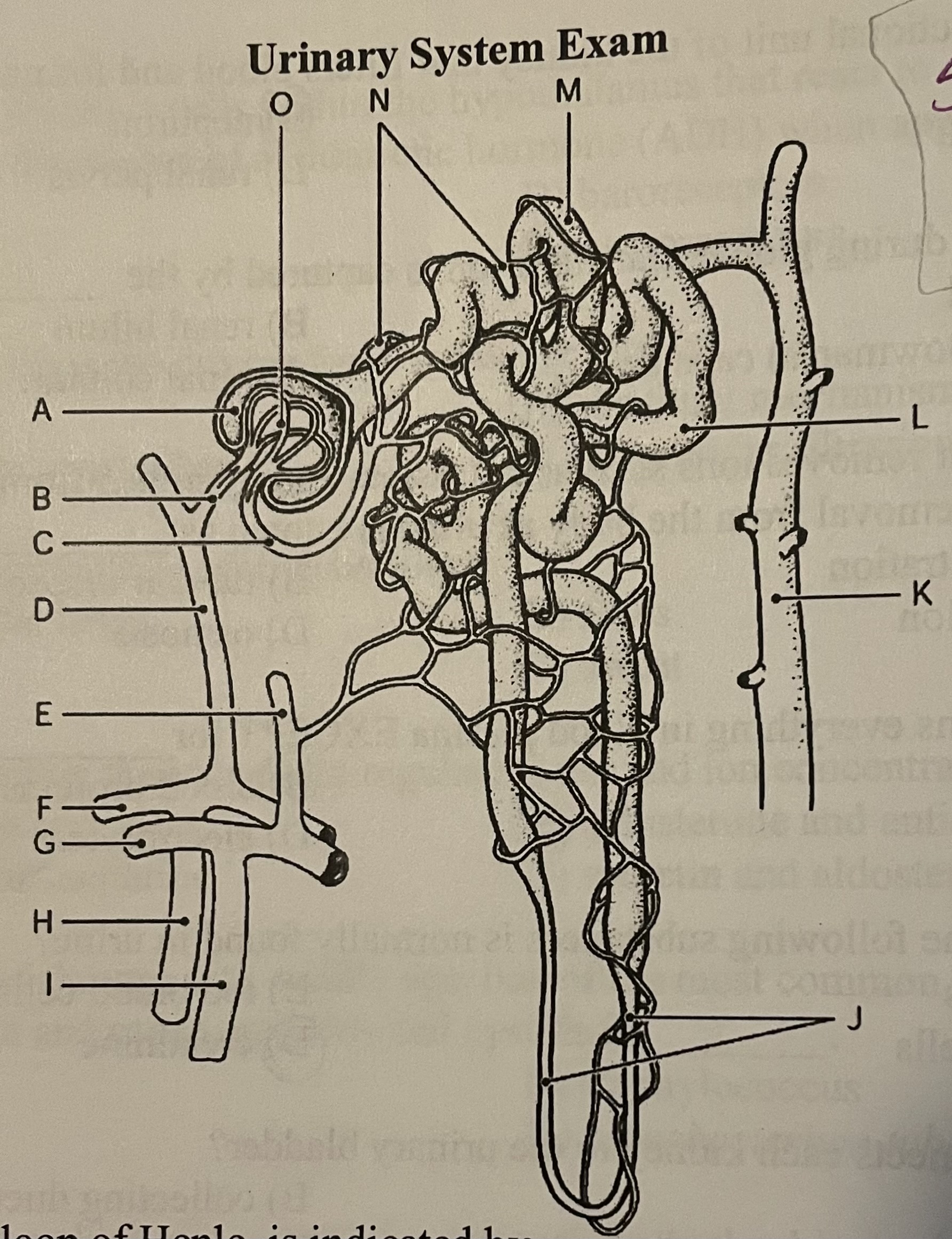
DIAGRAM The peritubular capillaries are indicated by ___
Label N, Label M, Label O, Label L
Label N
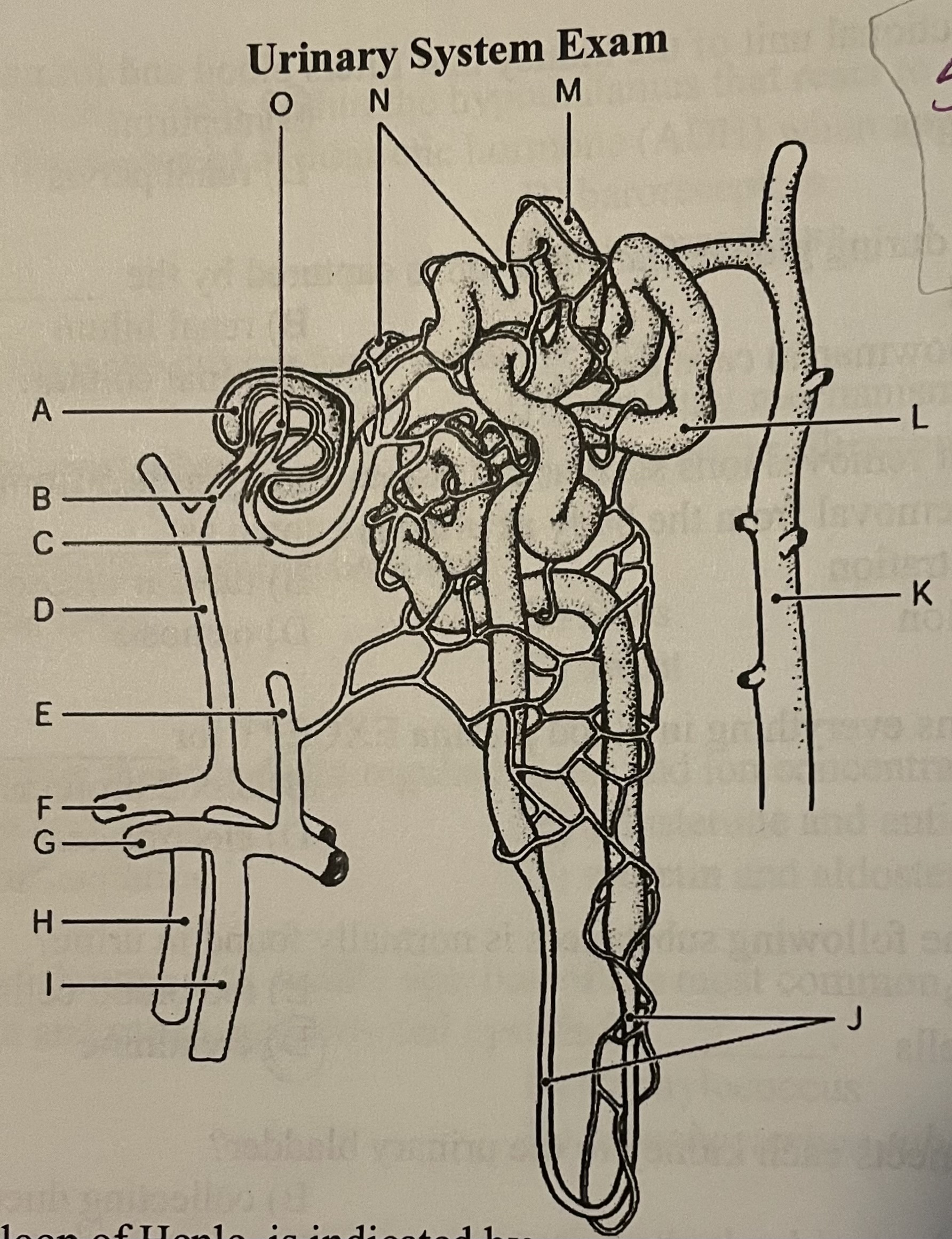
DIAGRAM The glomerular capsule (Bowman’s capsule) is indicated by ___
Label A, Label F, Label G, Label I
Label A
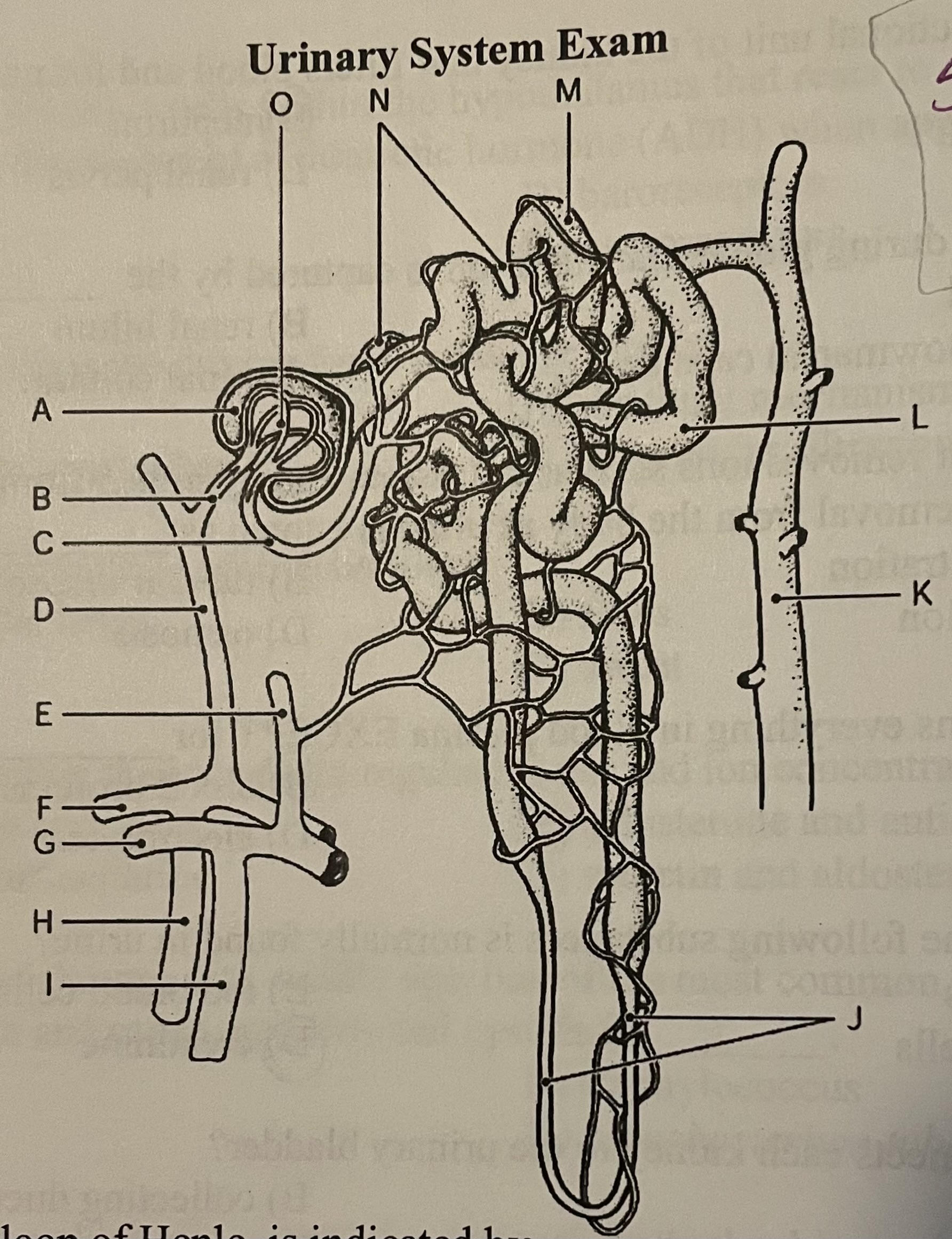
DIAGRAM The proximal convoluted tubule is indicated by ___
Label M, Label N, Label O, Label I
Label M
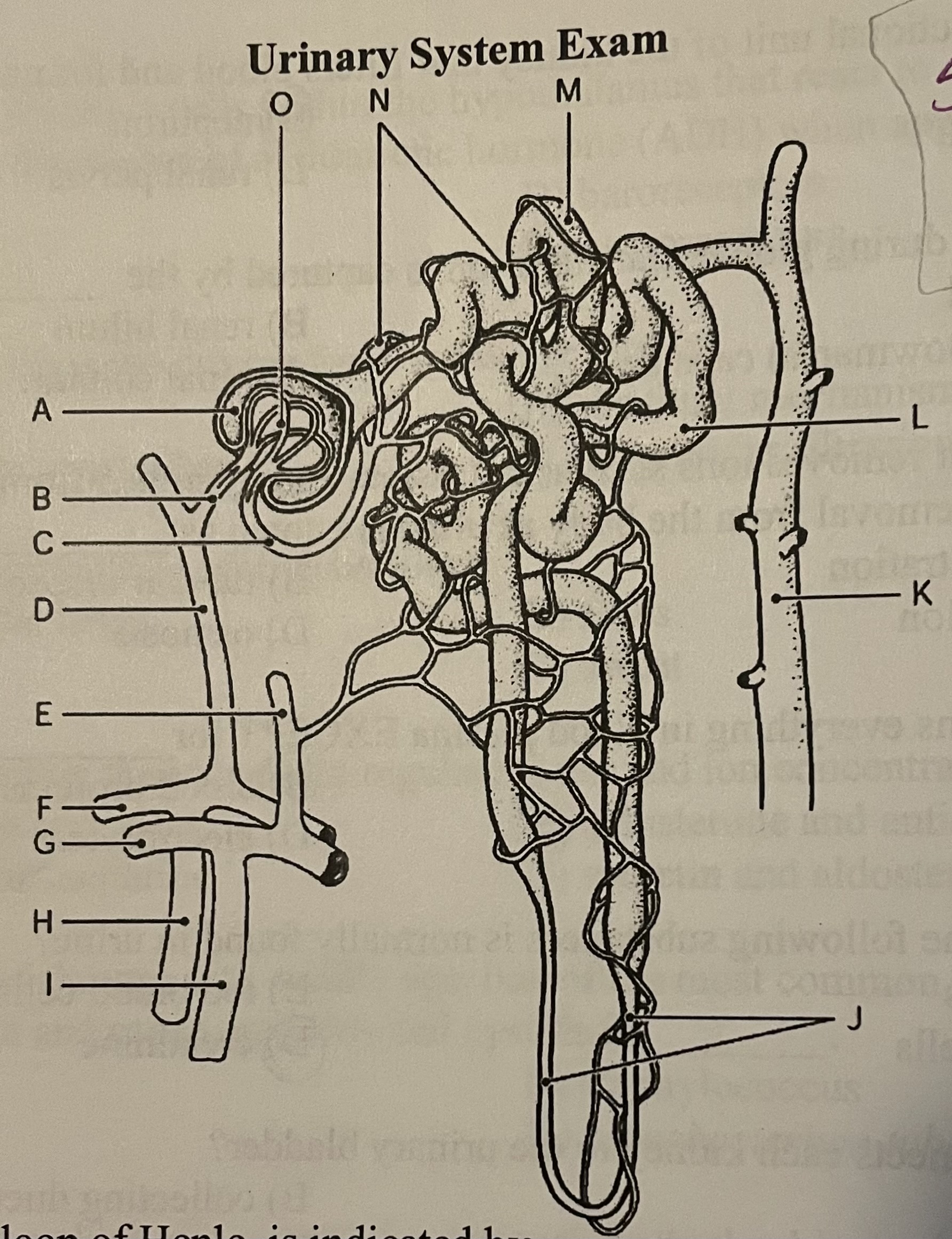
DIAGRAM The efferent arteriole is indicated by ___
Label K, Label B, Label C, Label D
Label D
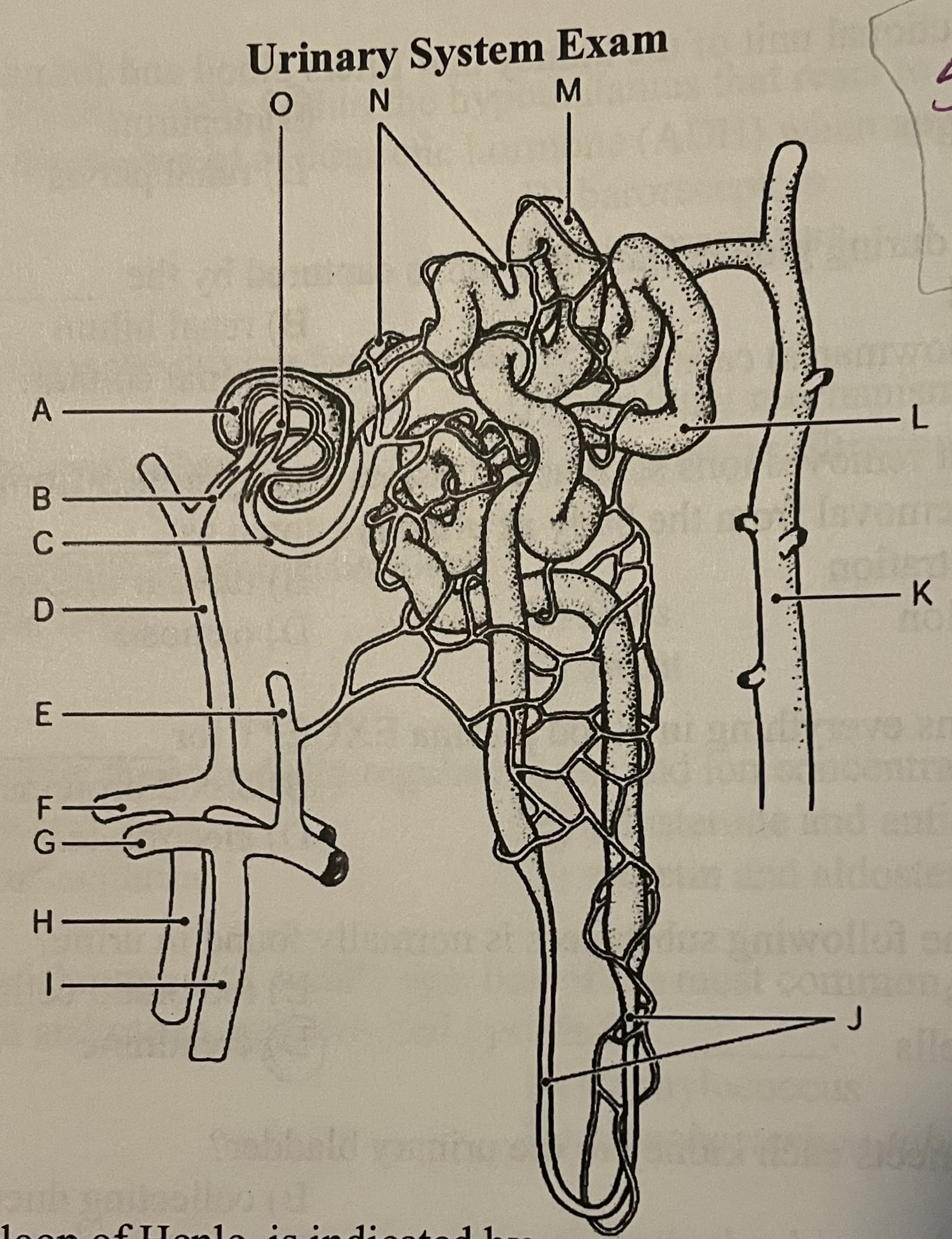
DIAGRAM The glomerulus is indicated by ___
Label F, Label I, Label K, Label O
Label O
What is the functional unit of the kidney that filters blood and forms urine?
glomerulus, nephron, renal pyramid, or renal pelvis
nephron
Filtrate formed during glomerular filtration is captured by the ____
renal pyramid, renal hilum, glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule, or renal column
glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule
The process that removes ions such as potassium and hydrogen from the blood and places them into the nephron for removal from the body as urine is known as _____
glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion, osmosis
glomerular filtration
Filtrate contains everything in blood plasma EXCEPT for ____
water, blood proteins, ions, or electrolytes
blood proteins
Which one of the following substances is normally found in urine?
blood proteins, red blood cells, white blood cells, or creatinine
creatinine
What tube connects each kidney to the urinary bladder?
urethra, collecting duct, ureter, or renal tubule
ureter
The urinary bladder is able to expand as urine accumulates within it due to the presence of a specialized mucosa called ______
simple squamous epithelium, transitional epithelium, stratified squamous epithelium, or pseudostratified epithelium
transtional epithelium
As the bladder fills with urine, what is responsible for transmitting impulses to the spinal cord?
stretch receptors, osmoreceptors, chemoreceptors, or nephrons
stretch receptors
Micturition can be delayed because…
A. osmoreceptors delay transmission
B. the external sphincter is made of smooth muscle
C. the hypothalamus delays transmission
D. the external sphincter is made of skeletal muscle
D. the external sphincter is made of skeletal muscle
What is the name of the involuntary sphincter that keeps the urethra closed when urine is not being passed?
external urethral sphincter, internal anal sphincter, internal urethral sphincter, or ileocecal sphincter
internal urethral sphincter
In males, the urethra is part of both the urinary system and ____
endocrine system, digestive system, Reproductive system, or respiratory system
reproductive system
What are the highly sensitive cells within the hypothalamus that react to changes in blood composition and cause the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) when appropriate?
thermoreceptors, baroreceptors, mechanoreceptors, or osmoreceptors
osmoreceptors
Which of the following is the driving force for water intake?
metabolism, the thirst mechanism, the renin-angtiotensin mechanism, or glomerular filtration
the thirst mechanism
What is the most common route for water loss?
water loss through the lungs, feces, urine, or sweat
urine
The hormones that act on the kidneys to regulate water and ion concentrations in urine are
A. antidiuretic hormone and renin
B. aldosterone and antidiuretic hormone
C. ephinephrine and norephinephrine
D. secretin and aldosterone
aldosterone and antidiuretic hormone
Match the description with a process:
Water and solutes pass from the blood into the glomerular capsule part of the renal tubule
A. tubular reabsorption
B. glomerular filtration
C. tubular secretion
B. glomerular filtration
Match the description with a process:
Water, glucose, amino acids, and needed ions are moved from the filtrate back into the blood
A. tubular reabsorption
B. glomerular filtration
C. tubular secretion
A. tubular reabsorption
Match the description with a process:
Substances such as potassium, urea, and creatinine are moved from the blood of the peritubular capillaries into the filtrate to be eliminated in urine
A. tubular reabsorption
B. glomerular filtration
C. tubular secretion
C. tubular secretion
Match the description with a process:
As long as blood pressure is normal, filtrate will be formed
A. tubular reabsorption
B. glomerular filtration
C. tubular secretion
B. glomerular filtration
Which formed element is the most abundant in blood?
erythrocyte, eosinophil, platelet, or basophil
erythrocyte
What is necessary for the transport of oxygen by an erythrocyte?
albumin, hemoglobin, granules, or mitochondria
hemoglobin
Erythrocytes __________
A. possess nuclei and cytoplasm is granules
B. lack a nucleus and most organelles
C. are the least common of all formed elements
D. travel through the walls of vessels
B. lack a nucleus and most organelles
Blood is composed of which of the following:
I. Formed elements
II. Hematopoiesis
III. Fluid matrix (plasma)
IV. Marrow
I and III (formed elements and fluid matrix)
White blood cells different from red blood cells because they contain _____
A. biconcave shape
B. a nucleus and most organelles
C. the ability to transport both oxygen and carbon dioxide
D. the iron-containing molecule called hemoglobin
B. a nucleus and most organelles
Monocytes
A. kill parasitic worms
B. contain heparin
C. fight chronic infection
D. are activated when you have a cold
C. fight chronic infection
Which type of leukocyte releases heparin at sites of inflammation?
eosinophils, basophils, neutrophils, or lymphocytes
basophils
Which type of leukocyte kills parasitic worms by deluging them with digestive enzymes?
monocytes, lymphocyte, basophil, or eosinophil
eosinophil
The process by which bleeding is stopped is called ______
Hematopoiesis, erythropoiesis, homeostasis, or hemostasis
hemostasis
What hormone controls the rate of erythrocyte production?
erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, colony stimulating factors, or interleukins
erythropietin
When antibodies bind to antigens on foreign blood types, clumping or ____ occurs.
anemia, hematopoiesis, agglutination, or alkalosis
agglutination
The ABO blood typing is based on the presence of absence of ______
A. A, B, and O antigens on the rbc
B. A, B and O antigens in the plasma
C. A and B antigens on the rbc
D. A and B antigens in the plasma
C. A and B antigens on the rbc
Where does hematopoiesis occur to produce new red blood cells?
yellow bone marrow, articular cartilage, red bone marrow, or epiphyseal line
red bone marrow
Molly has blood type A and her daughter has blood type B. Why can’t Molly donate blood to her daughter?
A. The antigens on the mother’s rbc will attack the antigens on Molly’s rbc
B. Blood type B contains anti-A antibodies, which will agglutinate with Molly’s type A blood.
C. Blood transfusions cannot be performed among relatives.
D. Only fathers can donate blood to their daughters.
B. Blood type B contains anti-A antibodies, which will agglutinate with Molly’s type A blood.
Which one of the following represents the proper sequence of hemostasis?
A. platelet plug formation, coagulation, vascular spasm
B. vascular spasm, coagulation, platelet plug formation
C. coagulation, vascular spasm, platelet plug formation
D. vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, coagulation
D. vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, coagulation
What is the muscular layer of the heart wall?
epicardium, myocardium, fibrous pericardium, or endocardium
myocardium
The heart is located in the ____
thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, cardiac cavity, or mitral cavity
thoracic cavity
The two superior reciving chambers of the heart are known as the ____, while the two inferior discharging chambers of the heart are known as the ____.
A. ventricles; atria
B. atria; ventricles
C. arteries; veins
D. veins;arteries
atria; ventricles
Which valve is located between the right atrium and right ventricle?
pulmonary semilunar valve, tricuspid valve, bicuspid valve, or aortic semilunar valve
tricuspid valve
Which vessels return oxygenated blood to the left atrium of the heart?
pulmonary arteries, superior vena cava, aorta, or pulmonary veins
pulmonary veins
An incompetent aortic semilunar valve would allow blood to backflow from the ____
A. right ventricle to the right atrium
B. left ventricle to the left atrium
C. aorta to the left ventricle
D. aorta to the left atrium
C. aorta to the left ventricle
The tricuspid valve is located between the ____
A. right atrium and left atrium
B. right atrium and right ventricle
C. left ventricle and pulmonary artery
D. left ventricle and aorta
B. right atrium and right ventricle
Which one of the following blood vessels carries oxygenated blood?
pulmonary vein, inferior vena cava, coronary sinus, or pulmonary artery
pulmonary vein
Blood leaves the left ventricle through an artery known as the ____
pulmonary trunk, aorta, superior vena cava, or coronary sinus
aorta
Oxygenated blood nourishing the myocardium comes from vessels that branch off the aorta called ____
pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, coronary arteries, or venae cavae
coronary arteries
Which valve is closed during heart relaxation to prevent blood from back flowing from the aorta into the heart?
bicuspid valve, tricuspid valve, pulmonary semilunar valve, or aortic semilunar valve
aortic semilunar valve
Which of the following is often called the pacemaker of the heart?
A. Purkinje fibers
B. sinoatrial (SA) node
C. atrioventricular (AV) bundle (bundle of His)
D. atrioventricular (AV) node
B. sinoatrial (SA) node
The sinoatrial (SA) node is located in the ____
aorta, right atrium, left atrium, or right ventricle
right atrium
Which one of the following represents the correct path for transmission of an impulse in the conduction system of the heart?
A. AV node, SA node, AV bundle of His, right and left bundle branches, Purkinje fibers
B. AV node, AV bundle of His, SA node, Purkinje fibers, right and left bundle branches
C. SA node, AV bundle of His, AV node, right and left bundle branches, Purkinje fibers
D. SA node, AV node, AV bundle of His, right and left bundle branches, Purkinje fibers
D. SA node, AV node, AV bundle of His, right and left bundle branches, Purkinje fibers
The first heart sound “lub”, is caused by the closure of the ___ valves.
semilunar, pulmonary, atrioventricular (AV), or aortic
atrioventricular (AV)
What large blood vessels carry blood away from the heart?
arteries, capillaries, veins, or venae cavae
arteries
Arteries are normally depicted as red while veins are colored blue due to he oxygenation of the blood being transported by each type of vessel. The exceptions to this rule are the ___ arteries and veins.
systemic, hepatic, coronary, or pulmonary
pulmonary
Large veins have ____ to prevent the backflow of blood.
tunics, sphincters, valves, or shunts
valves
What is the largest artery in the body?
barchiocephalic artery, pulmonary trunk, aorta, or common carotid artery
aorta
Veins draining the head and arms empty into the ____, which carries blood to the right atrium of the heart.
superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, common iliac vein, or great saphenous vein
superior vena cava
What are the two main subdivisions of the nervous system?
A. central and peripheral
B. somatic and autonomic
C. sensory and motor
D. autonomic and sympathetic
A. central and peripheral
What cells form the myelin sheaths around nerve fibers in the PNS?
satellite cells, Ependymal cells, Schwann cells, or microglial cells
Schwann cells
Which neuroglial cell circulates CSF?
oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, microglia, or ependymal cells
ependymal cells
The part of the neuron that typically conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body is the ___
dendrite, cell body, synaptic cleft, or axon
axon
The gaps between Schwann cells found at regular intervals in peripheral system neurons are called ____
synaptic clefts, axon terminals, nodes of Ranvier, or myelin sheaths
node of Ranvier