Bio 132 - Nervous System and Action Potentials: Learning Objectives
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
cerebrum
the largest part of the brain, responsible for a wide range of functions including thought, language, memory, and motor control
frontal lobe
planning, problem-solving, movement, emotional regulation, and personality
occipital lobe
processes visual information and perception of color and motion
temporal lobe
processes auditory information, visual memory, emotion, and language comprehension
parietal lobe
processes sensory information, spatial awareness, and the five senses
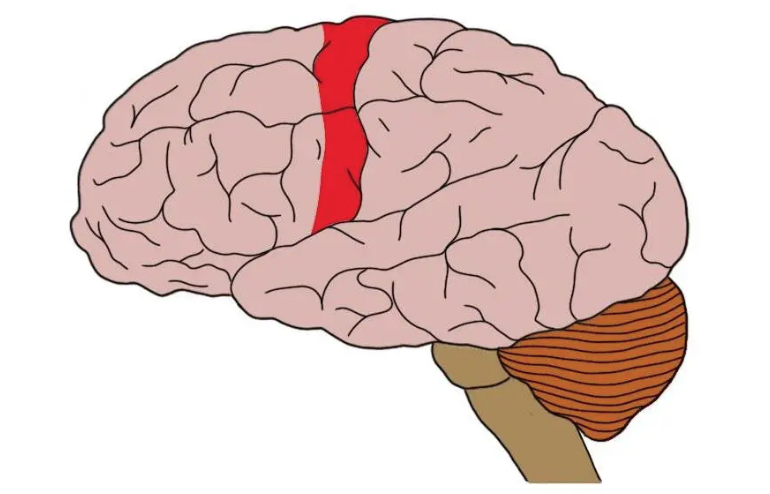
primary somatosensory cortex
processing sensory information from the body, including touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception
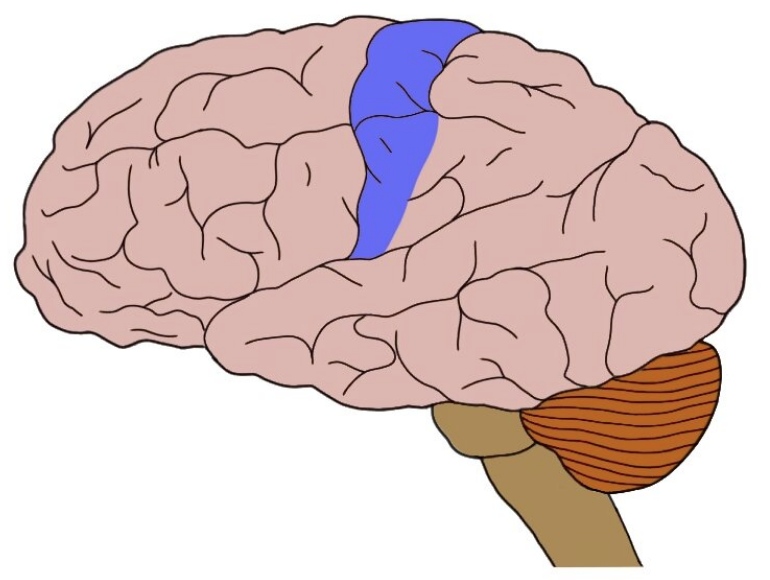
primary motor cortex
responsible for initiating voluntary movements, located in the posterior portion of the frontal lobe
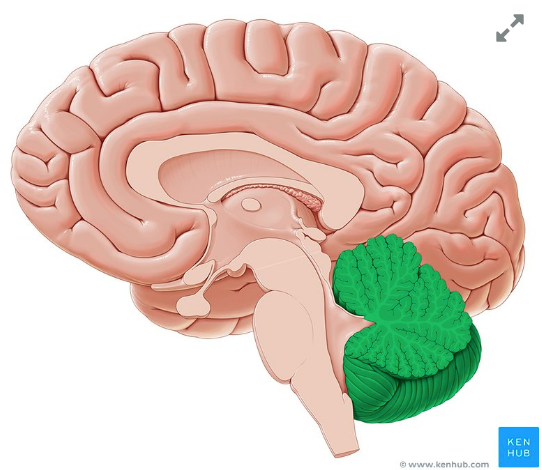
cerebellum
coordinates and regulates muscular activity
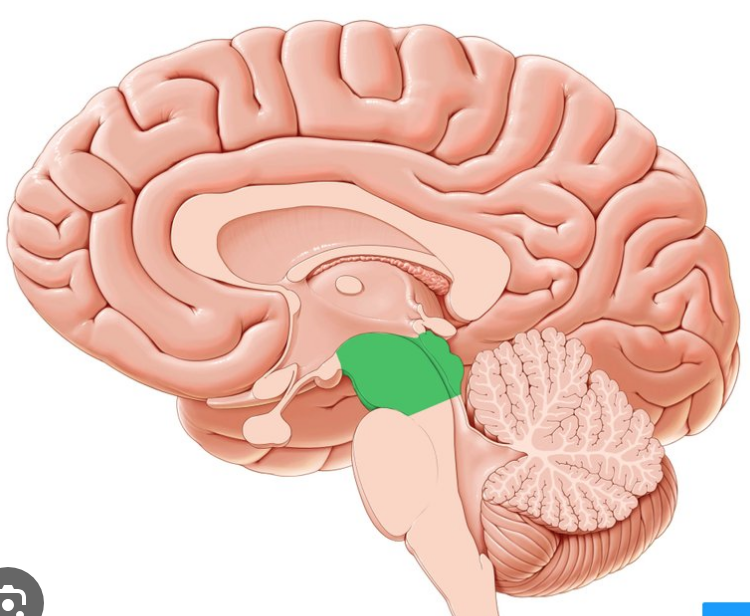
midbrain
motor movement, eye movement, and processes visual and auditory information
pons
respiratory control, balance and taste, and influences sleep cycles and facial movement and sensations
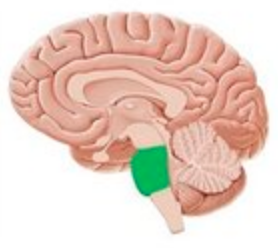
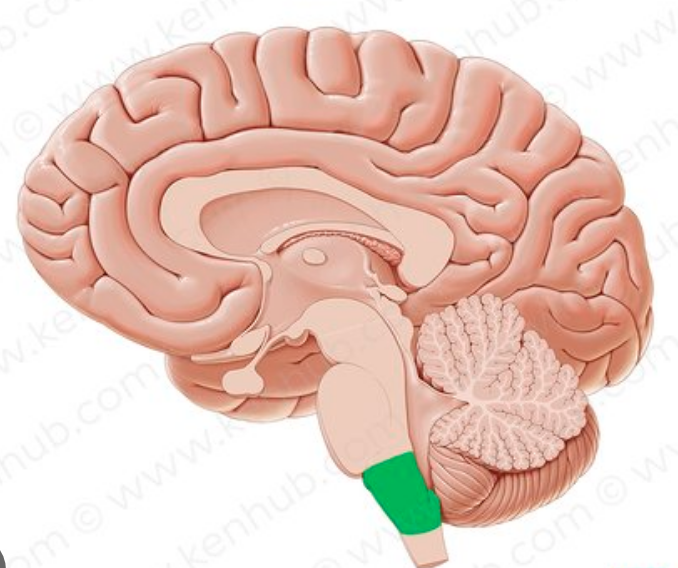
medulla oblongata
connects the pons and spinal cord and controls essential processes like breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and reflexes like swallowing and coughing
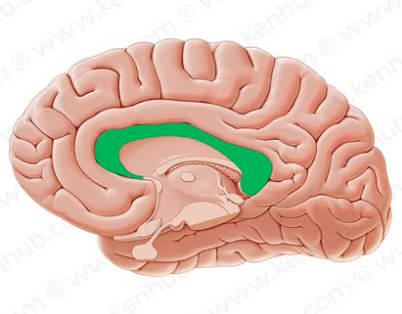
corpus collosum
language, memory, and sensory information processing
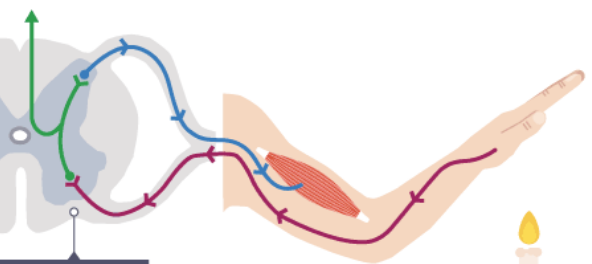
reflex arc
neural pathway that controls reflexes, which are rapid, automatic, and involuntary responses to stimuli
autonomic reflex
control blood pressure, breathing, ensure tissue oxygenation
somatic reflex
responsible for involuntary, automatic responses controlled by the somatic nervous system
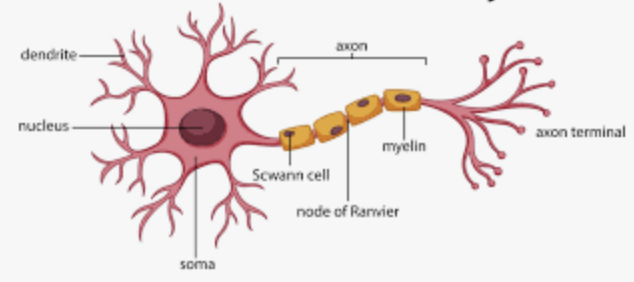
parts of a nueron
the cell body (soma), dendrites, and the axon
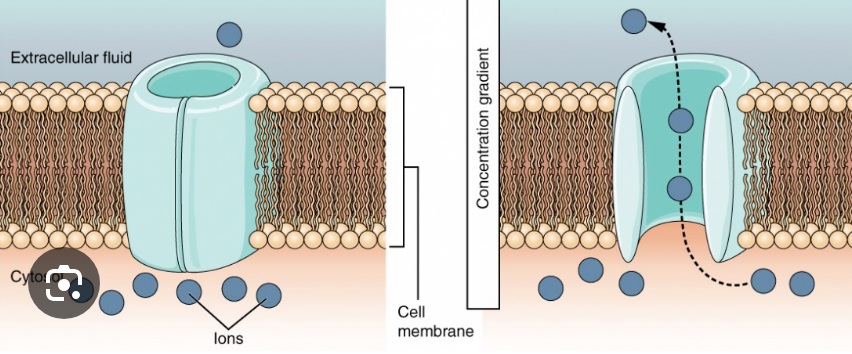
membrane resting potential
uneven distribution of ions between the inside and the outside of the cell
leaking channels
ion channel that are always open, allowing ions to flow across the cell membrane continuously without the need for external stimuli
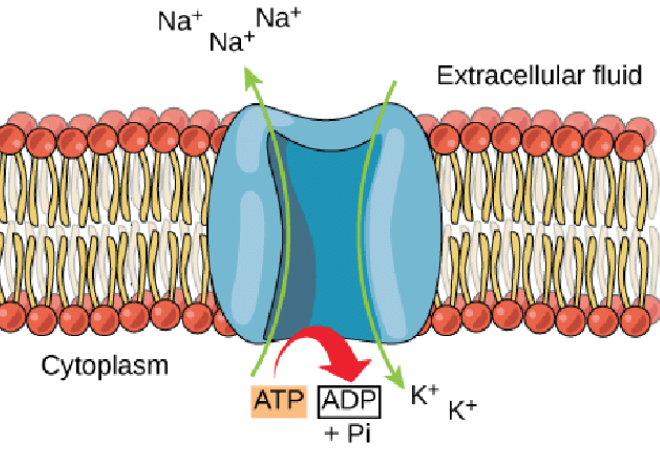
sodium-potassium pumps
moves three sodium ions out of the cell and two potassium ions into the cell, both against their concentration gradients, using energy from ATP
action potential
rapid change in electrical potential across a cell membrane, specifically the nerve cells (neurons), that allows for the transmission of electrical signals
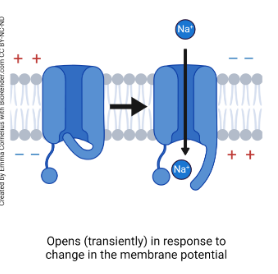
voltage gated ion channels
enable the passage of selected inorganic ions across cell membranes that open and close in response to changes in transmembrane voltage, and signal neurons
how is an action potential propagated along an axon
depolarization and repolarization, facilitated by voltage-gated sodium channels and potassium channels
changes in membrane charges as an action potential progresses
membrane is polarized, with a negative charge on the inside relative to the outside, then depolarization, the membrane potential becomes less negative (or even positive) due to an influx of positive ions followed by a repolarization phase where the membrane potential returns to its resting state as positive ions flow out
saltatory conduction
nerve impulses move down a myelinated axon with excitation occurring only at nodes of Ranvier
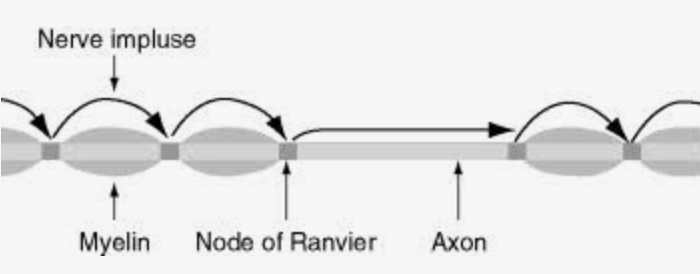
Schwann cells
glial cells that form the myelin sheath on axons outside the brain
Oligodendritic cells
type of glial cell in the brain that form the myelin sheath, while dendritic cells are a type of immune cell
Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another
an action potential triggers the presynaptic neuron to release neurotransmitters
excitatory postsynaptic potentials
a change in membrane potential of a postsynaptic cell that makes it more likely to fire an action potential
inhibitory postsynaptic potentials
decreases the likelihood of a neuron firing, effectively inhibiting the generation of an action potential
postsynaptic membrane potential
the change in electrical charge across the membrane of a neuron's postsynaptic terminal
spatial summation of postsynaptic potentials
multiple presynaptic neurons release neurotransmitters simultaneously, leading to a combined excitatory postsynaptic potential that may or may not reach the threshold for triggering an action potential
temporal summation of postsynaptic potentials
multiple postsynaptic potentials summate to produce a larger overall response