L 17 - drug solubility and dissolution rates 1
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Explain why changes in pH of the GI tract effect dissolution rate and solubility?
It changes ionisation
Solubility changes
A drug must be dissolved before it can be absorbed
So ionisation and drug solubility affects the rate and extent of absorption
Since the GI tract ph can't be changed the drug must be designed to behave accordingly.
How can you find the ratio of unionised to ionised form of a drug
First use the rate constant equation to find K
Then convert from K to PKA
Then use henderson-hasselback equation and input the pH of the environment to find the ratio!
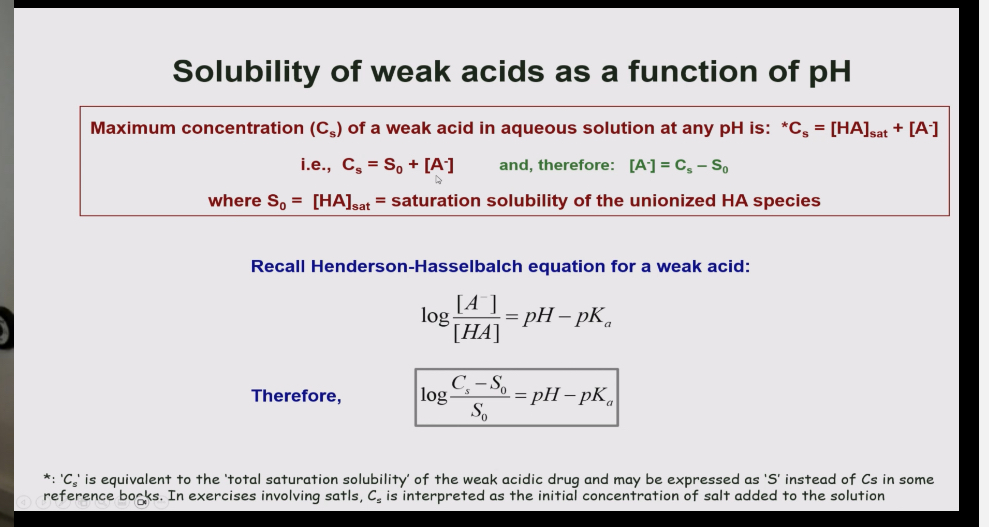
Explain the solubility of weak acids as a function of ph.
.in a weak acid when the pH of the area is acidic the equilibrium shifts towards the unionised side so the drug is less soluble.
But when the ph is increased and its more basic the equilibrium shifts so that it is in the ionised side so the drug is more soluble.
How do you calculate the solubility of a weak acid
Remember:
total solubility = solubility of ionised - concentration of ionised
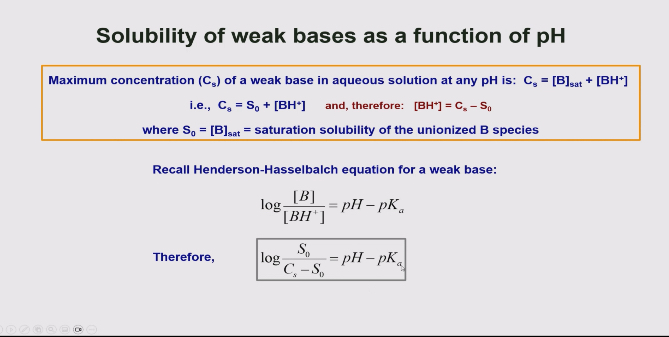
Explain the solubility of weak bases as a function of ph
When you increase the pH ( basic conditions) the equilibrium shifts towards the unionised side so its less soluble.
When you decrease the ph (in acidic conditions) it shifts towards the ionised so increased solubility.
How do you calculate the solubility of a weak base.
Explain what happens when the salt of a weak acid / base is used of the free form instead in a solution.
As a conjugate base is made the pH increases in the solution so the solubility also increases
In a weak base as a strong acid is made the pH is lowered in the solution so the solubility is increased also