Week 6
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What did residents of Cape Town, South Africa, start doing when the mayor issued a warning about Day Zero in 2018?
lined up to fill water jugs
Freshwater is defined as water having
less than 0.05% salt content.
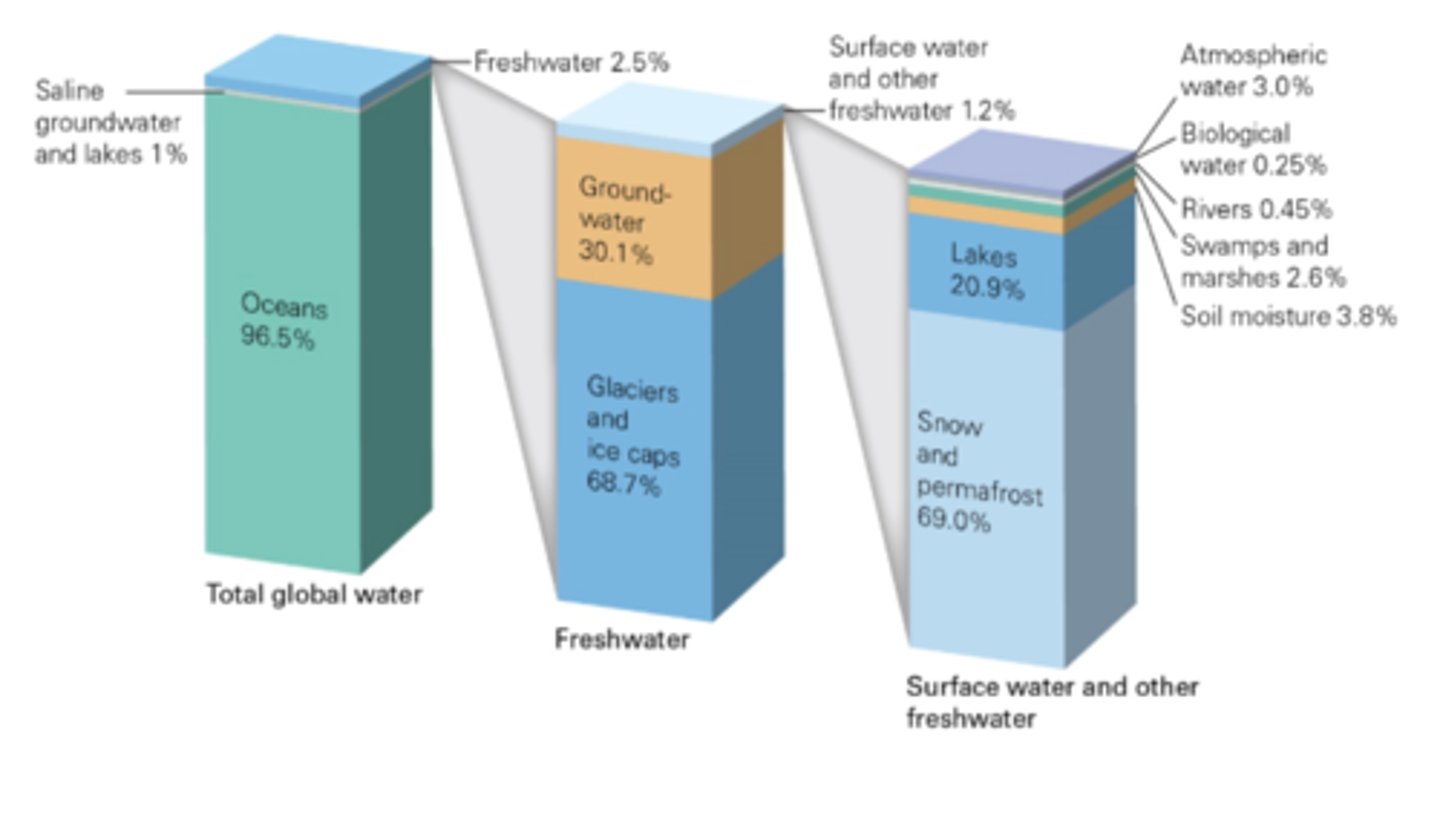
Referring to the figure below (Figure 7.4 in the textbook), the largest proportion of the freshwater on Earth resides in
glaciers, ice caps, and snow fields.
springs
natural outlets where groundwater seeps out of the ground and onto the surface
eutrophication
contamination of freshwater leading to algal blooms due to over-enrichment of nutrients
porosity
the total volume of open space (including pores and cracks) within a material
watershed
a portion of land that channels rainfall and snowmelt into a common outlet (river, lake, or other body of water.)
water table
the underground boundary between saturated and unsaturated zones
Aquifer
sediment or rock, with high porosity and permeability, that can hold a significant amount of groundwater
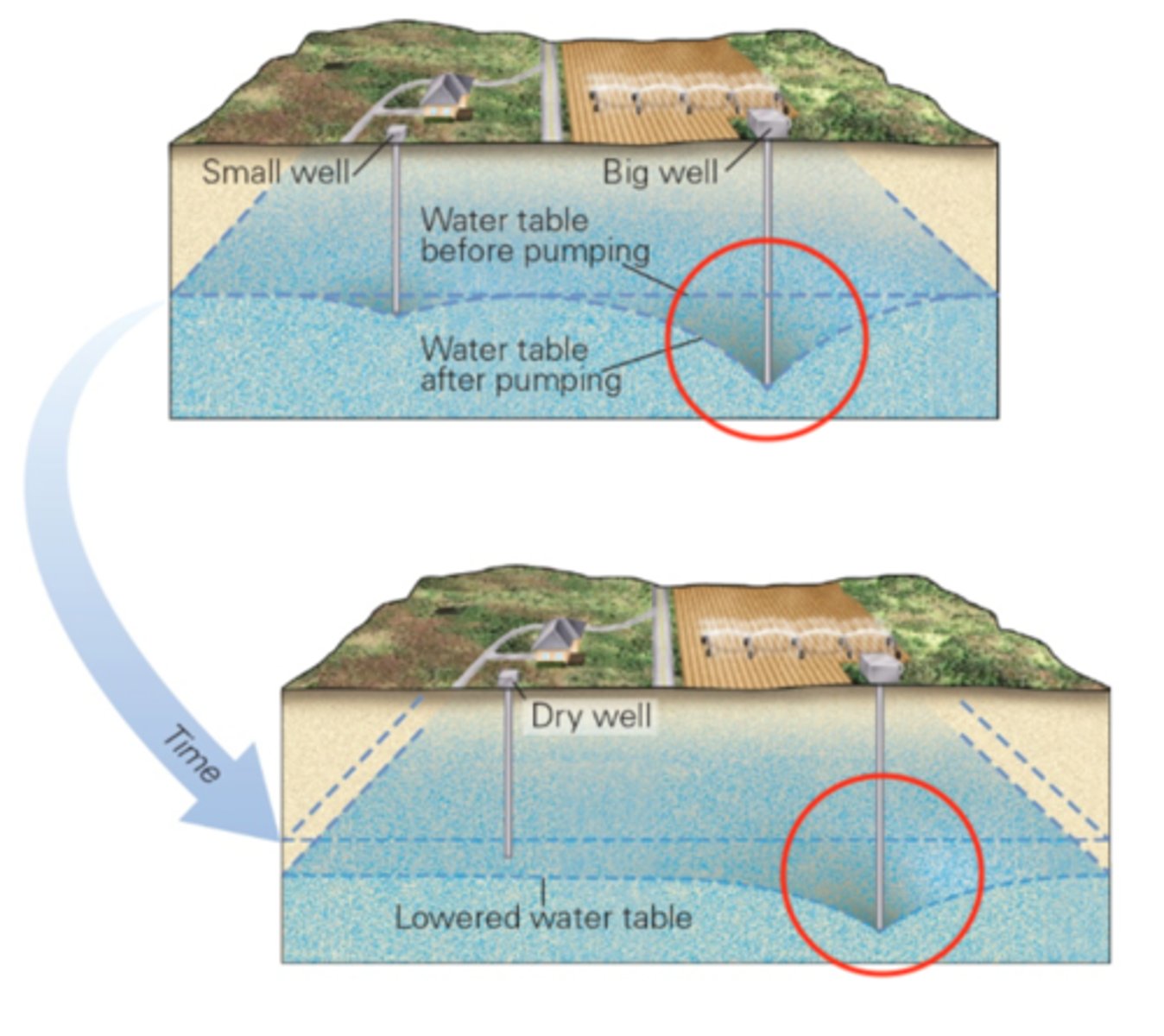
Pumping water out of a well faster than it can be replenished causes drawdown, the sinking of the water table. The image below (Fig. 7.15) illustrates how the overuse of groundwater results in the development of a three-dimensional surface described as a
cone of depression
Should groundwater be considered a nonrenewable resource?
Yes, recharge rates ranging from years to decades to centuries to millennia means that on a human time scale, groundwater is essentially a nonrenewable resource.
Scientific investigations to detect sinkholes include which of the following?
gravity surveys
seismic reflection surveys
resistivity surveys
ground-penetrating radar (GPR) surveys
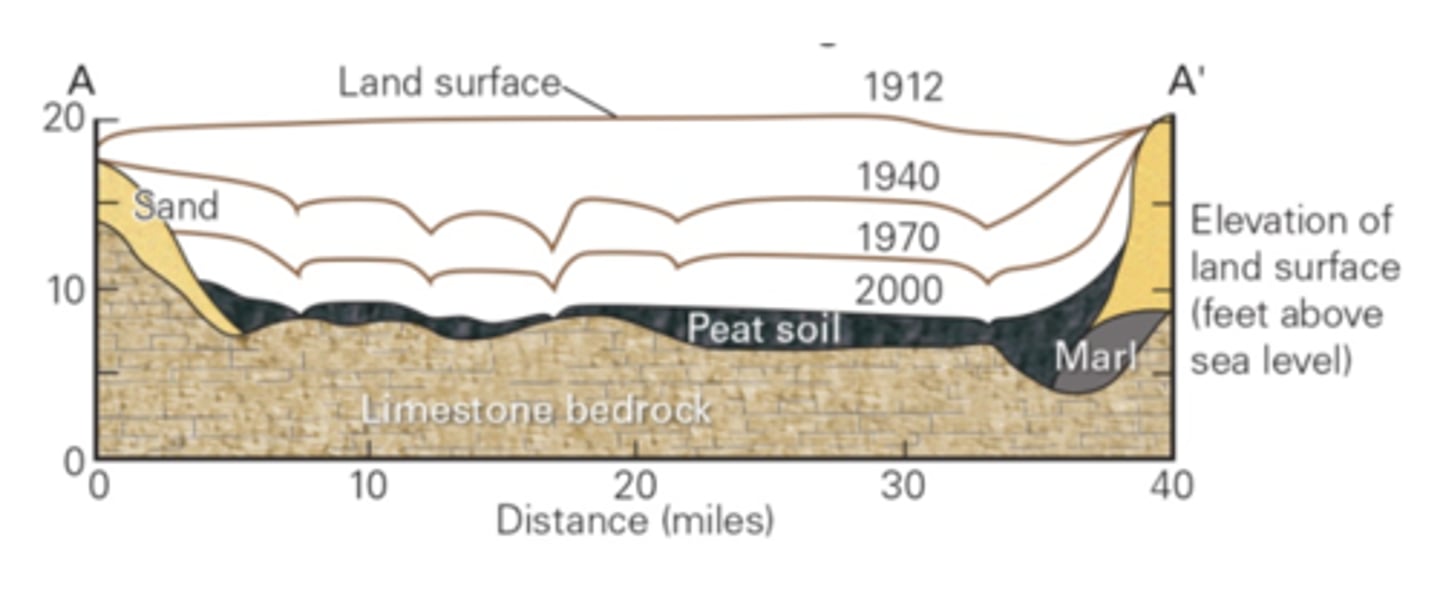
The figure below (Fig. 7.28) illustrates the degree of land subsidence that has occurred in the southern part of the state of Florida over the last century. What is a primary cause of subsidence in this region?
diversion of surface waters from their natural flow paths to the sea
headwaters
the region where the initial waters that flow in a stream originate
runoff
water flowing in an area in response to gravity
stream
A body of water flowing in a channel
tributary
a smaller stream that flows into a larger stream
competence
the maximum clast size that a stream can carry
alluvium
sediment load in a stream that settles out to form a layer of stream sediment
delta
where a stream empties into a standing body of water and sediment accumulates
With reference to the figure below, what is the definition of a floodplain?
the area of the stream gradient located in the lower reaches of a profile, near the area where ultimate base levels form
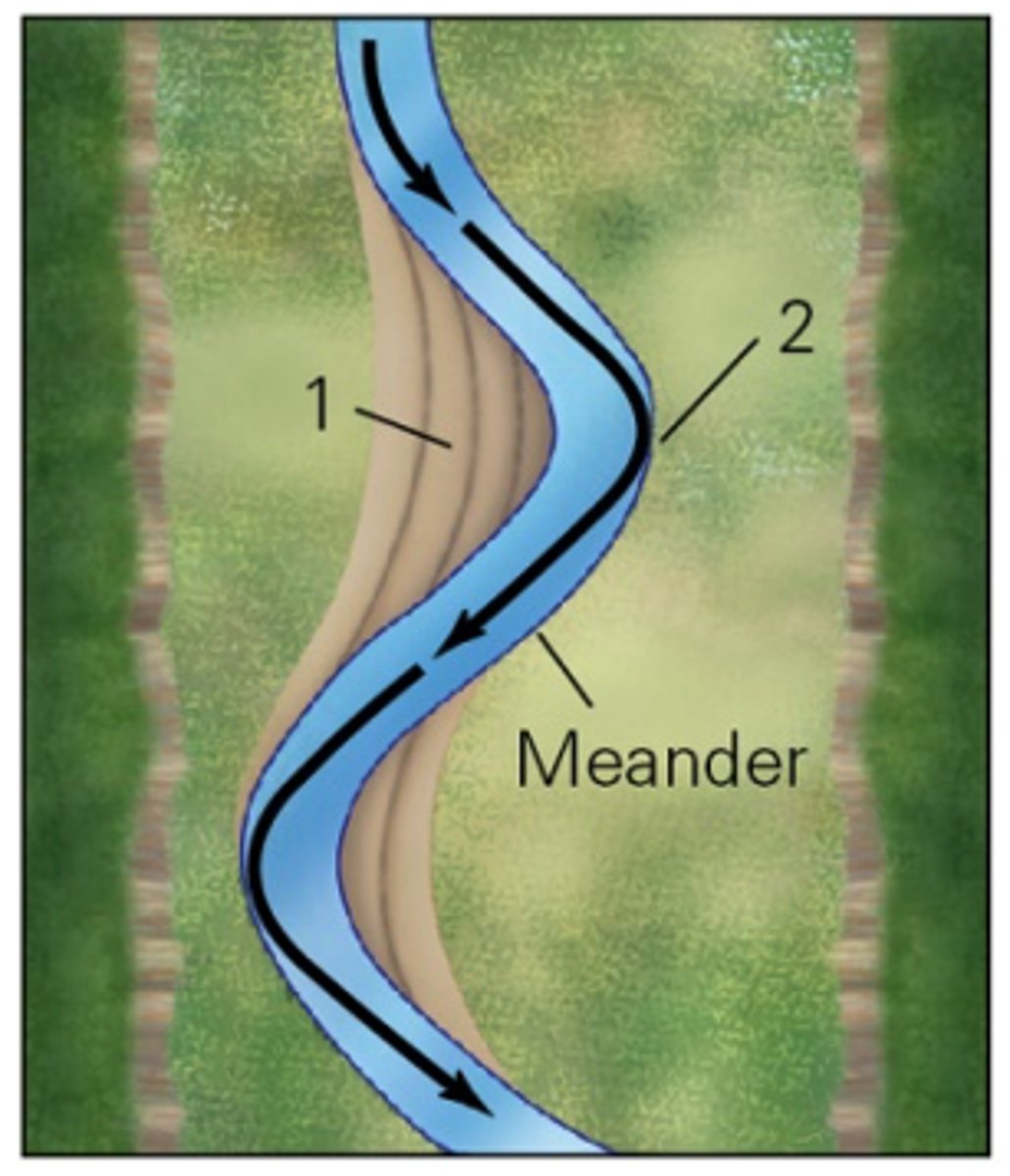
In the figure below, identify the two features labeled 1 and 2.
1. point bar
2. cut bank
As it relates to stream flow, discharge is a hydrological term that describes
The volume of water passing through a cross-sectional area of a stream over time.
When the media reports new stories about flooding events that develop over weeks to months, they are reporting on (choose all that apply)
events involving the highest flood stage, known as the flood crest.
the flood stage for a region, when water in streams overtops the
banks of the stream.
slow-onset flooding events.
Outburst floods occur when
dams made of ice or ice-deposited sediment fail.
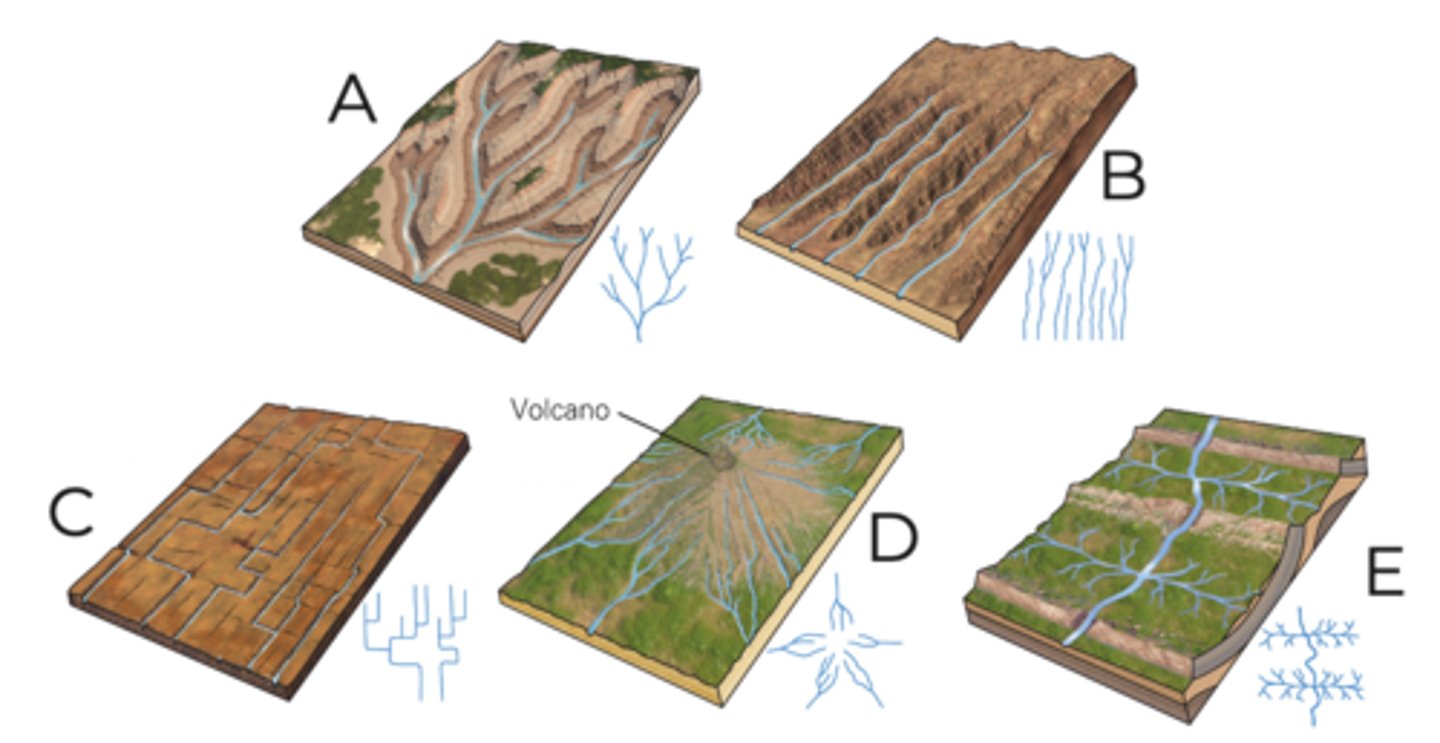
A
dendritic
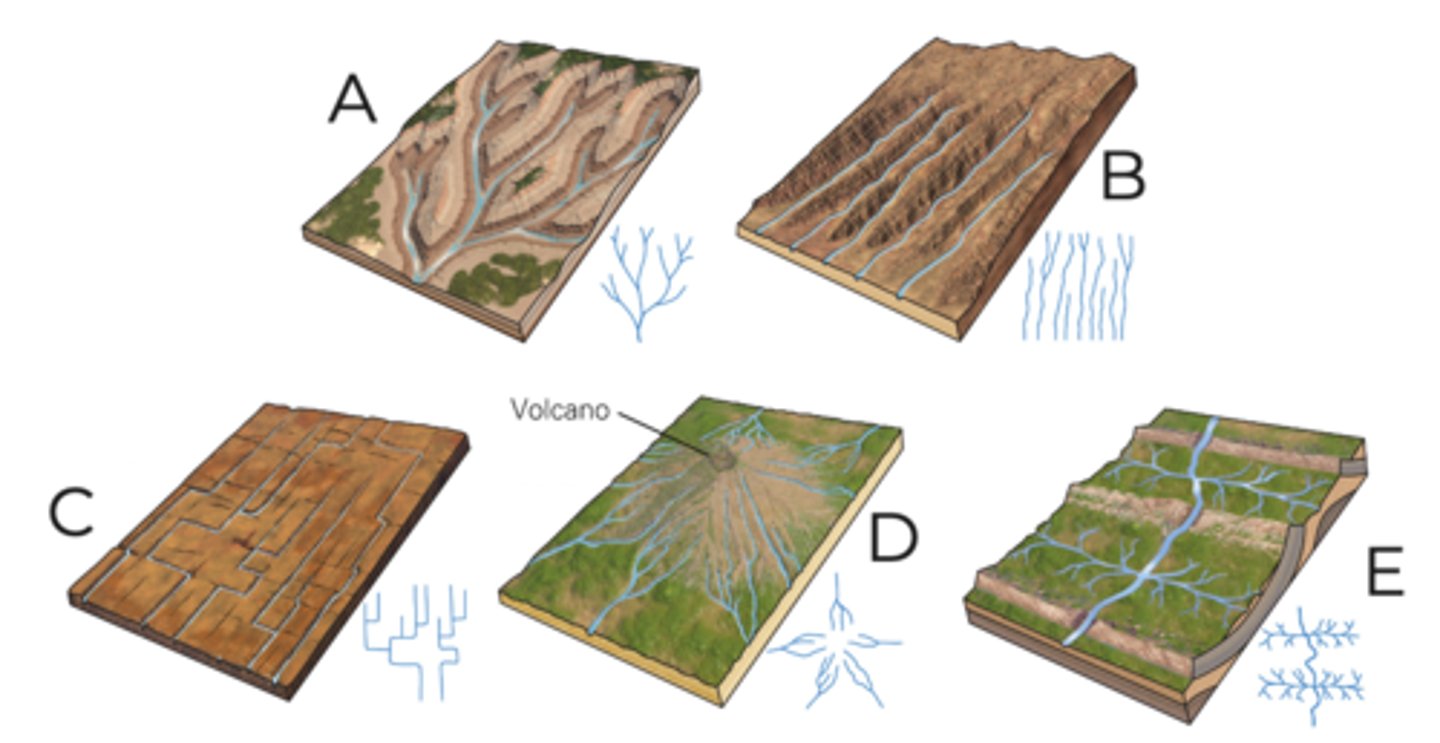
B
parallel
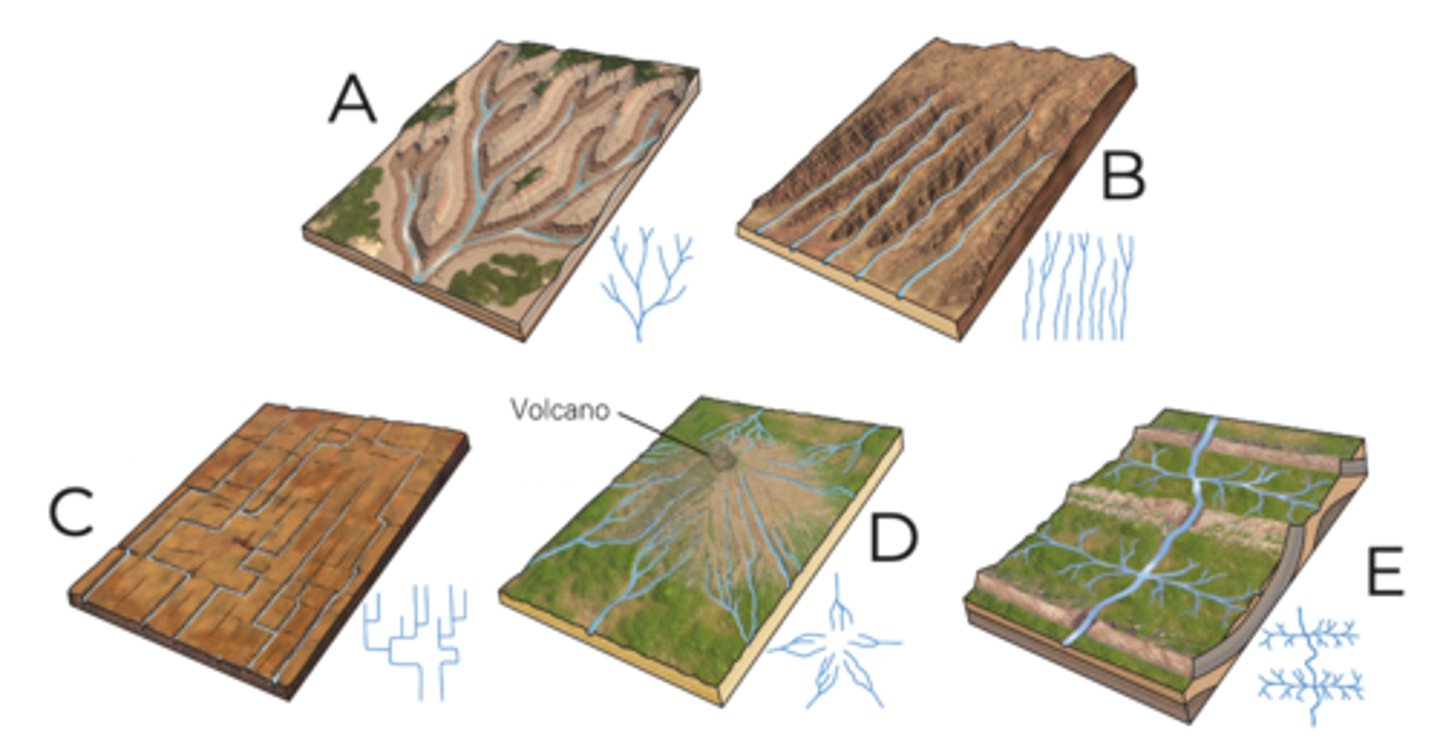
C
rectangular
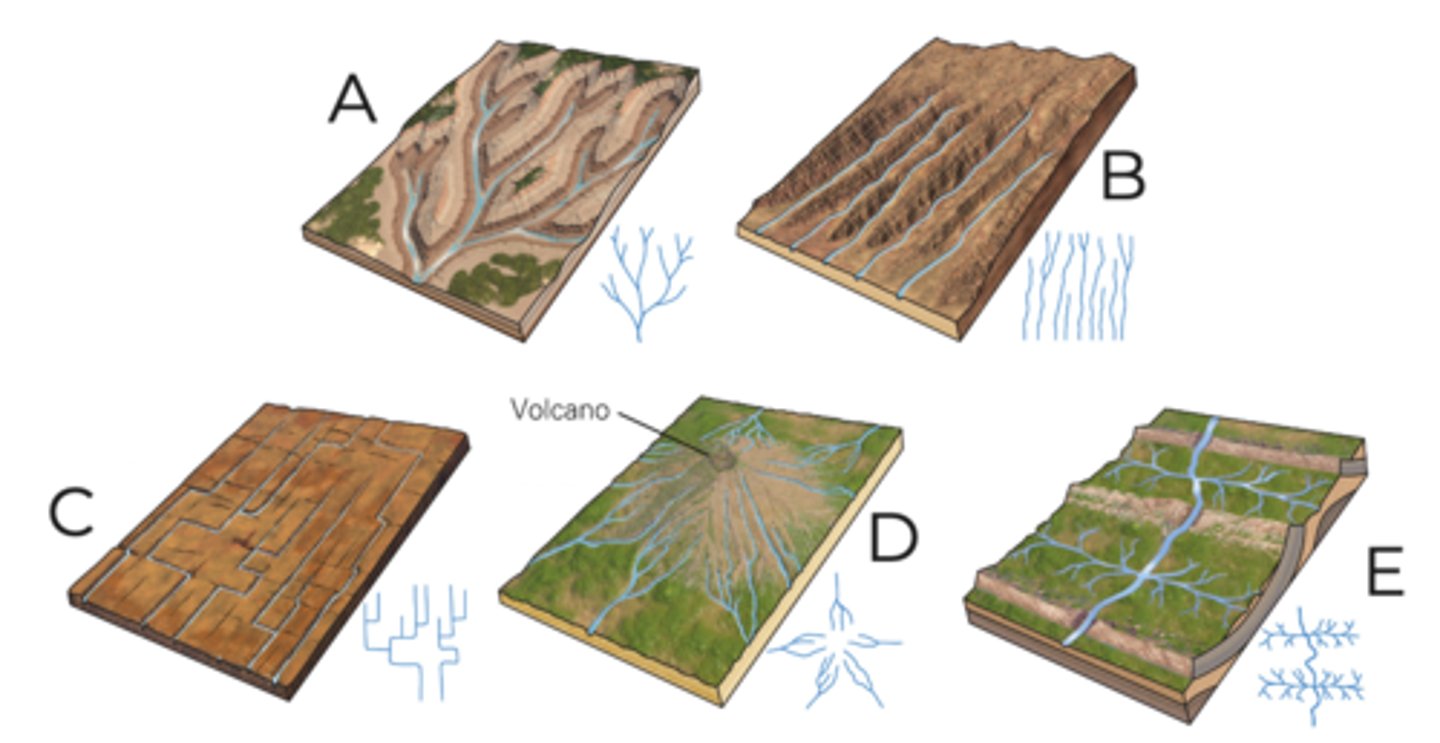
D
radial
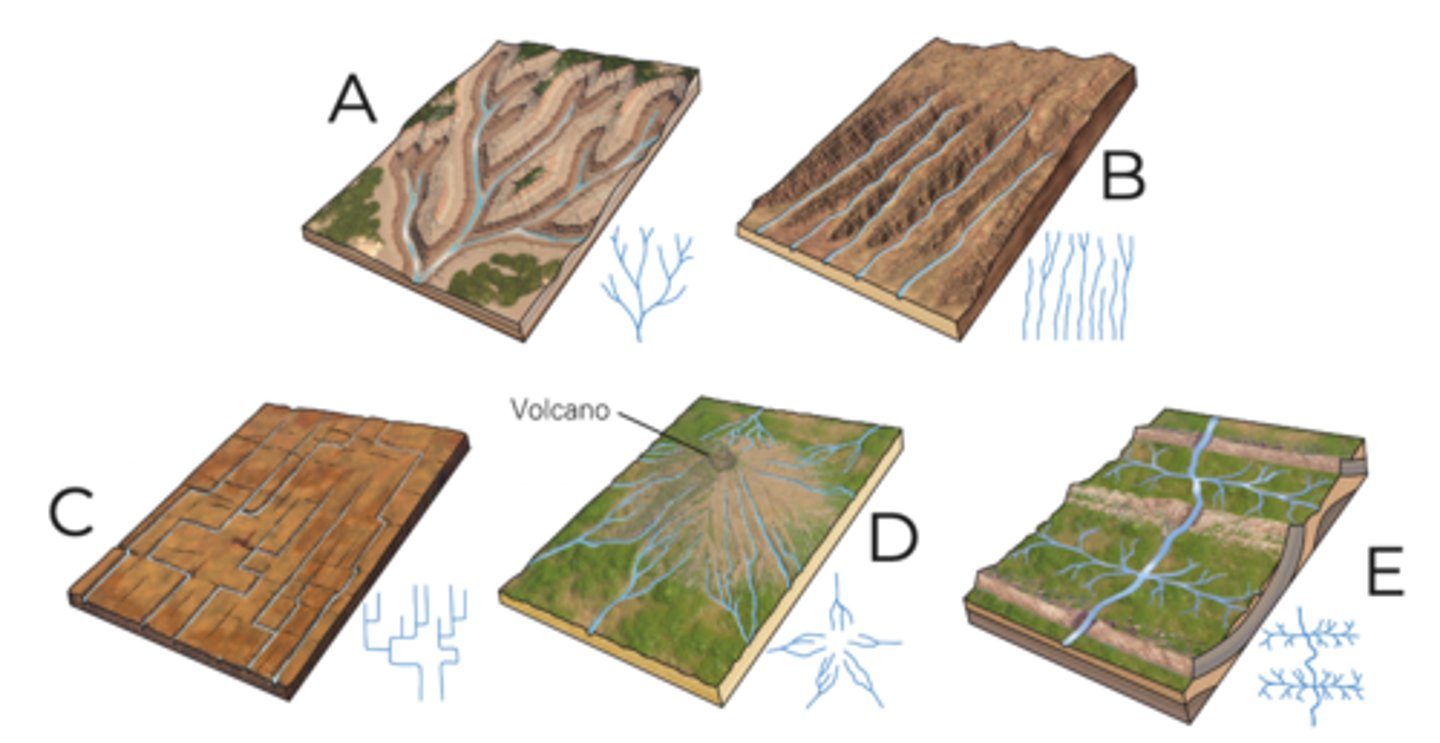
E
trellis
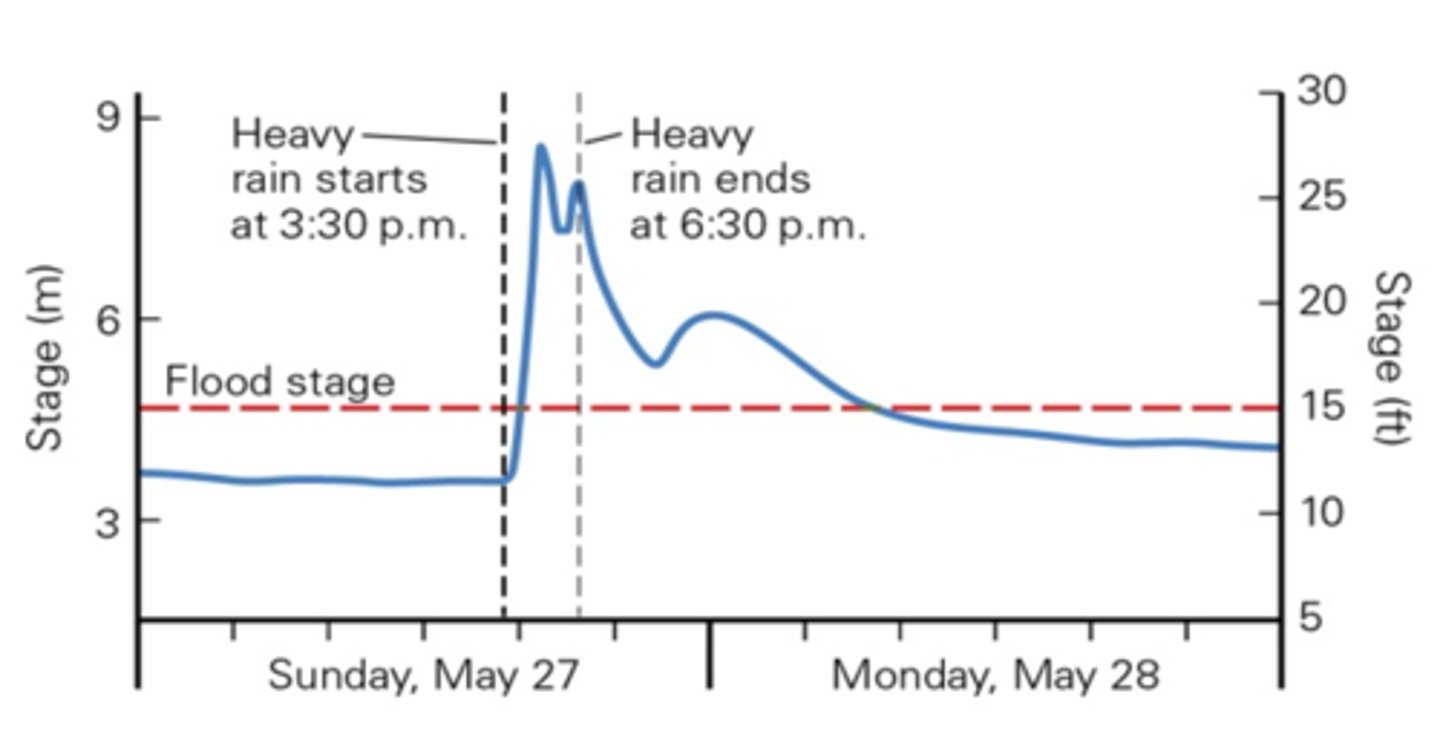
Referring to the hydrograph in the figure below, which type of flood event is indicated by the data?
a flash flood
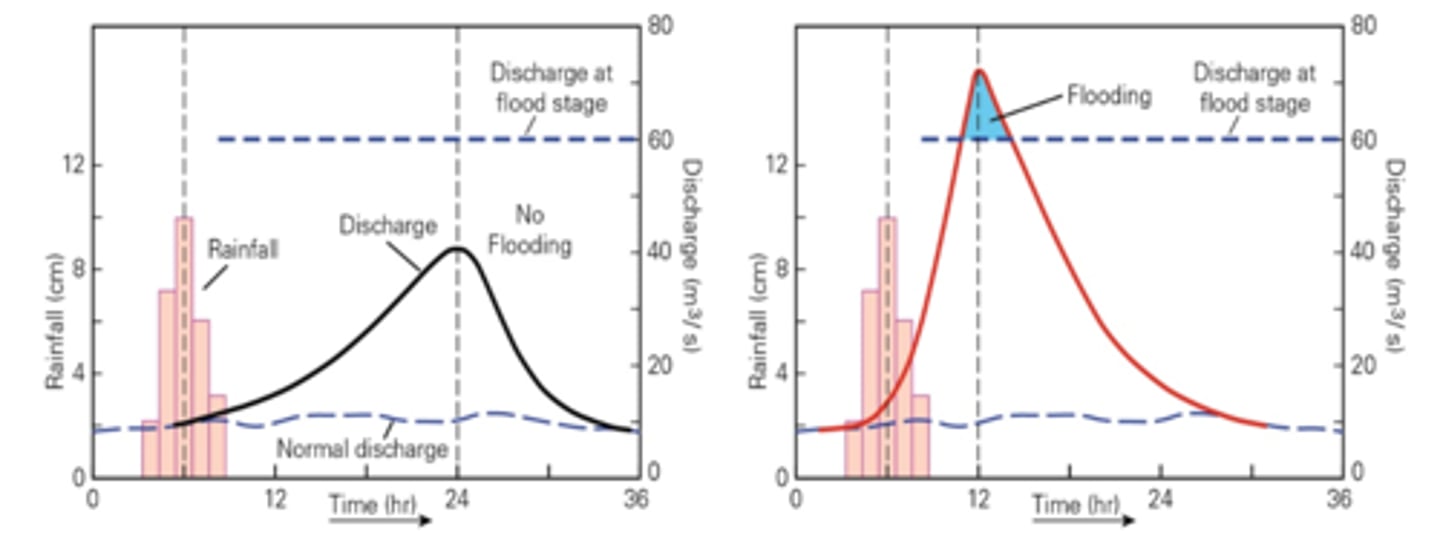
The figures below illustrate the pre-urbanization and post-urbanization effects on discharge rates for identical rainfall events. The main change due to urbanization illustrated below is that
after urbanization, rainwater flows directly into streams, so discharge rate is greater and lag time is shorter.
The definition of a monsoon is
a seasonally changing tropical wind circulation pattern.
The moisture sources for monsoonal rains in the southwest part of North America and northern Mexico are
the Gulf of Mexico and Pacific Ocean.
The recurrence interval for flooding events is based upon
the average time in years between two floods of a given discharge or greater at a given location.
The term flood describes an event in which
normally dry land is submerged in water.
Why aren't flood-control structures built in all places where there is a flood hazard?
Flood-control structures do not always work, despite the best efforts of engineers and government planners.
Flood-control structures often produce unintended consequences; for instance, shifting flooding away from one area to another
downstream.
The cost of extensive development of flood-control structures is cost prohibitive.
A strategy government agencies have followed to mitigate the risk of flood damage is to
establish buyout programs; land especially prone to flooding is purchased by the government and converted to uses that are not sensitive to flooding damage.
What are some of the downsides to using dams for flood mitigation and water resource containment?
Change water temperature
Prevent natural river channel flushing
Block fish migration
Flooding of upstream towns and ecosystems
Who should be the most interested in understanding flood risks for a given area?
individuals who live there
government institutions that must deal with disaster planning and response
the financial industry that grants mortgages and issues insurance policies
The Boneyard Creek Project in Champaign-Urbana is an example of what kind of flood mitigation strategy?
Nature-based flood mitigation