UCM Chapter 11 Biochem
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
monosaccharides
simple sugars
building blocks
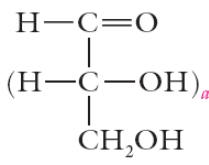
aldehydes are called aldoses
ketones are called ketoses
ketoses
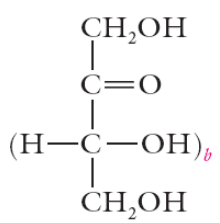
aldose
nomenclature of carbohydrates
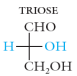
Trioses – 3 carbon sugars (C3H6O3)
Tetroses – 4 carbon sugars (C4H8O4)
Pentoses – 5 carbon sugars (C5H10O5)
Hexoses – 6 carbon sugars (C6H12O6)
Heptoses – 7 carbon sugars(C7H14O7)
2x = possibly # of sugars
x= # of chiral centers
highest # chiral carbon defines chirality
glyceraldehyde
glucose
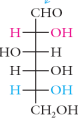
galactose
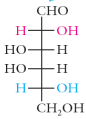
mannose
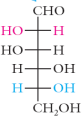
ribose

fructose
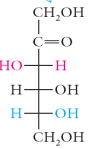
dihydroxyacetone
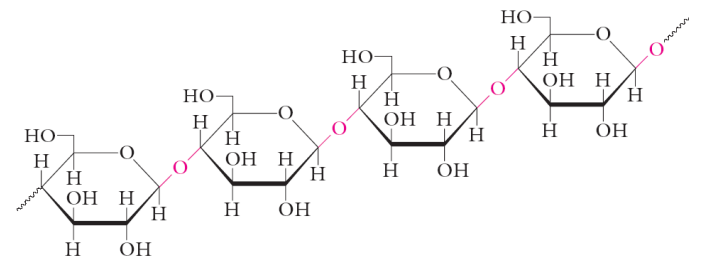
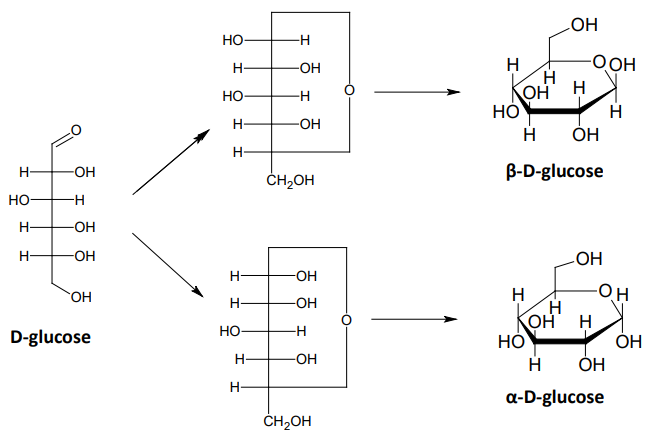
cyclic structures of monosaccharides
Sugars with 4 or more carbons exist primarily in cyclic forms
Aldehydes react with alcohols to form hemiacetals
Ketones react with alcohols to form hemiketals
Five and six member rings are the most common
anomeric carbon
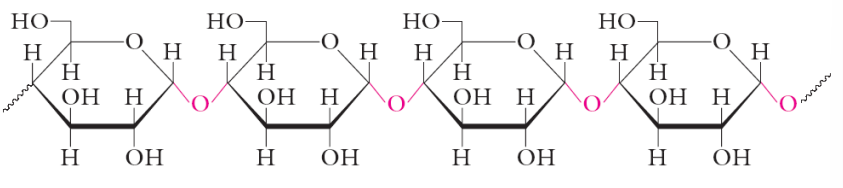
starch
Homopolymer consisting of only glucose units • energy reservoir in plants • source of carbohydrates for humans • two polysaccharides occur in starch: amylose and amylopectin
amylose
• long unbranched chains of D-glucose residues • linked with α(1,4) glycosidic bonds • typically several 1000 glucose units • form long tight helices
amylopectin
branched homopolymer of glucose • contains α(1,4) and α(1,6) glycosidic linkages • branch points occur every 20-25 units • few 1000s to a million units
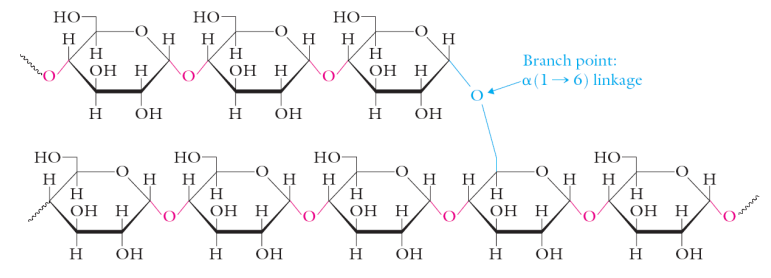
glycogen
carbohydrate storage molecule in vertebrates • greatest abundance is in muscles and the liver • contains α(1,4) and α(1,6) glycosidic linkages (same as amylopectin) • branch points occur more regularly • more compact for better storage
cellulose
composed of D-glucose units linked by β(1,4) glycosidic linkages • structural role in plants • most abundant organic molecule on Earth • we lack the enzyme to hydrolyze the β(1,4) linkages