Strain Gauges
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Definition of Transducers
convert sensored variable into detactable signal form
e.g
mechanical quantity → change in electrical signal (strain gauge)
What type of transducers is strain gauges
device that strain → change in electric resistance
tension→ increase in resistance
Basic equation of resistance
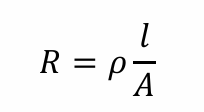
Reason why strain gauge create change in resistance
when strain,
there is changes to l and A values due to conservation of volume
piezo-resistive effect changes resistivity of material
(increases with tension)
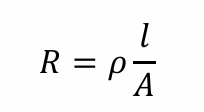
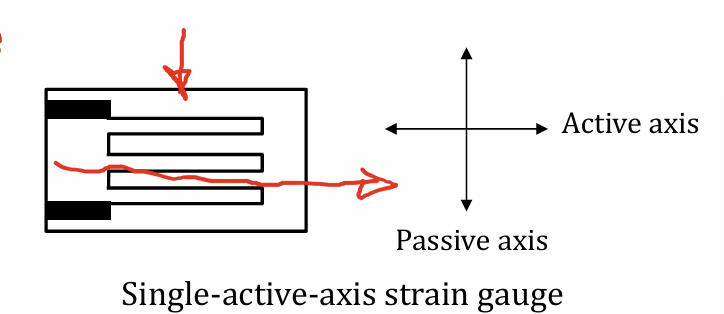
Structure of simple wire strain gauge
wire folded on flexible sheet
change in resistance in active axis is much greater than in passive axis
Definition of gauge factor
Gauge factor changes with different gauge
1.8<G<2.2
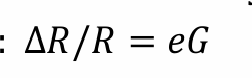
Structure of foil strain gauge
rolling thin foil of the resistive material on thin insulating paper
cutting away parts of the foil by a photo-etching process, to create the required grid pattern
adhesive to paper should be creep-free and allow heat dissipation
wire vs foil strain gauge
Foil is better
larger surface area for adhesion
accurate reproducibility due to photo-etching technique
small dimension for localised strain measurement

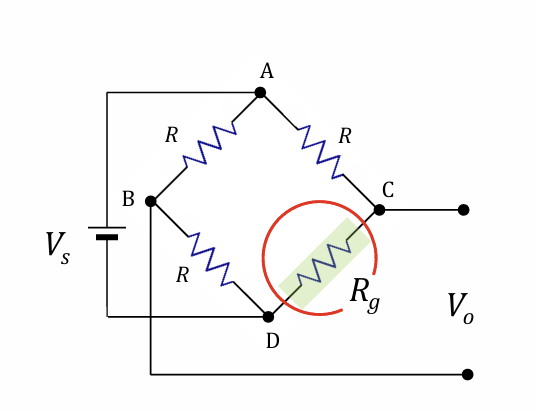
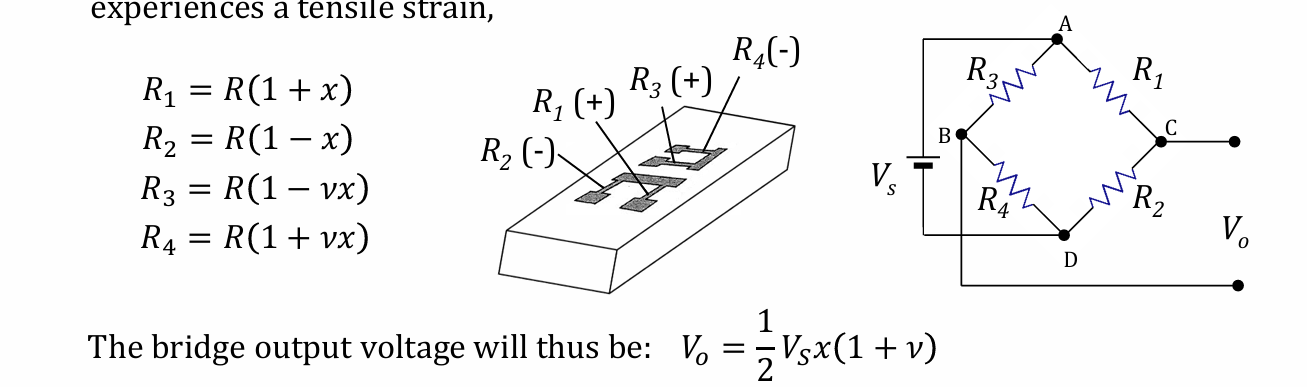
Derivation of V0/e=1/4VsG
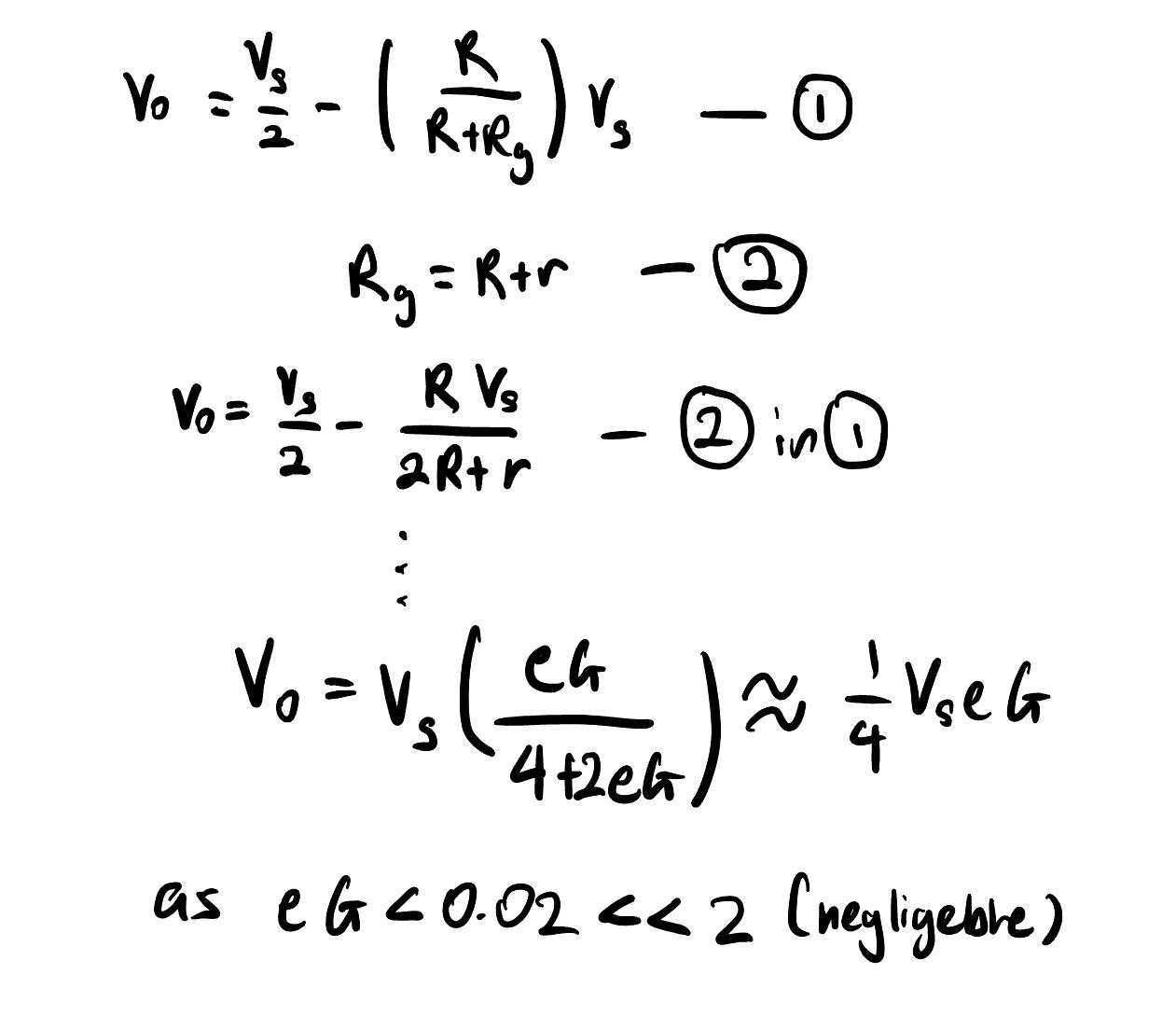
Reasons for temperature influencing strain gauge measurements
changes in temperature:
thermal expansion → change in dimensions of specimen and gauge
resistivity of gauge
Method of temperature compensation
Dummy gauge on separate specimen not under strain
Dummy gauge on same specimen perpendicularly
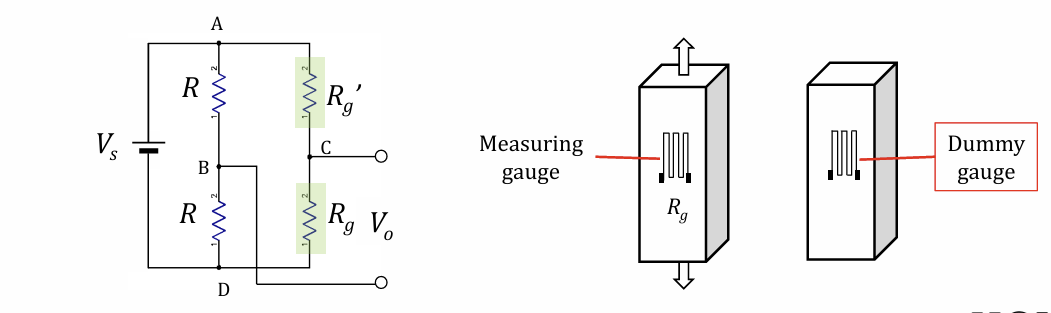
Proof that temperature is compensated for in strain gauge on unstressed specimen

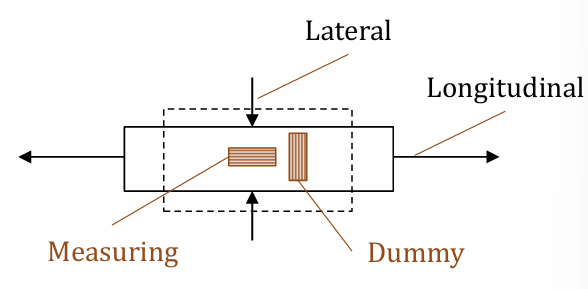
Proof that temperature is compensated for in perpendicular strain gauges
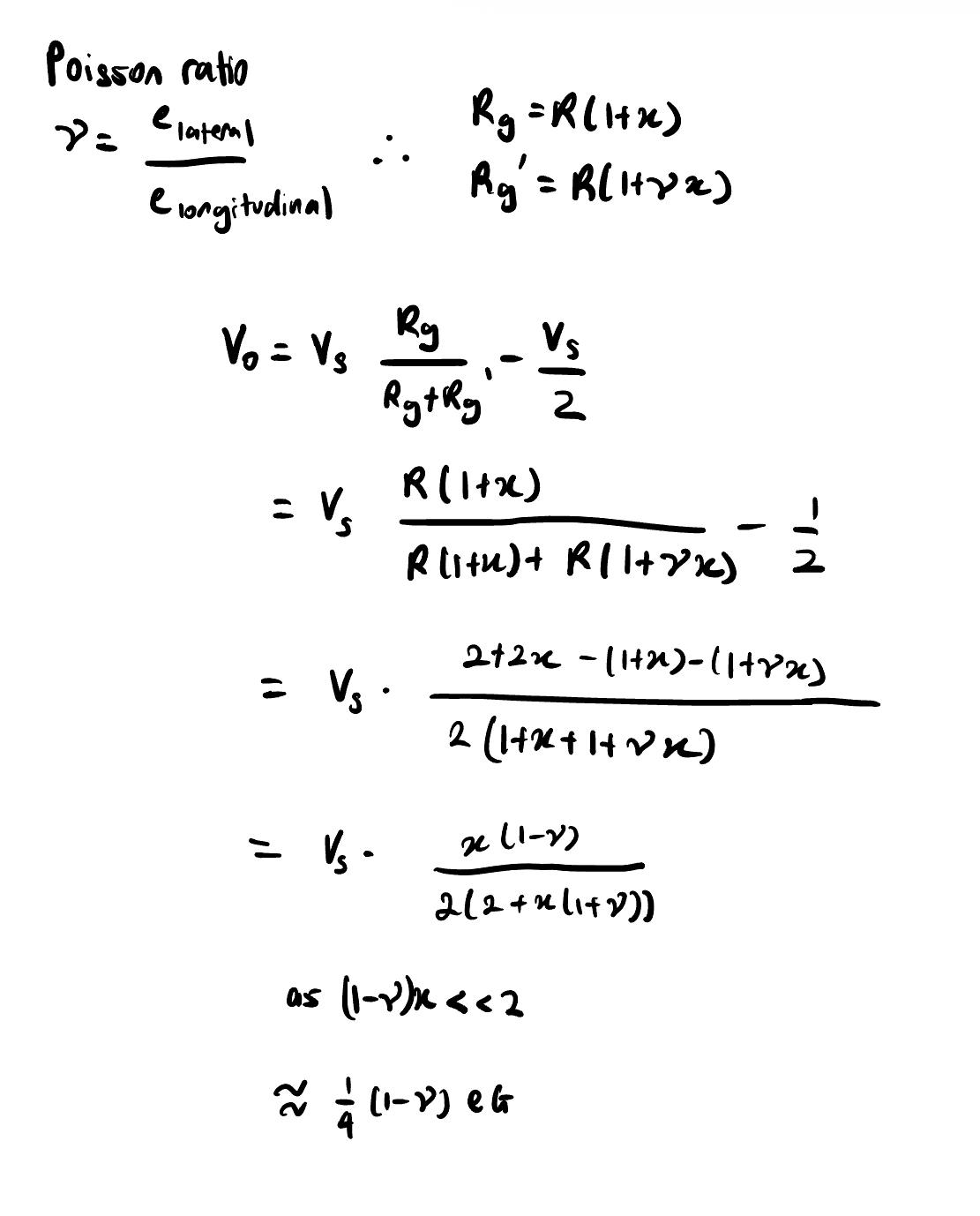
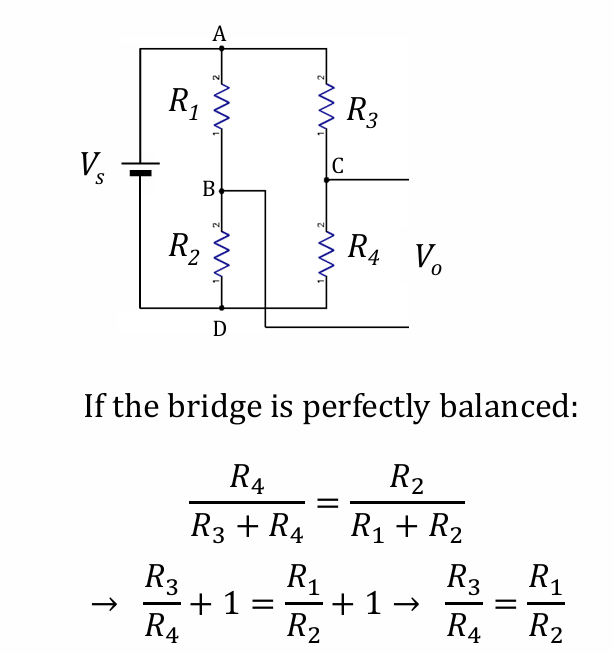
Reason for bridge balancing
resistance of each arm in bridge differ due to
manufacturing variance,
temperature difference btw gauges
static strain in one member
therefore cannot assume that ^^
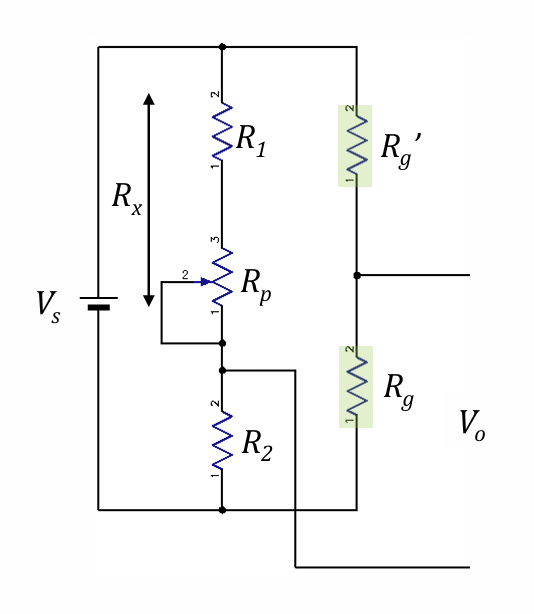
Method of bridge balancing
Connect a pot (potentiometer) before measurement
adjust pot ^^^, where Rx=R1+Rpot
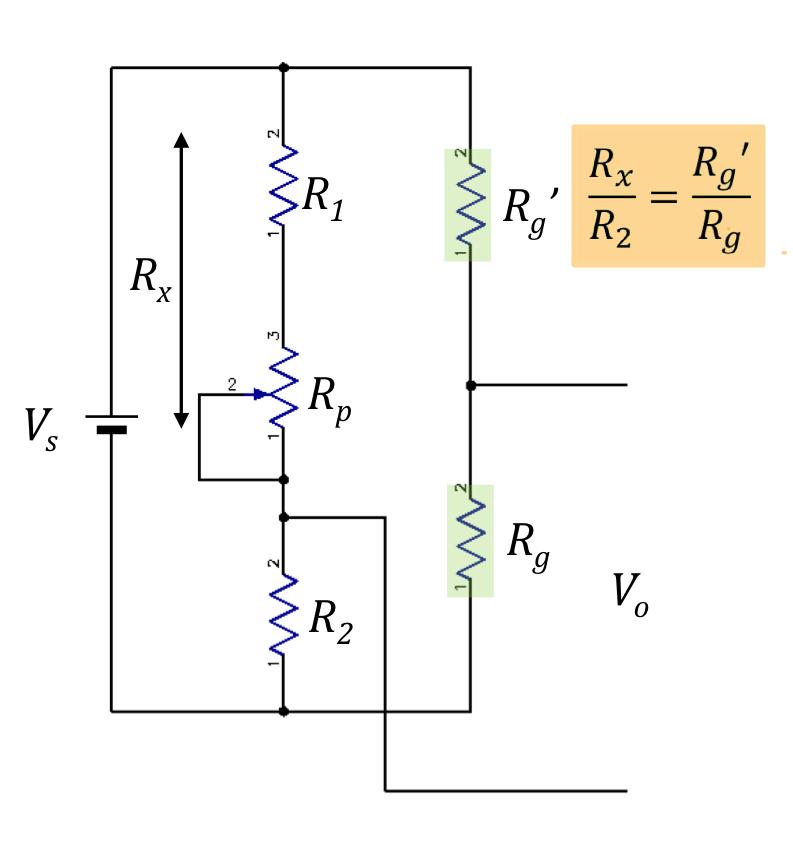
Method of semiconductor strain gauges working
semiconductor material has very large piezo-resistive effect
reach gauge factor from 100 to 300
magnitude of piezo-resistive effect determines sensitivity of gauge
Limitations of semiconductor strain gauge
Strain gauge material has a much smaller elastic limit than metal (4000microstrain compared to 20k microstrain for metal)
G is not linear at high strain
G changes significantly with temperature(temp coeff is large)
Method of temperature compensation for semiconductor strain gauges
connect 2 crystal in series but aligned parallel
All the crystal have the same temperature coefficient, temperature changes affect all crystal equally
As R1 and R2 increase/decrease same magnitude, and same for R3 and R4, changes in dimension cancels out.
Definition of bulk Modulus [K]
