Polishing
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is needed for polishing?
slow-speed handpiece
prophy angle
polishing cups
nylon brushes
Slow-Speed Handpieces are activated by _______
rheostat (foot pedal)
Maintenance of Slow-Speed Handpieces:
autoclave after each use
follow manufacturer’s recommendations
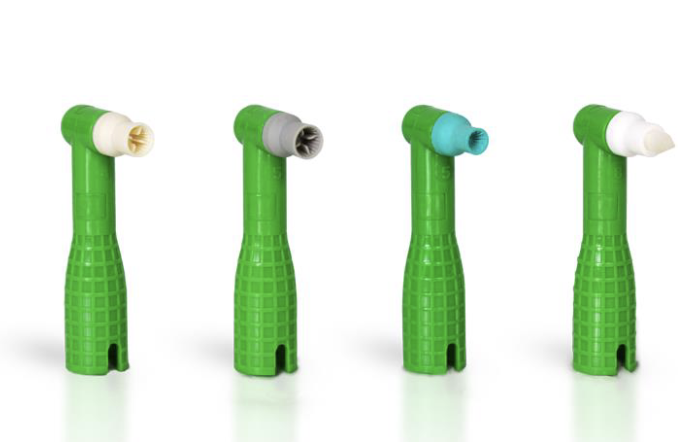

Examples of Different Prophy Angles:
straight
contra-angle
right-angled
disposable or autoclavable
Air pressure for disposable angles with firm cups is greater than __lbs. per sq. in. (p.s.i.)
20
Air pressure for disposable angles with soft cups is less than __p.s.i.
20
Polishing Cups:
latex or latex-free
used to apply abrasive material or polishing agent for cleaning tooth surfaces
can be disposable as part of disposable angle or screw-on (threaded) or slip-on types
Examples of Polishing Cups:
webbed-refers to design on internal surface of cup-contributes to cup’s degree of flexibility (less flexible than non-webbed cups)
non-webbed-design lacks webbing on internal surface of cup
pointed shape is conical and tapers to a narrow tip; designed to be used around brackets and wires with ortho
Rigidity of Polishing Cup:
Hard (firm) – not as flexible; removes stain at a faster rate
Soft – flares more at periphery when pressure is applied, therefore decreases operator fatigue since less pressure is required to flair cup subgingivally and into proximal areas
Parts of the Polishing Cup:
rim-used during polishing when cup is properly flared
center-holds polishing paste
Brushes:
Aid in removal of debris from pits and fissures, especially when preparing for sealant placement
Risk – may cause abrasion to gingiva
Purposes of Polishing:
removes pellicle, plaque, and extrinsic stains
leaves a smooth, clean feeling after scaling
prepares tooth surface for sealants (use plain pumice mixture only)
prepares teeth for pre-orthodontic bonding
Polishing will NOT remove intrinsic stain
REMEMBER: ALWAYS scale first
Use finest abrasive agent to minimize damage to tooth structure
TIP: Placing a drop of hydrogen peroxide into a fine or medium grit polishing agent will help remove stain
Adverse Effects of Polishing:
Aerosol and spatter production – use HVE or saliva ejector, and a pre-procedural antimicrobial rinse to reduce bacterial count in mouth
Bacteremia—review medical history to note any patient at risk
Heat production—polishing too fast can damage pulp; pressing too hard can damage pulp and cause tissue damage
Contraindications of Polishing:
xerostomia
demineralized areas or dental caries
sensitive teeth
newly erupted teeth
severe gingivitis
exposed root surfaces
respiratory disorders
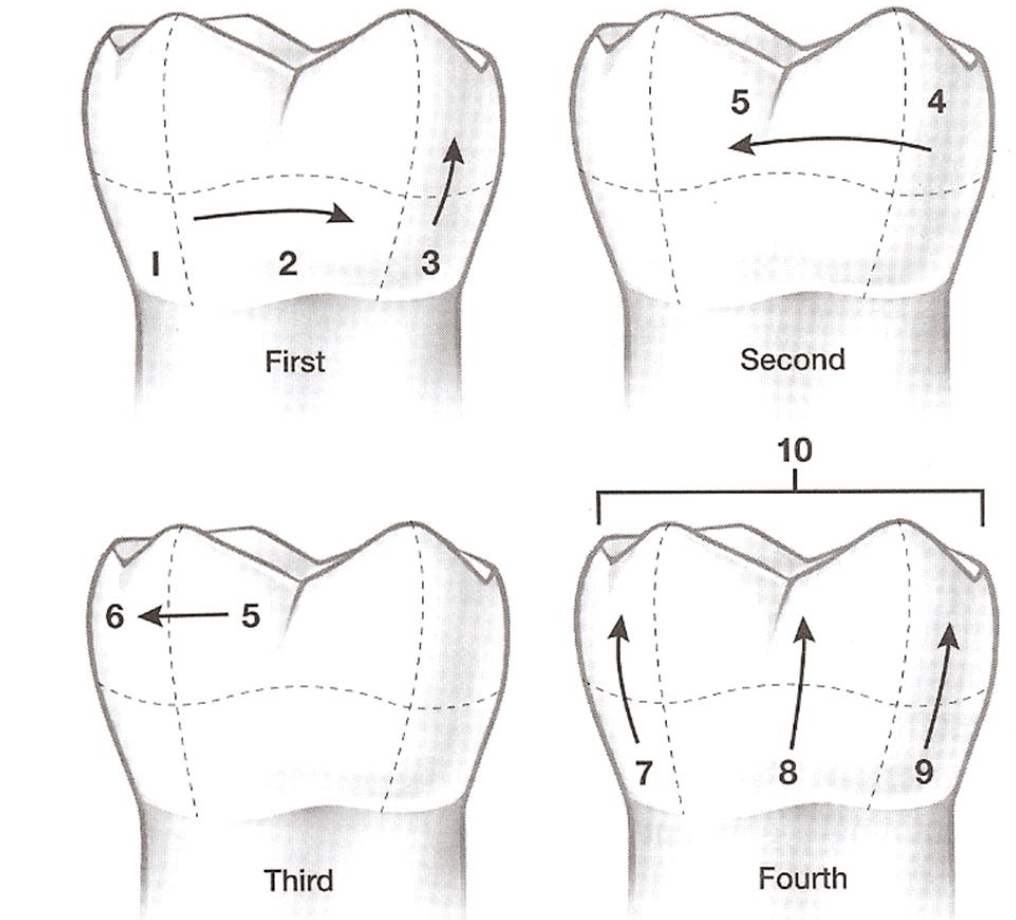
Process of Polishing:
Operator and patient wear protective eyewear
Operator wears a mask to cover mouth/nose
Review medical history for medical contraindications and possible latex allergy
Select proper abrasive for patient
Hold handpiece using modified pen grasp
Place abrasive in cup
Spread abrasive over at least 3 teeth— WHY?
Maintain a constant slow speed to control rate of abrasion
Use HVE or saliva ejector
Where should you sit to polish the maxillary occlusals?
11:00
Where should you sit to polish the mandibular occlusals?
7:30
A fast speed polisher increases rate of…
abrasion and heat generated, causing frictional heat which can damage the pulp