Lipid Metabolism
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
Triacylglycerols (TAGs)
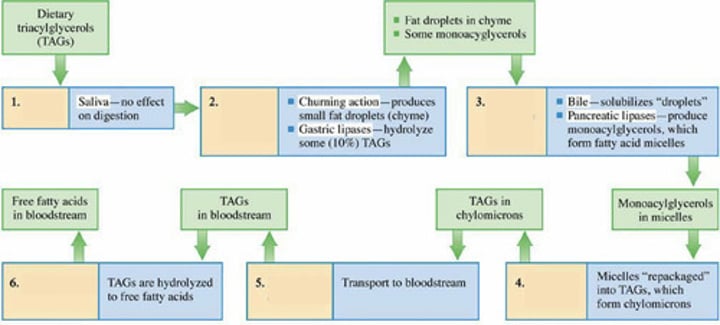
What is the primary component of dietary lipids, making up 98% of them?
No
Do salivary enzymes in the mouth have any effect on lipids, specifically triacylglycerols (TAGs)?
Chyme
What physical transformation do most, not all triacylglycerols (TAGs) undergo in the stomach, resulting in small globules or droplets known as what?
Physical
Is the transformation of most triacylglycerols (TAGs) into small globules or droplets called chyme in the stomach a physical or chemical process?
Stomach
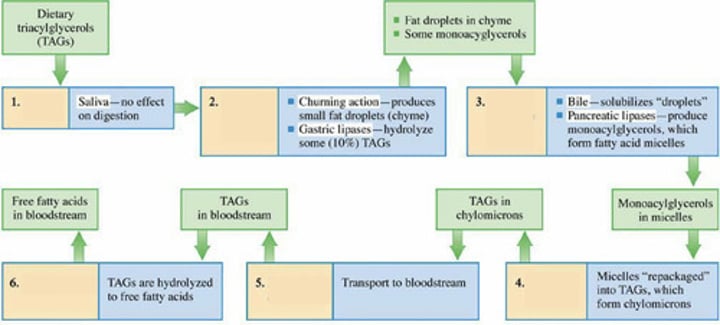
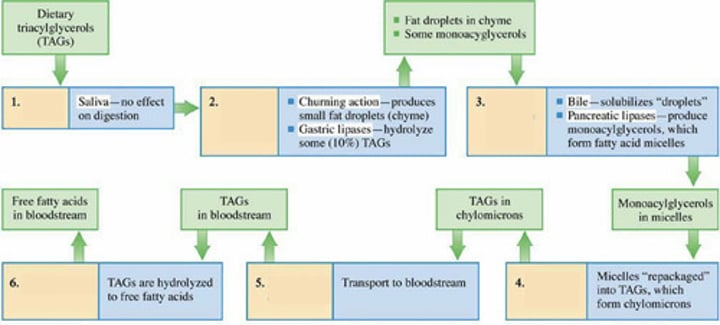
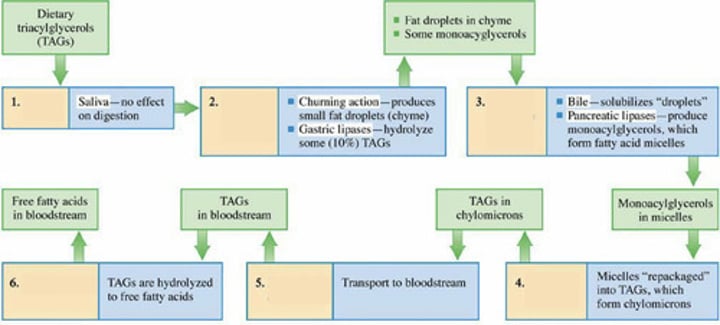
Where does lipid digestion start?
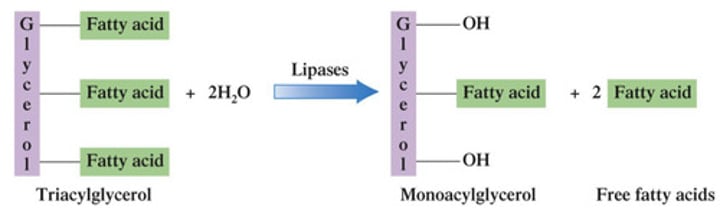
10%
Lipid Digestion in the Stomach
Approximately what percentage of TAGs are hydrolyzed in the stomach during lipid digestion?
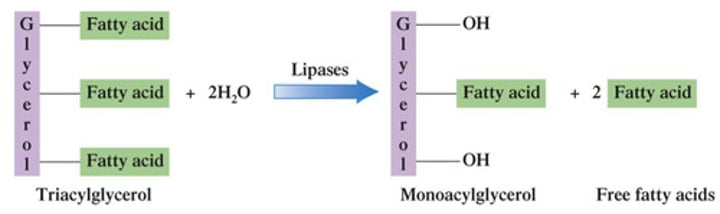
Gastric lipase enzymes
Lipid Digestion in the Stomach
What enzymes in the stomach hydrolyze TAG ester bonds?
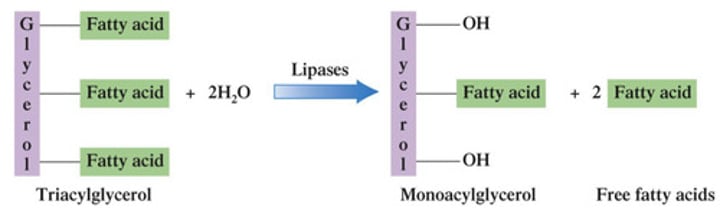
Emulsified with bile salts
Lipid Digestion in the Intestinal Cells
What happens to chyme when it enters the small intestine in the context of lipid digestion?
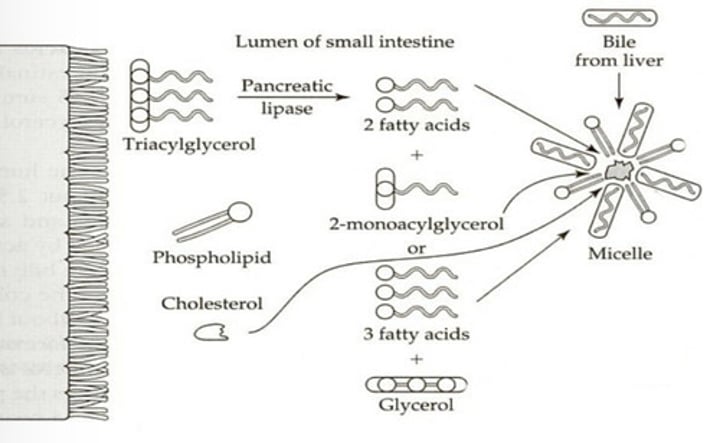
Pancreatic lipase
Lipid Digestion in the Intestinal Cells
Which enzyme hydrolyzes ester bond linkages between fatty acid units and glycerol
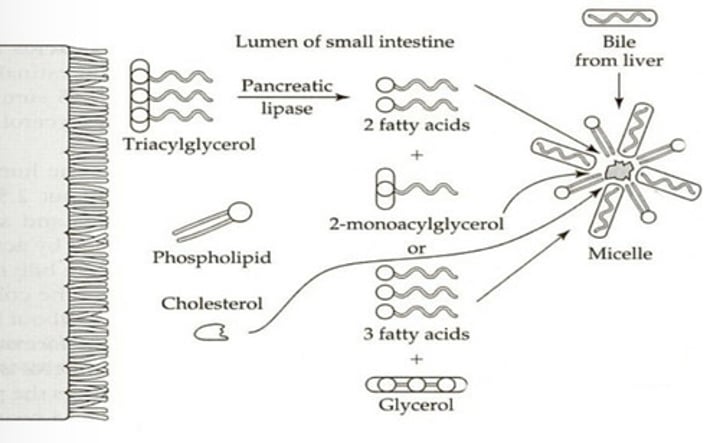
Micelles
Lipid Digestion in the Intestinal Cells
What is formed when fatty acids, monoacylglycerols, and bile salts combine in lipid digestion?
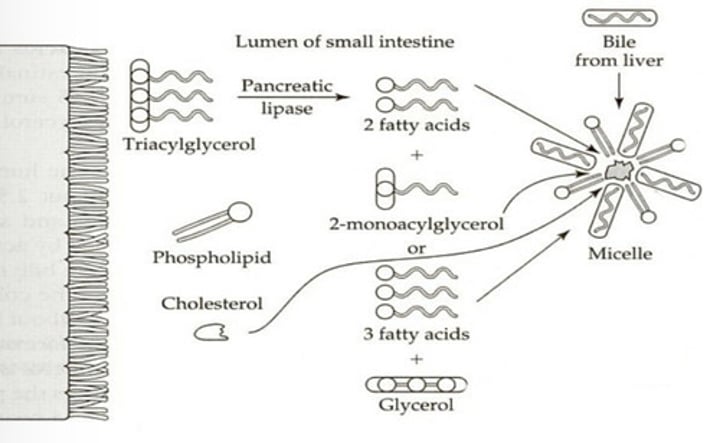
Monoacylglycerols; Free fatty acids
Lipid Digestion in the Intestinal Cells
In the intestinal cells, (?) and (?) are repackaged to form TAGs
Chylomicrons
Lipid Digestion in the Intestinal Cells
These new TAGs combine with membrane lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol) and water-soluble proteins to form?
Chylomicrons
What do you call the lipoproteins that transport TAGs from intestinal cells, via the lymphatic system, to the bloodstream?
Short-chain; Medium-chain; Long-chain
Enumerate the 3 types of fatty acids
Enterocytes
Short- and medium-chain fatty acids enter portal blood directly from?
Albumin
Short- and medium-chain fatty acids are bound to (?) in blood
Liver
Short- and medium-chain fatty acids are oxidized in (?) or elongated and used for triglyceride formation
Chylomicrons
Long-chain fatty acids form what?
Lacteals
Long-chain fatty acids drain into the lymphatics via the?
12
True or False? If false, replace the underlined word to make the statement correct.
“Long-chain fatty acids have more than 15 Carbons.”
Mouth
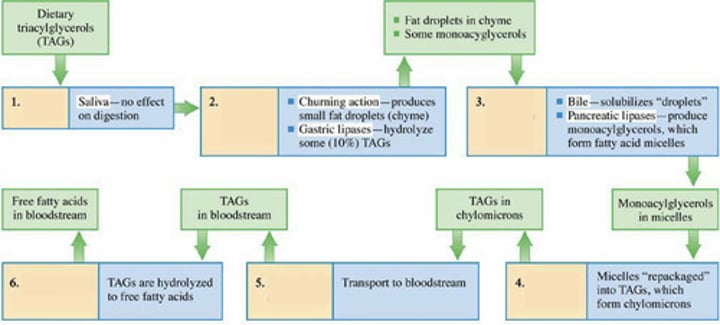
LIPID DIGESTION
Identify Step 1
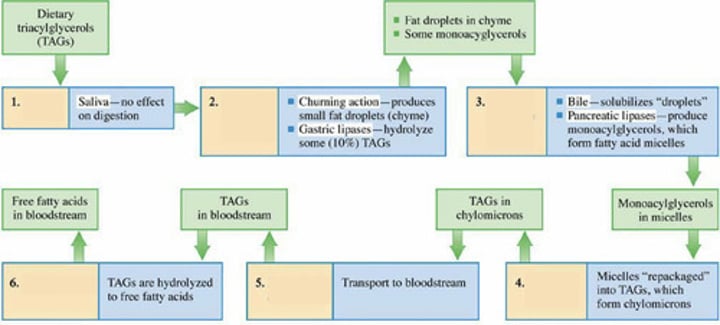
Mouth; Stomach; Small Intestine; Intestinal Cells; Lymphatic System; Bloodstream
Enumerate in order, the organs that lipid digestion goes through
Stomach
LIPID DIGESTION
Identify Step 2
Skin
Adipose tissue is located beneath the (?), especially in the abdominal region and vital organs
Small Intestine
LIPID DIGESTION
Identify Step 3
heat loss; physical shock
Adipose tissue serves as an insulator against (?) and protection against (?)
Intestinal Cells
LIPID DIGESTION
Identify Step 4
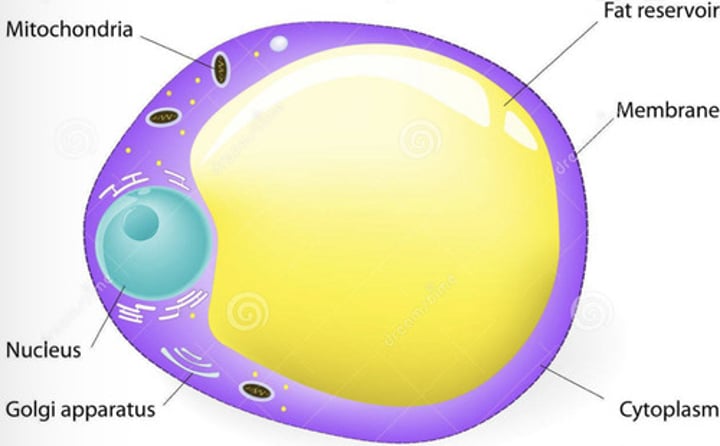
Adipose Tissue
Largest cells in the body where the cytoplasm is replaced with large TAG droplets
Beta Oxidation
What is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down to generate acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle, and NADH and FADH2, which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport chain
Lymphatic System
LIPID DIGESTION
Identify Step 5
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)
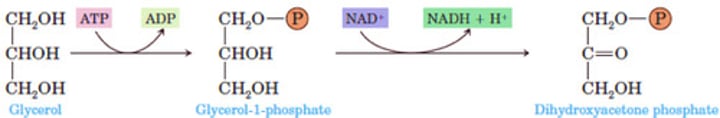
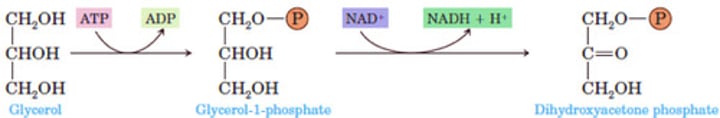
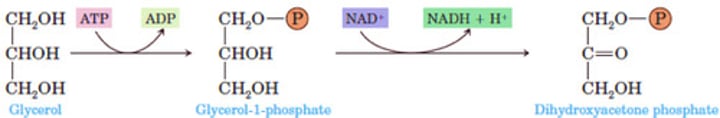
Glycerol Metabolism
What is glycerol, after entering the bloodstream, converted to in the liver or kidney?
Phosphorylation; primary
Glycerol Metabolism
Step 1: (?) of (?) hydroxyl group of the glycerol
Oxidization; secondary
Glycerol Metabolism
Step 2: (?) of (?) alcohol group of glycerol to a ketone
Muscle and Liver
Beta Oxidation
Where does it occur?
Tissues that can use fatty acids as energy source, primarily in the 2 organs?
Bloodstream
LIPID DIGESTION
Identify Step 6
Cytosol
Beta Oxidation
Where does it occur?
Fatty acid activation occurs in the (?)
Mitochondria; Peroxisomes
Beta Oxidation
Where does it occur?
β-oxidation occurs in the (?) and (?)
Fatty Acids (Palmitic acid and Linoleic acid)
What are the substrates involved in Beta Oxidation?
Acetyl-CoA; NADH; FADH2; Propionyl CoA
What are the products of Beta Oxidation?
Odd-numbered
Beta Oxidation
Prioponyl CoA is for (?) Carbon fatty acids
Mitochondria
Beta Oxidation
Which step is rate-limiting?
Translocation of fatty Acyl CoA from the cytosol to the (?)
Carnitine-palmitoyl transferase
Beta Oxidation
Which enzyme is involved in the translocation of fatty Acyl CoA from the cytosol to the mitochondria?
A
Beta Oxidation
➢ "Priming" of fatty acids for reaction
➢ ATP-dependent acylation to form fatty Acyl-CoA
➢ Enzyme: Acyl-CoA synthetases (thiokinases)
A.) Step 1: Fatty acid activation
B.) Step 2: Transport of fatty Acyl-CoA across the mitochondrial membrane
C.) Step 3: Degradation of fatty Acyl-CoA
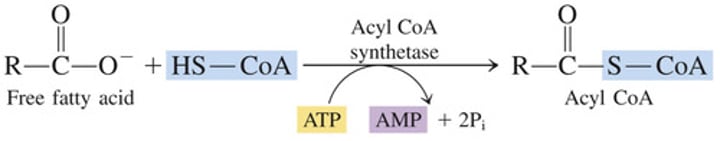
Acyl-CoA synthetases (thiokinases)
Beta Oxidation
What enzyme is involved in Step 1: Fatty Acid Activation?
Carnitine palmitoyltransferases I and II
Beta Oxidation
What enzyme is involved in Step 2: Transport of fatty Acyl-CoA across the mitochondrial membrane?
B
Beta Oxidation
➢ Transfer of acyl portion to carnitine
➢ Mediated by specific carrier protein
➢ Enzymes involved:
carnitine palmitoyltransferases I and II
A.) Step 1: Fatty acid activation
B.) Step 2: Transport of fatty Acyl-CoA across the mitochondrial membrane
C.) Step 3: Degradation of fatty Acyl-CoA
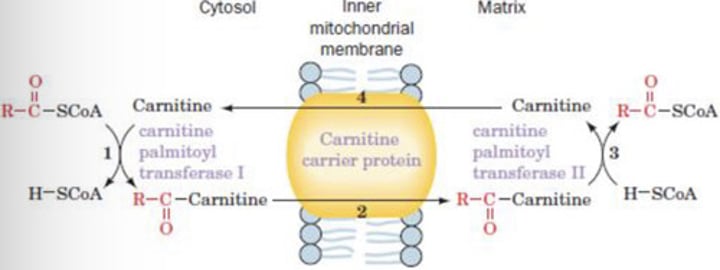
C
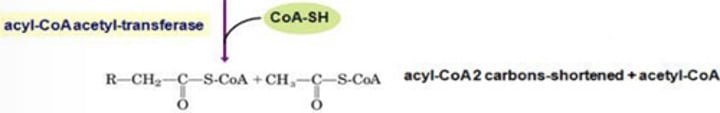
Beta Oxidation
➢ Four reactions repeatedly cleave two carbon units from the carboxyl end of the acyl CoA molecule
➢ This process is also called β-oxidation pathway because the second carbon or beta carbon from the carboxyl end of the chain is oxidized.
A.) Step 1: Fatty acid activation
B.) Step 2: Transport of fatty Acyl-CoA across the mitochondrial membrane
C.) Step 3: Degradation of fatty Acyl-CoA
C
Beta Oxidation
Oxidation → Hydration → Oxidation → Thiolysis
A.) Step 1: Fatty acid activation
B.) Step 2: Transport of fatty Acyl-CoA across the mitochondrial membrane
C.) Step 3: Degradation of fatty Acyl-CoA
Oxidation; Hydration; Oxidation; Thiolysis
Beta Oxidation
Enumerate the steps in Step 3: Degradation of Fatty Acyl-CoA
FAD; FADH2
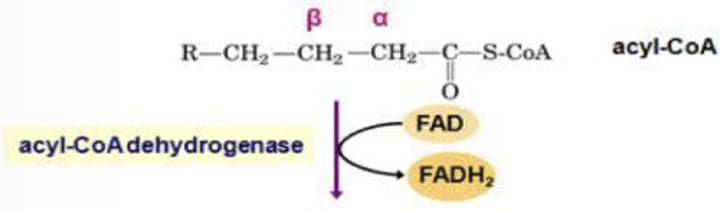
Beta Oxidation – Step 3: Degradation of Fatty Acyl-CoA
In Step 1: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation,
The oxidizing agent is (?)
The product is (?)
A
Beta Oxidation – Step 3: Degradation of Fatty Acyl-CoA
➢ Hydrogen atoms removed from α and β carbons, forming a double bond between them
➢ FAD serves as the oxidizing agent, producing an FADH2 molecule
A.) Step 1: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
B.) Step 2: Hydration
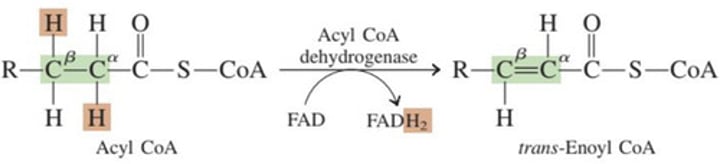
Acyl Coa dehydrogenase
Beta Oxidation – Step 3: Degradation of Fatty Acyl-CoA
In Step 1: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation,
What is the enzyme involved?
Enoyl CoA hydralase
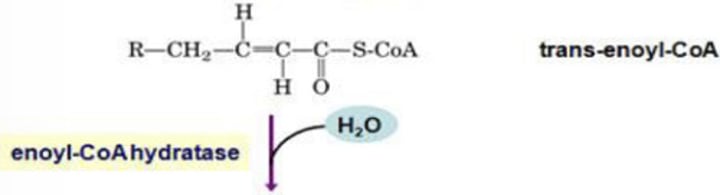
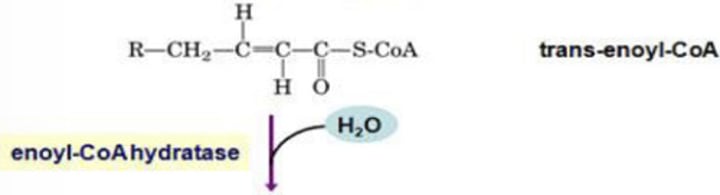
Beta Oxidation – Step 3: Degradation of Fatty Acyl-CoA
In Step 2: Hydration
What is the enzyme involved?
B
Beta Oxidation – Step 3: Degradation of Fatty Acyl-CoA
➢ A molecule of water is added across the trans double bond, producing a secondary alcohol at the β-carbon position
A.) Step 1: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
B.) Step 2: Hydration
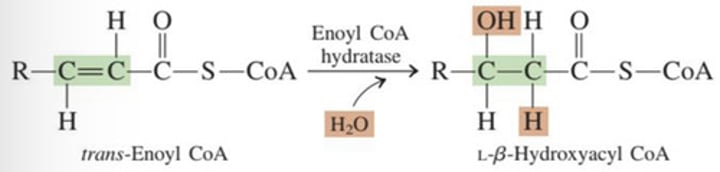
C
Beta Oxidation – Step 3: Degradation of Fatty Acyl-CoA
➢ This step requires NAD+ as a coenzyme.
➢ The two hydrogens and electrons removed are transferred to the NAD+ to form NADH+ and H+.
➢ Secondary alcohol is oxidized to a ketone at the beta carbon.
C.) Step 3: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
D.) Step 4: Thiolysis
NAD+
Beta Oxidation – Step 3: Degradation of Fatty Acyl-CoA
In Step 3: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
Which coenzyme is required?
B-Hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase
Beta Oxidation – Step 3: Degradation of Fatty Acyl-CoA
In Step 3: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
Which enzyme is involved?
2
Beta Oxidation – Step 3: Degradation of Fatty Acyl-CoA
In Step 4: Thiolysis,
The new Acyl CoA molecule is shorter by how many carbon atoms than its predecessor?
D
Beta Oxidation – Step 3: Degradation of Fatty Acyl-CoA
➢ Fatty acid chain is broken between the α and β carbons by
reaction with a coenzyme A molecule.
➢ The result is an acetyl CoA molecule and a new acyl CoA molecule that is shorter by two carbon atoms than its predecessor
C.) Step 3: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
D.) Step 4: Thiolysis
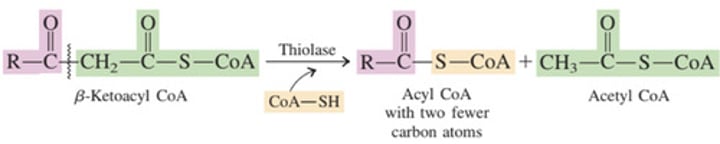
Thiolase
Beta Oxidation – Step 3: Degradation of Fatty Acyl-CoA
In Step 4: Thiolysis,
What is the enzyme involved?
2
Beta Oxidation – Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids differs to saturated fatty acids because it requires how many ADDITIONAL STEPS?
A
A.) Step 1: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
B.) Step 2: Hydration
C.) Step 3: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
D.) Step 4: Thiolysis
B
A.) Step 1: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
B.) Step 2: Hydration
C.) Step 3: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
D.) Step 4: Thiolysis
C
A.) Step 1: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
B.) Step 2: Hydration
C.) Step 3: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
D.) Step 4: Thiolysis
D
A.) Step 1: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
B.) Step 2: Hydration
C.) Step 3: Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
D.) Step 4: Thiolysis
Epimerase
Beta Oxidation – Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Which enzyme changes D configuration to an L configuration?
Cis-trans isomerase
Beta Oxidation – Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Which enzyme produces a trans-(2,3) double bond from a cis-(3,4) double bond
21
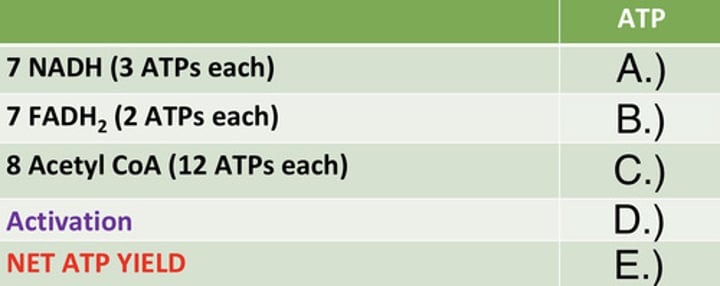
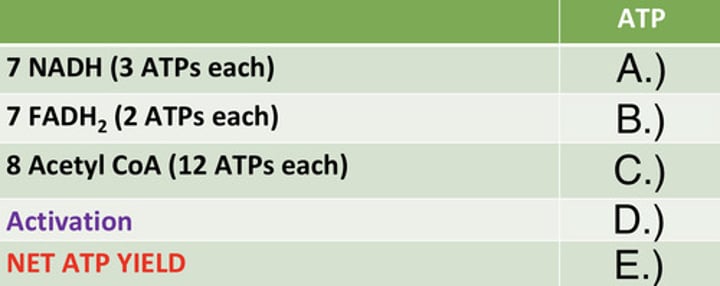
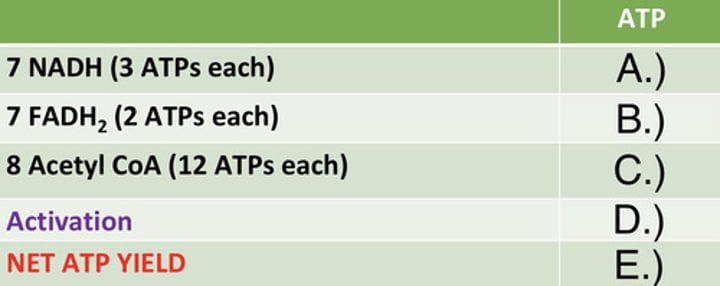
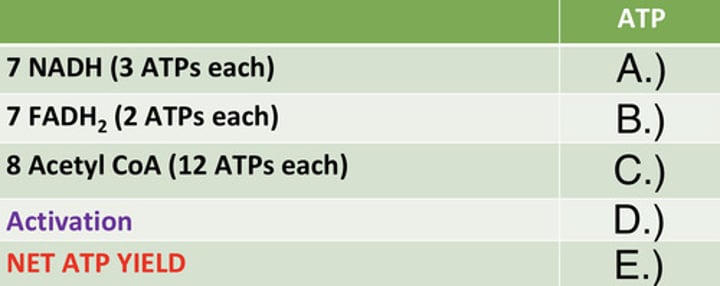
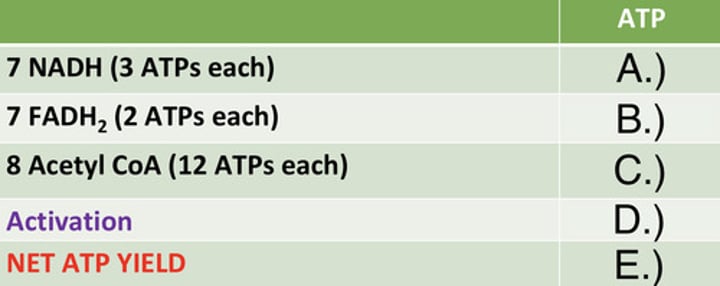
ATP Yield of Palmitate
Identify the ATP yield (A)
14
ATP Yield of Palmitate
Identify the ATP yield (B)
96
ATP Yield of Palmitate
Identify the ATP yield (C)
-2
ATP Yield of Palmitate
Identify the ATP yield (D)
129
ATP Yield of Palmitate
Identify the ATP yield (E)
carbohydrate; lipid metabolism
Beta Oxidation
Adequate balance in (?) and (?) is required
fat; carbohydrates
Lipid–carbohydrate metabolism can be disturbed by the following conditions:
Dietary intake is high in (?) and low in (?)
Diabetic conditions
Lipid–carbohydrate metabolism can be disturbed by the following conditions:
(?) where the body cannot use glucose properly
fasting
Lipid–carbohydrate metabolism can be disturbed by the following conditions:
Prolonged (?) conditions
Ketogenesis
Involves the synthesis of ketone bodies from acetyl CoA
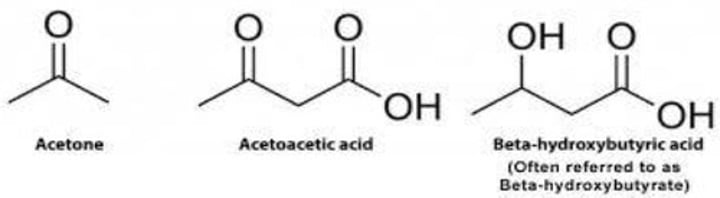
Ketone bodies
What are the water-soluble molecules containing the ketone group that are produced by the liver from fatty acids?
liver mitochondria
Where is the primary site for Ketogenesis?
Ketone bodies
What is produced by the liver when you don't eat much, follow low-carb diets, starve, exercise intensely, drink too much alcohol, or have untreated type 1 diabetes.
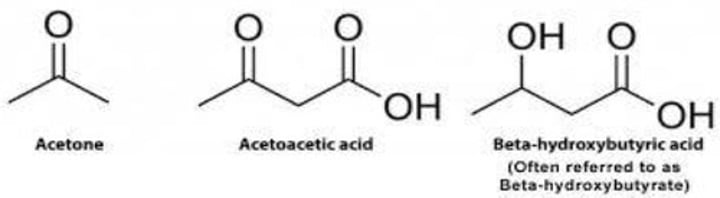
Acetoacetate; β-hydroxybutyrate; Acetone
Enumerate the 3 ketone bodies
Thiolase
Ketogenesis
In Step 1: First condensation, which enzyme is involved?
A
Ketogenesis
➢ Two acetyl CoA molecules combine
➢ Reversal of the last step of the β-oxidation pathway
➢ Result: Acetoacetyl CoA
A.) Step 1: First condensation
B.) Step 2: Second condensation
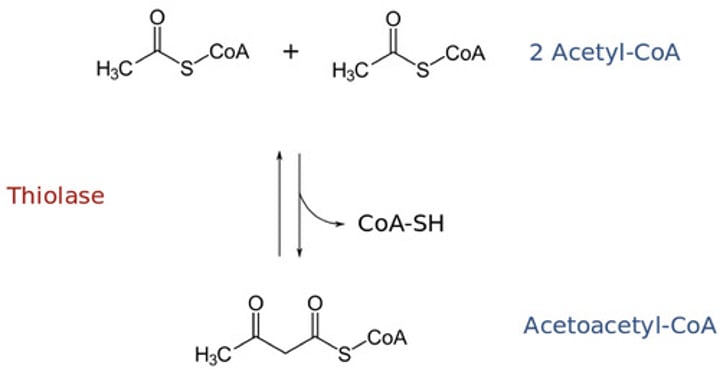
HMG-CoA synthase
Ketogenesis
In Step 2: Second condensation, which enzyme is involved?
B
Ketogenesis
➢ Acetoacetyl CoA + Third Acetyl CoA + Water → 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA (HMG-CoA) + CoA–SH
A.) Step 1: First condensation
B.) Step 2: Second condensation
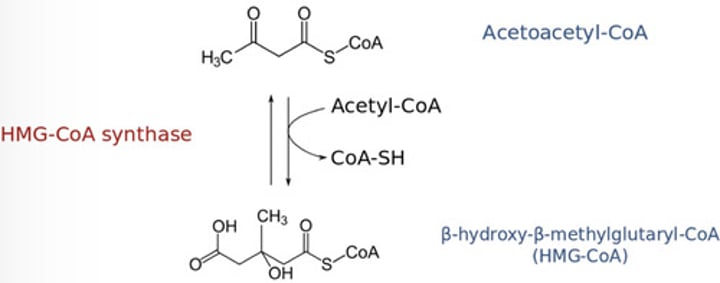
HMG-CoA lyase
Ketogenesis
In Step 3: Chain cleavage, which enzyme is involved?
C
Ketogenesis
➢ hahaha
C.) Step 3: Chain cleavage
D.) Step 4: Hydrogenation
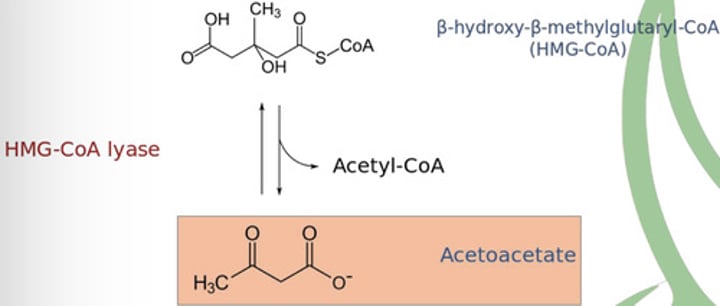
D-B-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
Ketogenesis
In Step 4: Hydrogenation, which enzyme is involved?
Complex
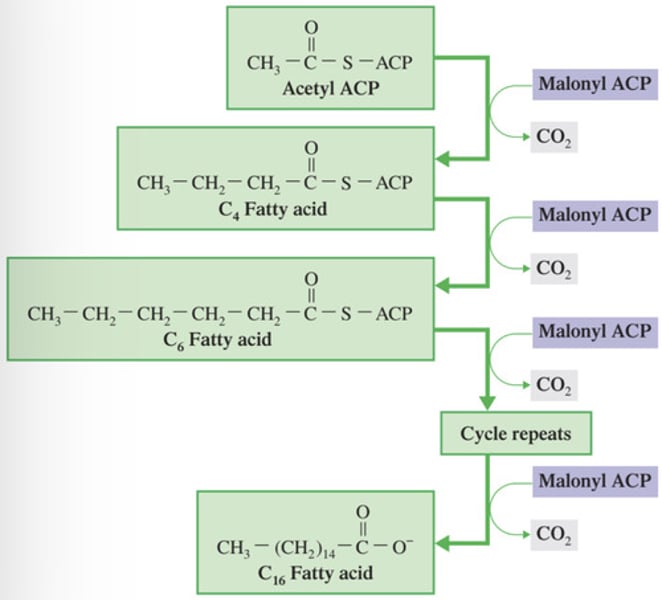
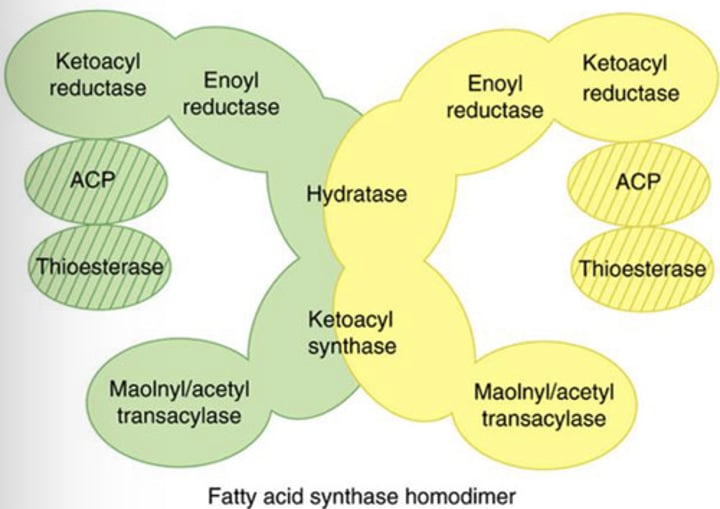
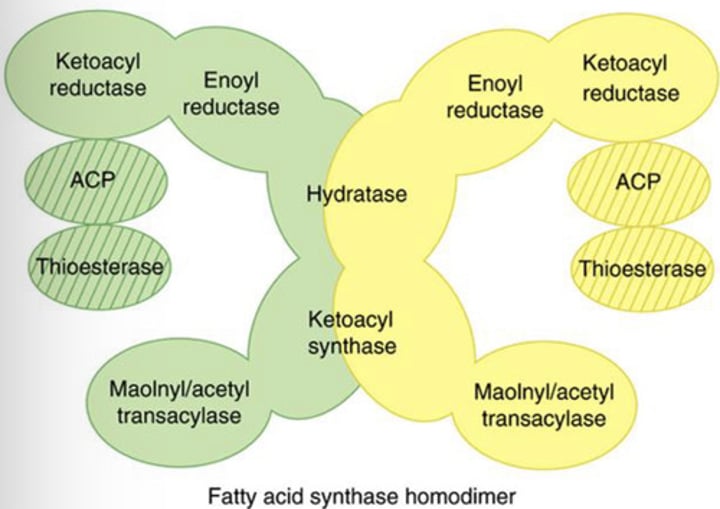
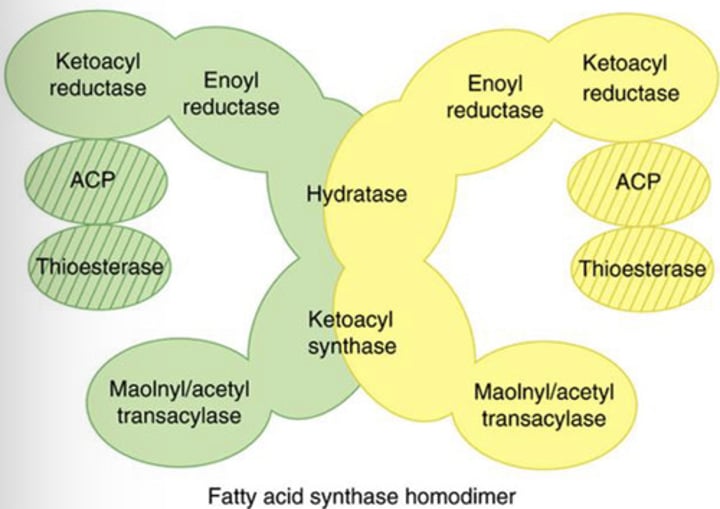
Lipogenesis - Step 2: Fatty Acid Synthase Complex
Fatty acid formation is made efficient as all reactions because the process takes place within the?
D
Ketogenesis
➢ Acetoacetate is reduced to β-hydroxybutyrate
C.) Step 3: Chain cleavage
D.) Step 4: Hydrogenation
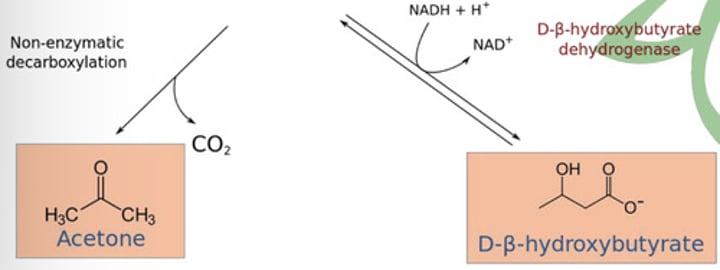
Lipogenesis
It is the process of converting protein into fatty acids
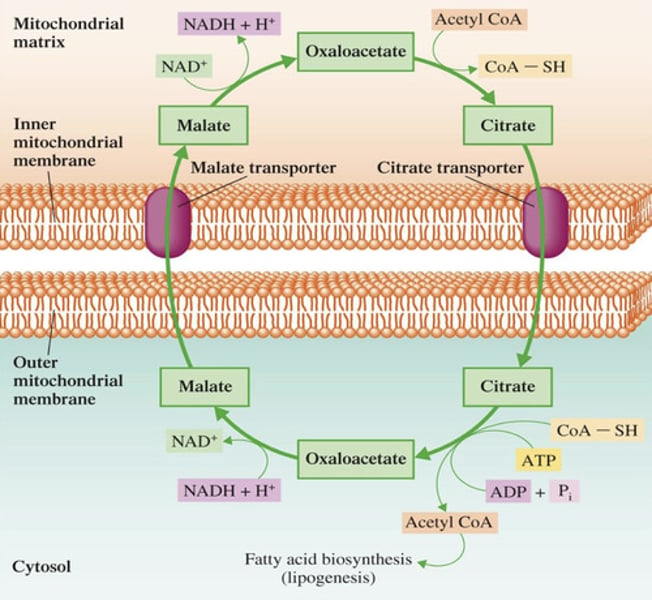
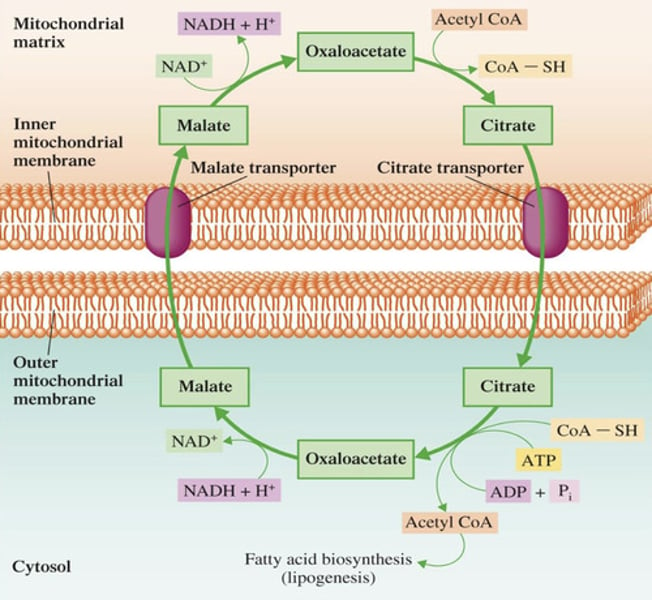
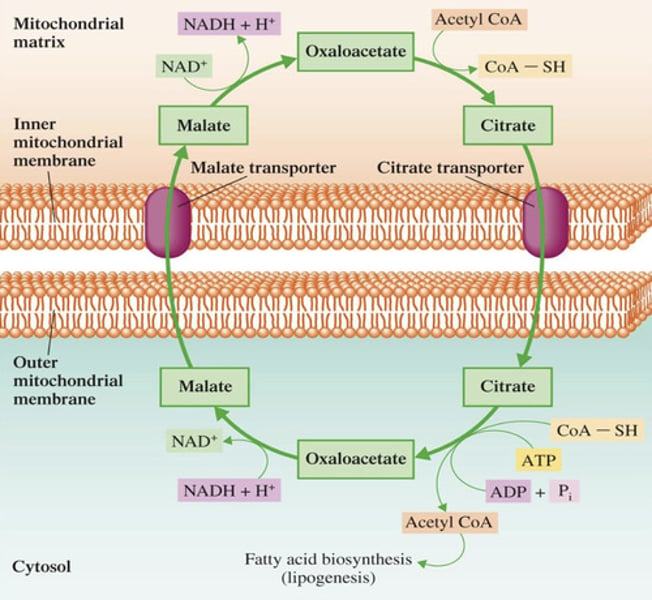
Mitochondria
Lipogenesis - Step 1: Conversion of Acetyl CoA to Malonyl CoA
Acetyl CoA is generated in which organelle?
Acetyl CoA
What is the starting material for lipogenesis?
Cancer
Enhanced lipogenesis is a characteristic feature of which sickness?
Tumor cell
Enhanced Lipogenesis
Which cell’s survival is influenced by deregulated lipid biosynthesis?
Cytosol
Lipogenesis - Step 1: Conversion of Acetyl CoA to Malonyl CoA
Once the Acetyl CoA is generated in mitochondria, it must first be transported where?
acyl carrier protein (ACP-SH)
Lipogenesis - Step 2: Fatty Acid Synthase Complex
All intermediates in fatty acid synthesis are linked to (?)
acyl carrier protein (ACP-SH)
Lipogenesis - Step 2: Fatty Acid Synthase Complex
(?) can be regarded as a “giant CoA molecule”
Malonyl CoA; palmitate
Lipogenesis - Step 2: Fatty Acid Synthase Complex
(?) is elongated by the FAS complex to produce (?)
Highly proliferating
Enhanced Lipogenesis
Leads to a continuous supply of fatty acids for membrane production of which type of cells?