AP Psychology- unit 6 Development vocabulary
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Crystallized intelligence
our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age (through experience)
Fluid Intelligence
our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease during late adulthood (creativity)
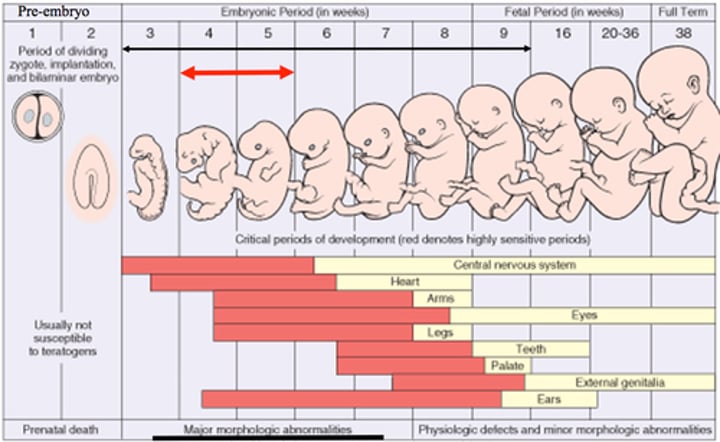
prenatal
9 month development period before birth. cells are forming specific organs.
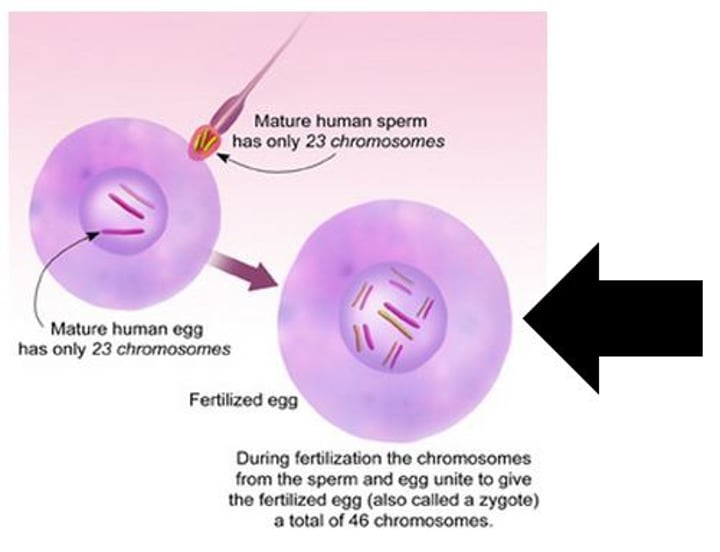
Zygote
the fertilized egg, first stage, 2 week period of rapid cell division, only half survive.
Embryo
2 week to 2nd month, important distinct human organs develop, heart begins to beat, neutral tube (Brain and spinal cord)
Fetus
9 weeks to conception of birth. Development of human organs continue, including stomach, muscle and bones. Dev. enough to survive without mother. Baby is able to hear and recognize sounds and light.
Teratogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm.
Fetal Alchohol Syndrome
physical and cognitive abnormalities in children caused by a pregnant woman's heavy drinking
Maturation
biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience
Cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
Schema
mental structures/ framework that organizes and interprets information/thinking "Building blocks"
Assimilation
interpreting our new experiences or information in terms of our existing schemas or what we already know
Accommodation (Piaget)
modifying/adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information
object permanence
the knowledge/axarness that an object exists even when it is not in sight
conservation
a child's ability to recognize that the volume or amount of a substance or object does not change when its form or shape changes.
Egocentrism
in Piaget's theory, the proportional child's difficulty taking another's point of view. "selfish" "world rotates around you"
Stranger Anxiety
the fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age, once they are able to recognize familiar faces.
Attachment
an emotional tie with another person; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to the caregiver and showing distress on separation
Critical Period
an optimal period shortly after birth when an organism's exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produces proper development.
Imprinting
the process by which certain animals/humans form attachments during a critical period very early in life
self-concept
idea we have about who we are—physically, emotionally, socially, spiritually, and in terms of any other aspects that make up knowledge about who we are
Adolescence
the transition period from childhood to adulthood, extending from puberty to independence
Puberty
the period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing
Social Clock
the culturally preferred timing of social events such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement