IB Chemistry Topic 2-Atomic Structure
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Position of protons in atom
inside of the nucleus
Position of neutrons in the atom
inside of the nucleus
Position of the electrons in the atom
spinning around outside the nucleus
Relative mass of proton
1 amu
Relative mass of neutron
1 amu
Relative mass of electron
1/1836 amu
What is the atomic number
The atomic number is the number of protons in the atom. This is given the symbol Z
What is the mass number
The mass number is the total mass of an atom, or; the sum of its protons and neutrons. It is given the symbol A.
isotopes
atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
isotope symbol notation
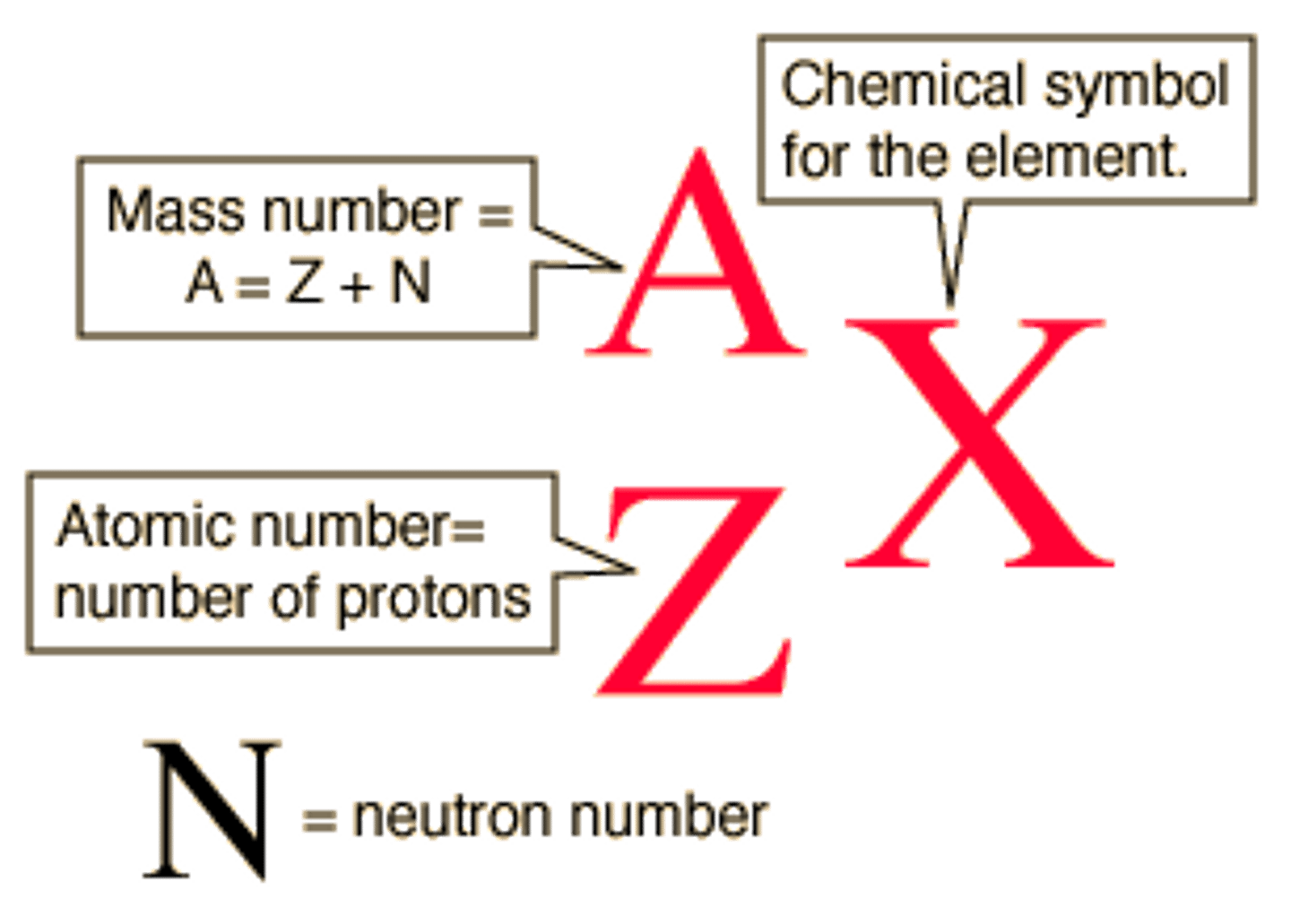
chemical properties of isotopes
the chemical properties of all isotopes are the same as their base elements because chemical properties are based on the outer electrons and isotopes of an element have the same number of electrons
physical properties of electrons
there are small differences in the physical properties of isotopes, allowing them to be separated apart from each other, such as with uranium (different weights of the isotopes is used to separate)
Uses of isotopes
Breaking down of many isotopes emits radiation. This radiation can be used for sterilization, dating of artifacts, nuclear power and many other things
use of mass spectrometer
a tool used to determine the masses of individual isotopes
mass spectrometer diagram STUDY THIS
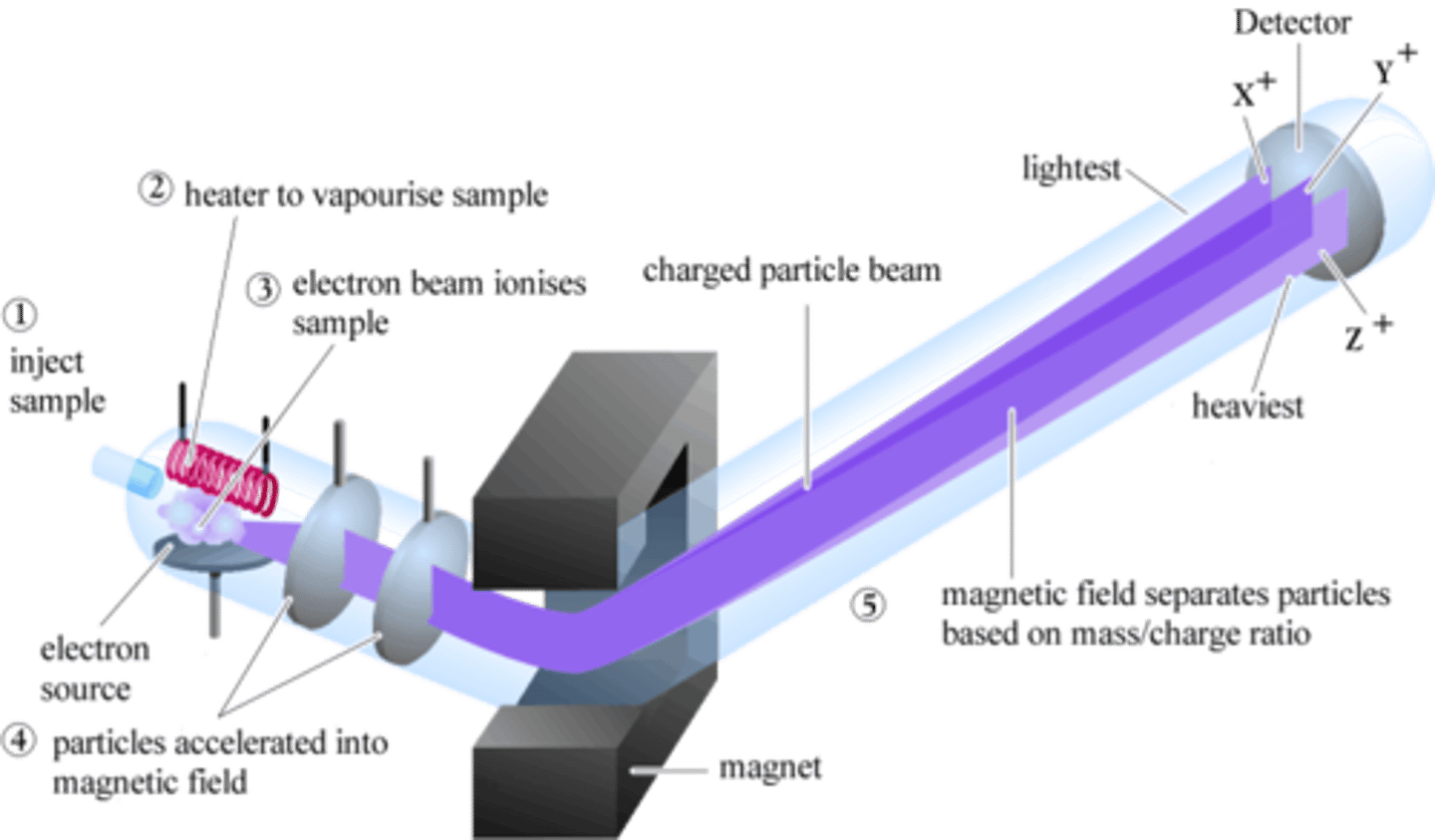
Mass spectrometer step 1: Injection
sample is injected into the ionization chamber
Mass spectrometer step 2: vaporization
It is vaporised and the gas streams into the ionisation chamber
Mass spectrometer step 3: ionization
The electron beam knocks an electron off the vaporised particles makong positive ions
Mass spectrometer step 4: acceleration
The positive ions are attracted towards the accelerating plates
Mass spectrometer step 5: deflection
The magnetic field deflects the lighter ions more than the heavy ions
Mass spectrometer step 6: detection
As the magnetic field is varied by the controller, ions with different masses are detected - these are recorded on the mass spectrum.
Calculating relative abundance of an isotope with a mass spectrometer
Add all the results of the test and then divide one of the results by the sum of all of them to find that isotopes relative abundance
Calculating relative atomic mass of an element
relative atomic mass = (isotope 1's mass × isotope 1's relative abundance) + (isotope 2's mass × isotope 2's relative abundance) and so on then divide by 100
Why do different elements burn different colors
because when the gaseous ions are given energy they emit different types of electromagnetic radiation
velocity of travel for electromagnetic waves
c (meters second⁻¹) = λ (meters) × f (second)⁻¹
where c is the velocity of travel, λ is the wavelength and f is the frequency
The energy of electromagnetic radiotion
E (joules) = h (Joules seconds) × f ( s⁻¹)
where E is energy, h is Planck's constant and f is frequency
Planck's constant value
6.63 x 10⁻³⁴ (J s)
electromagnetic spectrum
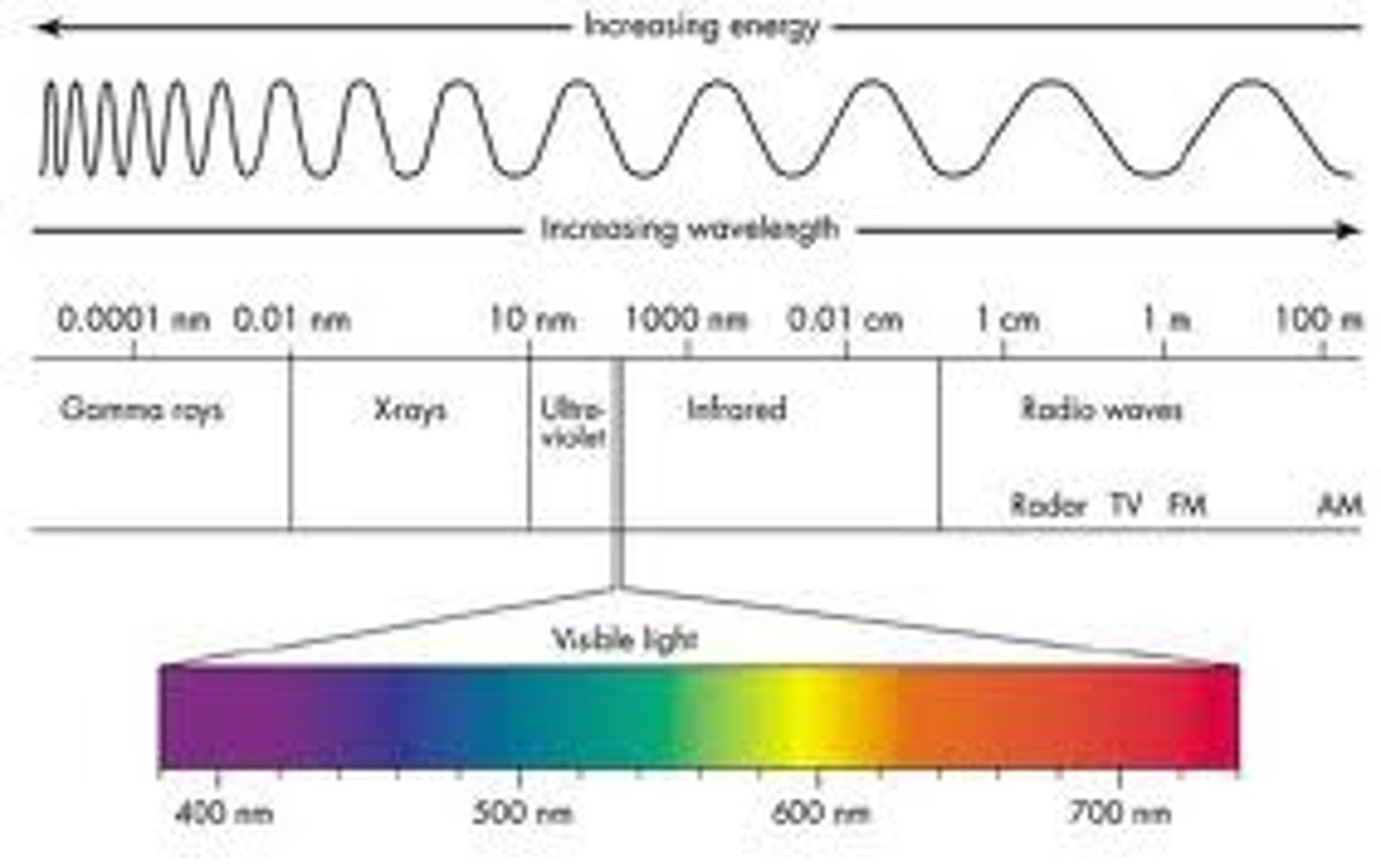
Continuous spectrum
Results when gas pressure is higher and the atoms collide a lot so all the lines are smeared together
Emission spectrum
produced by thin gases in which the atoms do not experience many collisions
absorption spectrum
An absorption spectrum occurs when light passes through a cold, dilute gas and atoms in the gas absorb at characteristic frequencies
What does it mean when an electron relaxes?
It falls back to its previous energy shell
What does it mean when an electron is promoted
Due to an increase in energy it jumps up to a higher energy shell (known as being in its excited state)
Definition of electron transitions
the movement of electrons between the shells
Explain how energy is created during electron transitions
when electrons jump between shells they releases energy if they go down in shells (in the form of a quantum) The farther down they drop the more energy they release. This amount of energy directly relates to lines on an emission spectra