Mammalogy lab terms
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Anterior
toward the front end; before, nose end, opposite of posterior
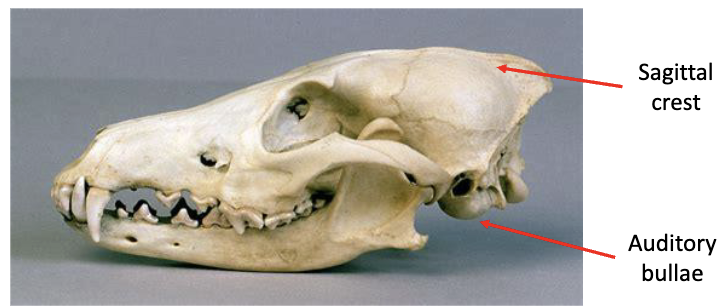
Bullae
rounded, hollow, thin-walled structure (ex. auditory bullae)
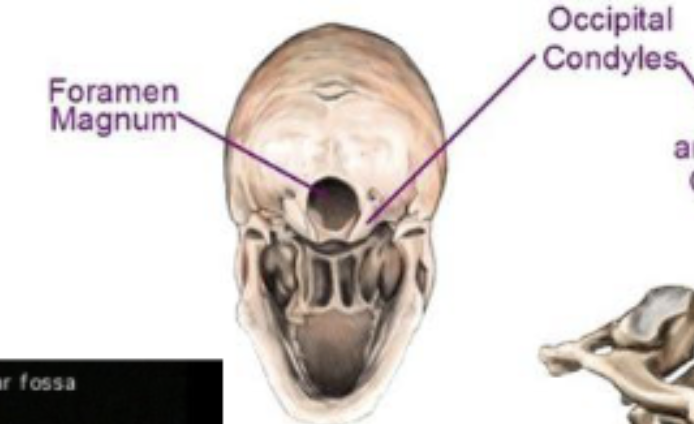
Condyle
Knob-shaped bump on bone that forms a joint with another bone
ex. occipital condyle
crest or ridge
elevated region (sagittal crest)
Distal
away from point of attachment, opposite from proximal
posterior
toward the rear
dorsal
back side
ventral
stomach side
proximal
situated near the point of attachment
Medial
lying in or near the plane dividing the body into two mirroring halves
Diastema
gap between teeth
Fenestra
opening through bone
foramen
opening in bone for blood vessel or nerve (example. foramen magnum)
Fossa
depression in bone for a blood vessel or nerve
Labial
pertaining to lips; side closest to tongue
Medial
Lying in or near the plane diving the body into two mirror image halves, inward side
perforation
a hole through a bone
posterior
rear; behind; tail end; opposite of anterior
process
projection of bone
example: postorbital process
proximal
situated near to point of attachment; opposite of distal
suture
junction between two contiguous bones of the skull. Different sutures close at different ages, and can help determine age of a specimen
Ventral
belly side; opposite of dorsal
auditory bullae
hollow structure on ventral/posterior portion of skull; used to amplify sound
braincase
part of the skull that encases the brain
foramen magnum
hole in the base of the skull through which the spinal cord passes
Palatine
hard roof of the mouth; also called the palate
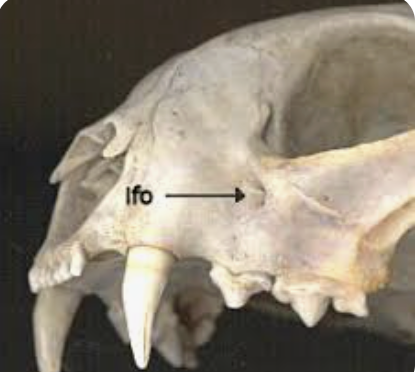
infraorbital foramen
hole in maxilla below the orbit; several important veins and nerves pass through here
Jugal
bone in the zygomatic arch; located between maxilla and squamosal
mandible
lower jaw bone
masseter
muscle; provides crushing/grinding force in back of mouth; compare to temporalis; more pronounced in herbivores
masseteric fossa
point of attachment for masseter
Maxilla
central bone in mid-face; upper jaw; often where upper teeth root
Orbit
area between zygomatic arch and cranium where eye rests
postorbital process
lateral projection above orbit; marks posterioer boundary of orbit
pre maxilla
bones that make up the anterior tip of the upper jaw; some teeth rooted here
rostrum
“face bones” anterior to zygomatic arches
makes up the nose
sagittal crest
ridge of bone running along dorsal midline of the skull; pronounced crest suggests strong temporalis muscles; often well defined in predators
squamosal
posterior bone in the zygomatic arch
temporalis
muscle; provides shearing/tearing power to front of mouth; compare to masseter; more pronounced in carnivores
temporal fossa
point of attachment for temporalis
zygomatic arch
cheeck bone; (made up of squamosal, jugal, maxilla); masseter attachment point
Edentate
no teeth
teeth growth
diphyodont, polyphyodont, monophydont
teeth heights
brachydont, hypsodont
teeth shape
homodont, heterodont
occlusal surface
where teeth meet each other
Upper teeth
grow from pre maxilla and maxilla
Lower teeth
grow from mandible
Diphyodont
species with deciduous teeth (teeth that fall off - milk teeth) and permanent teeth
examples: most mammals
Monophyodont
Species that grow only one set of teeth
examples; dolphins, whales, manatees, rodents
polyphyodont
more than 2 sets of teeth
examples; elephants
hypsodont
high-crowned teeth, enamel extends beyond gum line
examples; cow, horses
Brachydont
Low crowned teeth
example; humans, dogs, cats
Homodont
All teeth are the same shape
example: orca, bottlenose, dolphin
Heterodont
teeth are different shapes
example: dogs, cats, most mammals
Quadritubercular
4 cusp teeth
selenodont
lophodont
bunodont
secodont
Tribosphenic
3 cusp
Zalambdodont
dilambdodont
Selenodont
4 cusp
Crescent/moon shape, ridges run anterior>posterior
example: deer
Lophodont
Fused ridges, run labial> lingual, cusps appear folded
example: beavers, elephant, porcupine
Bunodont
Low-crown, flattened
Example:humans, raccoon, bear
Secodont
sharp, shearing teeth, line with sharped cusps
example: dogs
Zalambdodont
“V” shaped occlusal surface
Euloptyphla: shrews and moles
Dilambdodont
“W” shaped occlusal surface
opposums and tree shrews
Carnassial teeth
distinct carnivore teeth for ripping and shredding
bottom jaw - first largest molar
incisors
rooted in pre-maxilla
usually single cusped
for clipping and gnawing
canines
rooted along the pre-maxilla - maxilla suture
usually single cusped
for piercing and stabbing
herbivores - often lost or reduced
Pre-molars
rooted in maxilla
crushing, grinding, mashing
axis
second cervical vertebrate; has anterior projection, the odontoid process
atlas
first cervical vertebrae; lacks a centrum
ribs
long curved bones that surround the chest cavity
sternum (breastbone)
a series of bony segments that connects the rib bones with cartilage, forming the ribcage
baculum
penis bone (found in only some primates)
Vertebra
interlocking bones that form the spinal column. There are cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and caudal.
carpals
wrist bones, distal to radius and ulna
clavicle
collarbone ; extends from acromion process of the scapula to the sternum, and provides a firm brace for the anterior limb; together with the scapula forms the pectoral girdle
humerus
long bone of the upper forelimb. articulates distally with the two bones of the lower forelimb, the radius and the ulna.
this hinge joint is termed the elbow, and allows movement in only one plane
metacarpals
distal to carpals, elongate bones that extend to each digit of forelimb
phalanges
digits of forelimb or hindlimb
transverse coastal facet
where ribs attach
sacrum
5 fused bones, where penis attaches
radius
one of two bones of the forearm, the radius is the more medial of the two elements, and articulates at both ends in a manner that allows the two bones rotate around the other
scapula
shoulder blade; together with clavicle forms pectoral girdle
ulna
one of two bones of the forearm, generally larger than radius
calcaneus
heel bone; one of the tarsals; extends dorsally to provide leverage for the calf muscle via the Achilles’ tendon
Epipubis
additional set of pelvic bones extending anteriorly from the pubic region of the pelvis (only in monotremes and marsupials)
femur
long, proximal bone of the hindlimb, attaches to the pelvis with the deep acetabulum
fibula
distal to femur, and lateral to tibia; generally smaller than tibia
Metatarsals
distal to tarsals, elongate bones that extend to each digit of the hindlimb
pelvis
formed by ilium, ishium, and pubic
sacrum
3 to 5 vertebrae are few in number and not differentiated from lumbar vertebrate in mammals with reduced hind limbs
tarsals
ankle bones
tibia
one of the bones of the hindlimb; distal to femur, and medial to fibula; generally larger than the fibula
plantigrade
walking on the soles of the feet, like a human or a bear
digitigrade
walking on its toes and not touching the ground with its heels, as a dog, cat or rodent
uguligrade
walking on hooves
unguis
broad, hard upper portion of the hoof
subunguis
softer plate that covers the bottom of the toe and is extensively developed in hoofed animals to form a tough pad