9. enzyme regulation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
enzyme regulation mechanisms: Compartmentalization
Compartmentalization within specific organelles
(eg. enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis located in the cytosol, those responsible for FA oxidation in mitochondria)
Changes in protein expression (by activation/inhibition of gene expression)
control of proteolysis
(eg. digestive enzymes synthesized as pro-enzymes (zymogens) and are activated by removal of inhibitory fragment)
Covalent modifications
Allosteric regulation
Control of degradation
covalent modifications
most common = phosphorylation
phosphorylation
catalyzed by kinases, use ATP as phosphate donor
Depending on the enzyme, phosphorylation can increase or decrease its activity
generally under hormonal control
Glycogen phosphorylase
activated by phosphorylation
Glycogen synthase
inactivated by phosphorylation
dephosphorylation
catalyzed by phosphatases
Allosteric regulation
Regulation by allosteric factors
A. Change affinity of enzyme for substrate (Km)
B. Modify catalytic activity (Vmax)
allosteric factors
molecules that bind non-covalently at a site different from
the active site and induce conformational changes in the active site
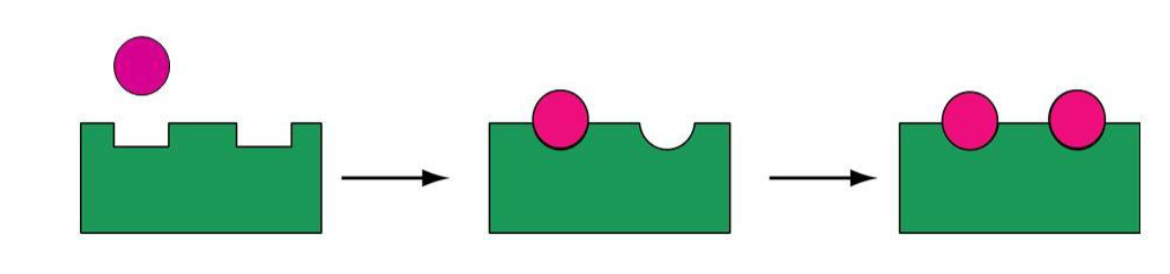
Allosteric modulators: homotropic effect
the substrate acts as allosteric regulator
Typically positive effectors
act by cooperativity (binding at one site, increases binding at other sites)
Allosteric modulators: heterotropic effect
the effector is different from the substrate
Can be positive or negative effectors
Generally act by feedback, where downstream products regulate upstream reactions
Allosteric enzymes
1. Catalyze mostly rate limiting reactions
2. Generally have multiple subunits
3. Do not follow Michaelis-Menten kinetics
4. Are regulated by allosteric activators or inhibitors
5. Activators and inhibitors do not need to have structural
similarity to the substrate structure
6. One enzyme can have one or multiple allosteric sites
7. The reaction is not affected by substrate concentration
Clinically relevant enzymes: Plasma enzymes
Actively secreted in blood (precursors of coagulation enzymes)
Released during cell turnover
Low and constant in healthy individuals
high concentrations of plasma enzymes can indicate
Tissue damage (concentration indicative of damage extent)
Liver damage: increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT)’
Increased cell proliferation
Isoenzymes
alternative enzyme forms (various subunit combinations) that can be separated electrophoretically and can catalyze similar reactions
Might be localized in different cellular compartments or different tissues
Lactate dehydrogenase **KNOW