NUTR 3360 Final - Short Answer Questions
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Does obesity alter life expectancy?
Early onset obesity has a greater impact on quality of life and life expectancy. Increased obesity correlates to years lost.
What is weight cycling? How does weight cycling impact risk of diabetes?
Weight cycling is the cyclic pattern of losing and gaining weight. This increases the risk of diabetes more maintaining an elevated BMI.Ex
Explain the c-value paradox.
Organismal complexity is not correlated with genome size.
The human genome was simultaneously sequenced using which methods?
BAC sequencing (public consortium) and shotgun sequencing (private consortium)
When studying a weight loss intervention between twins and between twin pairs, what is observed? What do these results imply?
Twins respond similarly to the same intervention, but there are many differences in response between twin pairs. This implies that there is a major genetic component to obesity.
Explain the genetic conflict theory.
Paternally expressed genes maximize maternal resources to the fetus so that the offspring has the best chance of survival. Maternally expressed genes minimize maternal resources to increase chances of the mother and offspring surviving.
What is genomic imprinting? Name 2 disabilities associated with genomic imprinting.
Genomic imprinting is the silencing of one gene copy (paternal or maternal) during egg or sperm formation. Prader-Willi Syndrome and Angelman Syndrome are possible results of incorrect gene imprinting.
What are SNPs? Name 2 genes where SNPs are strongly associated with obesity.
Single nucleotide polymorphisms are common (>5% of population) variations in a single allele, which may or may not change an amino acid. Strongest SNP and obesity associations are in FTO and MC4R genes.
What effect does the expression of FTO incur? What would result with FTO knock down?
FTO is anorexigenic. Decreased expression of FTO would increase energy intake.
Which would be more accurate prediction of obesity: parental BMI or genetic analysis?
Parental BMI.
In which trimester is maternal nutrition most important for the health of the offspring?
Mothers malnourished only in the first trimester birthed normal weight babies with higher rates of obesity and other health problems. Malnourishment only in the third trimester birthed small babies with lower rates of obesity.
What is the Barker Hypothesis?
Infant mortality is a marker for poverty due to the effect on maternal nutrition and quality of breastmilk.
What is the thrify phenotype hypothesis?
Poor nutrition in early life produces permanent changes in genes related to glucose-insulin metabolism.
Define epigenetics.
Changes in cell function that do not alter DNA sequence.
Give some examples of epigenetic influence.
Genetic conflict theory, fetal glucocorticoid exposure, mal/overnutrition in utero, malnutrition in early life.
Name 2 regions of the genome that are sensitive to epigenetic changes.
Promotor regions and metastable epialleles.
Which epiallele is completely determined by genetic variation?
Obligatory.
Which epiallele is determined partly by genetic variation but influenced by environmental factors?
Facilitated.
Which epiallele is completely determined by environmental influence?
Pure.
The agouti mouse is an example of which epiallele? Hypermethylation of IAP in these mice result in what phenotype?
Facilitated epiallele resulting in normal weight, brown fur mice.
Which type of obesity of most responsive to treatment?
Monogenic obesity.
Leptin expression increases with ______ energy balance, meaning leptin levels are _____ and _____ correlated with body fat.
positive, strongly, positively
Obesity is associated with ______ and ______
leptin, insulin
At age 3 with a weight of 40kg, where does this patient fall on the WHO growth chart?
97th percentile.
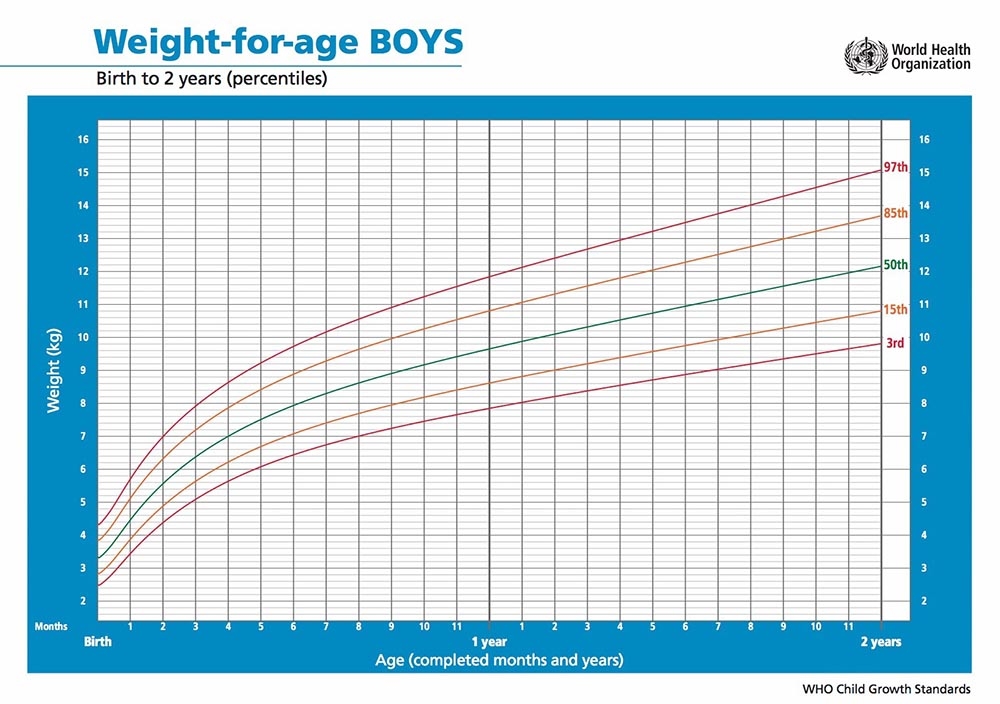
A pediatric patient is in the 97th percentile on the WHO growth chart and presents with hyperphagia, no developmental delays. Parents are a normal BMI. What kind of obesity do you suspect? What would you test in their blood to investigate this suspicion?
Monogenic obesity suspected. Can test for leptin.
The obese pediatric patient has no leptin in their blood plasma. What type of monogenic obesity would you diagnose? How would you treat this disorder?
Congenital leptin deficiency; can be treated with leptin therapy.
The obese pediatric patient has normal leptin levels in their blood. What type of monogenic obesity would you diagnose? Would you recommend leptin therapy?
LEPR mutation; leptin therapy would be ineffective since leptin is unable to act on the cells.
The obese pediatric patient has normal leptin levels but presents with hypocortisolism, malabsorption, and impaired glucose homeostasis. What type of monogenic obesity would you diagnose? Which enzyme is impacted by this mutation? What is a phenotypic trait that is indictive of this disorder, but not exclusive?
POMC mutation effects PC1 enzyme (PC1 cleaves POMC); red hair is characteristic of this mutation.
Why is cortisol production impacted by POMC mutation?
POMC in the adrenal glands is cleaved by PC1 to stimulate cortisol production.
A pediatric patient was a normal birth weight and is now in the 97th percentile on the WHO growth chart and presents with hyperphagia, no developmental delays. One parent is a normal BMI, the other was also a normal birth weight before remaining in the 97th percentile of BMI. The patients sibling is a normal BMI. What kind of obesity do you suspect? Why?
MC4R mutation from the obese parent. This mutation is autosomal dominant and the most common cause of monogenic obesity.
Activation of POMC/CART neurons will ______ food intake and ______ energy expenditure.
inhibit, increase.
Activation of NPY/AgRP neurons will ______ food intake and _______ energy expenditure.
stimulate, decrease.
MC4R activates _______ neuron and inhibits ______ neuron.
PVC, NPY/AgRP
Describe signal integration of ghrelin, glucagon, insulin, and leptin following a meal in an (a) healthy adult and (b) adult with T2D.
(a) low ghrelin, low glucagon, high insulin, no acute response of leptin.
(b) low ghrelin, high glucagon, low insulin, no acute response of leptin
Ghrelin activates ______ neurons to _______ energy intake.
NPY/AgRP, promote
What are the two most diverse and abundant gut bacteria families in the human GIT?
Firmicutes and bacteriodetes.
What are the different ways a GIT could be considered healthy in terms of gut bacteria?
Stable (resistant to stress, return to equilibrium after stress perturbation), optimal collection of microbial genes and functions (not specific microbes, but microbes to perform necessary functions), and diversity .
Reduced microbial diversity in the GIT is associated with ______ and _______ _______ ______
obesity, inflammatory bowel disease.
When performing SSU RNA on two different, healthy people, their microbial population is very different. Is this normal? Why or why not?
Yes, it is normal for large variation between people, but the functional potential is consistent.
A mother births twins, one vaginally and the other through a C-section. Are the twins expected to have similar microbial populations? Is one twin expected to be metabolically healthier than the other?
The twins will have different microbial populations. In utero, there is no microbial population. When birthed, the gut is populated with the environment. The vaginal birth is populated with secretions of the vagina while the C-section birth is populated with skin bacteria. The twin birthed vaginally is expected to be metabolically healthier due to its microbial population.
Aiden decides to try new diets and perform SSU RNA on his feces following each diet. After 2 days of starting a new diet, what changes should he expect in SSU RNA analysis?
Very little impact as temporary changes in diet have little impact on the microbiome.
Aiden has now completed 5 days of a plant based diet. What changes should he expect to see in SSU RNA analysis?
No major changes in the microbiome.
Aiden completes 5 days of an animal based diet. What changes should he expect to see in SSU RNA analysis?
Rapid increase in microbial diversity for as long as the diet continues.
Describe how increased gut bacteria influences adipocytes.
↑gut bacteria → ↓FIAF expression → ↑LPL → ↑fatty acid uptake by adipocytes → ↑body weight
Obese gut microbial proportions are likely to have more ______ and less ______
firmicutes, bacteriodetes
Fecal samples are analyzed for energy content of an obese patient and a lean patient on the same diet. Which sample is likely to have more energy content and why?
Lean is more likely to have more energy in their feces because they have less firmicute populations. Firmicutes digest dietary starch, which contain a lot of energy.
An obese patient is recommended treatment with fecal transplant from a lean donor. What changes are seem with respect to BMI, bile acids, microbial diversity, and satiety?
no change BMI, ↓ bile acids, ↑diversity, ↑satiety (GLP-1)
A high fat diet is expected to impact gut permeability through what lipid molecule? What are the downstream effects of this lipid molecule?
LPSAppl is present in high fat diets and interacts with CD14 on immune cells to initiate a pro-inflammatory response.
What happens with KO CD14?
Protected from an inflammatory response from LPS, preserving metabolic health.
Apply the incretin effect to two metabolically healthy patients taking a glucose tolerance test. Patient A was given oral glucose and patient B was given glucose through an IV.
Patient A would show better glucose tolerance because incretins promote the release of insulin, whereas glucose bypassed the gut in patient B, meaning no incretin release.
What are the two primary incretins released?
GIP and GLP-1.
What is the primary transporter to stimulate incretin release? What molecule is it sensitive to?
SGLT1 is sensitive to glucose.
KO SGLT1 is expected to demonstrate what effect?
Decreased GIP and GLP-1 expression, decreasing insulin release.
How is obesity expected to impact GIP and GLP-1 levels?
No change for inactive GIP, decreased active GIP, and total GLP-1.
Tristen has been recommended to take an incretin mimetic. How would this change his insulin response?
An incretin mimetic has the same structure as GIP or GLP-1 but is resistant to DDP. There would be an increased insulin response for longer and improved whole-body glucose homeostasis.
Tristen does his own research and finds an incretin enhancer. How would this be a different response than an incretin mimetic?
An incretin enhancer inhibits the activity of DDP, giving active GIP and GLP-1 a longer half-life. There will be an increased insulin response for longer and improved whole-body glucose homeostasis.
Tristen has been taking Ozempic for a few days and has experienced some side effects: ______, ______, and ______
nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea
What is the most common bariatric surgery? Describe the BRAVE effects that occur as a result.
Most common is RYGP
B- bile flow alteration
R- reduced gastric size
A- anatomical rearrangement
V- vagus nerve manipulation
E- enteric gut hormone modulation
Lauren has had T2D for 6 years, Rachel for 11 years. Both are recommended RYGB. Who will have a more successful diabetes remission? What is expected to occur for both patients 10 years post-surgery?
Lauren will have better remisson from <10years with T2D. Both are expected to regain some weight after 10 years.
After RYGP, a patient is expected to have a stronger incretin effect. Describe why this occurs.
Bile acid mixes with nutrients lower in the SI and often is still present when in the LI. Bile acids in the LI increase GLP-1 release.
After RYGP, a patient is prescribed nutritional supplements. Which vitamin/mineral deficiency is most common in these patients?
Anemia (↓iron), vitamin B12, and calcium.
Kim K has started taking Orlistat. What effect does this have on her GIT and body weight?
Decreased fat absorption due to lipase inhibition in the GIT, decreasing body weight over time.
How many phases is insulin released in? Describe the different phases.
Phase 1 is rapid release from the ready release pool (RRP). Phase 2 is synthesizing insulin from the reserve pool (RP)
How does impaired glucose tolerance and T2D impact the phases of insulin release?
Impaired glucose tolerance reduces RRP and RP. T2D has no RRP and little RP.
When insulin is injected to treat T2D, how does glucagon levels respond? Why?
Glucagon level spike because the pancreas thinks it needs to suppress insulin production since insulin was injected into the periphery, not the portal vein.
A 2 year old patient severe hyperglycemia, but is negative for T1D. What is the alternative diagnosis?
Monogenic diabetes (MODY).
What is knocked out in LIRKO mice? How is whole-body glucose homeostasis altered in LIRKO mice?
LIRKO is the know out of insulin receptors on the liver, meaning HGP is always high.
Does increasing hepatic glucose metabolism improve metabolic disorders seen with LIRKO mice?
Overexpression of hepatic glucokinase (glucose storage enzyme) can partially compensate for lack of insulin signaling.
What are the 4 stages of NAFLD? At what point is NAFLD irreversible?
Steatosis, NASH, cirrhosis, HCC. Once cirrhosis (liver scarring) occurs, the changes are irreversible.
The “first hit” of NAFLD corresponds to _______ ______ in hepatocytes.
Lipid accumulation.
The “second hit” of NAFLD corresponds with inflammation and oxidative stress in the liver. What stage of NAFLD does the second hit progress to?
Steatosis → NASH
Insulin resistance in the liver fails to suppress ______ but continues to activate ______ pathways
gluconeogenesis, lipogenesis.
Why is NAFLD commonly underdiagnosed in early stages?
Diagnostic methods lack sensitivity and accuracy.
Insulin resistance _______ (increases/decreases) NEFA suppression which _______ (increases/decreases) blood glucose.
LPL KO had what effect regarding adipocytes? How did this impact body weight and FA in the blood?
LPL KO reduces FA uptake into adipocytes, so these mice were protected from weight gain. However, there is increased TAG in the blood.
HSL KO had what effect regarding adipocytes? How did this impact FA in the blood?
HSL KO reduces lipolysis, but does not eliminate it. There is reduced FA in the blood.
What are the two mechanisms adipocytes undergo to compensate for excessive energy intake?
Hyperplasia and hypertrophy.
An obese patient is recommended to take TZD treatments. How will this impact metabolic health and body weight?
Improved metabolic health and increased body weight.
Curtis is AA genotype for PPar-alpha gene. Is he expected to be responsive to aerobic exercise for fat loss?
Yes, AA allele is responsive to aerobic exercise.
Chronic nutrient excess promotes macrophage phenotypic switch from _______ → _______
M2, M1
Alyssa is a professional athlete while Sareena works a sedentary job. Both have comparable IMCL levels, but Sareena has low insulin sensitivity. Describe the key difference that prevents IMCL from corresponding with insulin sensitivity.
Alyssa has high oxidative capacity, keeping her insulin sensitivity high. Sareena has high IMCL and low oxidative capacity, corresponding with low insulin sensitivity.
How does FAT/CD36 respond to exercise? What signaling molecule causes this to occur?
AMPK increases with exercise, increasing the amount of FAT/CD36 transporters on muscle cells to increase FA uptake.