Stage 2 Chemistry, Unit 2 - Managing Chemical Process
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
units 2.1, 2.2 and 2.3.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
What 5 factors effect rate of reaction?
Concentration
Pressure
Surface Area
Temperature
Catalysts
What is collision theory?
for a collision to result in a chemical reaction particles must overcome activation energy (Ea) and with the correct orientation. Activation energy is the energy required for a reaction to occur
Rate of Reaction is dependent on
the number of successful collisions which occur within a time span
successful collisions must have
the required activation energy and the correct orientation
How can rate of reaction be measured for gases?
products forming: Gas forming in a syringe (mL/sec) Number of moles forming (mol/sec)
Reactions being consumed: mass being reducing (g/sec)
Concentration of reaction being reduced (mol/L/sec)
What is the product rate of reaction formula?
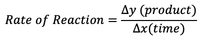
What does a steep gradient mean for a rate of reaction graph
that reactants are rapidly being converted into products
What does a shallow gradient mean for a rate of reaction graph
that reactants are slowly converting into products
How does an increase of concentration increase the rate of reaction?
Increasing the concentration will increase the number of particles, as there is more particles, more collisions will take place. Reactions will occur faster with a high concentration.
How does an increased pressure increase the rate of reaction?
a decrease in the volume of a vessel is the same as an increase in pressure. An increase in pressure means there is less space for the particles to bounce, making it more likely to collide
How does a increase of surface area increase the rate of reaction?
When particles are in a lattice, there are many particles unexposed. By increasing surface area, more particles become readily exposed to to undergo a reaction, meaning all particles can react quicker than in their lattice form.
How does a change in temperature increase the rate of reaction?
by increasing temperature, the number of particles that have sufficient activation energy to undergo a reaction increases. More over, the speed of the particles increases, leading to more collisions.
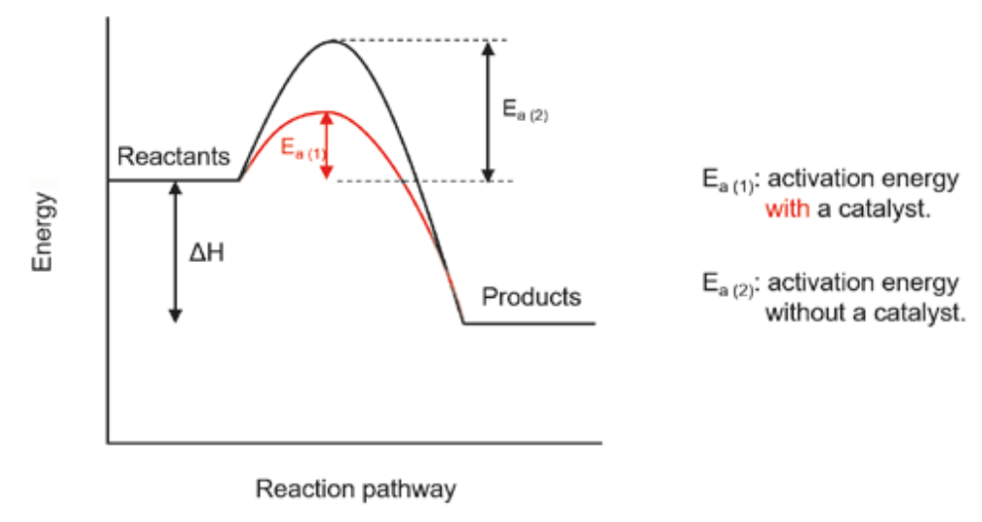
How do catalysts increase the rate of reaction?
Catalysts allow for an alternative pathway in a reaction, which has a lower activation energy, because of this, more reactions will take place through this pathway.
In chemical reactions, energy is needed to
break the bonds of reactants
in chemical reactions, energy is released when
new bonds are formed.
If a reaction has an overall increase (absorption) of energy
it is endothermic
If a reaction has an overall loss (release) of energy,
it is exothermic.
What are energy profile diagrams?
they are diagrams display a system’s change in energy throughout a chemical reaction. (display either an exothermic or endothermic reaction)
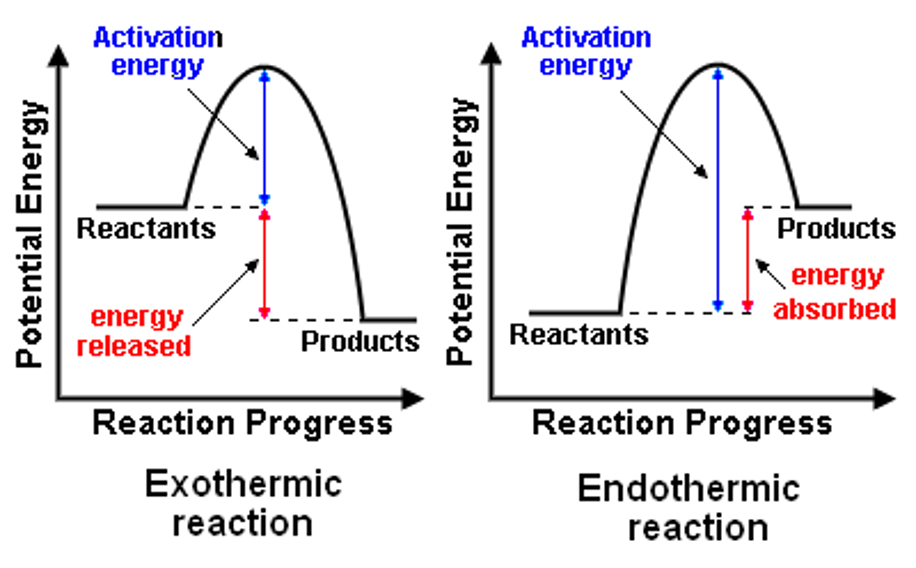
What is a characteristic of an exothermic reaction?
the energy of the reactants is greater than the products (will overall release energy at the end)∆H-
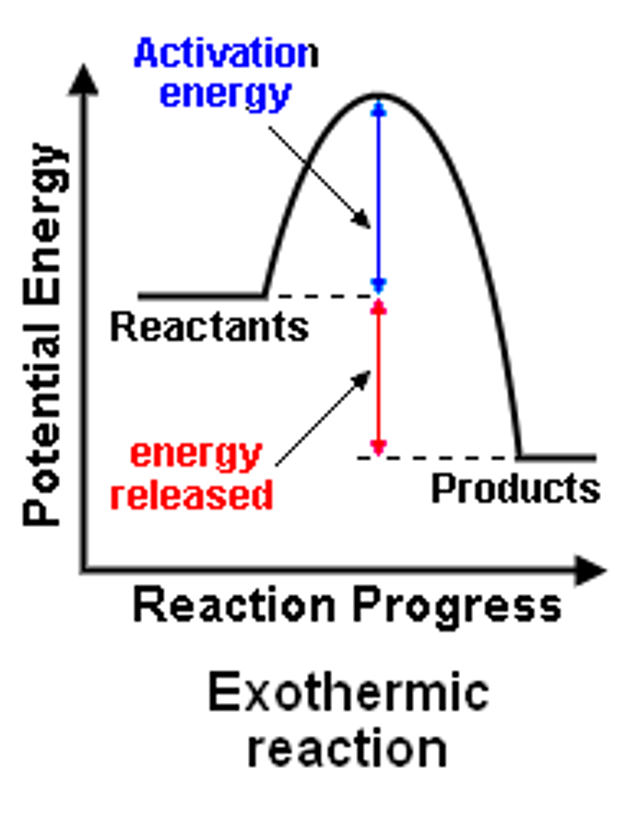
What is a characteristic of an endothermic reaction.
The energy of the products is greater than the reactants ( more energy is needed to be absorbed ) ∆H+
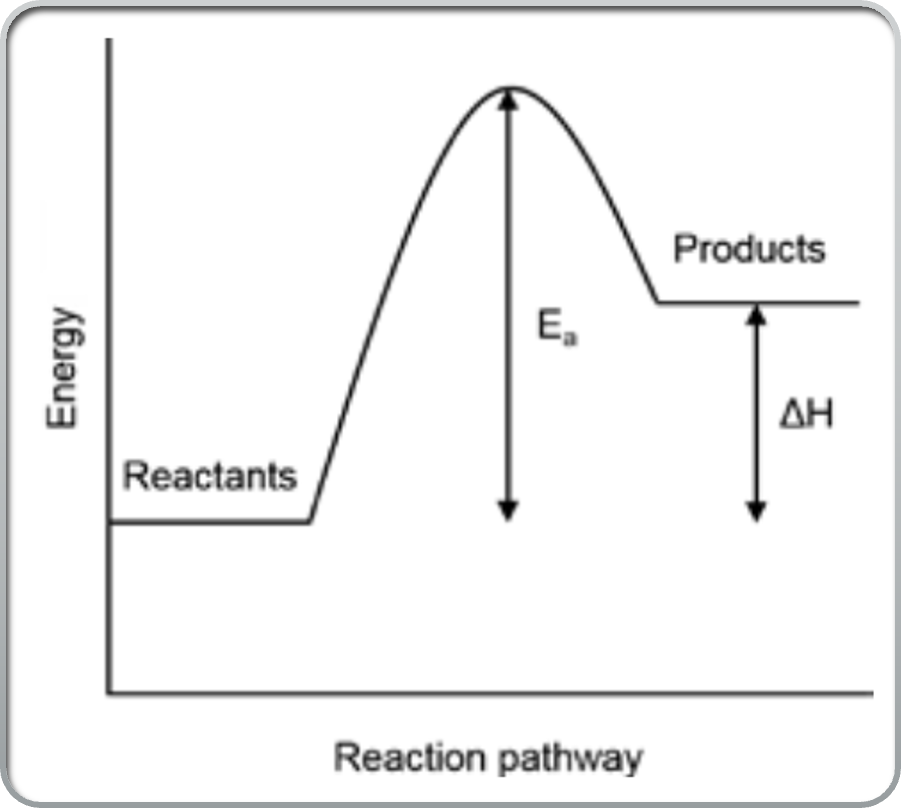
What is an energy profule diagram?
a diagram which displays the reaction pathway of a reaction with and without a catalyst
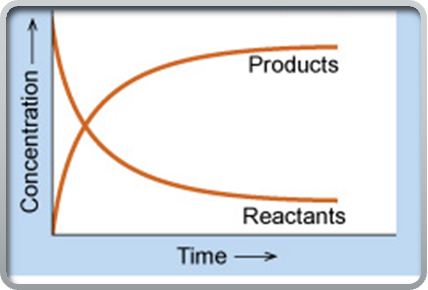
What is Chemical Equilibrium
When the rate of reaction of the forward (reactants → products) is equal to the backwards reaction (products→reactants)
When at equilibrium
the concentration of the reactants and products do not change (as they are reacting at a constant speed, cancelling each other out.
Equilibrium must be conducted
within a sealed container so component’s concentration can’t be altered.
it takes
time for a reversible reaction to reach equilibrium
If the equilibrium lies to the right
the forward reaction is favoured, meaning the concentration of products is greater than the concentration of reactants
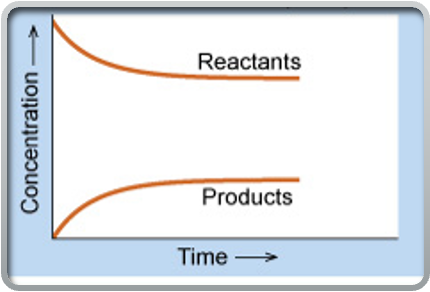
if equilibrium lies to the left
then the reverse reaction is favoured, meaning the concentration of reactants is greater than the concentration of products
What is the equilibrium Constant?
a formula that allows for the position of equilibrium at a given temperature to be found
What is the Equilbrium constant formula (Kc)
[C]c [D]d
[A]a [B]b
(concentration of products to the power of their coefficients over the reactants to the power of their coefficients
Kc measures
how much a reaction proceeds/ yields
If Kc is very large (>104)
An almost complete reaction occurs, with the concentration of products being much higher than the concentration of reactants at equilibrium
(the forward reaction is being favoured, and equilibrium lies to the right)
If Kc is very small (<10-4)
A reaction hardly occurs, as the concentration of reactions is much higher than that of the products at equilibrium
(the backward direction is being favoured, and the position of equilibrium lies to the left)
If Kc is between 10-4 and 104
both concentrations of reactants and products are present at equilibrium
Why does the Kc value have no units?
because it is a constant
ICE Boxes
are used to find the concentration of all species at equilibrium, with limited information
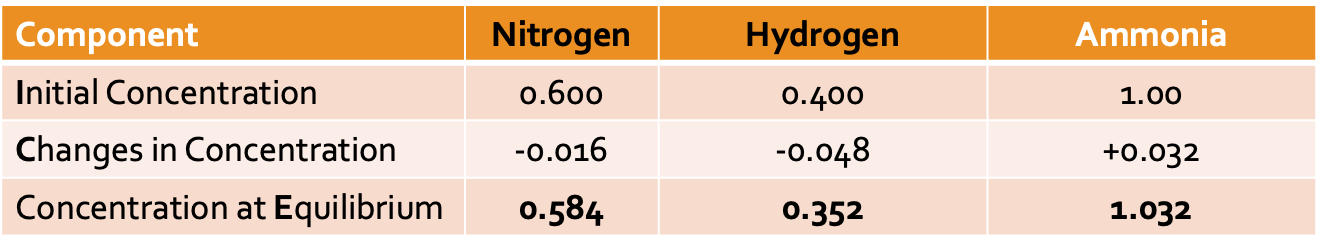
ICE box steps
Step 1: Place the known values in the table to calculate the equilibrium moles of the reactants
Step 2: Determine the change in moles for the products
Step 3: Determine the change in moles for the reactants. This requires multiplying the change in moles of the products by the stoichiometric ratio.
Step 4: Calculate the equilibrium moles for the reactants by subtracting the change in moles from the initial moles
Step 5: Determine the concentration at equilibrium by dividing by the volume.
Step 6: Now that concentrations at equilibrium are known, the value can be determined
What can push the position of equilibrium?
Concentration
Pressure
Temperature
What is Le Châtelier’s Principle?
If a system at equilibrium is disturbed, the position of the equilibrium will shift to counteract this change.
How is an equilibrium shifted with a change in concentration?
If the concentration of a reactant or product is changed, the equilibrium will shift to oppose this change
If a product’s concentration is decreased
the equilibrium will counteract this change by converting more reactants to products (forward reaction is favoured)The equilibrium shifts to the right
If a reactant’s concentration is decreased,
the equilibrium will counteract this change by converting more products to reactants, favouring the backwards reaction. The equilibrium shifts to the left
If a product’s concentration is increased,
the equilibrium will try to counteract this change by creating more reactants with the new increased amount of products to establish equilibrium again. the equilibrium shifts to the left backwards reaction is favoured.
If a reactants concentration is increased,
the equilibrium will try to counteract the change by converting more reactants into products, the equilibrium shifts to the right, favouring the forward reaction
A graph example of an increase in concentration diagram
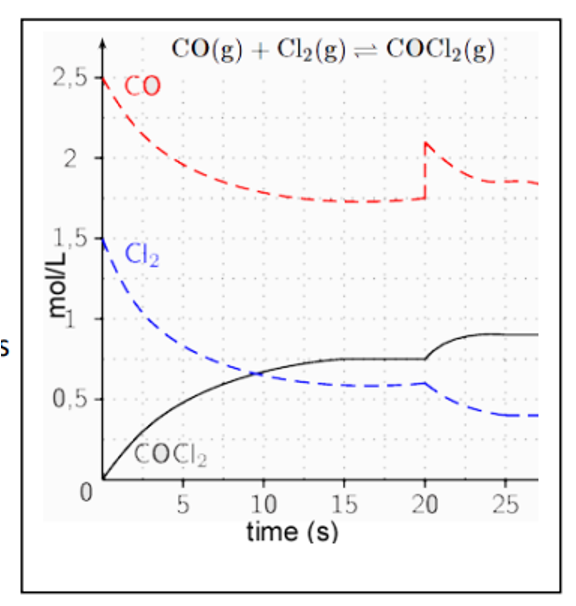
How does a change in pressure shift the equilibrium?
increasing pressure (decreasing volume) means increasing collisons occuring.
if pressure is altered, the system will shift the equilibrium to counteract that change (moving to the side with the least or most moles)
If the pressure of a system at equilibrium has increased
the equilibrium will shift to the side of the reaction that has the fewest moles, the decrease the change in pressure and counteract the change
If the pressure of a system at equilibrium has decreased
the equilbrium will shift to counteract the change in pressure, and shift to favour the side of reaction with the most moles to increase the pressure
Example of a change in equilibrium due to a pressure change
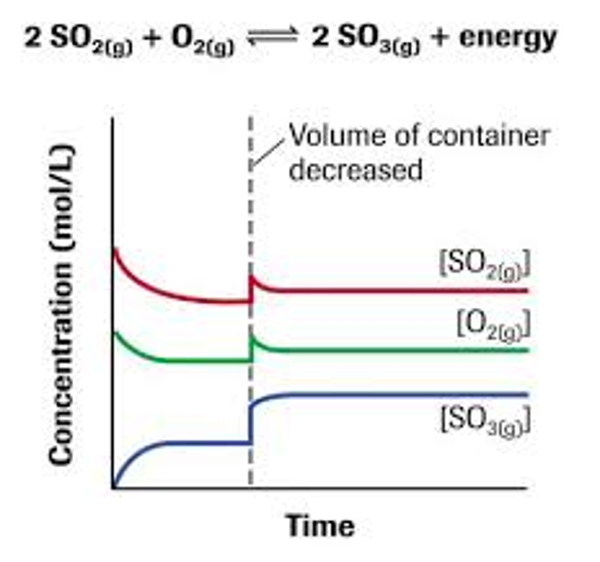
KC occurs at
a set temperature
How does a change in temperature affect equilibrium
The equilibrium will shift the side of the reaction which counteracts the change in heat (exothermic or endothermic) the shift in equilibrium is dependent on the change in heat and the ∆H
If there is an increase of temperature for a system at equilibrium
the system will shift to the side of reaction which will use up this heat (endothermic side)
If the temperature is decreased
the equilibrium will move to counteract this change, increasing the heat (shifted to exothermic side)
Example of change in heat at equilibrium graph
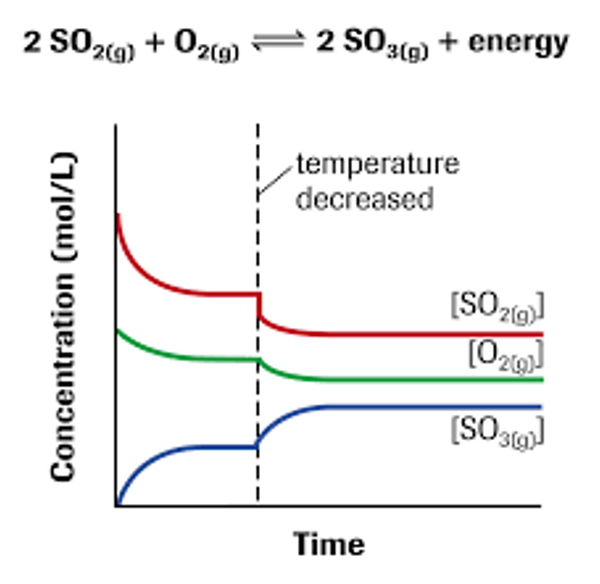
A change in temperature at equilibrium
changes the Kc value.
If an increase in temperature increases the Kc value:
the products are endothermic (products are favoured
If an increase in temperature decreases the Kc value:
the products are exothermic
If an decrease in temperature increases the Kc value:
the products would be exothermic. (forward reaction)
If a decrease in temperature decreases the Kc value:
the products would be endothermic (backwards reaction
Chemical pathways
contain multiple steps which turn Raw products into By-products while displaying waste products emitted by the reaction
Raw Material
Raw Materials are unprocessed reactants that are used to produce more useful materials or create energy
By Products
are the usable product of a reaction, which can be used for another reaction
Waste products
Products of a industrial reaction that cannot be further reacted. Can be unwanted or difficult to dispose of or use
In industrial processes, how is Yield maximised
Compromises are made to maximise profits and minimise the impact on the environment
compromises are made between Collision theory and Le Châtlier’s Principle to maximise yield
Theoretical Yield
the quantity of products found by doing stoichiometric equations
Actual Yield
the actual product obtained
Percentage Yield
the ratio of actual yield to theoretical
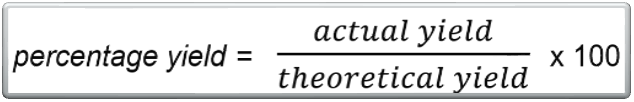
High Pressure in yield reactions
Due to Le Châtlier’s principle, this will cause the equilibrium to shift to the side with the least amount of particles, however, maintaining high pressure is costly.
This high pressure is only worth it if an additional profit can be made of the improved yield.
High Temperature for maximising yield
High temperature can increase the rate of reaction (collision theory) and also can influence the equilibrium depending if the forward reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
It takes a lot of energy to maintain high temperature conditions, so a a compromise needs to be made to ensure that there is a good rate of reaction as well as yield
What are some limitations for utilising High temperatures in industrial reactions
It is expensive, and may generate greenhouse gases and contribute to the formation of photochemical smog or acid rain.
emission must be reduced, which limits productions
Catalysts for increasing Yield
there is no downside to utilising catalysts to increase yield, as it can improve the rate of reaction while reducing the costs of operating, by introducing a new pathway for the reaction to occur. Moreover, they are no consumed within the reaction