3-Carbonate System and Equilibria
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
How does CO2 move around the earth cycle?
Dissolution of atmospheric CO2 to make carbonic acid making rainwater acidic
CaCO3 also a major sink of dissolved carbon in long term global carbon balance.
Carbonate system of ocean plays a key role in controlling the pressure of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, regulating earth’s temperature
What chemical species are in the CO2-H2O system, and what equations include these species?
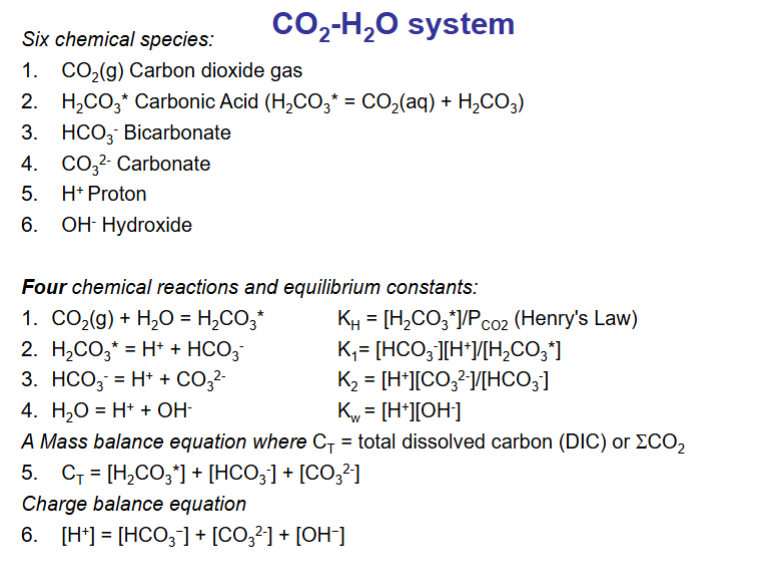
What is the order of these equation of the story of carbonate in the environment?

How do we calculate the concentration of CO2 in rainwater? if there is 398 ppm of CO2 in atmosphere? and constant is 0.0338M/atm

What is Henry’s Law: gas solubility?
Henry’s Law - at a constant temperature, the amount of gas that dissolves in a volume of liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas in equilibrium with that liquid.
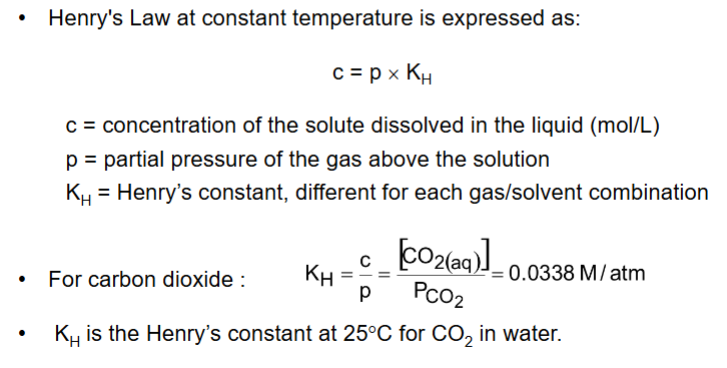
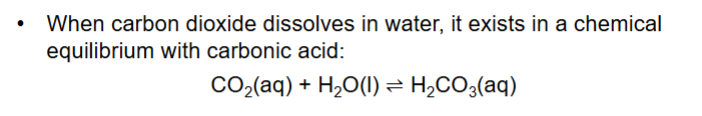
What is equilibrium constant for this?
H2O ignored, because effectively the concentration of water does NOT change
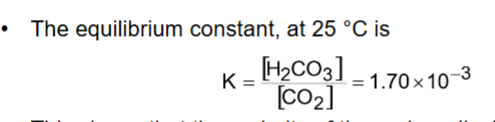
Why do we often use a * on H2CO3?
Only tiny amount of CO2 dissolves, so treat them together CO2 + H2CO3


How do we calculate the pH of rainwater? (answer over multiple flashcards)
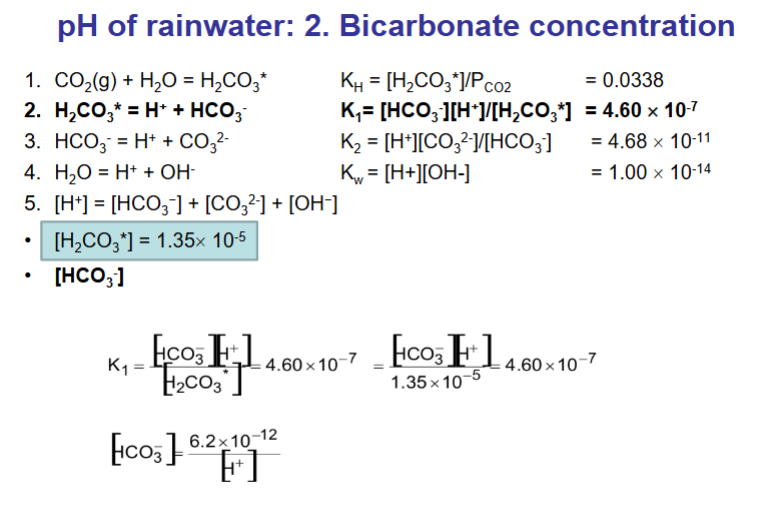
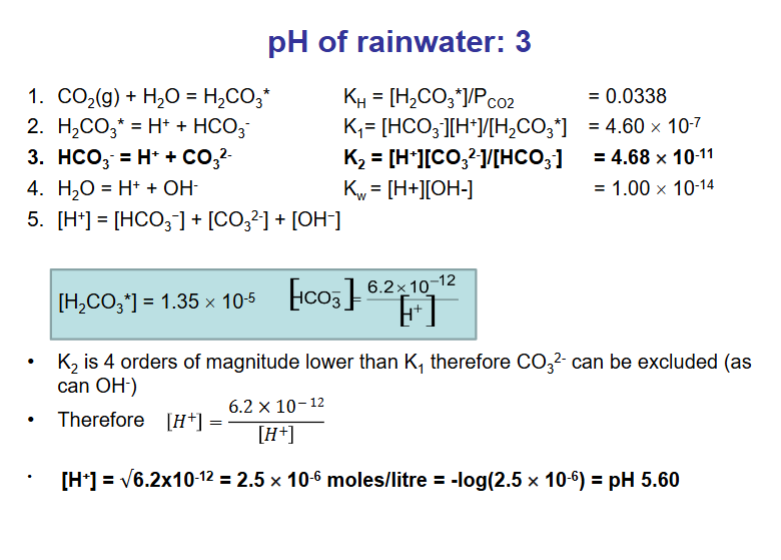
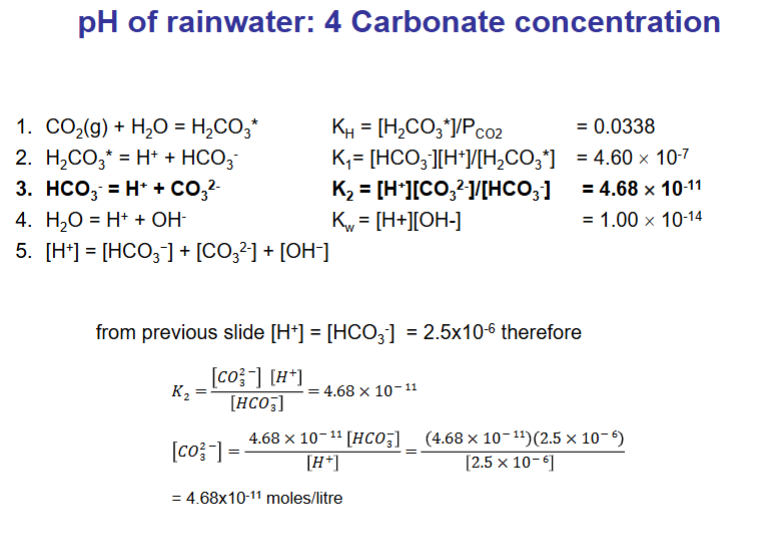
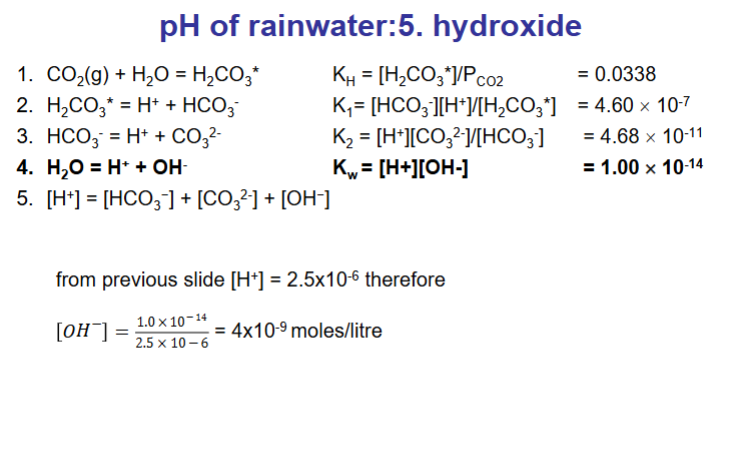
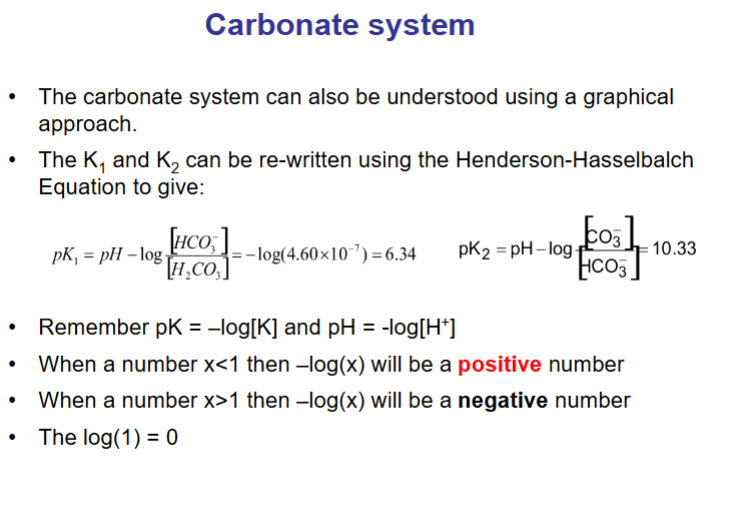
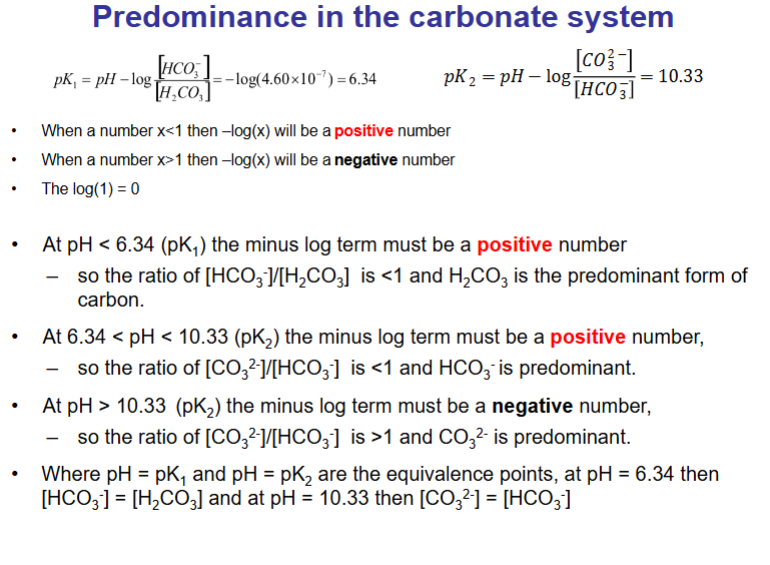
How can this carbonate system also be re-written using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
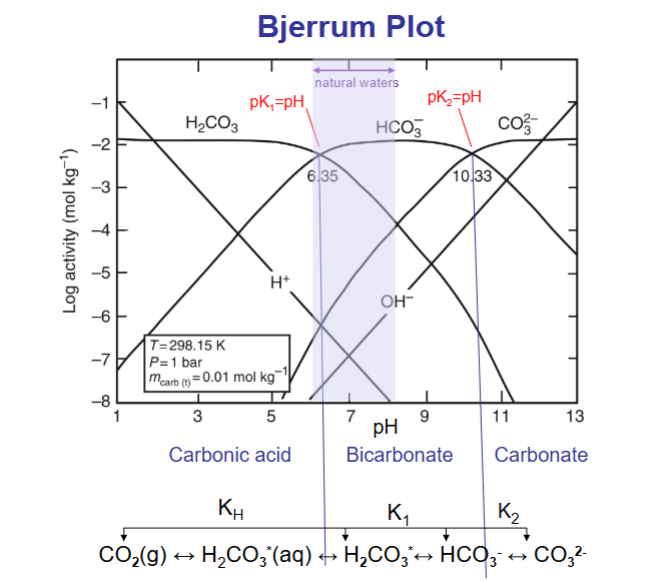
Bjerrum plot shows the relative importance of the various species in an acid-base system under closed conditions (total concentration of all species is constant)
What is the solubility produce for calcite CaCO3?
Note calcium carbonate exists in two polymorphs: calcite and aragonite. Both minerals are highly insoluble, calcite slightly more insoluble, aragonite slightly more soluble.

How do the factors T, pH and p(CO2) affect calcite solubility?
As pCO2 increases, the pH decreases, so more acidic.
As pCO2 increases, solubility increases.
Decrease in calcite solubility as temperature increases.
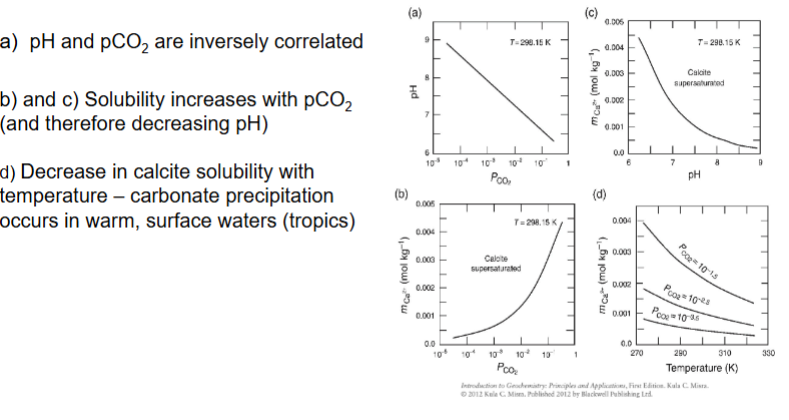
How does Pressure affect calcite solubility?
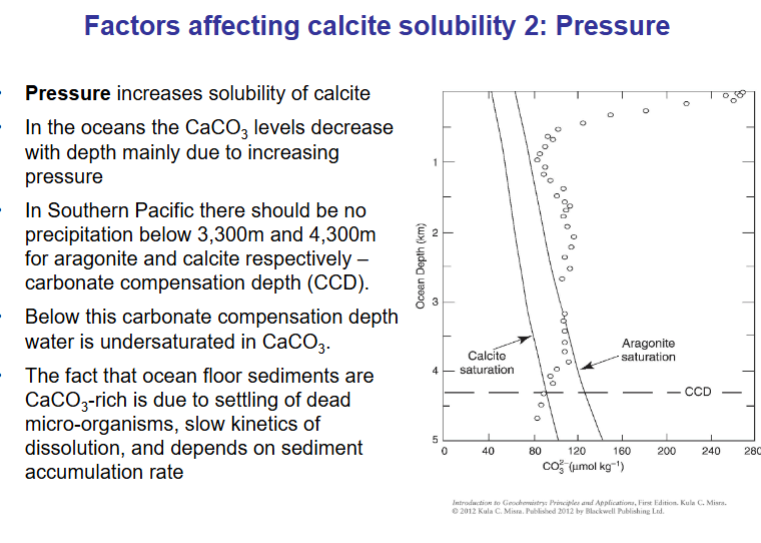
Do we get inorganic CaCO3 precipitation from oceans?
Oceans are oversaturated in calcium carbonate however inorganic precipitation is rare.
Most precipitation is biologically mediated and in the form of aragonite despite it being slightly more soluble than calcite.

How do we get biological precipitation of calcium carbonate in oceans?
biological precipitation - biomineralisation
foraminifera and coccolithophores important for calcite
pteropods for aragonite
biological ppt of CaCO3 is an important buffer of ocean chemistry and atmospheric CO2 levels. Increasing CO2 acidifies ocean, so buffering response is to dissolve CO2.
What are the most important factors affecting calcium carbonate solubility?
pCO2 and pH
What is CCD?
Carbon compensation depth
The ocean depth where calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) dissolves as fast as it is deposited — below this depth, no carbonate sediments accumulate.