DNA structures and replication one pager
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
How does cell divsion start
begins with DNA replication
DNA replication
An exact copy of all the cells DNA must be made. includes Copying all 46 chromosomes
DNA is a what
Nucleic acid
Dna does what
Stores cellular information needed to build and maintain a cell
What is DNA composed of
nucleotide monomers
Nucleotide includes
Nitrogenous base
Sugar molecules (deoxyribose)
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous Bases
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
Bonds in DNA
DNA exists as 2 strands are held together by interactions between nitrogenous bases (Hydrogen bonds)
2 groups for nitrogenous bases
Purine
Pyrimidines
Purines
Two rings (A and G)
Pyrimides
One ring, T and C
Bonds and nitrogenous bases
2 hydrogen bonds between A and T
3 hydrogen bonds between C and G
Anti Parallel
Two strands run in opposite directios
5’ end
3’ end
5’ prime
has a phosphate group
3’ prime
has an OH group where dehydration reactions take place
RNA
single stranded
U instead of T
contains ribose
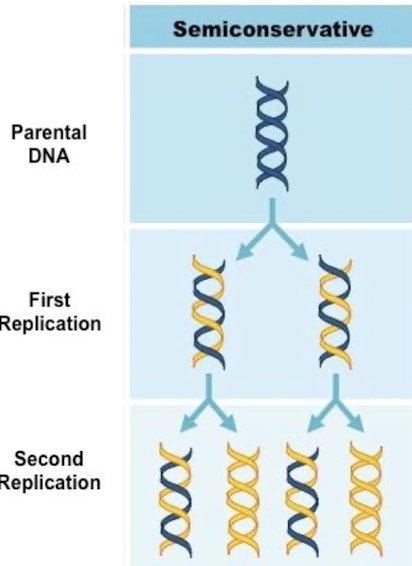
Semi conservative replication
One of the original strands is conserved in the new double stranded DNA molecule
DNA replication steps
Two strands of orginal DNA are seperated
Each stand is used as a template to build a new DNA strand
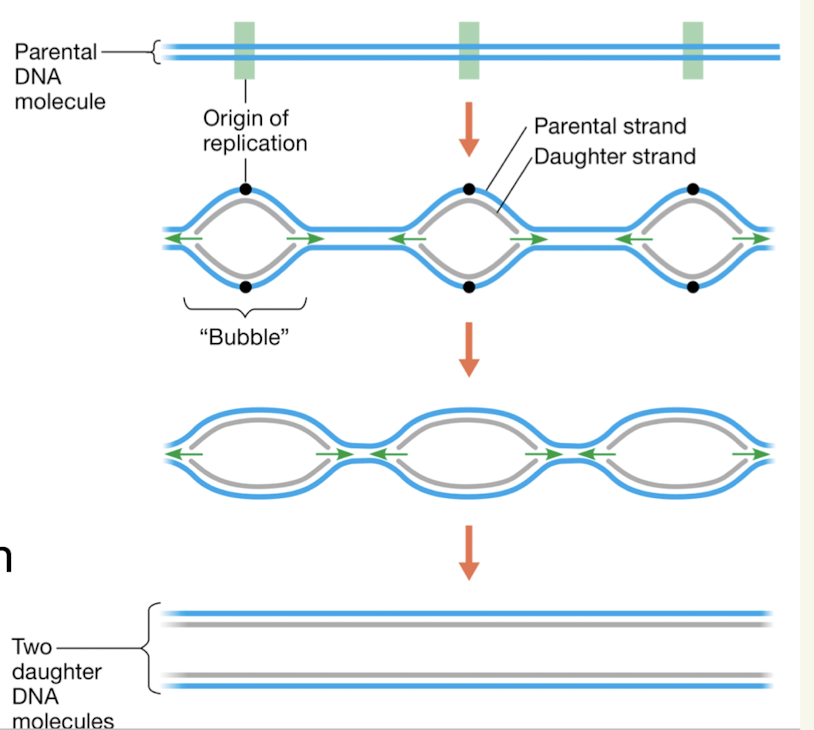
3 basic ideas of DNA replication
First step is to unwind and seperate 2 strands of DNA
New DNA nucleotides are added in the 5’ to 3’ direction
One strand is built continuously (leading) while the other strand is made in segments (lagging)
Orgins of replication
DNA replication occurs at these regions along DNA simultaneously
Bubble
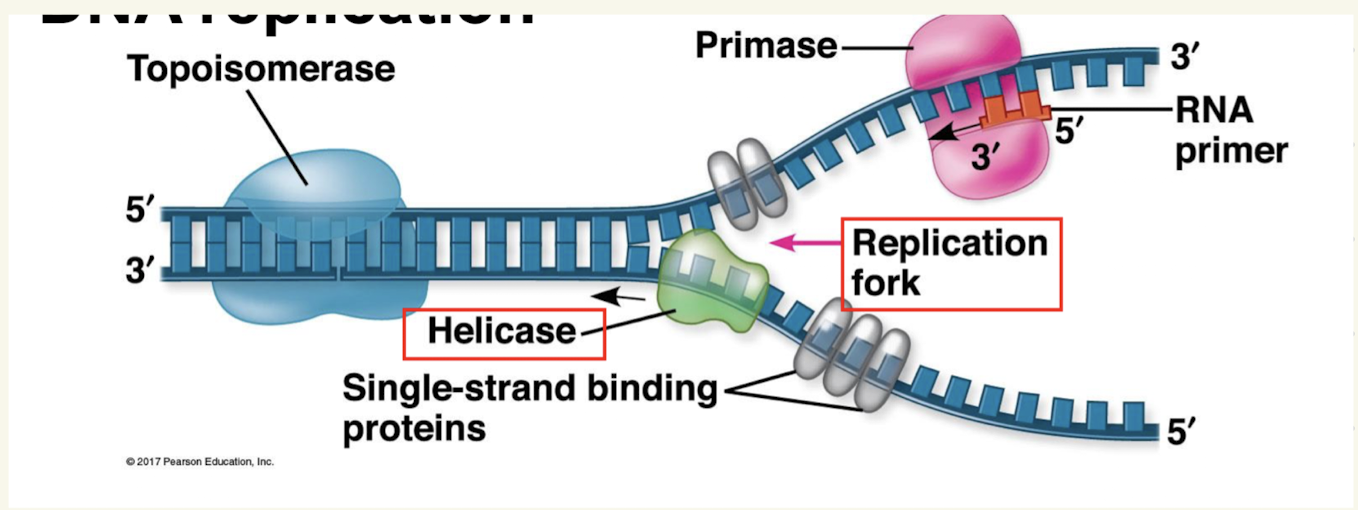
DNA helicase
unzips the DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the two strands and produces a replication fork
Tapoisomerase
An enzye that unwinds the DNA just before the replication fork to ensure smooth unzipping
Single strand binding protiens
Prevent the unzipped DNA from re-zipping
Primase
An enzyme that adds termpoary RNA nucleotides to the unzippled DNA strands (5’ to 3’ direction)
RNA primer
RNA nucleotides which provide a starting point to add a new DNA nucleotide
Provides an OH group that DNA nucleotides need to be attached to
DNA polymerase III
Enzyme responsabile for the addition of the DNA nucleotides for the new strands
Leading strand
Easy to make becayse it grows in the direction of the replication fork (5’ to 3’)
Lagging strand
Built in the direction away from replication fork
requires strand to be made in segments instead of continuously
Lagging strand Steps
RNA primers are added, however they are spaced out
RNA polymerase III can add new DNA nucleotides between the primers
RNA primers are removed and gaps are filled in by DNA polymerase I
DNA backbone (phosphate and sugars) are attached by DNA ligase
is DNA replication accurate
YES EXTREMELY
Terms to know
this important pic