Intro to Communications Chapters
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Non-Verbal Communication (body language, facial expressions), Paralanguage Communication (non-verbal elements - tone, pitch, volume, & vocal quality), and Language Communication (verbal - spoken or written words)
What are the three Communication Codes?
Stimulus
Something needs to happen in order for you to be motivated to communicate
Encoding
Converting thoughts or information into a comprehensive message for transmission
Decoding
Understanding and interpreting the message
External Noise
Distraction that is outside of the communicators' exchange (ex. lawnmower noise, side conversation, construction)
Internal Noise
Distraction which is internal for the communicators (ex. headache, anxiety, anger, biases, cognitive limitations)
Level of Observation
Question of Intent
Point of View
Issue of Outcomes
The Definition of Communication can change based on looking at..
Message
Any symbol or collection of symbols which have meaning or utility; ex. speeches, letters, emojis, comics, paintings, poems, advertisements
Explain, predict, control, everyday, everyday, granted, stable, change
Personal theories: Helps _______, ________, and _______ ________ phenomena and circumstances
Based on ________ Experience
Taken for _______
Stable
Private
Resistant to ______
Question, assumptions, needs
Uncommon sense: Allows us to continually ________ our own __________ and become attentive to others' _____ and perspectives
Scholarly theories
Systematic frameworks used to explain, predict, or understand phenomena within specific academic disciplines, often based on empirical evidence and rigorous analysis.
Public
Questioned
Subject to change
Systemic testing and observation
Systems Perspective
Multiplicity of factors: multi-dimensional, multi-directional, and extremely complex process of involving messages that can be intentional or unintentional
Simplies the communication process into five key elements: who (the sender), says what (the message), in which channel (the medium), to whom (the receiver), with what effect (the outcome).
Lasswell’s View
Linear model that conceptualizes communication as a process involving a sender, a message, a channel, a receiver, and noise
Also distinguished between a message and signal
Information source and transmitter
Receiver and destination (decodes and interprets message @ the destination)
Shannon and Weaver’s View
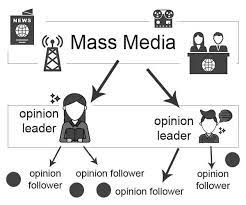
Suggests that media messages first influence opinion leaders, who then disseminate and reinterpret these messages to the broader population
Katz and Lazarsfeld’s View
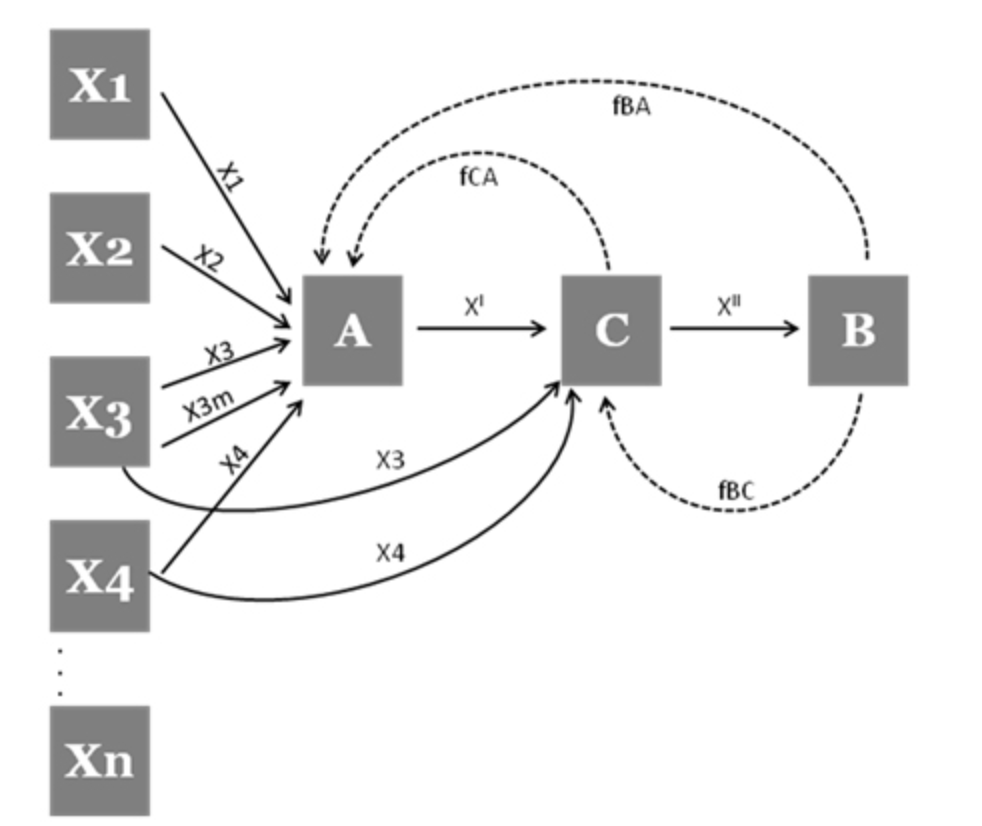
Highlights feedback loops between these elements, recognizing that communication is not a linear process but rather one that involves continuous interaction and adjustment between sender and receiver.
Westley and MacLean’s View
Open Systems
Those (animals and humans) that continually participate in give-and-take transactions with their environment which are essential to survival
Visual
Tactile
Gustatory
Olfactory
Auditory
What are the Communication Models?
Self-Reference
The meanings we learn attach to the symbols we use always reflect our own experiences. The things we say or do and how we interpret others’ words and actions are a reflection of our experiences and expectations.
“Kimchi is spicy,”
“It sure is cold today”
“That teacher was excellent”
Self-Reflexivity
Allows individuals to view themselves "self" - as part of and apart from their environment (allows us to theorize about ourselves and our experiences)
The Principle of Nonidentity
Words are not the same order of stuff as the realities they refer to
We don't deal with reality, we deal with what we say about reality
World is constantly changing, while language may not
The Principle of Non-Allness
Our language can never represent all the objects, events, or people to which we are referring
No matter how good a map you make, you can't represent all of the territory
The Principle of Self-Reflexiveness
When we use concepts, we become increasingly abstract and away from the world of the tangible
One cannot be a success or failure but only seen or interpreted as one by someone
The Pygmalion Effect
Higher expectations lead to an increase in performance
- If a person is given higher expectations or treated as though they are capable of achieving more. , they are likely to perform better
- Conversely, low expectations can lead to diminished performance and potential.
Authentic Theory of Communication
"Prose ought to be maximally transparent and minimally self-conscious"
Ex. Undamaged, intact messages through the transmission process such as through telephone and video
- Clear, concise, trustworthy
- Unified by authentic human communication
Reflective Theory of Communication
- George Mead: Being human is more than our ability to be ourselves
- Communication is collected by social norms and expectations of common cultural values
- We are less our own authors than we might believe
- Person's ability to integrate social activities of background / culture --> living to your highest potential
- People are like mirrors to one another
- When we interact with others we can see parts of ourselves
- We define ourselves by what we see in the reflections
Artful Theory of Communication
Privileges the individual
- Concentrates on how human identity is built rather than revealed
- People craft and select their identities as a desire to influence how others see us; "designing ourselves"
- Automobile industry: Social competition and status symbolism
Euphemism
Words used in places of terms that some people might find offensive (Ex. flight attendent vs stewardess)
Bypassing
When two individuals miss each other’s meaning because they are using equivocal language (She’s super nice and The class will be easy - both are subjective and dependent on the individual)
Fundamental Attribution Error
Refers to an individual's tendency to attribute another's actions to their character or personality, while attributing their behavior to external situational factors outside of their control.
Social Comparison Theory
Image of self is based on the way we compare ourselves to others
Reflected Appraisal Theory
Image or self reflects the way we believe others see us
Self-Appraisal
Wherein an individual assesses their own performance, skills, strengths, weaknesses, and contribution
Confirming Responses
__________ support our self appraisal (others treat us how we are expected to be treated)
Rejecting Responses
__________ negate our self appraisal (others treat us in a way we do not expect, based on our self-concept)
Disconfirming Responses
__________ rob us of our sense of self (others treat us as if we were irrelevant)