Honors Bio Unit 8 Evolution
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Descent with modification
All of life is connected by common ancestry
Why is natural selection considered a theory?
It is broader than a hypothesis, generates new hypotheses, and is supported by a large body of evidence
Allopatric speciation
New species form due to geographic barriers splitting populations
Sympatric speciation
When a new species arises within the same geographic area as its parent species
Fossils
The remains of past-living organisms, used to document changes between past and present
Evolutionary tree
- Represents patterns of a descent
- Homologous structures can be used to determine the branching sequence
Example of artificial selection
Dog breeding
The three key points about evolution by natural selection
- Populations evolve, not individuals.
- Evolution has no goal.
- Natural selection depends on time and place.
Stabilizing selection
Favors intermediate phenotypes in natural selection
Directional selection
Favors one extreme phenotype (causes allele frequency to shift in one direction)
Disruptive selection
Favors both extremes in natural selection
Sexual selection
A form of natural selection in which individuals with certain characteristics are more likely to obtain mates than others
Microevolution
Small genetic changes in a population over generations
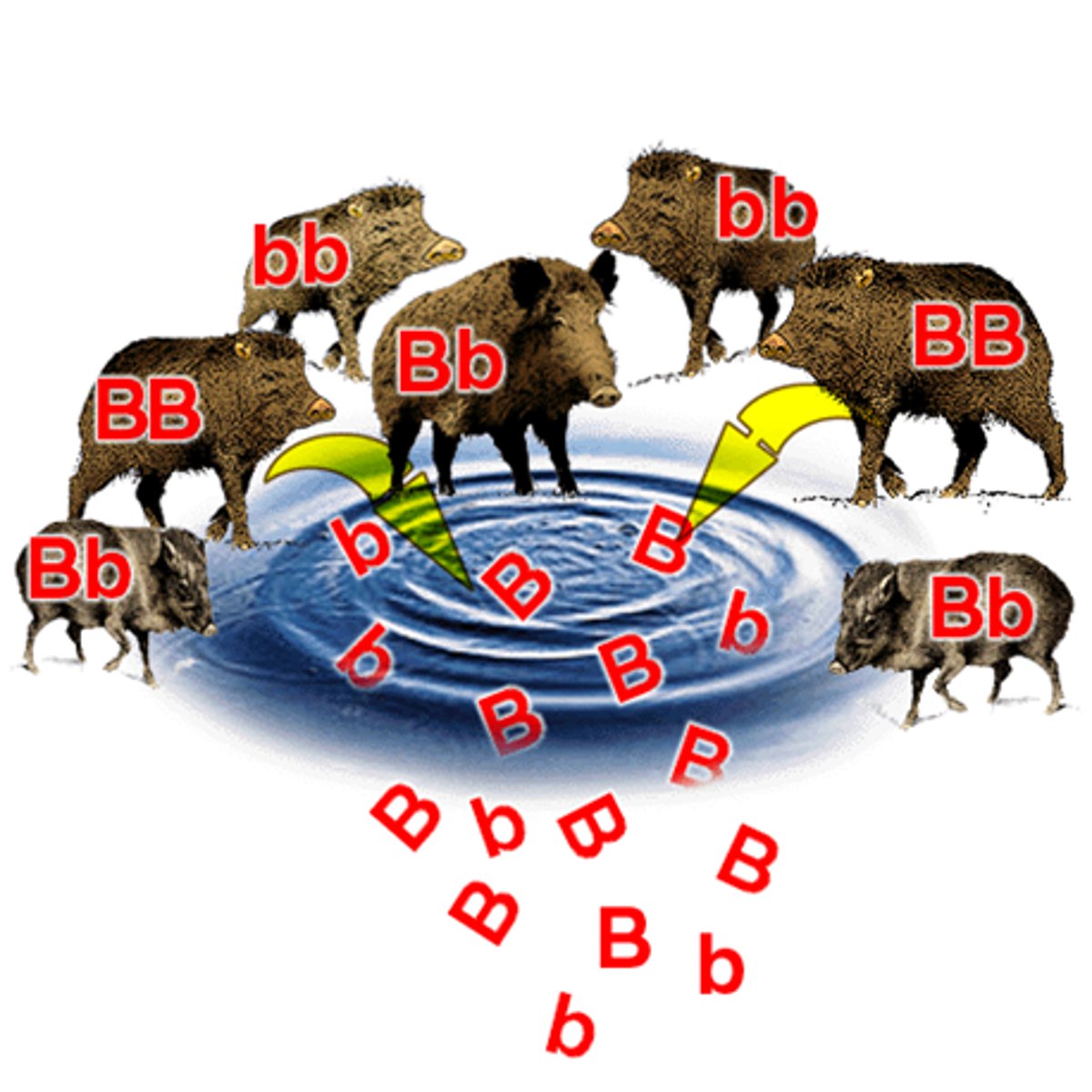
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
States that allele and genotype frequencies will remain constant if:
- A population is large
- Mating is random
- There is no mutation, gene flow, or natural selection
Gene pool
A collection of every type of allele in a population
Relative fitness
The contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation
How fossils, homologous structures, and vestigial structures provide evidence for evolution
Shows the gradual change of species over time, shared ancestry between different organisms, and the adaptation of traits to new environments
Prezygotic barriers
Prevents fertilization
- Example: Different mating behaviors or times
Postzygotic barriers
Prevents hybrids from being fertile (being able to reproduce)
- Example: mules
Speciation
When one species splits into two or more, increasing diversity
Intrasexual selection vs Intersexual selection
Intra - Competition between individuals of the same sex for mates
Inter - Individuals of one sex choose their mate based on their traits
Polyploidy
Organism has more than 2 complete sets of chromosomes
Biological species concept
The ability of a species to interbreed and produce fertile offspring
Ecological species concept
Defines a species by ecological niches (e.g., fish in different lake zones)
Hybrid zones
Areas where closely related species interbreed and produce hybrids
Adaptive radiation
The evolution of diverse species from a common ancestor
- Driven by isolation, speciation, and recolonization on island chains
Punctuated equilibrium
The hypothesis that evolutionary development is marked by isolated episodes of rapid speciation between long periods of little or no change
Role of reproductive barriers
Serve to isolate the gene pools of species and prevent interbreeding
Habitat differentiation
Populations adapt to different resources (e.g., insects on different plants)
How natural selection, mutation, and genetic drift contribute to microevolution
By altering allele frequencies in a population over time
Macroevolution
Large-scale changes leading to major groups or extinctions (e.g., birds from dinosaurs)
Radiometric dating
Measures the radioactive decay of isotopes
- Can be used to date rocks and fossils, building Earth's timeline
Three domains of life
(Classified by cell type and complexity)
- Prokarya
- Archaea
- Eukarya
Fossil record
Tracks evolutionary history through the sequence in which fossils appear in the rocks
Geologic record
Divides time into eras and periods marked by major events
Mass extinctions
Permian and cretaceous are the most popular; wiped out species and allowed for evolution
Pangea
Supercontinent that affected species distribution
Homoeotic genes
Determine basic features and body plans (e.g., where a pair of legs develop on a fruit fly)
Convergent evolution
Unrelated species develop similar traits in similar environments (e.g., bird and bat wings)
Horizontal gene transfers
Genes transfer between species
- Resulted in the origin of mitochondria
Abiogenesis
The origin of life from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds.
Panspermia
The hypothesis that life exists throughout the universe and is distributed by celestial bodies.
Oxygen Revolution
A period when cyanobacteria produced oxygen, allowing aerobic respiration to occur.
Anaerobic Respiration
A type of respiration that occurs without free oxygen.
Autotrophs
Organisms that produce their own food, typically via photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
Gene Flow
The transfer of genetic material between populations, which can affect allele frequencies.
Natural Selection
The process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
Gradualism
The idea that changes on Earth occur gradually over long periods of time.
Catastrophism
The theory that the Earth's history has been marked by catastrophic events that cause widespread extinctions.
Homologous Structures
Body parts that share a common embryonic origin but may have different functions.
Analogous Structures
Structures that serve similar functions in different species but do not share a common ancestry.
Vestigial Organs
Body parts that have lost their original function through evolution.
Evolutionary Theory
A well-supported explanation of how species change over time through natural selection and other mechanisms.
Transitional Fossils
Fossils that exhibit traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group.
Adaptation
A trait that increases the chances of survival and reproduction of an organism.
Divergent Evolution
When two or more related species become more dissimilar over time, often due to differing environmental pressures.
Cultural Evolution
The transmission of knowledge, behaviors, and norms across generations.
Cause of Evolution
Change in environment
Who is Lamarck?
French naturalist best known for his early theory of evolution which proposed the idea of inheritance of acquired characteristics
Who is Charles Darwin?
English naturalist best known for his contributions to the theory of evolution, particularly through the concept of natural selection.
Structural Adaptations
Physical features of an organism that enhance its survival and reproduction in its environment.
Behavioral Adaptations
Actions or behaviors that organisms perform to survive in their environments.
What are physiological adaptations?
Internal body processes that enhance an organism's ability to survive in its environment.
Bottleneck effect
A sharp reduction in the size of a population due to environmental events or human activities, leading to a loss of genetic diversity.
Founder Effect
A genetic drift that occurs when a small group of individuals establishes a new population, leading to reduced genetic diversity and different allele frequencies compared to the original population.
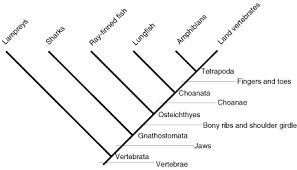
Cladogram
Diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among various biological species based on shared characteristics.
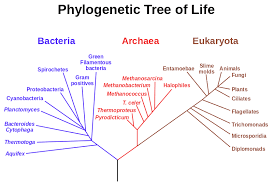
Phylogenetic Tree
Branching diagram that represents the evolutionary history of a group of organisms based on genetics, illustrating how they are related through common ancestry.
Paraphyly
Group of organisms that includes a common ancestor but does not include all of its descendants.
Polyphyly
Grouping of organisms that do not share a recent common ancestor, often including members from different lineages.
Monophyly
Group of organisms that includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants, representing a complete branch on the tree of life.