RC circuits
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
charge, capacitor, powers
When you use a flash camera, it takes a few seconds to ______ the _________, that ______ the flash.
RC circuit
A circuit that contains both resistance and capacitance.
Two-pole switch RC circuit
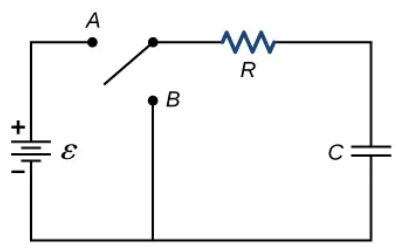
Charging capacitor
In-series connection of the voltage source, resistor, capacitor
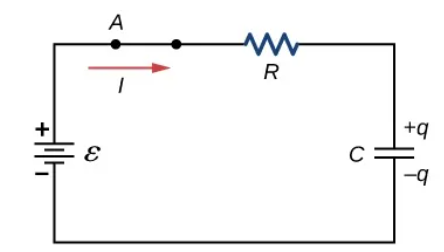
Discharging capacitors
The voltage source is being removed in this part.
C = q/V
Mathematical representation of the definition of Capacitance
Vc = q/C
Voltage across the capacitor
Vr = I R
Formula for the potential drop across the resistor
I = dq/dt
Mathematical representation of the definition of current
ε - Vr - Vc = 0
Equation given by the Kirchhoff’s loop rule to understand the charging of the capacitor.
ε - IR - q/C = 0
Substituting the definition of Vr and Vc inside the Equation of the Kirchhoff’s loop rule to understand the charging of the capacitor.
ε - R(dq/dt) - q/C = 0
Substituting the definition of current inside the Kirchhoff’s current loop that explains the charging of the capacitor (Definitions of Vr and Vc have already been substituted)
dq/dt = (εC-q)/(RC)
Solving for “the definition of current”inside the Kirchhoff’s current loop that explains the charging of the capacitor.
∫(from 0 to q) (dq)/(εC - q) = (1/RC) ∫(from 0 to t) dt
Integrating the differential equation of the Kirchhoff’s current rule that helps us to understand the charging of capacitor.
u = εC - q
The u-substitution inside the integration equation of the Kirchhoff’s current rule that helps us to understand the charging of capacitor.
du = -dq
du inside the integration equation of the Kirchhoff’s current rule that helps us to understand the charging of capacitor.
-∫(from 0 to q) (du/u) = (1/RC) ∫(from 0 to t) dt
Integration equation of the Kirchhoff’s current rule that helps us to understand the charging of capacitor. AFTER THE substitution of u and du
ln(εC - q/εC) = -(1/RC)*t
Kirchhoff’s current rule that helps us to understand the charging of capacitor. AFTER THE integration is done.
(εC - q)/(εC) = e^(-t/RC)
The ultimate final form of the Kirchhoff’s current rule that helps us to understand the charging of capacitor.
q(t) = Cε(1 - e^(-t/RC)) = Q(1 - e^(-t/τ))
Simplifying the results from the ultimate final form of the Kirchhoff’s current rule that helps us to understand the charging of capacitor.
In an equation for the charge on the charging capacitor as a function of time.
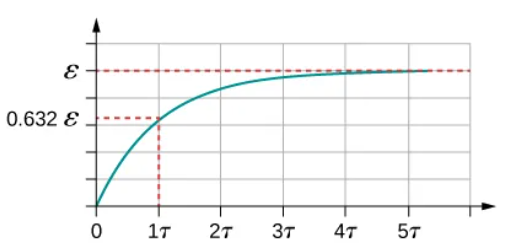
Capacitor’s Charge v/s Time function
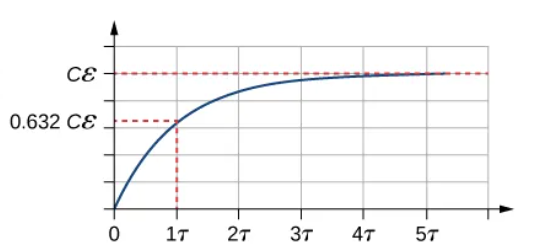
infinity, zero, slope, t = 0.0 s, zero
Capacitor’s Charge v/s Time function shows that as time approaches ________, the exponential goes to ____. The _____ of this graph is large at time ______ and approaches ____ as time increases.
decreases
As the charge on the capacitor increases, the current through the resistor _________
I(t) = dq/dt = d[Cε(1-e^(-t/RC))]/dt
Substituting the equation for the charge on the charging capacitor as a function of time inside the mathematical representation of the electrical current
I(t) = Cε(1/RC)e^(-t/RC) = (ε/R)e^(-t/τ) = I0e^(-t/τ)
Derivation of the formula for the current in the resistor inside the RC circuit.
1 - e^(-1) = 1 - 0.368 = 0.632
At time t = τ = RC, the charge is equal to ________ of the m
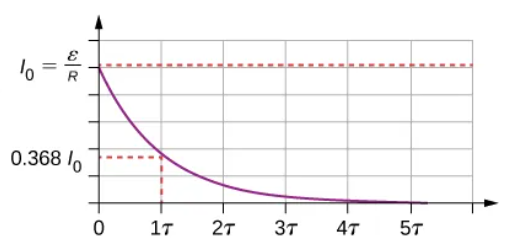
Resistor’s Current v/s Time function
Capacitor’s Voltage v/s Time function
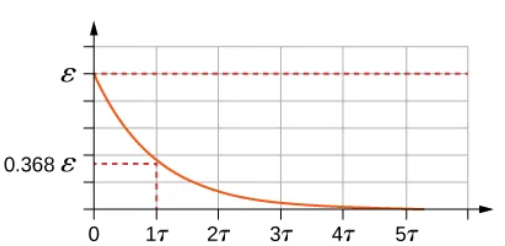
Resistor’s Voltage v/s Time function
Q = Cε
Max. Charge formula
I0 = ε/R
Initial current through the resistor formula at time t = 0.0s
I(t = τ) = I0*e^-1 = 0.368*I0
Inside the resistor in the charging RC circuit, at time t = τ, the current through the resistor will be I(t = τ) which will be…
I(t) = I0*e^-t/τ
Current through the charging RC circuit.
V(t) = ε(1 - e^-t/τ)
Voltage difference across the capacitor when it’s increasing
Vr(t) = (I0*R)e^-t/τ = εe^-t/τ
Voltage difference across the resistor
decreases, decreases, increases
As the charge on the capacitor increases, the current through the resistor _________ and the voltage across the resistor _________. The voltage across the capacitor _________.
-Vr - Vc = 0
Equation given by the Kirchhoff’s loop rule to understand the discharging of the capacitor.
IR + q/C = 0
Substituting the definitions of Vr and Vc in the equation given by the Kirchhoff’s loop rule to understand the discharging of the capacitor.
(dq/dt)R = -q/C
Substituting the mathematical representation of the current inside equation given by the Kirchhoff’s loop rule to understand the discharging of the capacitor (Definitions of Vr and Vc are already substituted)
q(t) = Q*e^(-t/τ); Q represents the initial charge
Charge on the capacitor (while discharging) formula
Yes, it is true
Is it true, that the charge in the capacitor during the discharge decreases exponentially from the initial charge, approaching zero as time approaches infinity?
resistance, Internal resistance, resistance, internal resistance, slower
The __________ while charging is significantly greater than while discharging.
___________________ of the battery accounts for most of the __________ while charging.
As the battery ages, the increasing ___________________ makes the charging process even ______.
Relaxation oscillator
A device consisting of a voltage source, resistor, capacitor, and neon lamp.
Used for controlling the indicator lights to flash at certain frequencies, also used for controlling the windshield wipers.
open-circuit (infinite resistance), zero resistance, capacitor, discharges
Neon lamp acts as a _____________, until it reaches a specific voltage, at that voltage, the lamp acts like a short-circuit (__________) the _________ __________ through the neon lamp and produces light. Before that it is charging the capacitor.
Functionality of the relaxation oscillator
Neon in the lamp breaks down, and allows the capacitor to discharge through the lamp, producing a bright flash.
tunnel diode, transistor
Other uses of the relaxation oscillator inside the electronic circuits where the neon lamp replaced with the __________ or ___________.
It’s like a voltage controlled switched. Normally open but when the right voltage is applied it closes and conducts
The switch can be used to turn on the another circuit (turn on light or run a small motor)
The relaxation oscillator can be used to make the turn signals or to vibrate the phone.
F = 1/T
Formula to calculate frequency.
increases, increases
Increasing the resistance ________ the RC time constant, which _________ the time between the operation of the wipers
Heart rate
Normally controlled by the electrical signals, which causes the muscles of the heart to contract and pump the blood.
Pacemaker
A device that have sensors that detects the body motion and breathing to increase the heart rate during physical activities, thus meeting the increased need for blood and oxygen.
In this device an RC timing circuit is used to control the time between voltage signals to the heart.
RC filters
Device used in the AC circuits to filter out the unwanted frequencies from the signal
555 timer
A device that provides timed voltage pulses. The time between these pulses is controlled by an RC circuit.
Rheostat
A variable resistor with a knob of slider, that gets used to control the current by adjusting the resistance in a circuit. (Is sometimes the part of an RC circuit)
output of the capacitor, voltage-controlled switch, discharging, capacitor, capacitor
Inside the windshield wipers, the ___________________ is used to control a ______________________; that normal is open but when the output reaches a certain.value it closes, energizing an electric motor, and __________ the _________. The motor causes the windshield wipers to sweep once across the windshield and the ___________ begins to charge again.