Week 2: Lecture 3 - Physical Growth & Motor Development through the Lifespan
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Phylogeny
- Evolutionary development of a species
• Hundreds or thousands of years
Ontogeny
Development that occurs over the life span of one individual
What type of change happens in the prenatal period?
- One of immense physical change
What does the Prenatal begin with?
- Begins with genetic transmission and continues through a number of cellular and structural variations
What is development like in the prenatal period?
- Development of the embryo and fetus is genetically predetermined, but there are several environmental influences on prenatal development
- Significant stages of growth and development within this period are the embryonic period (up to 8 weeks) and the fetal period (8 weeks to birth)
What is the time range of the prenatal period?
(from Conception to Birth)
What is the first month of infancy known as?
- The first month of infancy is known as the neonate period
What is the time range for infancy?
(from Birth to 2 Years)
Why is infancy a popular area of study?
- Popular area for specialized study because of the possibilities for observing initial motor responses and infant survival characteristics
Who are infants dependent on?
- Extensive dependency on adults
What is Infancy the beginning of?
- Beginning of many motor and psychological activities such as language, symbolic thought, and sensorimotor coordination
What happens in Early childhood (2 to 6 years)
• Time in which the child prepares for and enters school
• Significant stage in the development of fundamental motor skills, perceptual- movement awareness, and the ability to care for onesel
What happnes in Later childhood (6 to 12 years)
• Period of fundamental motor skill refinement and the mastery of certain academic skills
• Physical growth slows substantially
• Thought processes are usually more concrete than in the adolescent period
What does adolescere in Latin mean?
"to grow into maturity"
Adolescence (from 12 to 18 Years)
Physical changes relating to one of the major landmarks in human development: puberty
What are a few characteristics of puberty
• Accelerated growth in height and weight
• Appearance of secondary sex characteristics
• Ability to reproduce
• Deepening of the voice
• Degree of logical and abstract thought increases as well as a concern about identity
and independence
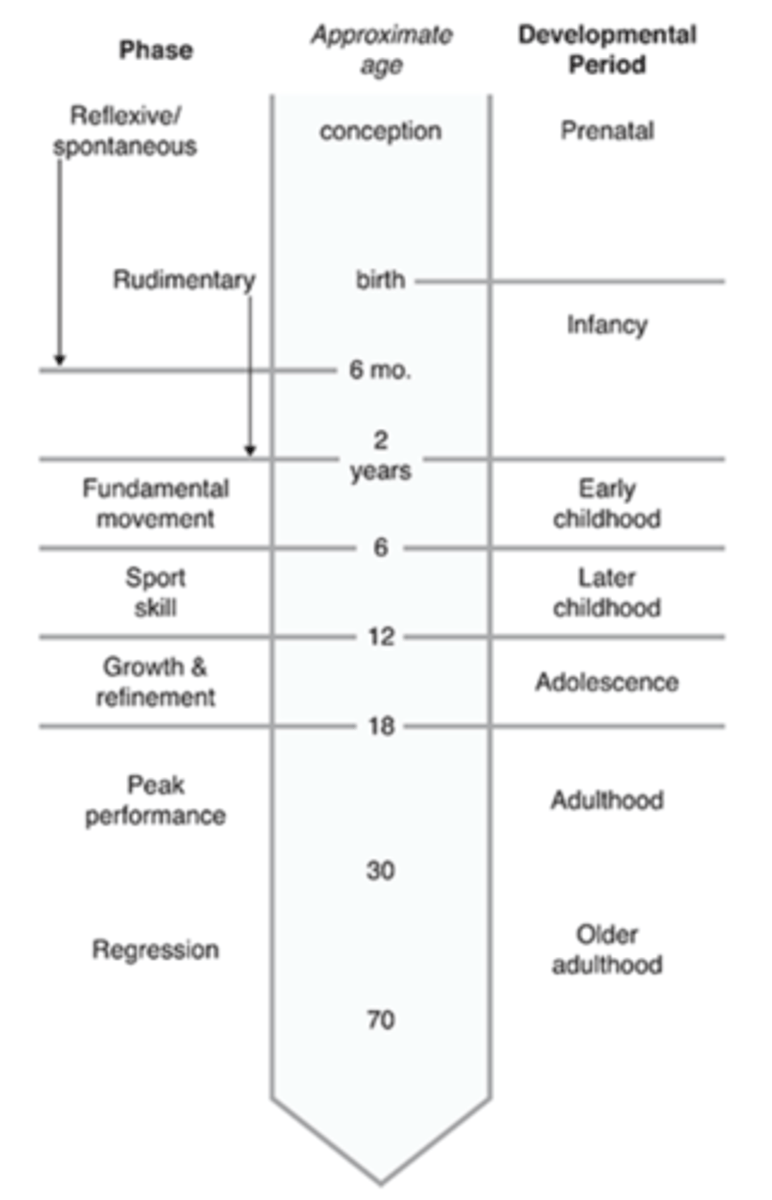
Seven Movement Phases through the Lifespan
1. REFLEXIVE/SPONTANEOUS
2. RUDIMENTARY
3. FUNDAMENTAL
4. SPORT SKILL
5. GROWTH & REFINEMENT
6. PEAK PERFORMANCE
7. REGRESSION
What is the age range for adulthood?
18 years old
What is the age range for young adulthood?
18 years to 40
What is the age range for middle-aged adulthood?
40 to 60 years
What is the age range for older adulthood?
60 years and older
Reflexive/Spontaneous Movement Phase
- As the system matures, reflexes & spontaneous movements are gradually phased out as voluntary control increases
When is the reflective phase?
- Span of motor behaviour that begins at about the third fetal month and continues after birth into the first year of life
What do movements in the reflexive phase mirror?
- Movements at this phase mirror the relative immaturity of the nervous system
What are Reflexes?
Involuntary motor response
What is Spontaneous movements?
Stereotypic rhythmic patterns of motion that appear in the absence of any known stimuli
When in the Rudimentary Phase?
- Corresponds with infancy
What is the Rudimentary Movement Phase?
- Voluntary movement in its first form
- Motor control generally develops in cephalocaudal/proximodistal order
What are movements determined by?
- Movements are determined to a large extent by maturation and appear in a somewhat predictable sequence
What are rudimentary movements characterized by?
Characterized by such behaviours as crawling, creeping, walking, and voluntary grasping
When is the fundamental movement phase?
- A major milestone of early childhood and of life-span motor development
- An outgrowth of rudimentary behaviour
what is Fundamental Movement Phase?
- Establish the foundation for efficient and more complex human movement in later phases of development
- More than 30 characteristic movement skill abilities that emerge during the early childhood period have been identified
What are a few fundamental movement abilities?
•Perceptual-motor awareness (body awareness, balance)
•Locomotor skills (running, jumping)
•Nonlocomotor skills (twisting/turning, stretching/bending)
•Manipulative skills (throwing, kicking
What is the Sport Skill Movement Phase?
- Motor skills and movement awareness abilities the child acquires during the fundamental movement phase gradually become more refined and, in many instances, adapted to sport and recreational activities
What is the importance of primary stimulus in the sport skills phase?
- The primary stimuli during this phase are the individual's
increased interest in sport skill events and the ability to learn and practice these movements
When does growth occur?
- Growth may occur during all periods of development
When is the most significant motor behaviour change occurs?
- Most significant motor behavior change is seen at the time of puberty and the accompanying growth spurt that generally marks the first stage of adolescence
Growth & Refinement Movement Phase - what is the importance of hormones?
- As the levels of hormones rise in the body, changes in muscle and skeletal growth provide a new dimension within which acquired motor skills can be asserted
Growth & Refinement Movement Phase - sex differences
- During the later stages of adolescence, sex differences (mainly favoring males with regard to physical size) become more apparent due primarily to the increased amount of androgen hormones
Peak Performance Movement Phase
- Time of peak performance (peak physiological function and maximal motor performance) is between 25 and 30 years of age
- As a general rule, females tend to mature at the lower end of the range (from 22 to 25 years) and males at the upper end of the range (from 28 to 30 years)
Especially evident in three of the most influential factors in motor performance:
• Strength
• Cardiorespiratory function
• Processing speed
What is the time of peak performance?
The time of peak performance (peak physiological function and maximal motor performance) is between 25 and 30 years of age
When do females and males begin to mature?
Females tend to mature at the lower end of the range (22-25)
Males at the upper end of the range (28-30)
What is peak performance, especially evident in?
- most influential factors in motor performance
- Strength
-Cardiorespiratory function
-Processing speed
When does the regression phase occur?
- Considerable variation among individuals is apparent after 30 years of age
What is the regression phase?
- Most physiological and neurological factors decline at a rate of about 0.75% to 1% a year
What appears first in the regression phase?
- Psychomotor slowing (primarily in speeded tasks) appears
- The earlier developmental process of differentiation begins
to reverse
- Similar performance characteristics among the very young and the older adult
What do you see decreases in during the regression phase?
- Decreases in:
Cardiovascular capacity
Muscle strength and endurance
Neural function
Flexibility
Increases in body fat
Regression Movement Phase and Exercise Influence
- Although exercise has not been shown to stop the aging process, it does allow the individual to perform at a higher level
Physical Growth & Motor Development through the Lifespan