Study Guide for Biology H Midterms
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
DNA definition
Directs all cell activity from the nucleus.
Amino Acid definition
The basic building block of proteins- 20 different types of amino acids.
Anticodon definition
a set of three bases on a tRNA molecule.
Transcription definition
the process of making a strand of mRNA from DNA in the nucleus.
Codon definition
3 letter code on a strand of mRNA that represents a specific amino acid.
Translation definition
the process of making a protein by following the code on the mRNA.
mRNA definition [Messenger RNA]
a molecule that is made in the nucleus, then travels into the cytoplasm to begin protein synthesis.
tRNA definition
transports amino acids to the mRNA where the protein is being made and matches the anticodon with the codon on the mRNA.
Protein definition
a type of large molecule in living things that are made of a chain of amino acids.
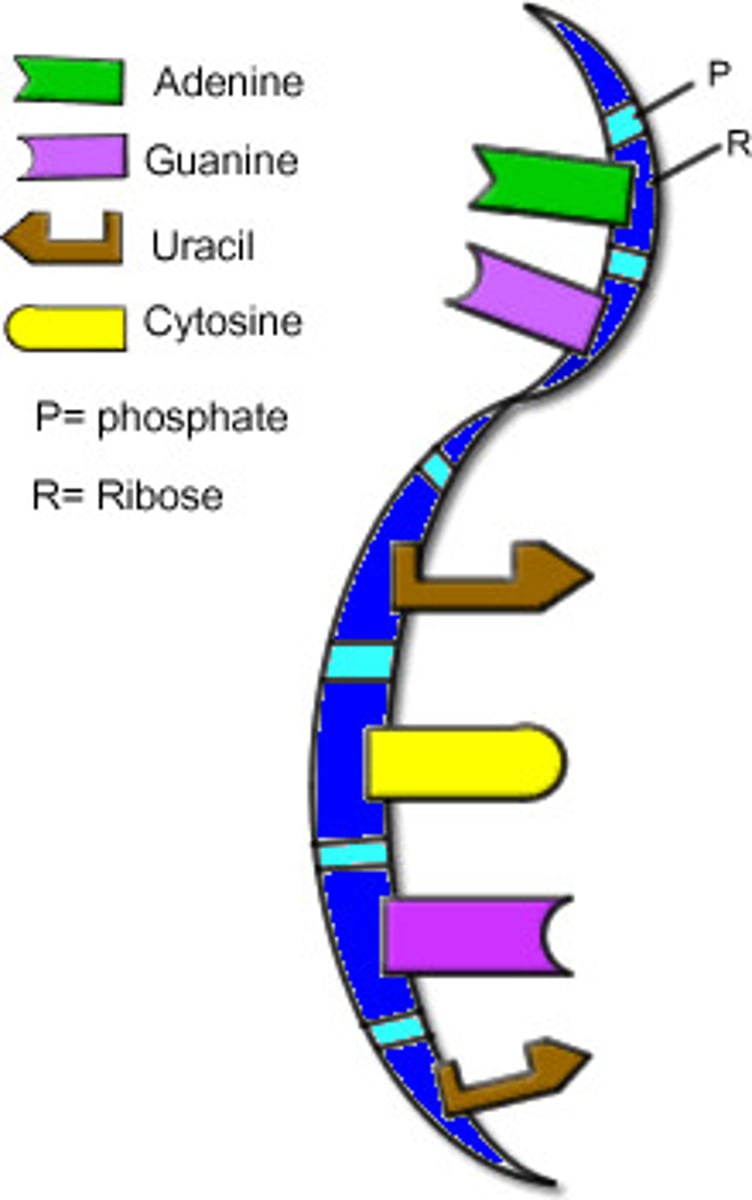
Nucleotide definition
the basic building blocks of either DNA or RNA that is made of a sugar group, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base.
Substitution definition (in a DNA or RNA chain)
When a base in a DNA/RNA chain is substituted for another base.
Deletion definition (in a DNA or RNA chain)
When a base in a DNA/RNA chain is removed/lost, causes a "frameshift" and can cause visible mutations.
Insertion definition (In a DNA or RNA chain)
When a base is added into a DNA/RNA chain. Causes a "frameshift" and can cause visible mutations.
Neutral/Silent mutation
When a DNA sequence is changed (insertion, deletion, or substitution), but no visible mutations occur.
What part of a cell translates RNA into proteins?
A Ribosome
DNA -> RNA -> Protein This process is called...?
Central Dogma
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
Nitrogenous base, Phosphate, and deoxyribose sugar.
What are the four nitrogenous bases?
Adenine, Cytosine, Thymine, and Guanine. (Also Uracil, but only for RNA translation.)
Daughter Strand
The new strand after DNA replication.
Okazaki Fragment
"Chunks" of bases being put onto the lagging strand.
What keeps the backbone of DNA together?
Hydrogen Bonds.
Leading Strand
The parent strand that is added to continuously during DNA replication.
Lagging Strand
The parent strand that is not added to continuously.
Replication fork
Where DNA is separated.
Helocase
"Unzips" DNA.
DNA Polymerase
Builds daughter strand by adding bases.
Semi-Conservative Replication
Made of one "conserved" strand and one new strand.
Evolution
Change in an organism over a long period of time.
What are the 8 characteristics of life?
1. Maintains Homeostasis (maintains a stable "inner environment")
2. Responds to Stimuli (Any change in environment, i.e. pupils expanding when a light is shut off, etc)
3. Can Evolve
4. Reproduces
5. Growth & Development (gets bigger, its functions can change, etc)
6. Displays Organization (cells build in a predictable and orderly fasion)
7. Has a Metabolism
8. Made of Cells
Abiotic
something that's non-living (can be determined with 8 characteristics of life).
Bionic
Something living (can be determined with 8 characteristics of life).
Feedback Loops
The process the brain (or anything) uses to processes information and respond to it. Can be positive (i like the outcome, continue to do what I'm doing) or negative (i don't like the outcome, change what I'm doing).
Positive Feedback loop i.e. Wound Repair
Negative Feedback loop i.e. Sweating/shivering (lowering/raising temperature)
Parts Of a Feedback Loop
1. Stimuli (i.e., temperature outside increases.
2. Variable (what's being monitored- in this case, its temperature.)
3. Sensor (Taking in info [five senses] i.e. noting a change in temp and sending this info to the brain.)
4. Control (Brain processes info and decides response.)
5. Effector (Response to stimuli. In this case, you would sweat if you got too hot.)
Set Point
Whatever the normal level for something is. (i.e. Humans are around 98.6 degrees fahrenheit usually.)
Properties of Water
1. Its cohesive (water molecules stick to other water molecules --> makes surface tension)
2. Its adhesive (water molecules can stick to other non-water molecules)
3. It's a polar molecule (has an uneven charge)
4. It's a universal solvent.
5. It has a high heat capacity. (It can heat up a good amount before boiling)
6. It gives off energy/takes energy in very slowly.
7. Forms hydrogen bonds
8. It's more dense then ice.
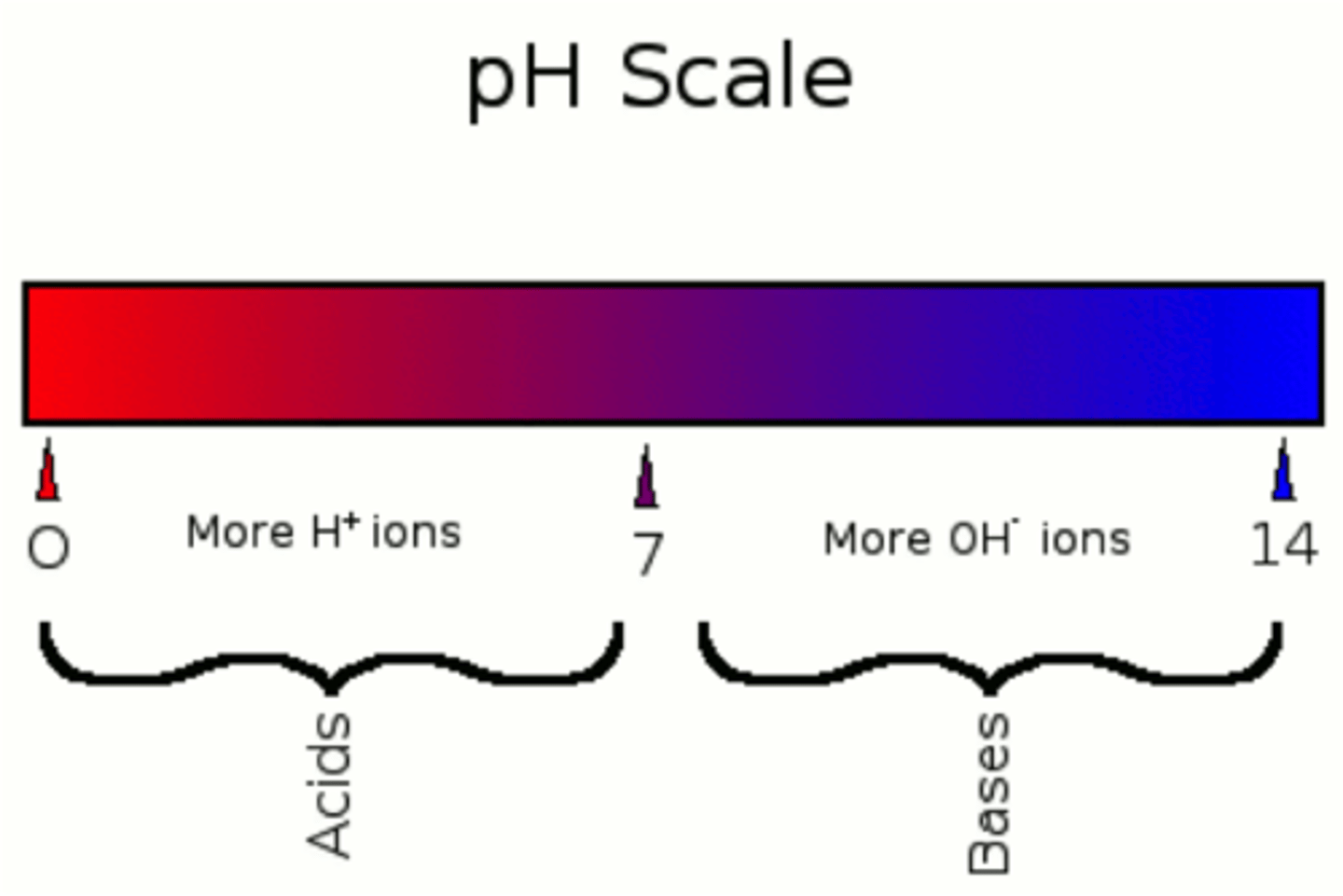
PH Scale
0 is acidic
7 is neutral
14 is basic
more OH --> basic
more H --> Acidic
Solution (mixture, not equation)
One part (a solute) is dissolved into another (solvent.) Very hard to separate.
Solute
thing that dissolves in solvent
Solvent
thing that dissolves the solute
Does an acid donate or accept hydrogen?
It donates
Does a base donate or accept hydrogen?
it accepts
What are the 6 most important molecules / elements?
1. Carbon
2. Hydrogen
3. Nitrogen
4. Oxygen
5. Phosphorus
6. Sulfur
THINK CHNOPS!
Carbohydrates
polysaccharide
one monomer --> monosaccharide
made of the elements C:H:O (1:2:1 ratio)
Lipids
triglyceride (when it looks like an E)
made of fatty acids
made of the elements C:H:O
Proteins
polypeptide
peptide
made of amino acids
made of the elements C:H:O:N:(S) "S" is sometimes found- not usually
Nucleic Acids
DNA/RNA
Nucleotide
made of the elements C:H:O:N:P
Dehydration synthesis
the creation of a macromolecule when macromolecules form
Hydrolysis
requires a water molecule to break bonds.
hydro--> water
lysis--> breakdown
what type of energy do carbs give you?
quick energy!
what type of energy do lipids give you?
low, long term energy.
what type of energy does protein give you?
low, long term energy
what type of energy do nucleic acids give you? (Trick question!)
Only hold genetic info- no energy given
Enzymes
Specialized proteins (Amino acids) used to speed up chemical reactions
[i.e. digestion, breaking up macromolecules]
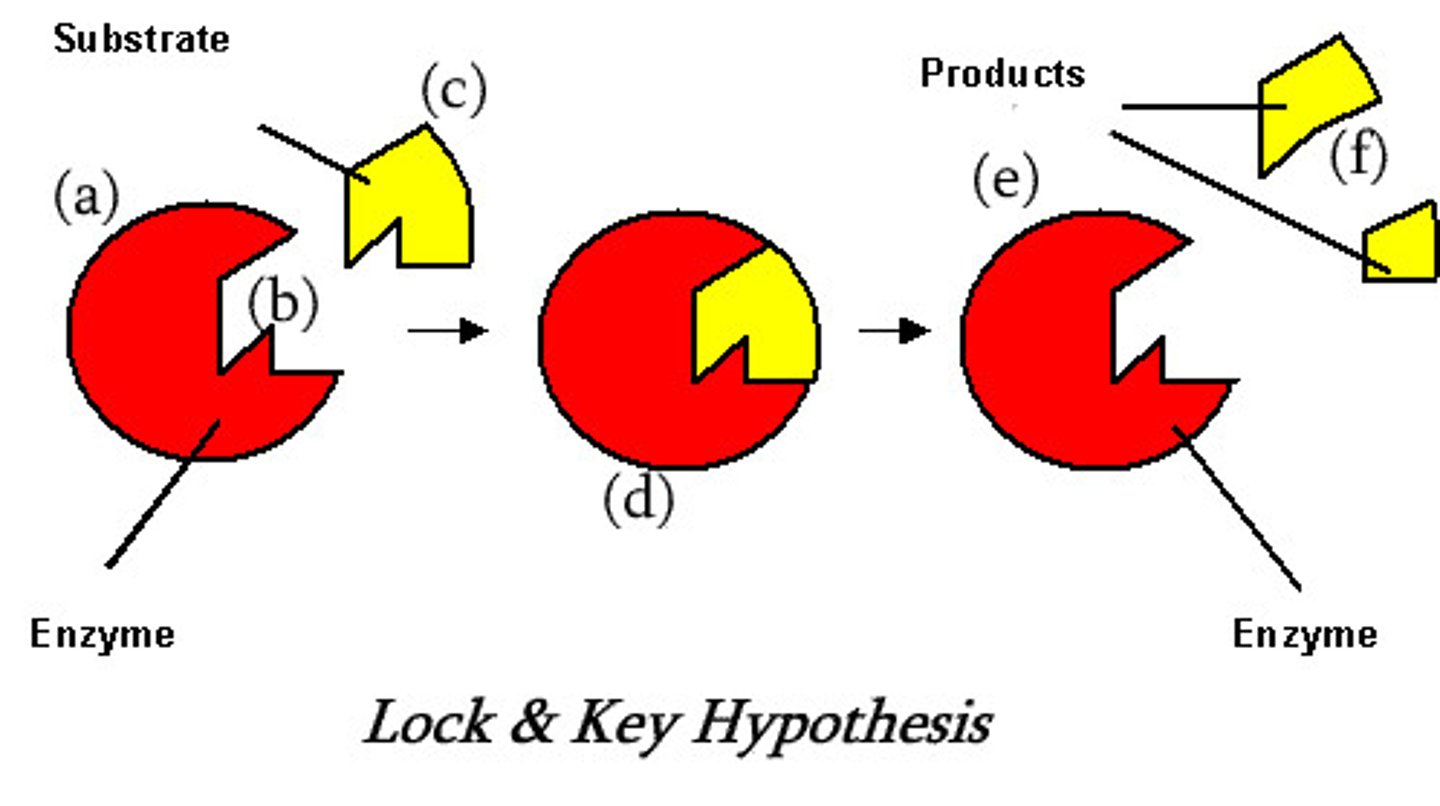
Enzymes use a KEY AND LOCK model. What are the different parts on an enzyme?
the active site (where the substrate connects to the enzyme), the substrate (the chemical reaction needing to be sped up, and the enzyme. The products are what is made by the chemical reaction & enzyme. IF THEY ARENT IN THE RIGHT PH OR TEMP THE MODEL WILL NOT WORK.
Unsaturated fatty acid
has room for more bonds- can break and bend
Saturated fatty acid
cannot add more bonds- all possible bonds have already been made.
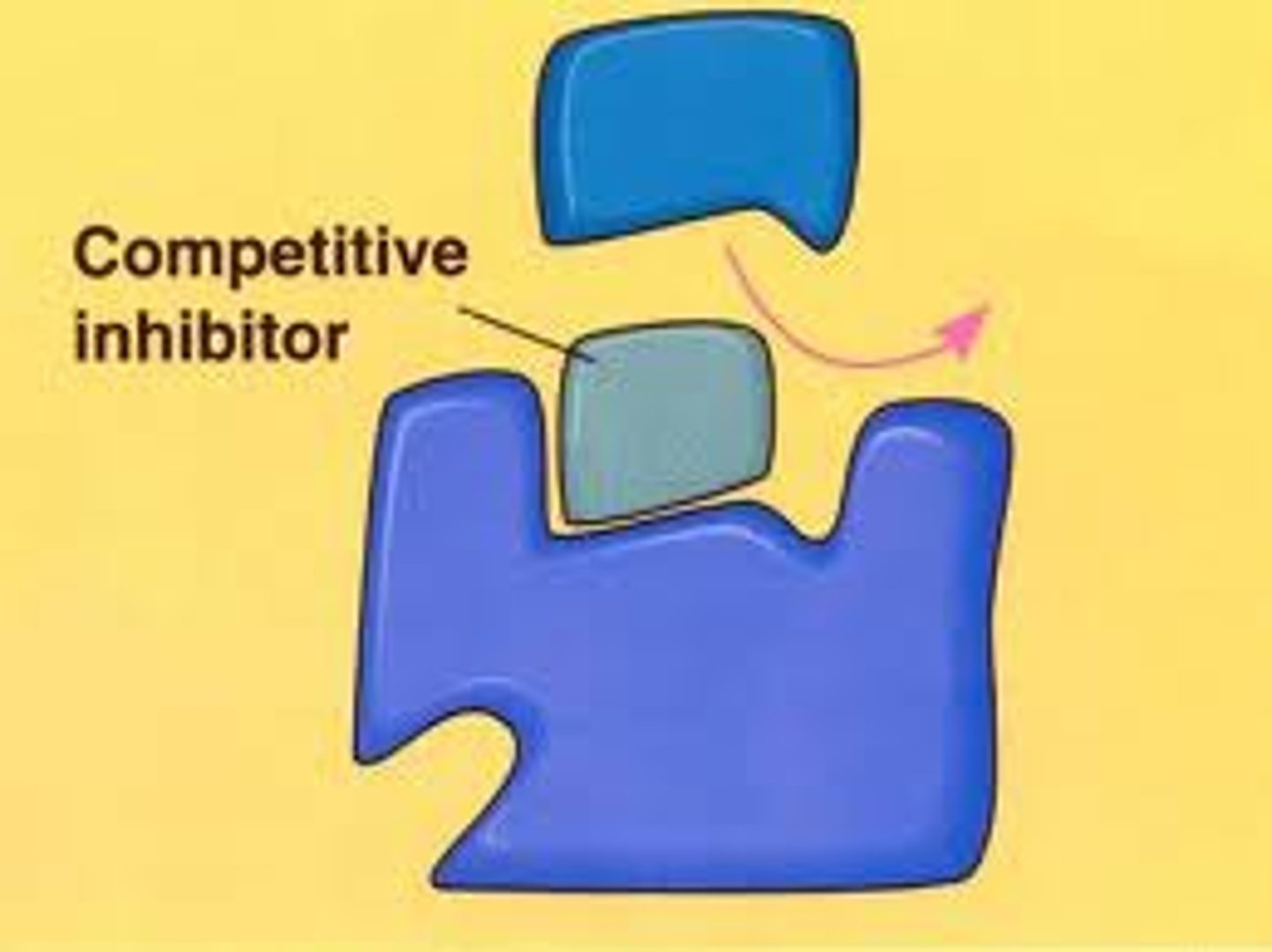
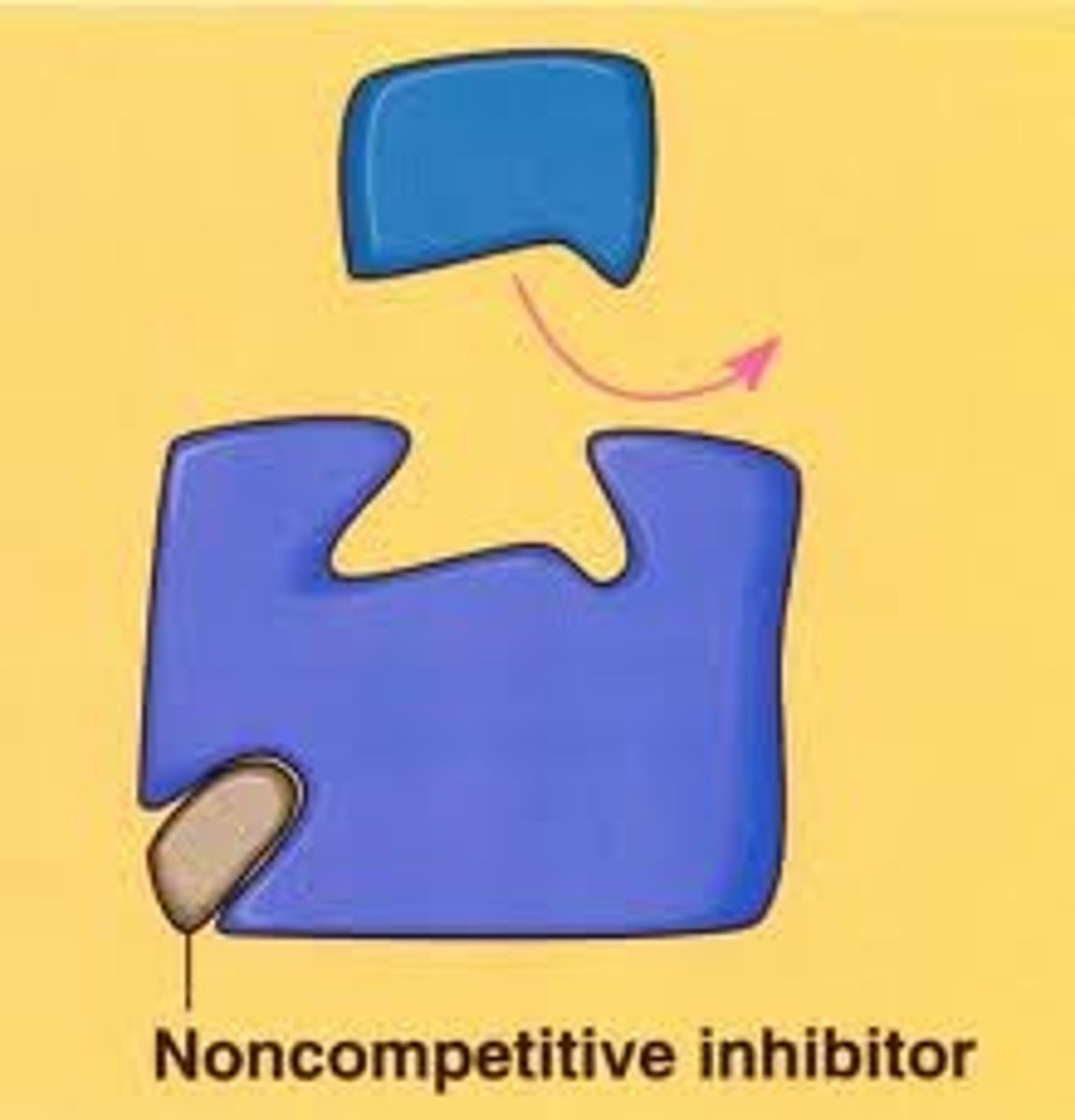
Inhibitors
things that might stop the enzyme from connecting with its specific substrate
Competitive inhibitor
direct competition (blocks active site)

Allosteric Inhibitor (indirect/noncompetitive inhibitor)
Changes the shape of the active site by attaching itself to the enzyme.
Prokaryote
a cell with no nucleus- smaller, less evolved (i.e. bacteria cell)
Eukaryote
A cell with a nucleus- more evolved and complex (i.e. plant or animal cell)
Cell Theory
1. Cells are the building blocks of life
2. All living things are made up of cells
3. All cells come from pre-existing cells
The Cell Membrane
1. semi-permeable (allows certain molecules to enter/exit cell
2. a fluid mosaic model (can change shape, made of different molecules)
Phospholipid bilayer.
Made like a sandwich
Phosphate (hydrophilic)
Lipids (hydrophobic)
Phosphate (hydrophilic)
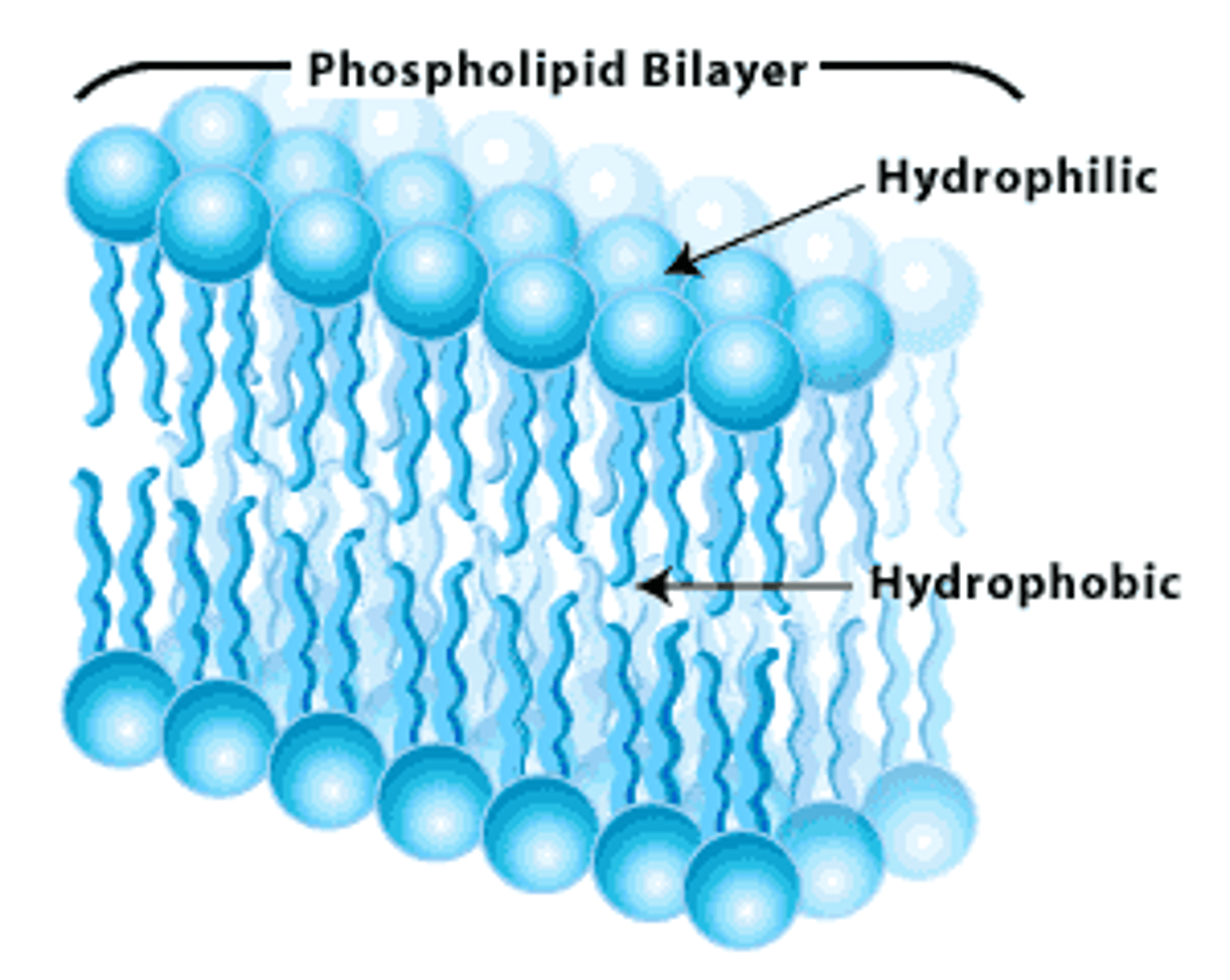
How do things move across a membrane?
DIFFUSION!!!!!
Diffusion
Any particles moving from an area of high concentration to low concentration. Uses NO ENERGY.
Simple Diffusion
Something small can go through the membrane- gasses, dissolvable

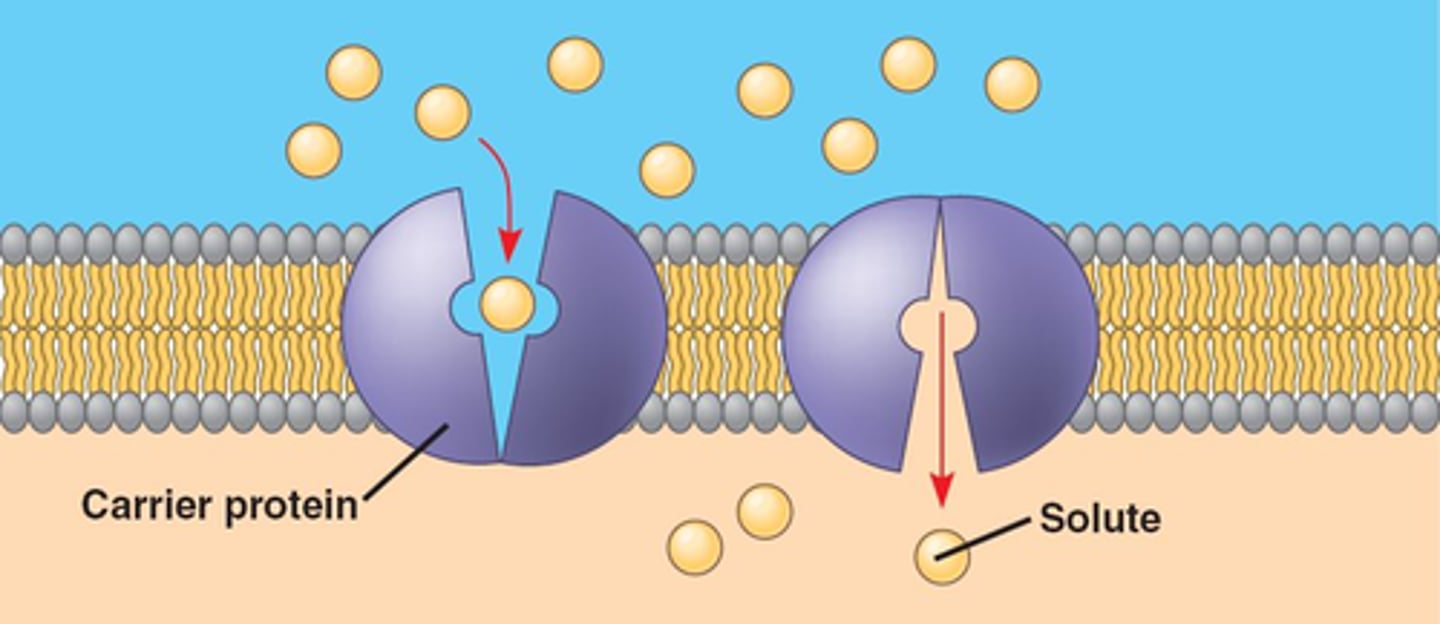
Facilitated Diffusion
will open in response to a chemical/electrical signal
Osmosis
The diffusion of water.
Hypertonic
More solute (Hyper- above, more)
Hypotonic
Less solute (hypo- below, less)
Isotonic
Equal part solute and water. (Iso- Equal)
Why is it important for a cell to be small?
A small cell allows for waste to be removed/nutrients to be brought in and get to their destination more efficiently than if the cell was big. If a cell is too small, it might not have enough room for the necessary organelles.
What are the parts of a cell cycle?
Interphase (G1, S Phase, and G2) and Mitosis.
What occurs during G1 and G2?
Growth and development of a cell.
What occurs during S Phase?
Synthesis/DNA replication [also called duplication]
What are the stages of Mitosis?
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
What occurs during Prophase?
The nuclear membrane dissolves and DNA condenses into chromosomes.
What occurs during Metaphase?
Sister chromatids (Chromosomes) line up in the middle of the cell to form a line.
Centrosomes also send out microtubules that connect to the centromeres of the chromosomes.
What occurs during Anaphase?
The sister chromatids are pulled away from each other- one on each side of the cell.
What occurs during Telophase?
Two cells start to form (elongation begins and "pinching" occurs in the middle.) The nucleus reforms. Cytokinesis IS NOT A PART OF TELOPHASE! They occur at the same time but AREN'T a part of the same process.
Cytokinesis
The splitting of the cell. (NOT A PART OF MITOSIS)
rRNA [Ribosomal RNA]
Makes up the ribosome.
What are the phases of Meiosis?
PMAT |
Prophase |
Metaphase |
Anaphase |
Telophase |
PMAT ||
Prophase ||
Metaphase ||
Anaphase ||
Telophase ||
What occurs during Prophase | and ||?
Prophase | --> Crossing over happens between homologous chromosomes, nucleus dissolves
Prophase || --> Nucleus dissolves
What occurs during Metaphase | and ||?
Metaphase | -- > Homologous Chromosomes meet in the middle of the cell
Metaphase || -- > Sister Chromatids meet in the middle of the cell
What occurs during Anaphase | and ||?
Anaphase | --> Homologous chromosomes move away from each other
Anaphase || --> Sister Chromatids move away from each other
What occurs during Telophase | and ||?
Telophase | & || --> Splits cell apart
How many cells do you end up with in Meiosis / what are some characteristics they have?
You end up with four unique daughter cells with 23 chromosomes each.
Why is Meiosis so important?
It's the sole reason for genetic information.
Diploid/2N
a cell that contains 2 copies of each chromosome (Has 46 chromosomes)
Haploid/N
a reproductive cell with 23 chromosomes.
Zygote
A newly fertilized egg
Circulatory System
(aka cardiovascular system) This system works to move blood around the body. It consists of the heart, blood, and blood vessels. It transports substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients in the body.
Nervous System
the network of nerve cells and fibers that transmit nerve impulses between parts of the body.
Brain, spinal cord, and neurons.
Respiratory System
Exchanges O2/CO2
Mouth, Nose, throat, pharynx, larynx, bronchi, alveoli, lungs
Digestive System
Breaks down / takes in nutrients
mouth, esophagus, liver, stomach, pancreas, gallbladder, intestines
Excretory/Urinary System
removes waste from body
Excretory:
kidneys
bladder
Urinary:
liver
skin
lungs
What are the main five body systems?
Nervous, Excretory/urinary, digestive, respiratory, and circulatory.
X-Linked definition
a gene located on the X chromosome