10.3 The Sarcomere Anatomy and General Function
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
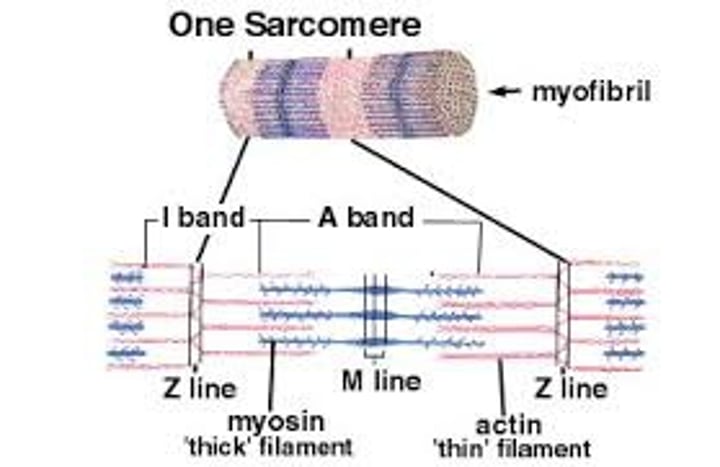
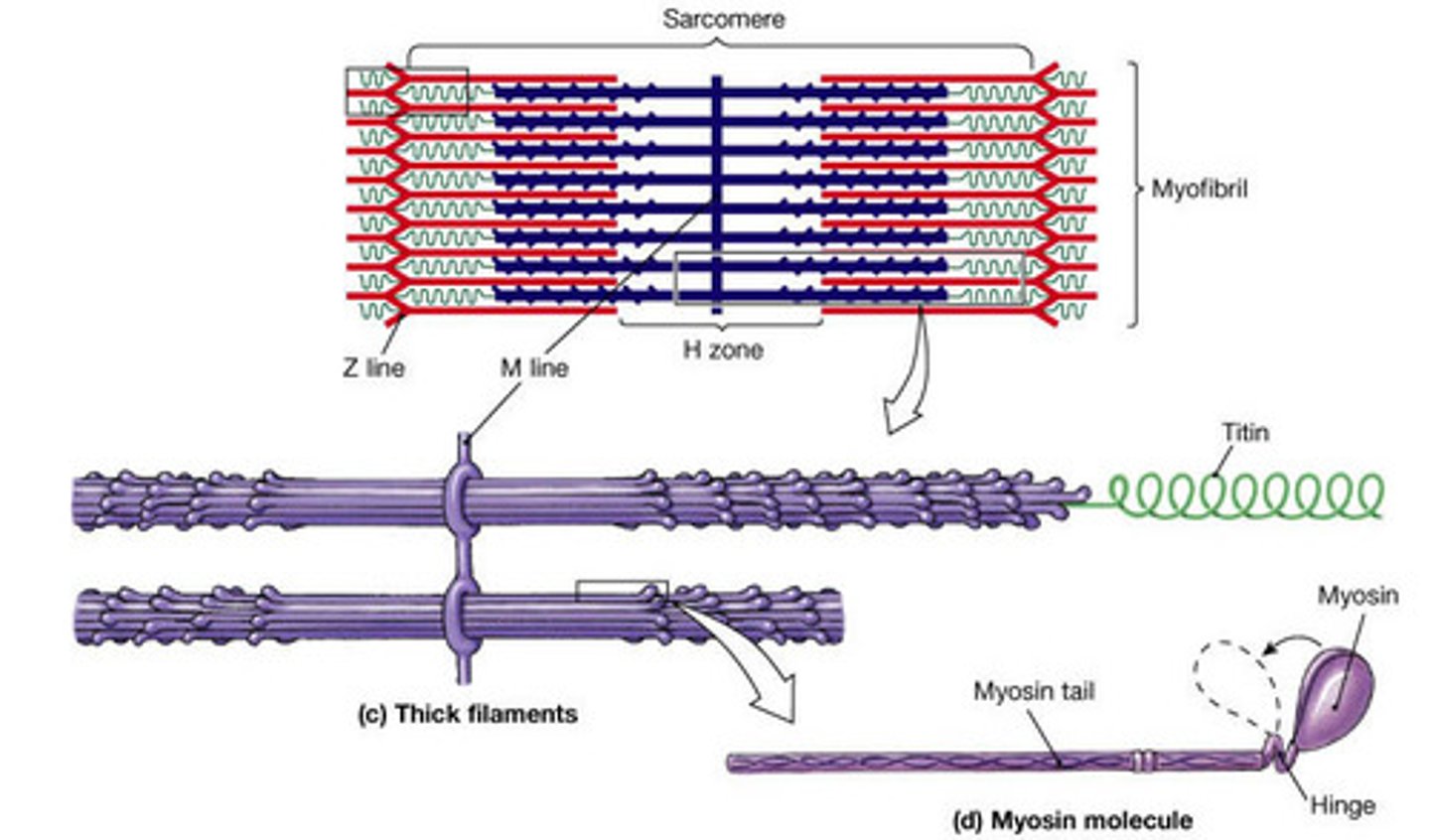
What are sarcomeres?
Repeating units of myofilaments that are found along the length of myofibrils
What is the function of a sarcomere?
Muscle contraction and relaxation
What are four things that make up a sarcomere?
- Thick filaments
- Thin filaments
- Proteins that stabilize the position of the myofilaments
- Proteins that regulate interactions between the myofilaments
What is the main protein that makes up the thick filament of the sarcomere?
Myosin
What is the main protein that makes up the thin filament of the sarcomere?
Actin
What are the two divisions of a sarcomere?
- A bands
- I bands
The A band is the ____ band?
a) Light
b) Dark
Dark
The I band is the ____ band?
a) Light
b) Dark
Light
What are the three subdivisions of the A band?
- M line
- H Band
- Zone of overlap
Where is the M line located?
The center of the A band
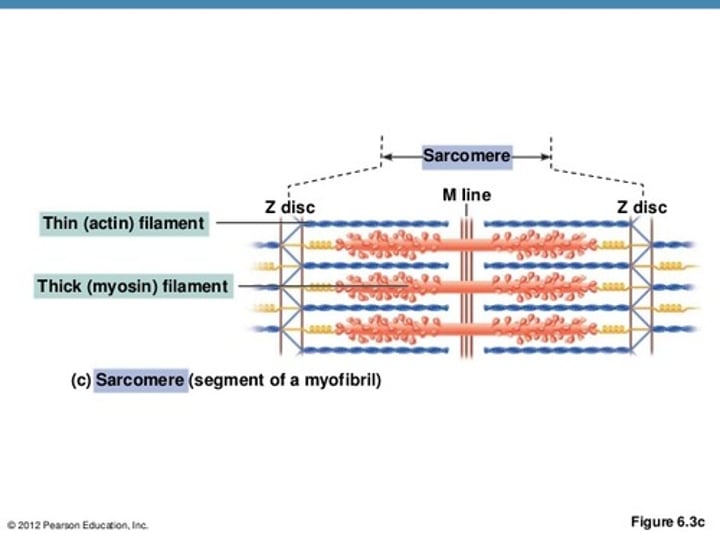
What are the two functions of the M line?
- Connects neighboring thick filaments together
- Stabilizes the positions of the thick filaments
Where is the H band located?
On either side of the M line
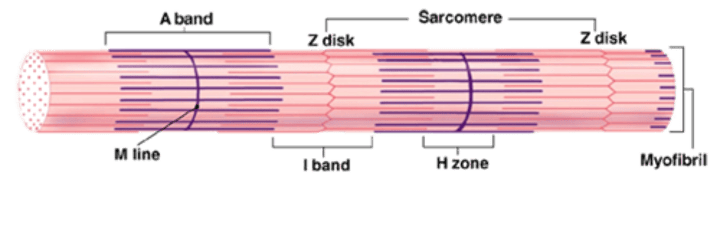
What types of filaments are found in the H band?
Only thick filaments
Where is the zone of overlap located?
On the outer edges of the A band
What types of filaments are found in the zone of overlap?
Thick and thin filaments
What types of filaments are found in the I band?
Only thin filaments
What structure bisects the I band?
The Z line
What are two proteins found at the Z line?
- Actinin
- Titin
What is the function of actinin?
Connects the neighboring thin filaments together
What is the function of titin?
- Stabilizes the positions of the thick and thin filaments
- Restores resting sarcomere length after contraction
What are the four proteins that make up a thin filament?
- F-actin
- Nebulin
- Tropomyosin
- Troponin
What does F-actin stand for?
Filamentous actin
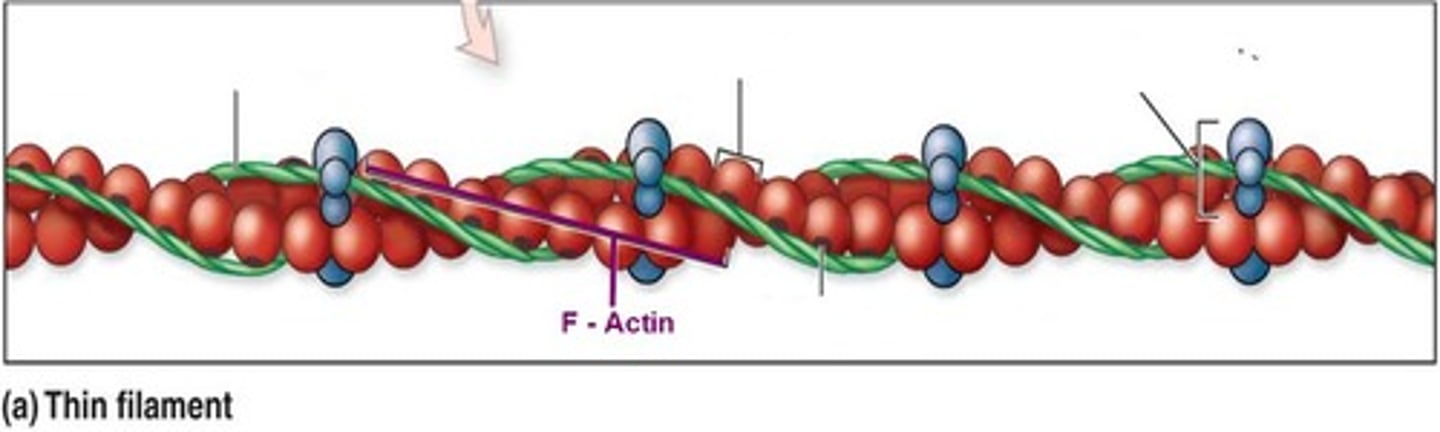
What protein is F-actin made up of?
G-actin
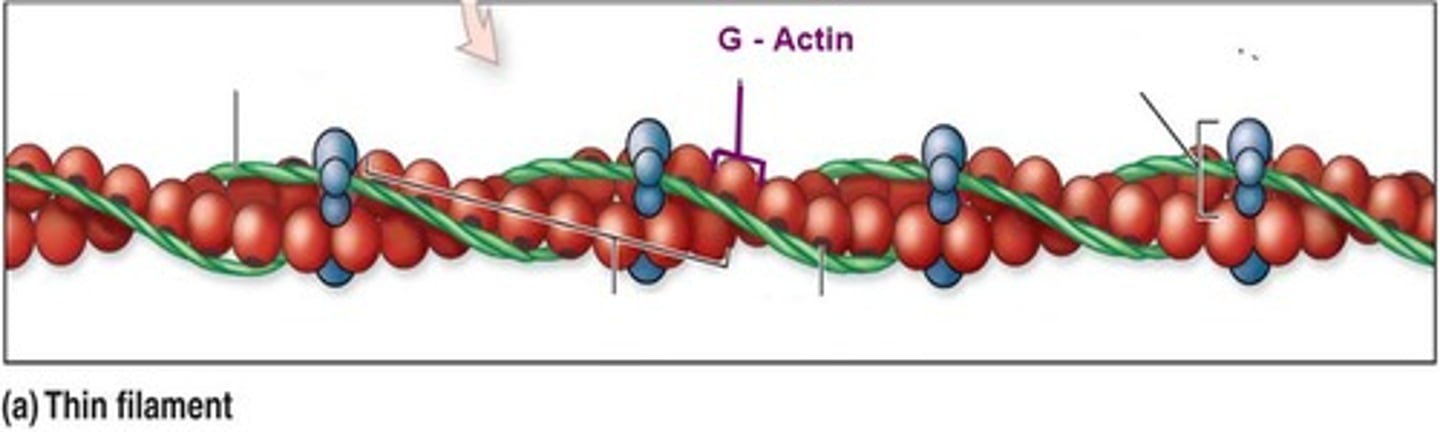
What is a structure found on G-actin?
Active site
What is the active site on G-actin?
It is the binding site for myosin from the thick filament
What is the function of nebulin?
Holds the F-actin together
What is the function of tropomyosin?
It blocks the active sites on G-actin and prevents myosin from binding
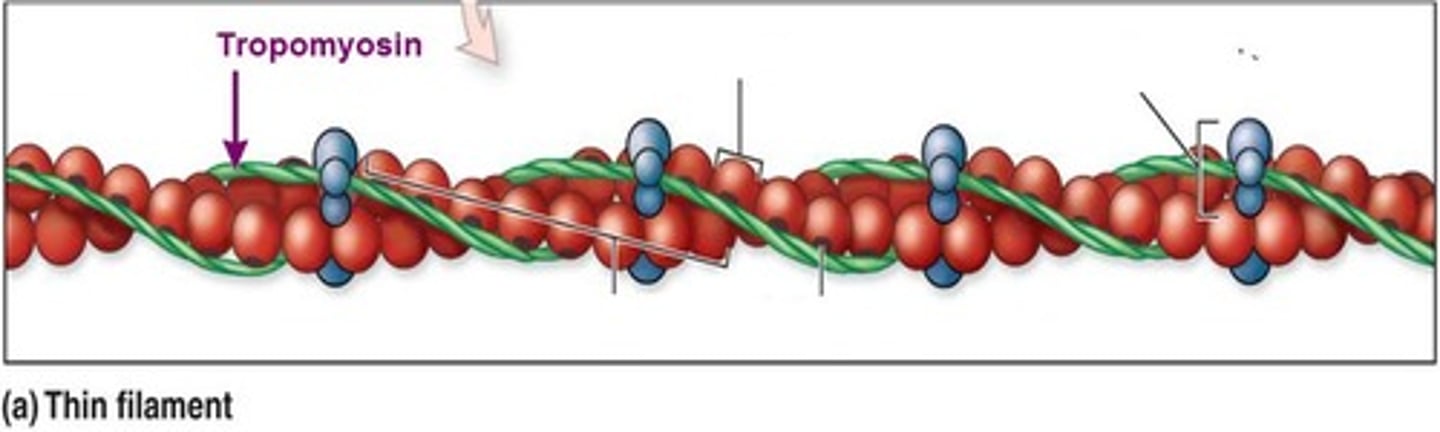
How many active sites can one molecule of tropomysin cover?
Seven
What other molecule is tropomyosin bound to?
Troponin
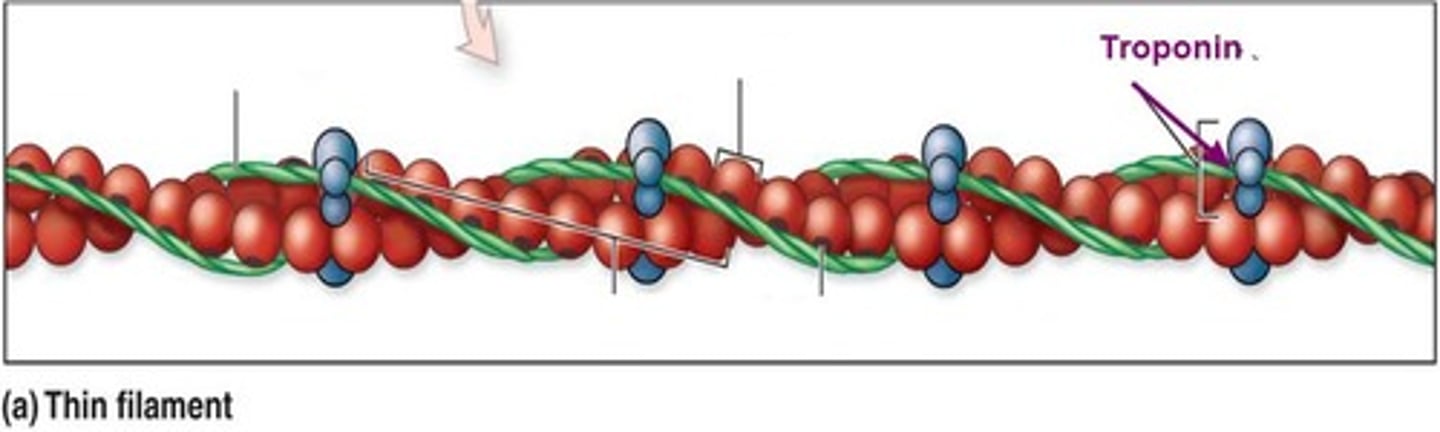
How many subunits does troponin contain?
Three
What are the functions of the three subunits of troponin?
- One subunit binds to tropomyosin
- One subunit bonds to a G-actin
- One subunit has a calcium receptor
How many calcium ions can one troponin bind?
Two
What type of molecules is a thick filament composed of?
Myosin molecules
About how many myosin molecules make up a thick filament?
300
Describe the structure of a myosin molecule.
- Composed of two subunits twisted around one another
- Has a long tail and a free head composed of two globular protein subunits
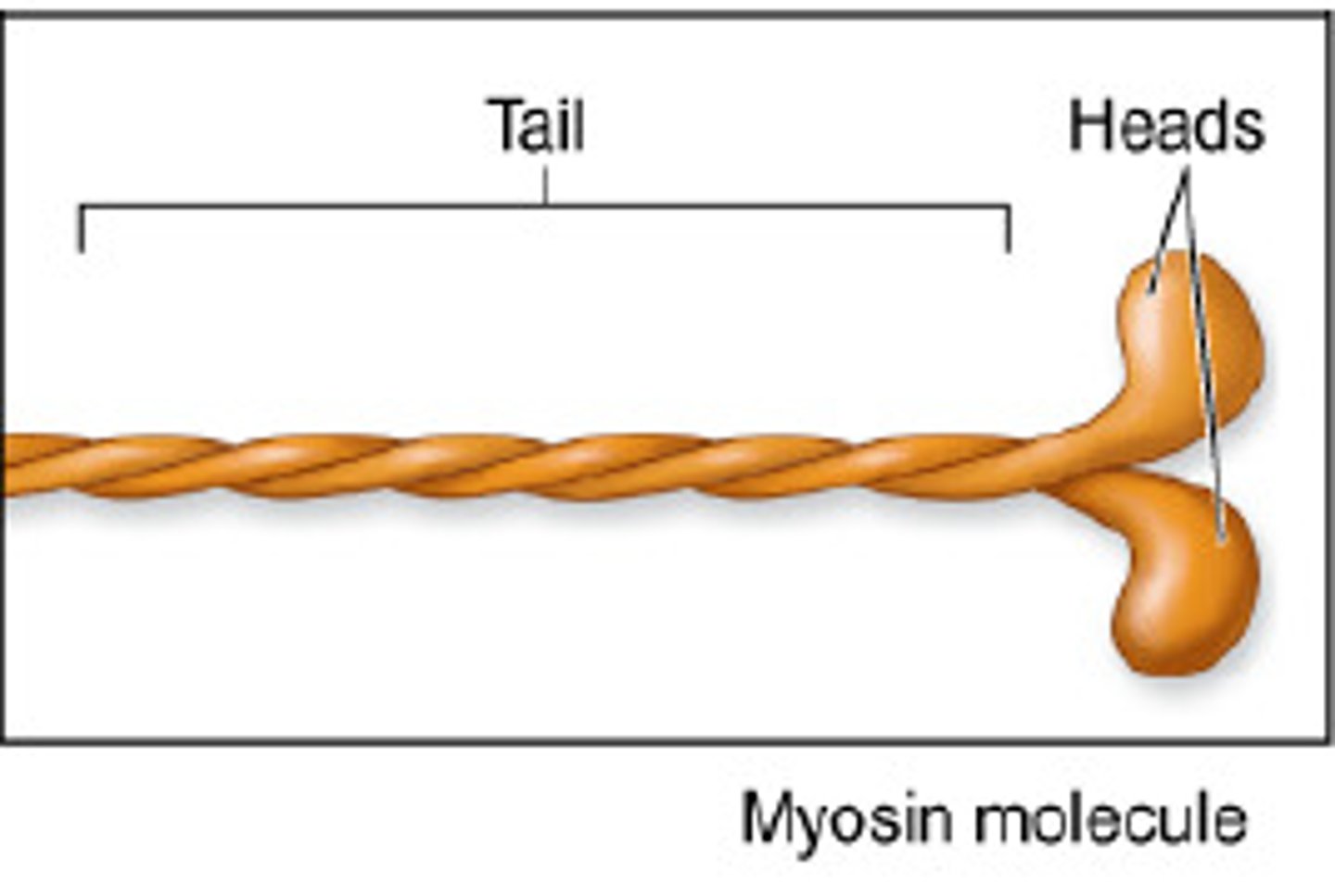
What is the function of the myosin tail?
It binds to other myosin molecules in the thick filament
What is the function of the myosin head?
Binds with the active site on a thin filament
The ____ of a myosin molecule points toward the M line?
a) Tail
B) Head
Tail
What is the connection between a myosin head and the active site on a thin filament called?
Cross-bridge
What protein is found at the core of a thick filament?
Titin
How do sarcomeres shorten?
Myosin heads bind and form a cross-bridge with actin molecules. The myosin heads then pull on the actin molecules causing them to slide along the myosin filaments. Thus, sarcomeres shorten.
What is the sliding filament theory?
A theory that postulates that the thin filaments slide toward the center of a sarcomere during muscle contraction