Photosynthesis
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Autotrophs
uses inorganic substances such as water and carbon dioxide (CO2) to produce organic compound
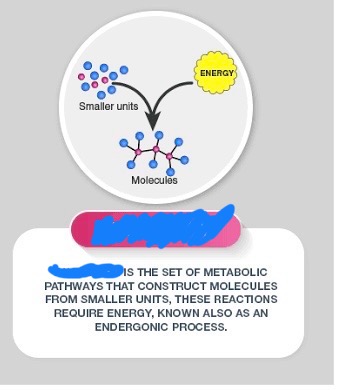
anabolic
In a way, photosynthesis is the reverse of cellular respiration and is considered an _______ process, where complex and larger compounds are made from simpler building blocks.
Heterotrophs
organisms that obtain carbon by consuming pre-existing organic molecules
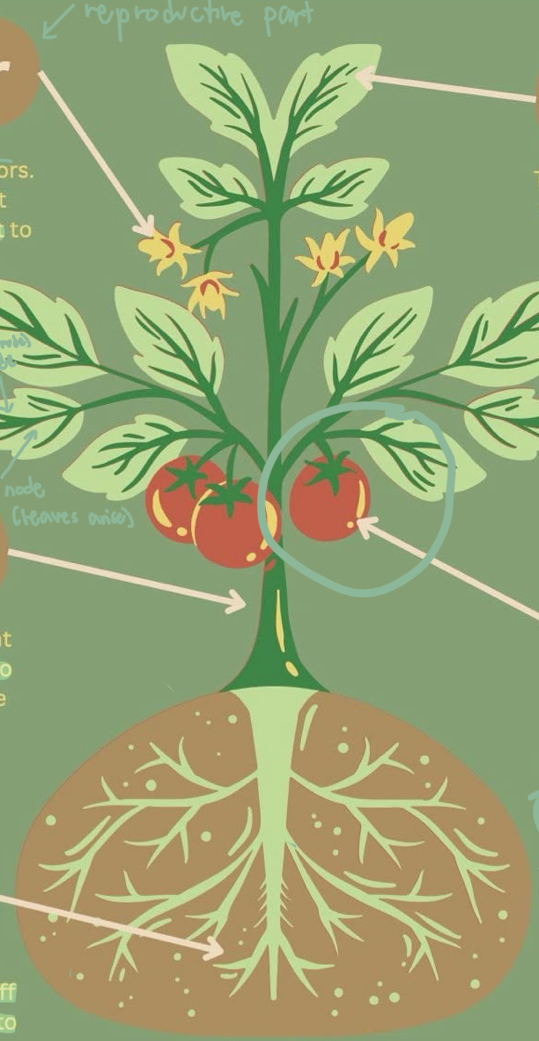
Parts of Plants - Roots
essential underground parts of a plant; root system

Parts of Plants - Stem
above ground, supports shoot system, bears leaves, flowers, fruits; young = green, old = brown bark; space between nodes = internode.
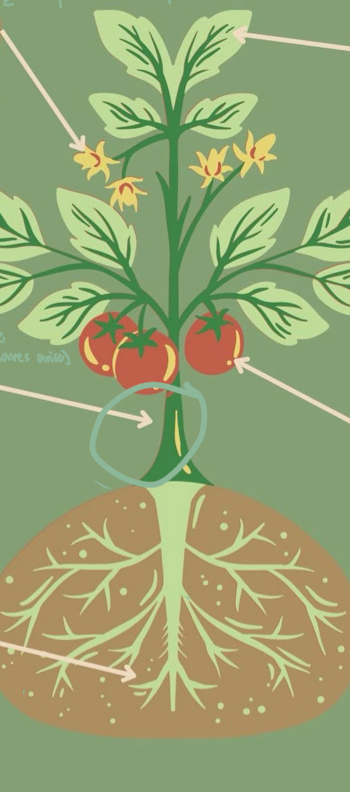
Parts of Plants - Leaves
They contain chlorophyll that helps the plants to prepare their food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. A _____ consists of three main parts: petiole, leaf base, and lamina.
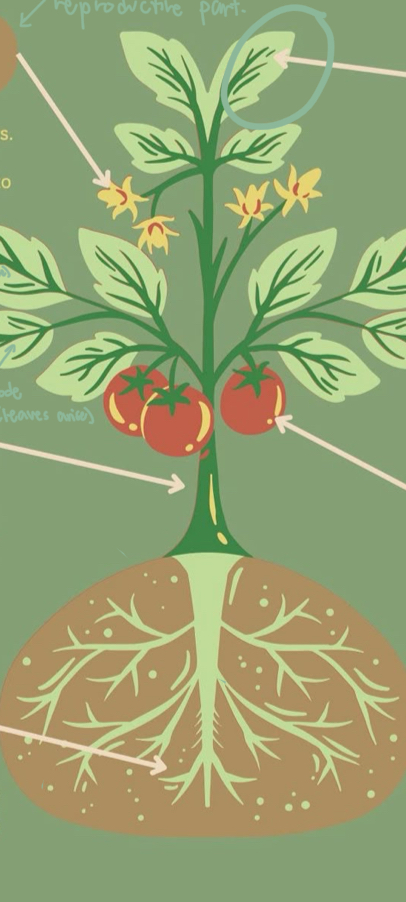

Parts of Plants - Flowers
They are the reproductive part of a plant.
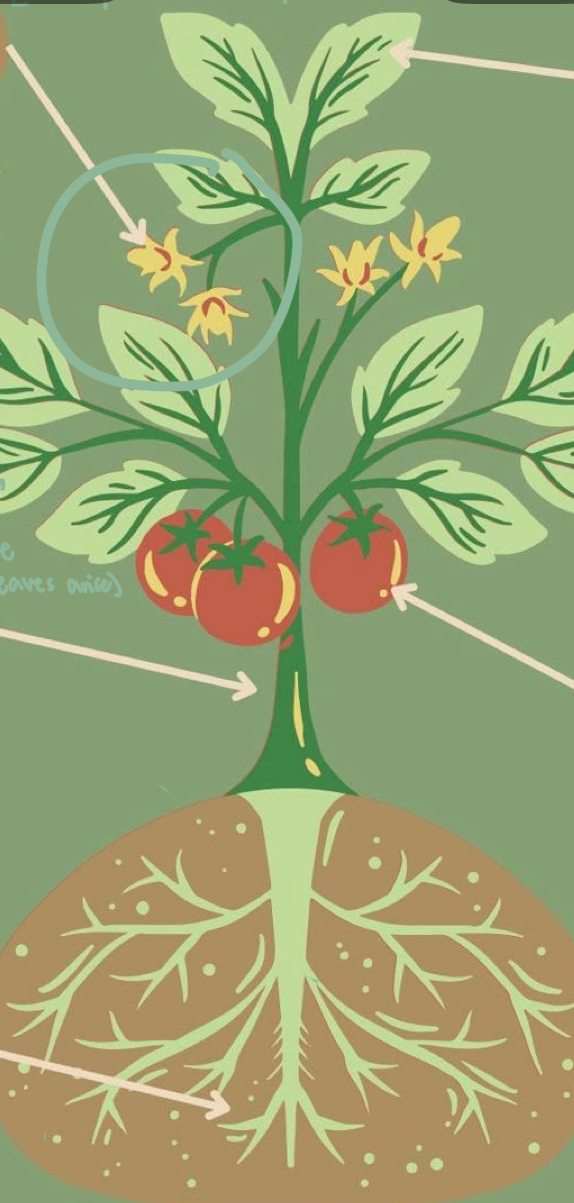
Parts of Plants - Fruits
It is an ovary that develops after fertilization. Some _____ are developed without fertilization and are known as parthenocarpy.
Parts of flower - petals
It is a colorful part of a flower that attracts insects and birds.
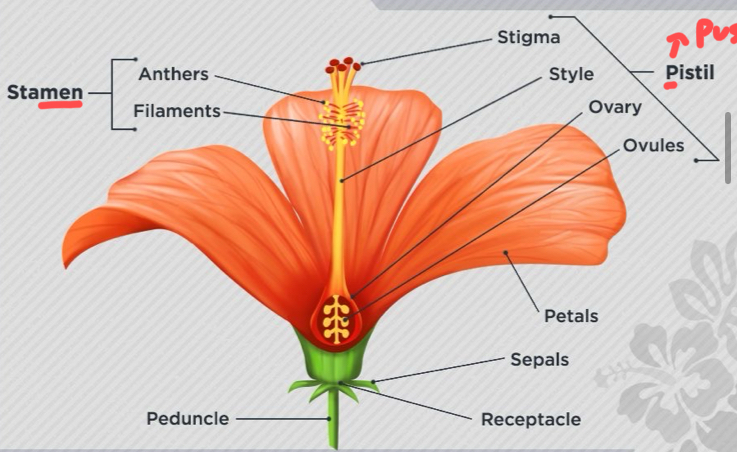
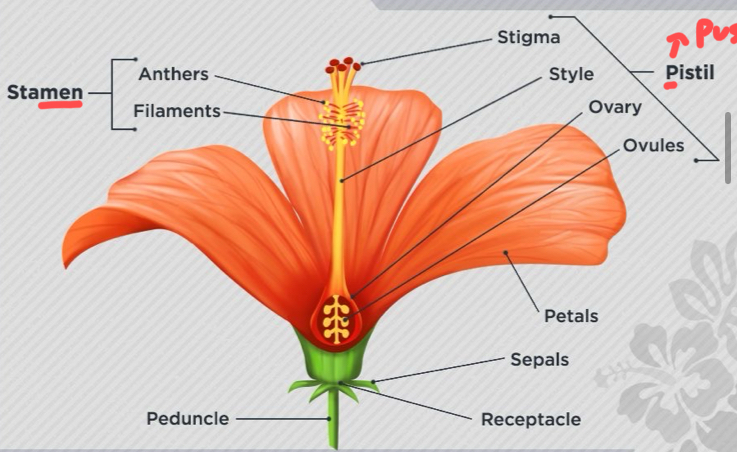
Parts of flowers - sepals
are green leafy parts present under petals and protect the flower buds from damage.
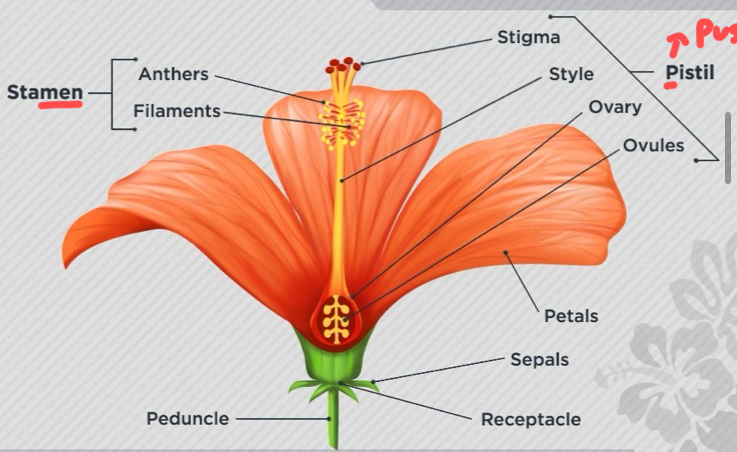
Parts of flower - stamen
This is the male part of the flower consisting of anther (makes pollen) and filament (holds UP anther).
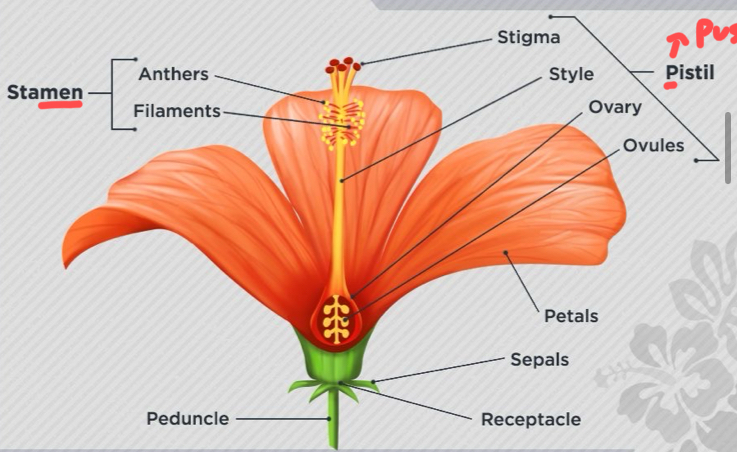
Parts of flower - pistil > pussy
This is the female part of the flower consisting of stigma (sticky) style (tube connected) and ovary (ovules = after fertilization).
Function of leaves - photosynthesis
Green leaves prepare food for plants by using water (6H20) and carbon dioxide (6CO2) in the presence of sunlight. This process is called __________. glucose + oxygen = energy
Function of leaves - transpiration
Other than photosynthesis, leaves play a crucial role in the removal of excess water from plants through tiny pores called stomata. This is the process of __________.
Function of leaves - reproduction
Leaves of some plants help in _______. E.g., leaves of Bryophyllum give rise to a new Bryophyllum plant.
electromagnetic radiation.
Sunlight reaching Earth consists of ultraviolet radiation, visible light, and infrared radiation, all of which are just a small part of a continuous spectrum of _________ ________
Photons
______ with the shortest wavelengths carry the most energy. = more kinetic energy per photon.
Chlorophyll a
is the main green pigment in plants that captures sunlight energy for photosynthesis. It absorbs mostly violet-blue and red light and is found in all photosynthetic plants and algae. Basically, it’s the boss that kicks off the whole energy-making process.
Chlorophyll b
is the accessory pigment that helps plants catch more light by absorbing blue and orange wavelengths. It’s mostly found in green plants and green algae and works like a sidekick, broadening the range of light the plant can use.
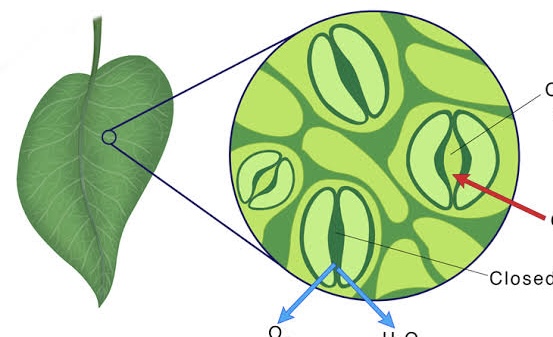
stomata
Plants exchange gases with the environment through pores called _____.
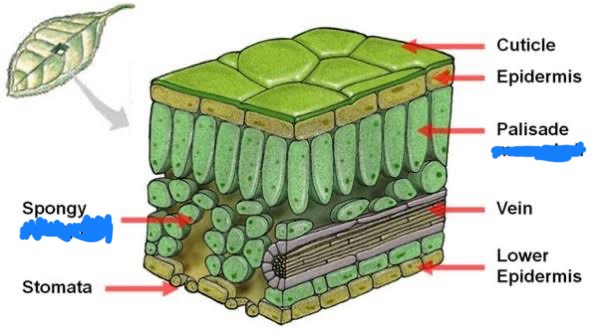
Mesophyll
_______ cells are the inner tissue of the leaf, packed between the upper (palisade) and lower (spongy) layers. They’re loaded with chloroplasts, which are the green organelles where photosynthesis happens
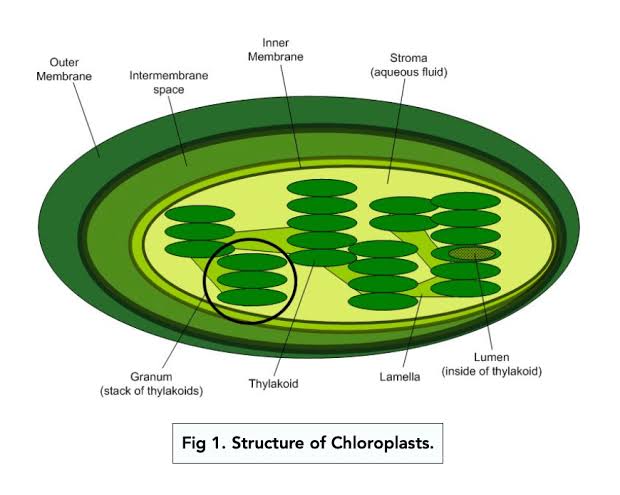
Stroma
The fluid-filled space inside the inner membrane of the chloroplast; where the Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions) happens — glucose gets made here and holds enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, and building blocks for sugar = glucose
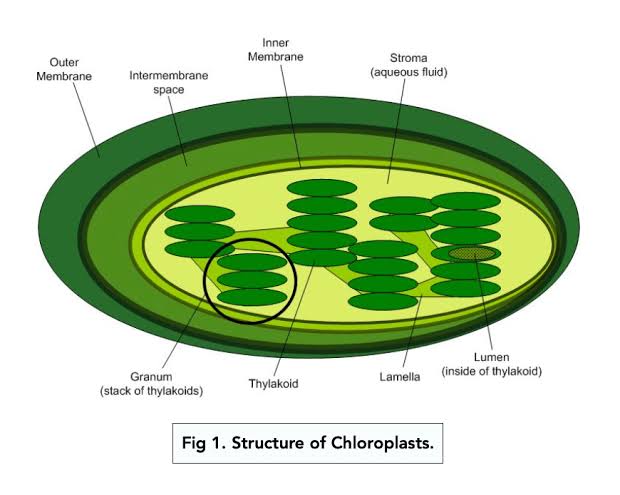
Grana/granum
More stacks = more surface area for light absorption; connected by stromal lamellae (thin tubes) to keep the system organized.
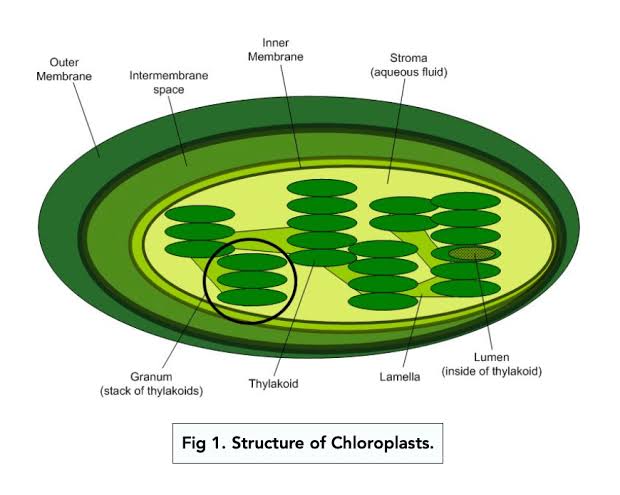
Thylakoid Membranes
Flattened membrane sacs (like green pancakes); the light-dependent reactions happen; where the sunlight gets captured and turned into ATP & NADPH (plant energy money)
which enclose the thylakoid space. |
Antenna pigment
They absorb light energy and funnel it toward the reaction center
reaction center
A special chlorophyll a molecule uses the energy to kick off electron transfer
proteins
hold pigments and the reaction center in place and help transfer energy and electrons during the light reactions.
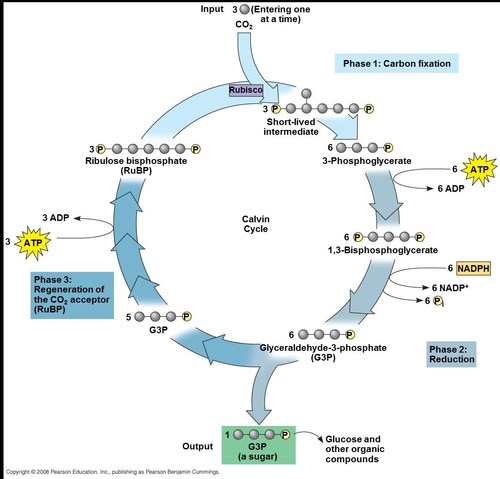
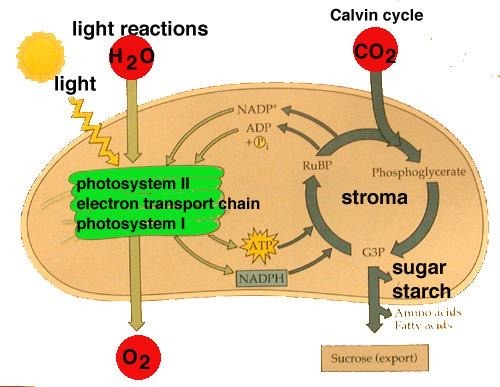
Light Independent Reaction
A.K.A Calvin Benson Cycle, it occurs in the STROMA and requires ATP, NADPH, AND CO2
Light Dependent Reactions
These occurs in the thylakoid membrane and thylakoid space/lumen, using light energy (photons) and water (H2O) as reactants.
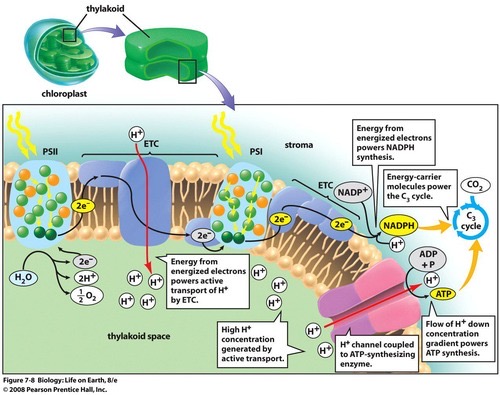
Products of Light Dependent Reactions (Light Reactions)
O2, ATP , NADPH
Reactants for Light Independent Reaction (Carbon Reaction)
CO2, ATP, NAPH
Ultimate Product of Light Independent Reaction
Carbohydrates from G3P and fats
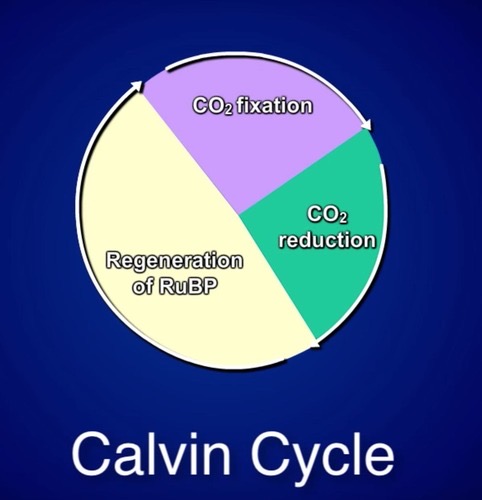
(3) Major Steps of Light Independent Reaction
Fixing of carbon dioxide (gets attached to a 5-carbon molecule RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate) = 6 split = 3 - carbon molecules (3-PGA)
Reduction by NADPH (powered up by ATP and NADPH and converts it into G3P)
Replacement of the 5-carbon molecule RuBP = repeat
Carbon Fixation
This is the process of CONVERTING carbon from an inorganic form (CO2) to an organic molecule = 3-PGA
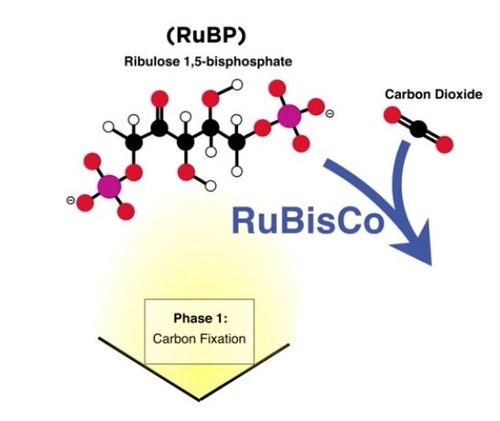
RuBP
Ribulose bisphosphate, a 5-carbon starter molecule that is regenerated by the Calvin Cycle
3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG)
Stable 3-carbon molecules formed from the breakdown of an unstable 6-carbon molecule during carbon fixation
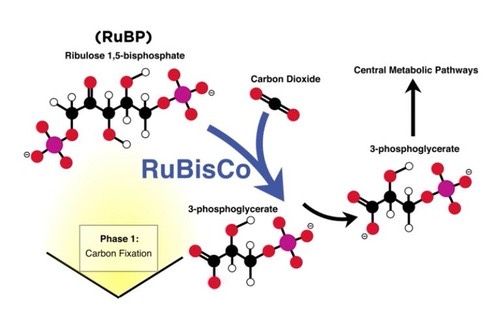
Reduction Step
The 3-carbon compound (3PG) are converted to a higher-energy state activated by ATP and reduced by NADPH
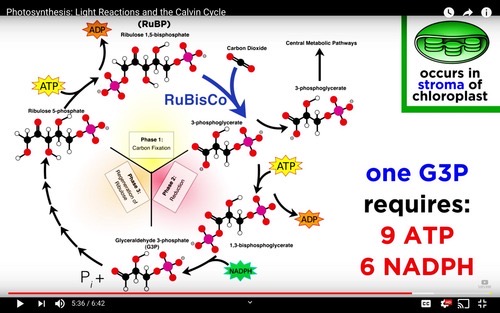
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P or PGAL)
Produced during the reduction step; some exit the cycle to form glucose while most generate RuBP (5-carbon sugar)
Glucose Production
It requires 6 cycles of the Calvin cycle to produce 1 glucose molecule
Regeneration of RuBP
Most G3P/PGAL molecules are uses to regenerate RuBP, requiring energy from ATP.
Calvin Cycle
A series of biochemical reactions that take place in the stroma of chloroplasts, involving carbon fixation and regeneration of RuBP.
Melvin Calvin
Awarded the 1961 Nobel Prize for his work on the Calvin cycle.
Calvin-Benson Cycle
Another name for the light independent reaction, named after Melvin) & Calvin and his colleagues.
Dark Reactions
Another term for light independent reactions, as they do not require light directly.
Photosynthesis vs. Cellular Respiration
Photosynthesis converts light energy into chemical energy, while cellular respiration breaks down glucose to release energy.
Importance of Concentration Gradients
are crucial for ATP generation through passive and active transport.
Enzyme Rubisco
The enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of CO2 with RuBP during carbon fixation.
High-energy phosphate = battery LOT of energy
Products of the Calvin cycle, including glucose and other carbohydrates.
Stoma
Where carbon dioxide enters the leaf.
Xylem
Where most of the water comes from.
Chloroplast
Organelle responsible for photosynthesis.
Chromatography
A method of separating pigments from plant and other tissues.
Photosynthesis
Process by which plants and other photosynthetic organisms trap the & Sun's energy and transform it into energy-rich chemical compounds.
Photosystem
Clusters of chlorophyll and other pigments embedded in thylakoid membrane.
Photosystem I (PSI)
One of the two different photosystems in chloroplasts.
Photosystem |I (PSIl)
Comes first in the light reaction.
Photolysis
Light energy causes the splitting of water, donating electrons and releasing oxygen to the environment.