Repro Exam 1 Review
1/71
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
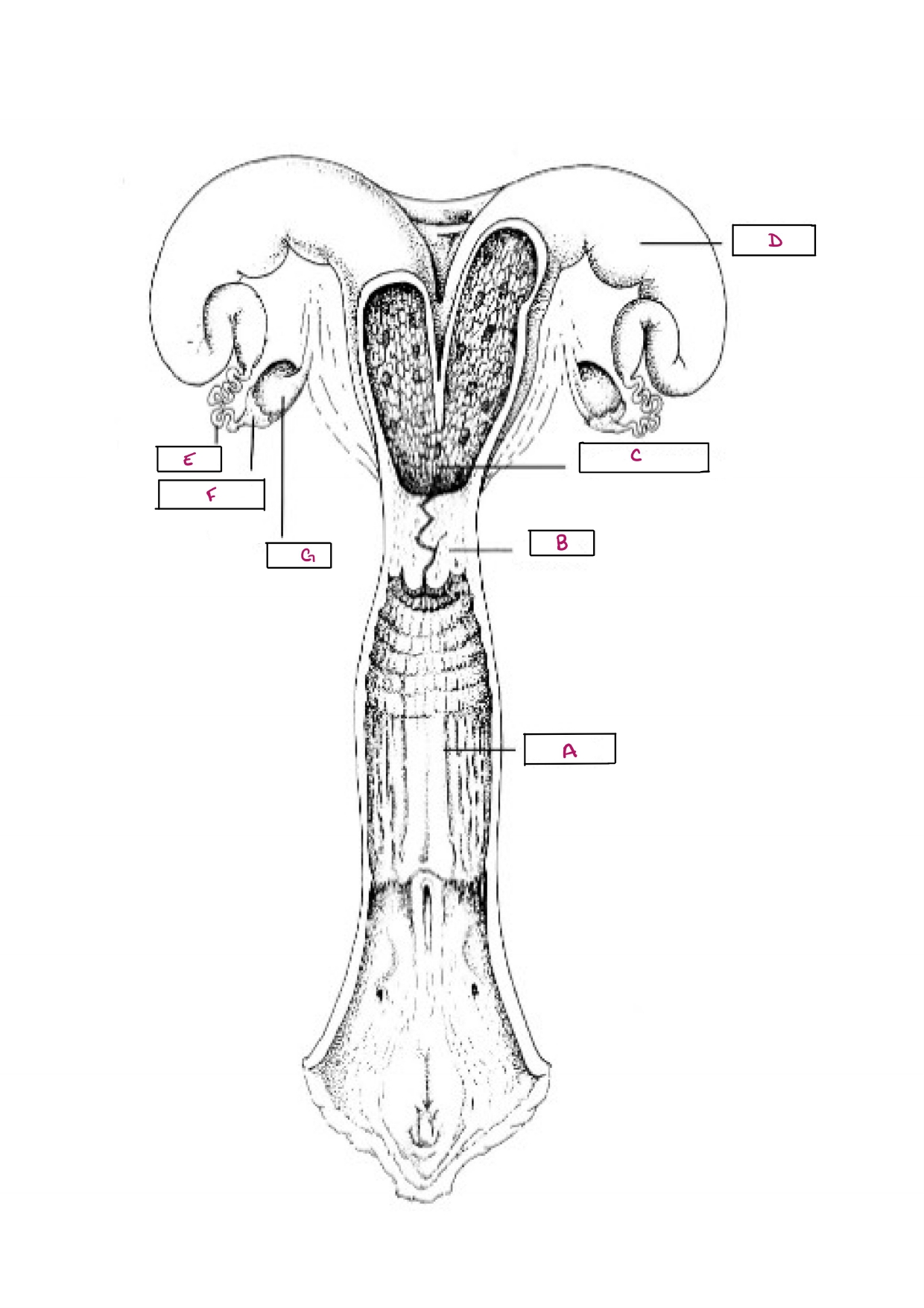
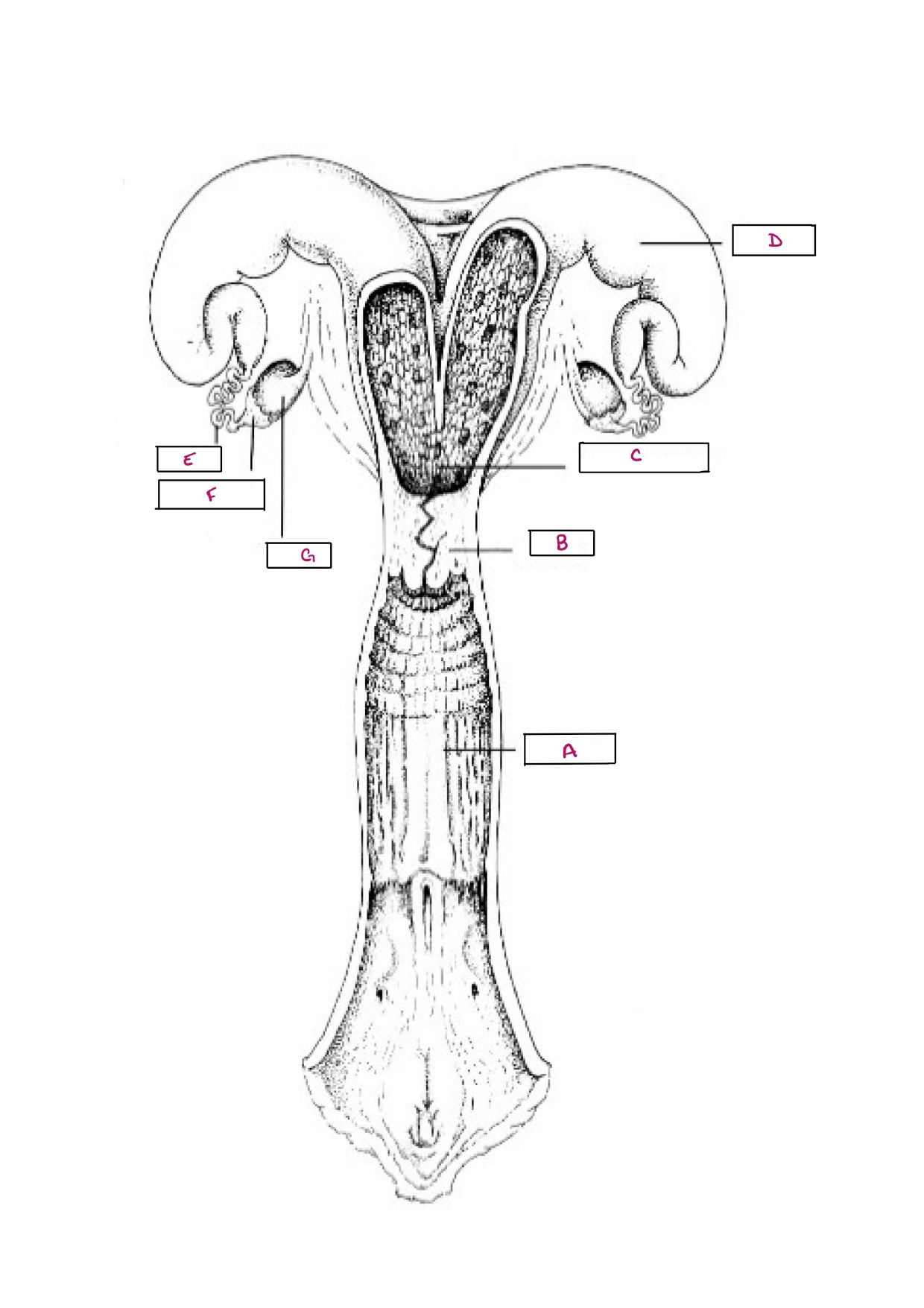
Name A
Vagina
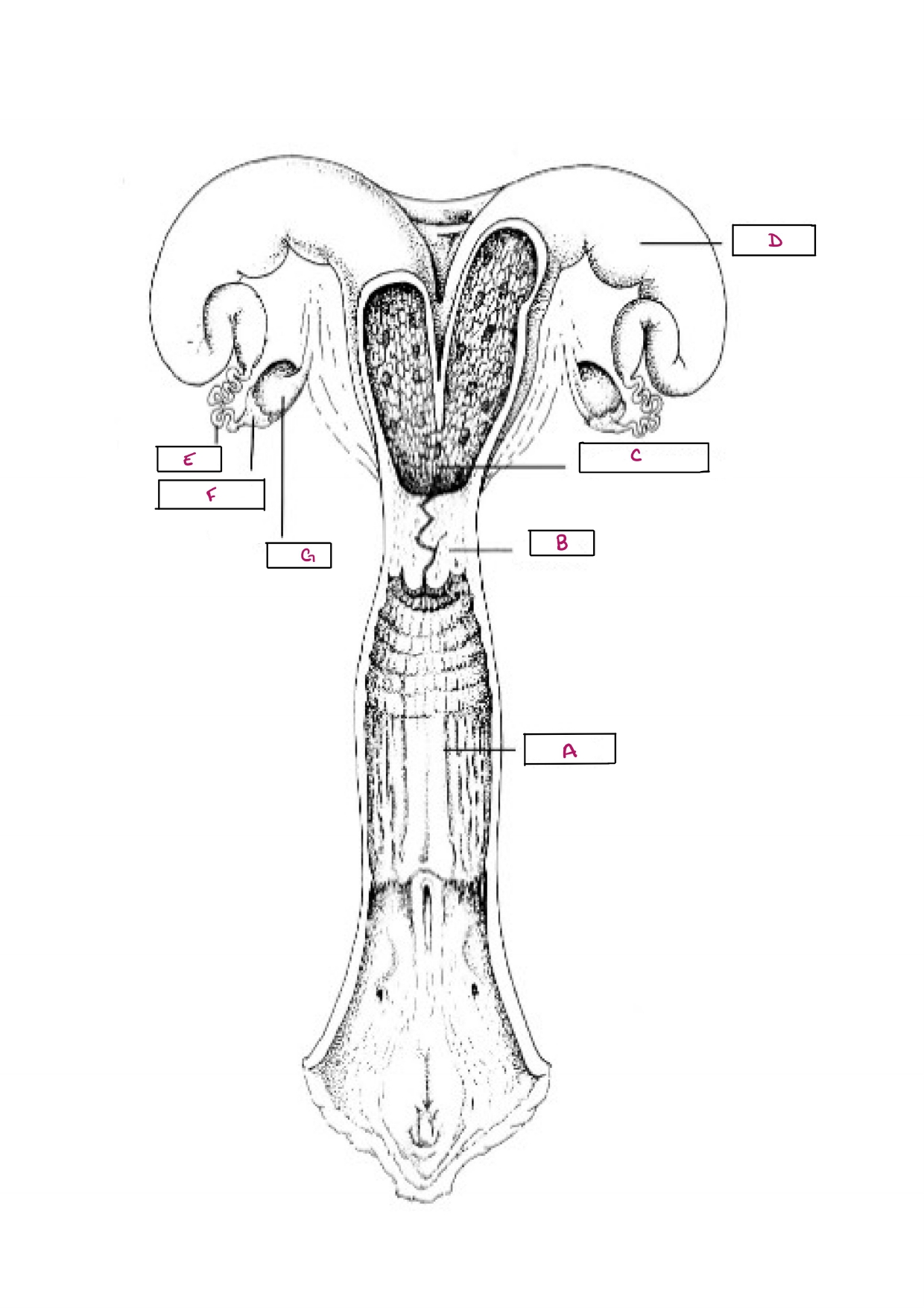
Name B
Cervix
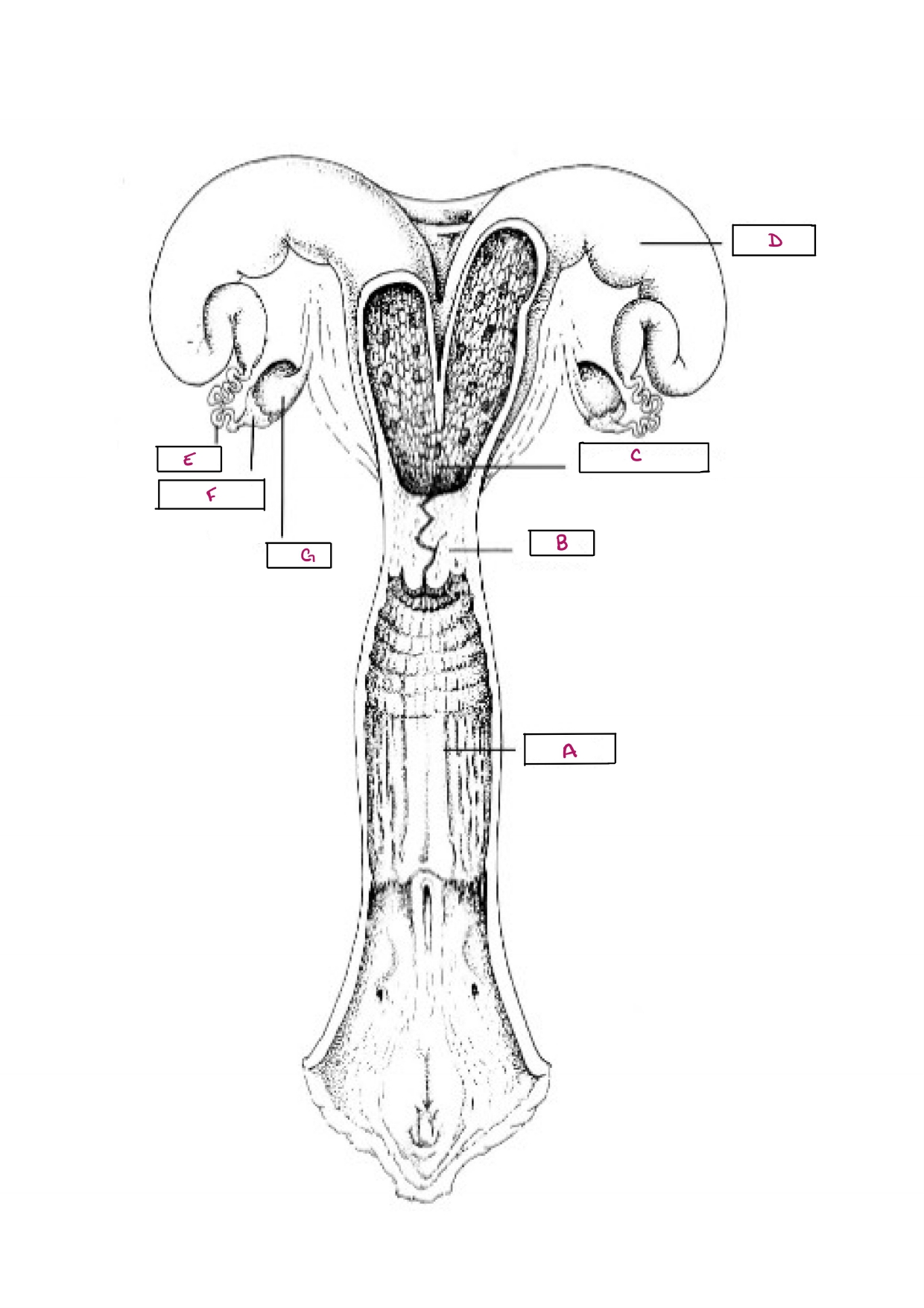
Name C
Body of Uterus
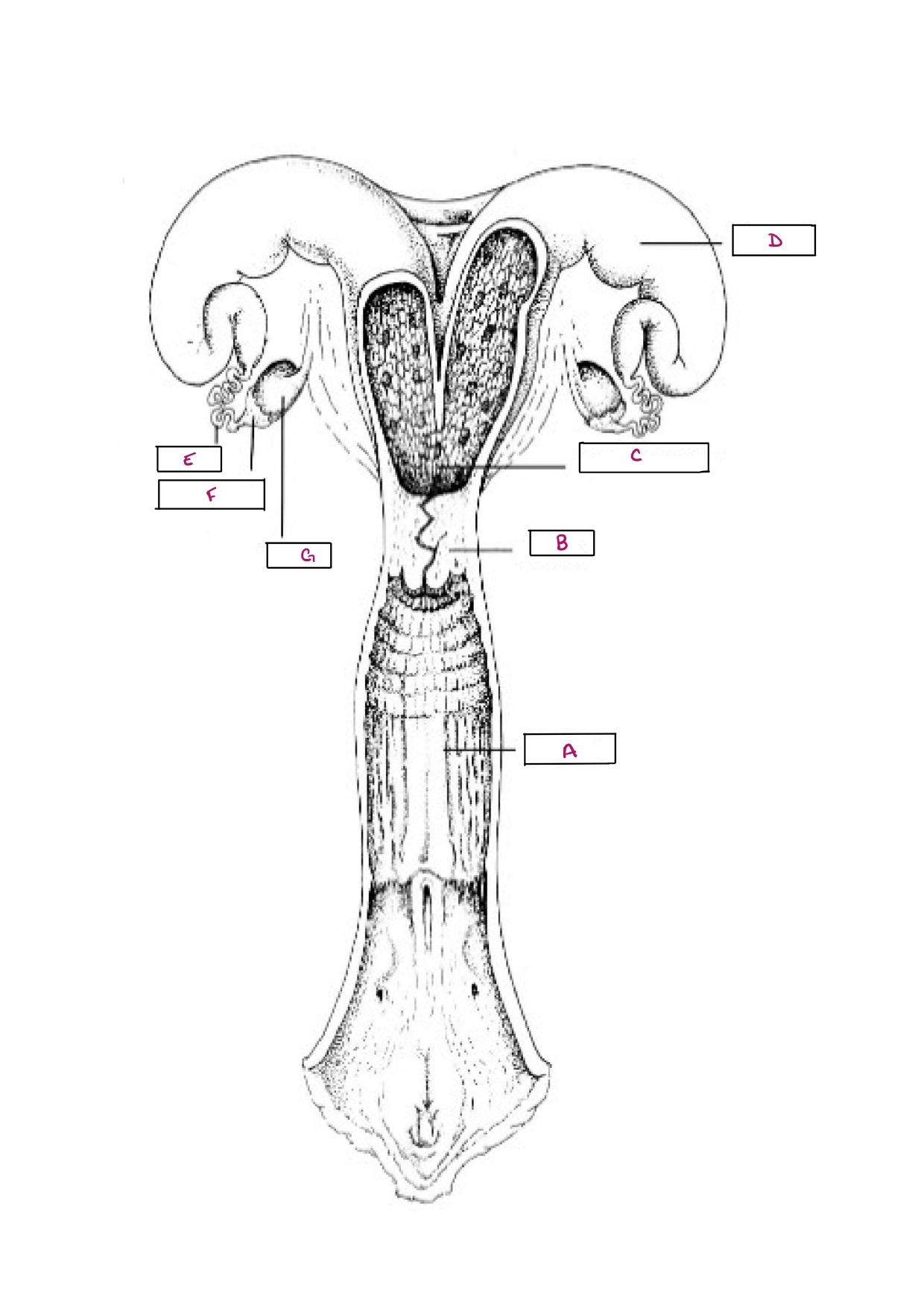
Name D
Uterine Horn
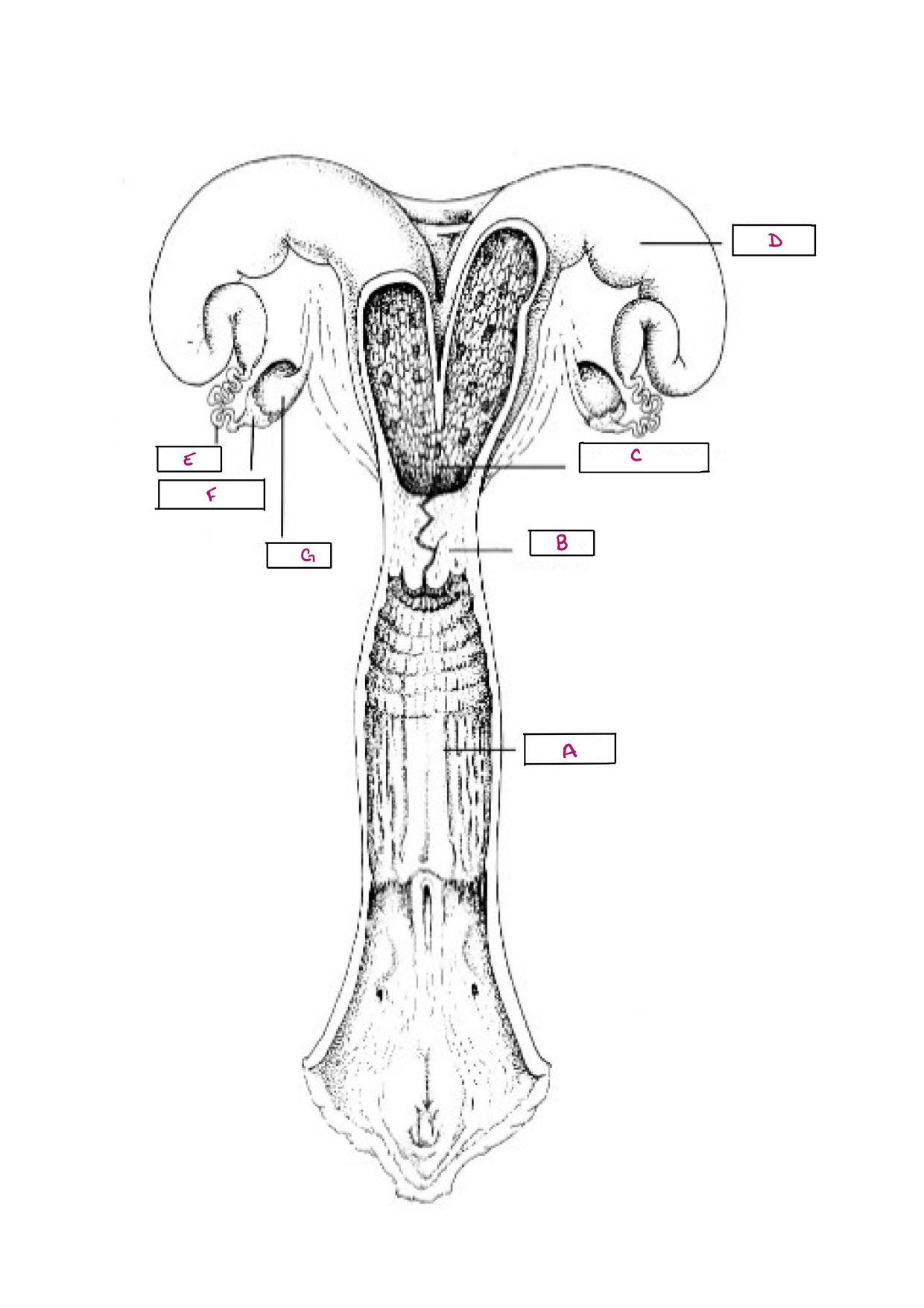
Name E
Oviduct
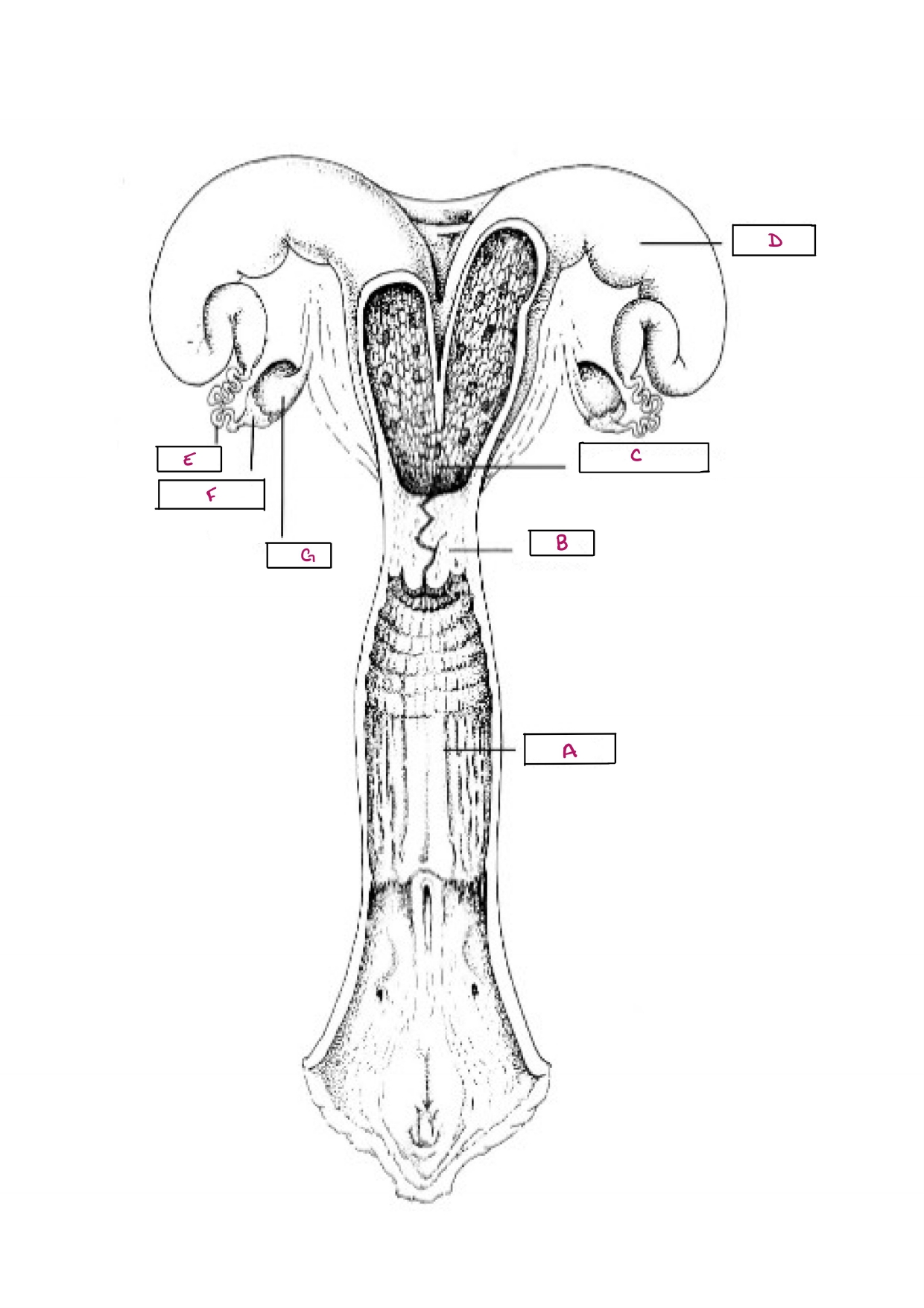
Name F
Infundibulum
Name G
Ovary
Andrology
Is the branch of reproductive physiology that deals specifically with the study and treatment of male animals, including humans. (Greek Androus = male)
Gynecology
The branch of reproductive physiology and medicine that deals specifically with reproductive issues in women (Greek Gyne = women)
Theriogenology
Branch of veterinary medicine that focuses on the reproductive system in animals (Greek therio = beast of animal, Gen = creation or generation, ology = study of)
Obstetrics
Branch of reproductive physiology, veterinary medicine and/of human medicine that specialized in the female before, during and after parturition
Career opportunities in reproductive physiology
Molecular medicine, veterinary medicine, companion animals
The glans penis is populated with what?
Sensory nerves
The penis of the bull can be divided into how many parts?
3; Root, Body and Glans Penis
List 3 sperm abnormalities
Double head
Coiled tail
Double tail
Identify an imperament of a penis
warts
hair
cuts
What female reproductive organ is codle to the vagina?
Vulva
What female reproductive organ is codle to the cervix?
Vagina
What is the function of the rectal penis muscle?
When it release; it extends
When it comes back; it retracts
What book did Aristotle write
Generation of Animals
What was Aristotles though of menstrual blood?
Aristotle believed that the fetus came from menstrual blood
What was Aristotles though of semen?
Semen was derived from all parts of the body and that the sperm head was thought to contain a microscopic, yet fully formed individual
What was Fallopius known for?
Discovered the oviducts; Fallopian tubes
What was Coiter known for?
Discovered the corpus luteum; follicle on ovary
What was Reginar de Graaf known for?
Described the antral follicle; Graafian follicle
What was Van Leeuwenhoek known for?
Developed the simple microscope
What was Spallanzani known for?
Father of modern AI
Explain what occured in the 1940’s and 1950’s
Understanding of spermatozoa physiology and how cells function in test-tube environments led to successful AI in several species
Explain what occured in the 1960’s
Understanding that prostaglandin F2α regulated the length of the estrus cycle in most mammalian females
What is the Rectogenital pouch?
Space between the rectum and genital organs
What do the ovaries do?
Produce ova
What does the oviduct do?
Transport tubes
What does the uterus do?
Acts as the body/house
What does the cervix do?
Acts as a barrier separating the external genitalia from the internal genitalia
What does the vagina do?
Serves as a birth canal, protective barrier
What does the external genitalia do?
Protects from bacteria
Identify the fetal size relation to common animals at 4 months
Small cat
Production
Sperm is produced
Transport
Sperm is transported from the testis, through the body and out
Transfer
Sperm is transferred from the male to the female
What is Embryogenesis?
The formation and growth of an embryo
What is Differentation?
The development of structure and function that is more specialized than the original cells or tissue
What are the 3 germ layers and where are they located?
Endoderm - inside
Mesoderm - middle
Ectoderm - outside
What organs/systems are “created” in the ectoderm?
Skin, hair, nails, sweat glands
Nervous system
Oral cavity
Nasal cavity
Reproductive tract
What organs/systems are “created” in the mesoderm?
Muscle
Blood vessel
Reproductive system
Urinary system
Skeletal system
What organs/systems are “created” in the endoderm?
Digestive system
Respiratory system
Most glands
What occurs in the 1st trimester?
Migration of primordial germ cells from yolk sac
Sex cords develop in gonad, paramesonephric ducts develop
Sex evident from structures (Development of the male ducts and testes; Development of the female ducts and ovaries)
What occurs in the 2nd trimester?
Formation of broad ligament
Testicular descent (Bull and Ram)
What occurs in the 3rd trimester?
Testicular descent (Boar and Colt)
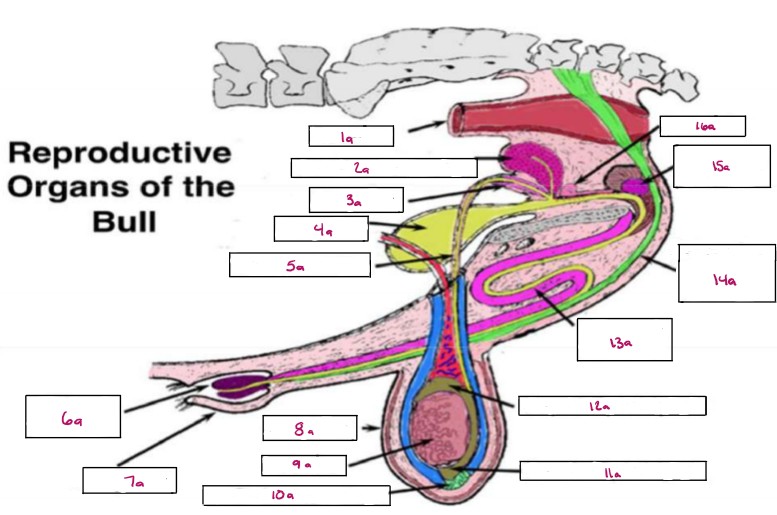
Name 1a
Rectum
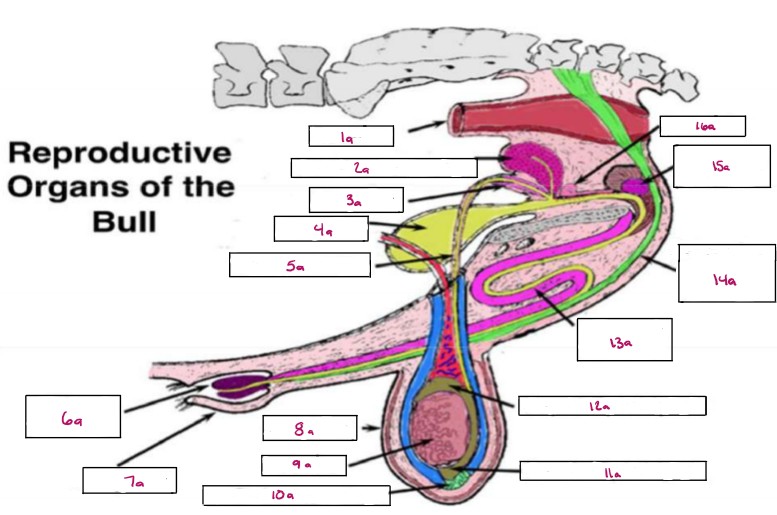
Name 2a
Seminal Vesicles
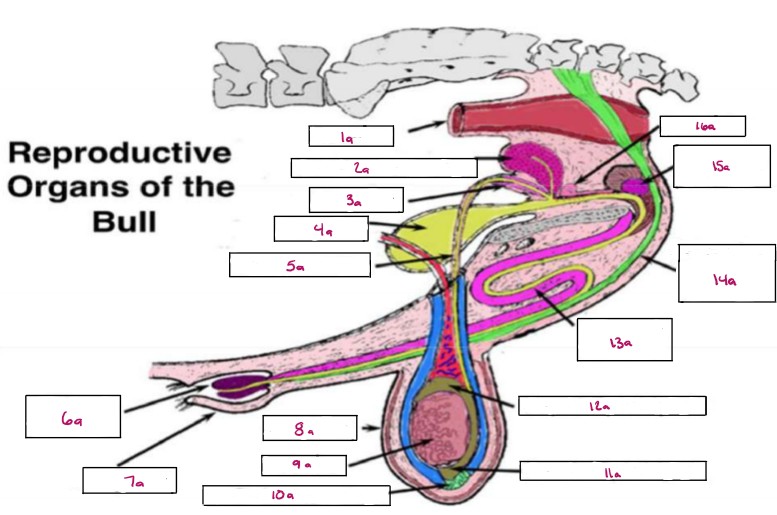
Name 3a
Ampulla
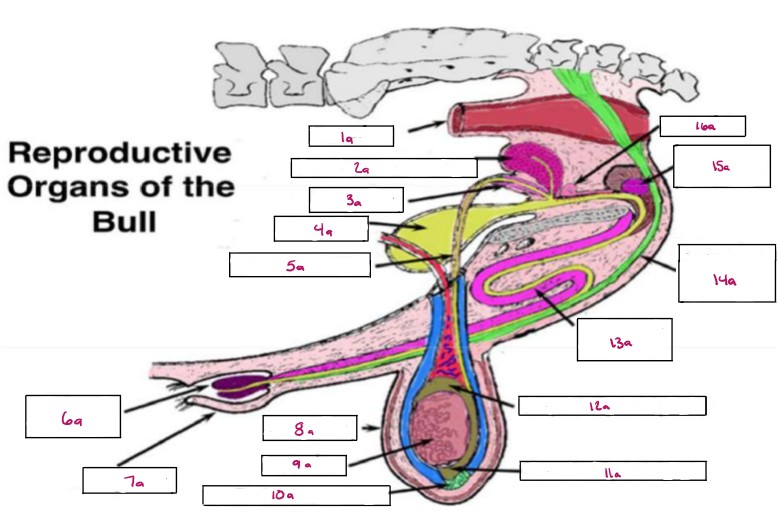
Name 4a
Bladder
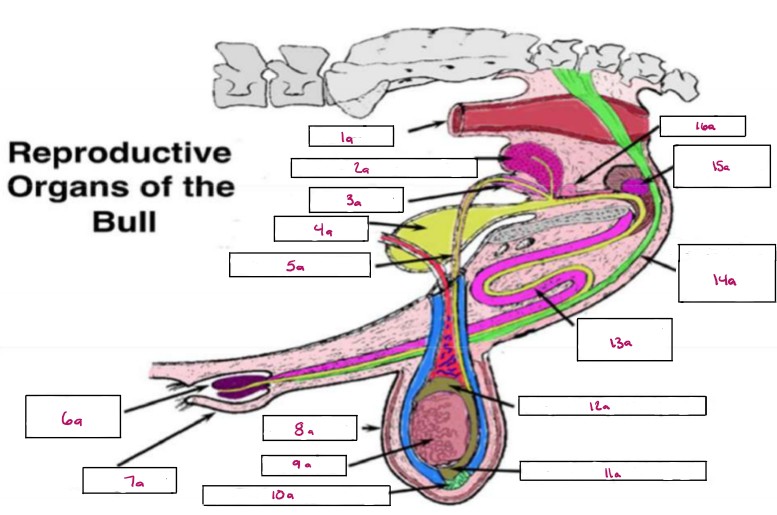
Name 5a
Vas Deferens
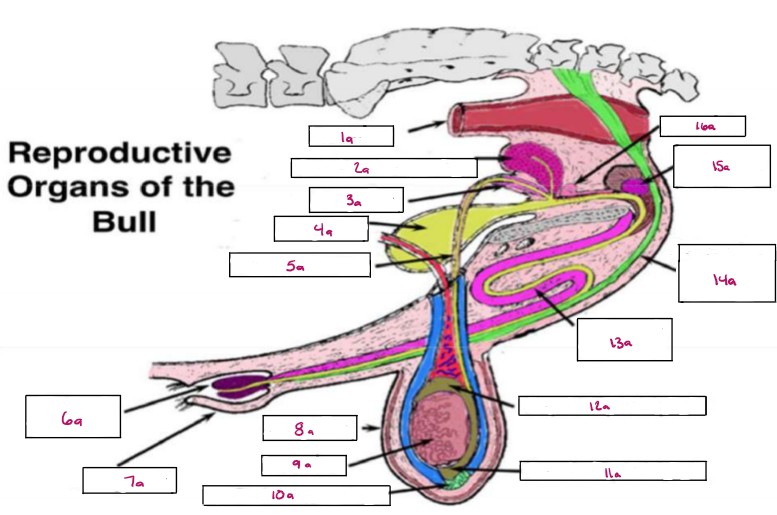
Name 6a
Glans Penis
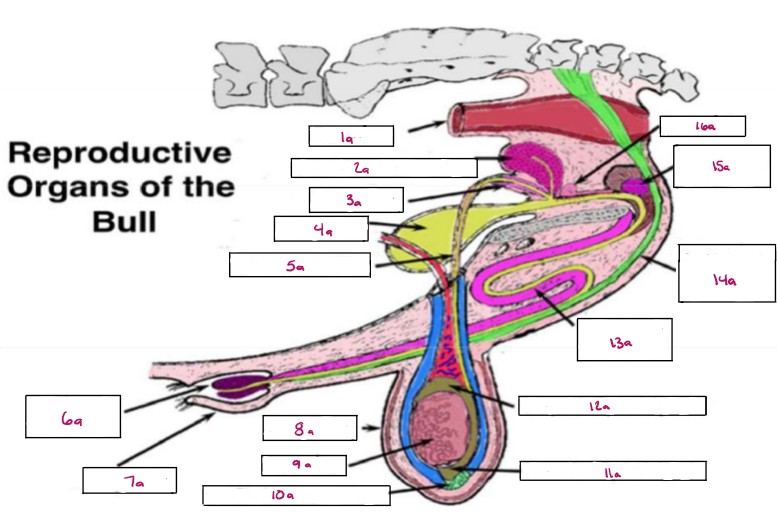
Name 7a
Prepuce
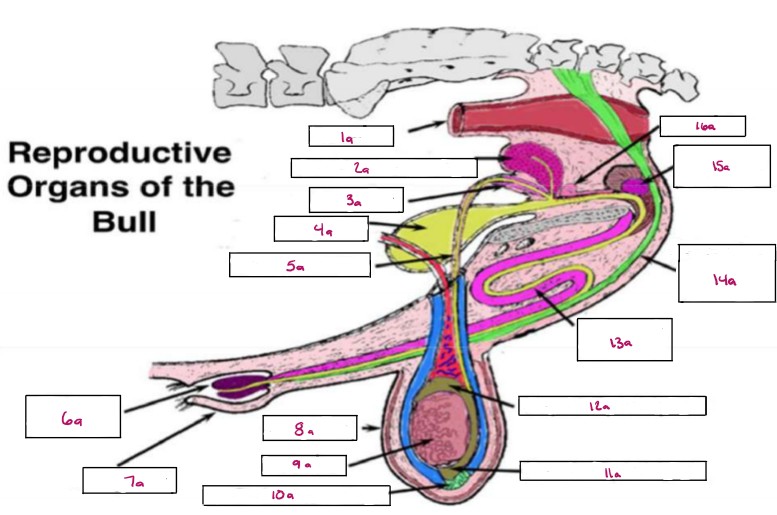
Name 8a
Scrotum
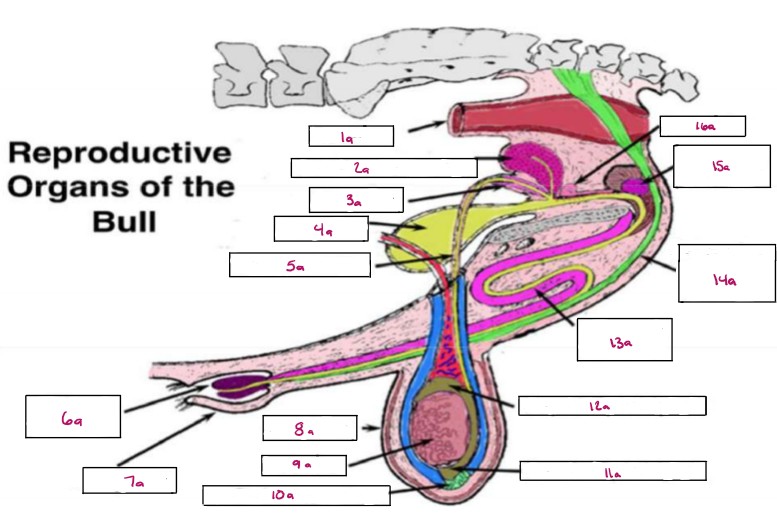
Name 9a
Testis
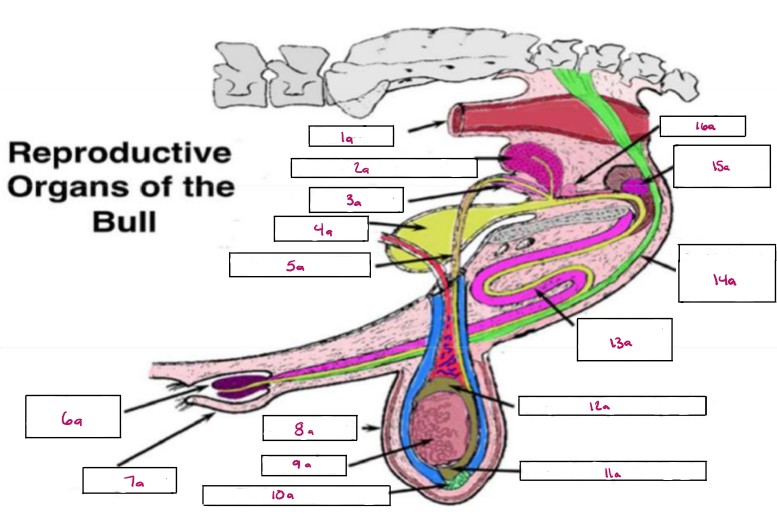
Name 10a
Gubernaculum
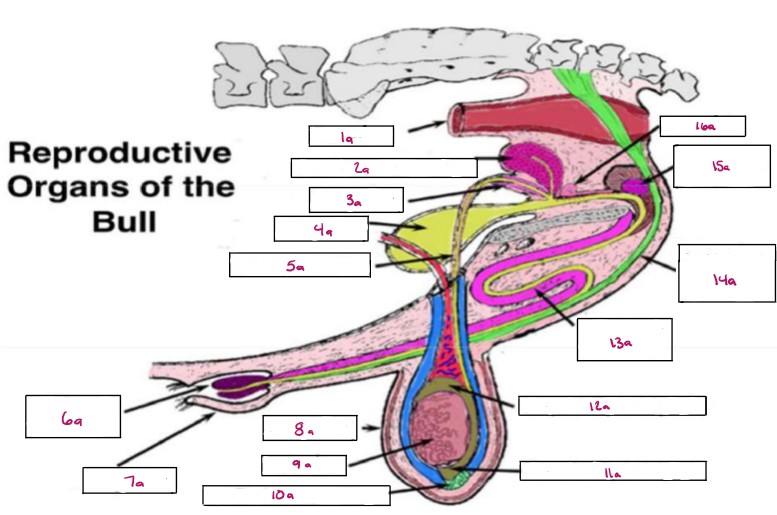
Name 11a
Cauda Epididymis
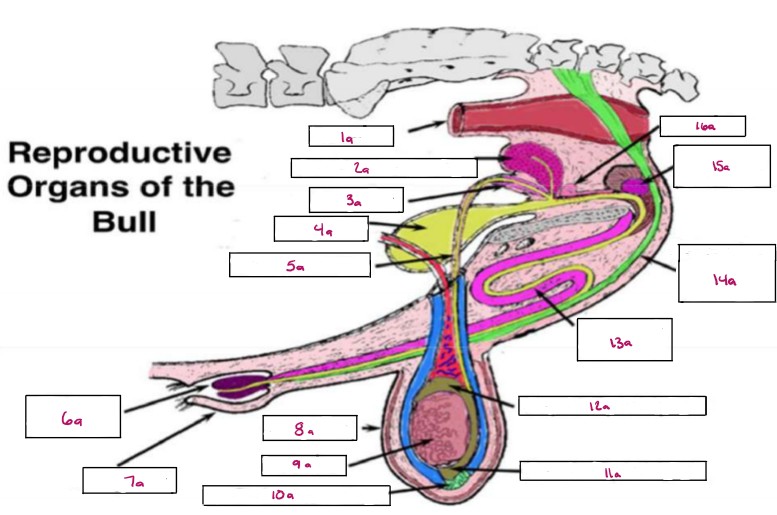
Name 12a
Caput Epididymis
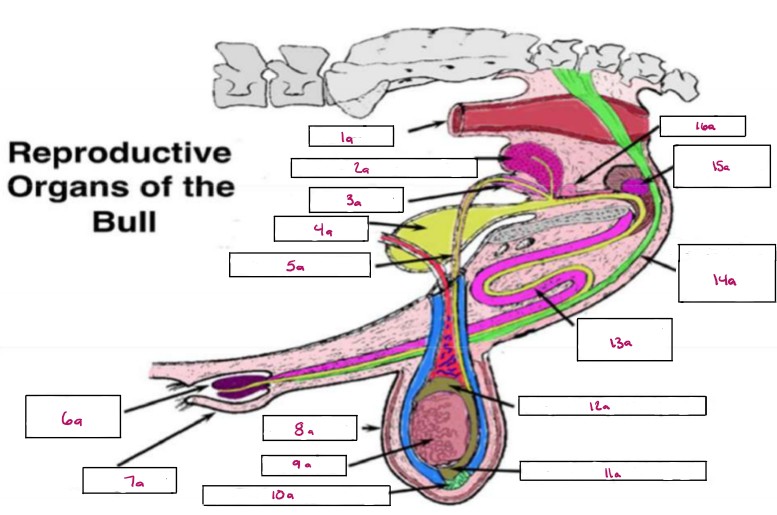
Name 13a
Sigmoid Flexure
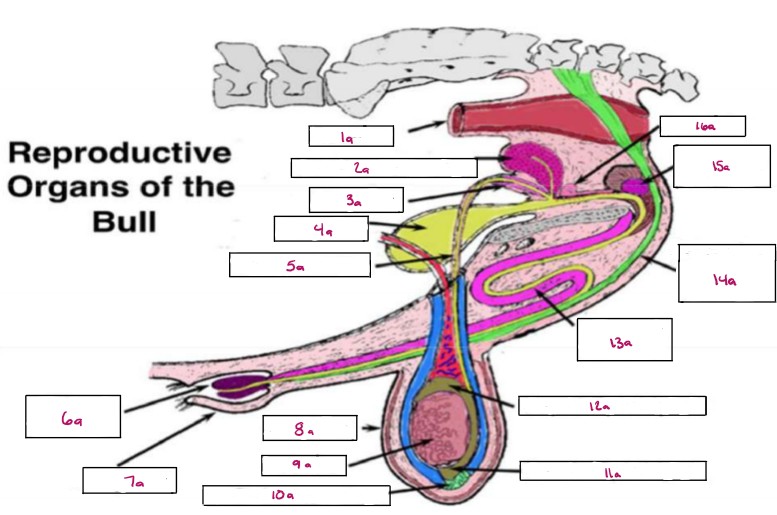
Name 14a
Retractor Penis Muscle
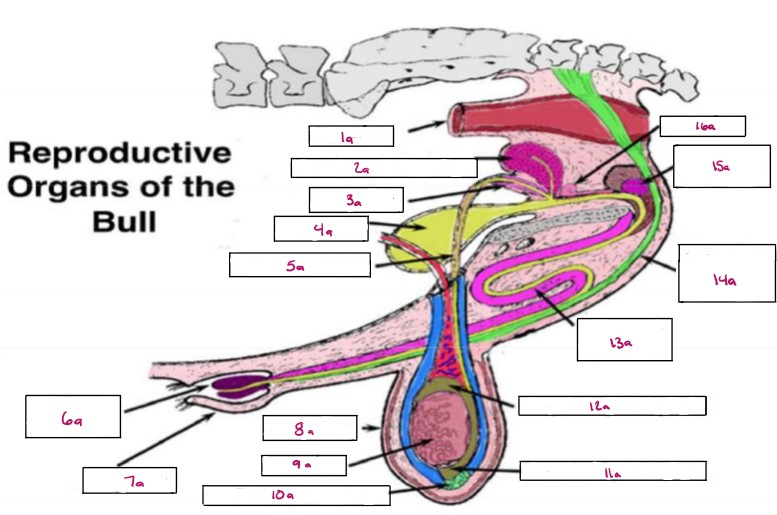
Name 15a
Cowpers Gland
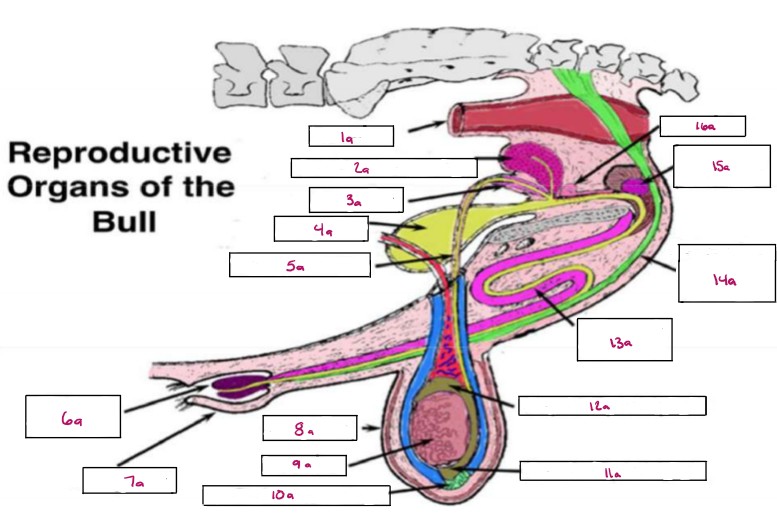
Name 16a
Prostate
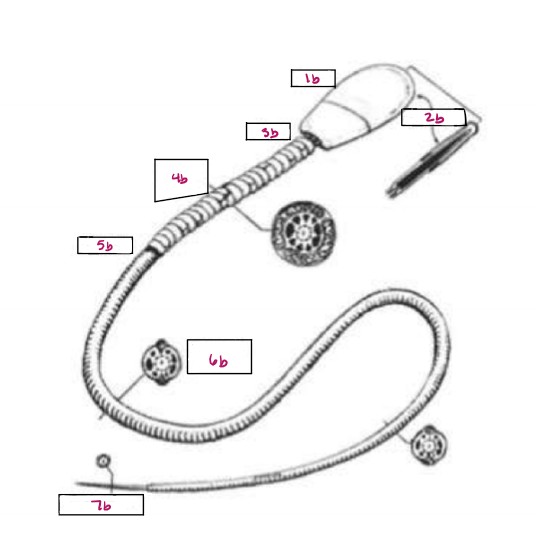
Name 1b
Head
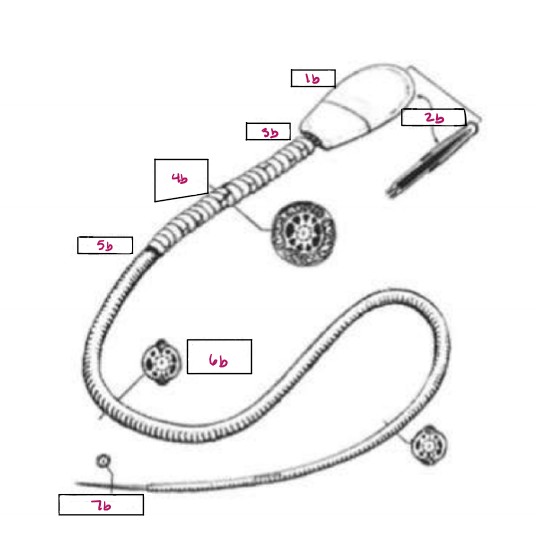
Name 2b
Acrosome
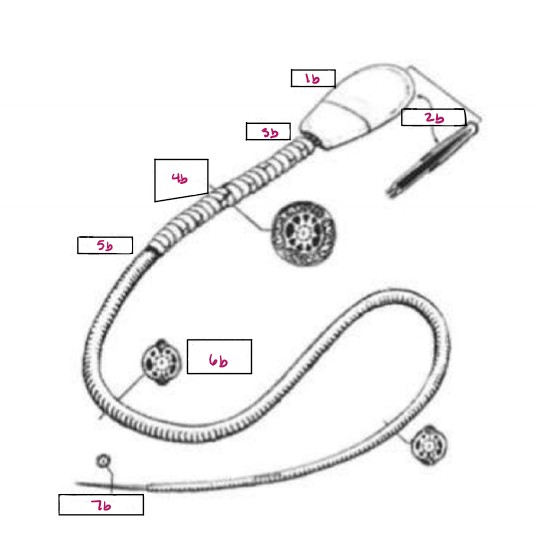
Name 3b
Neck
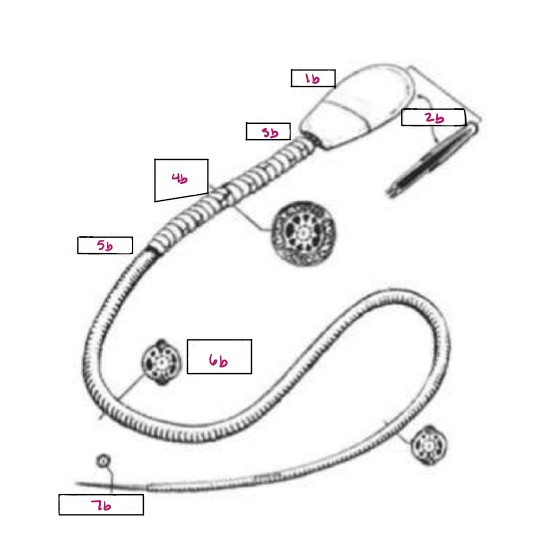
Name 4b
Middle Piece
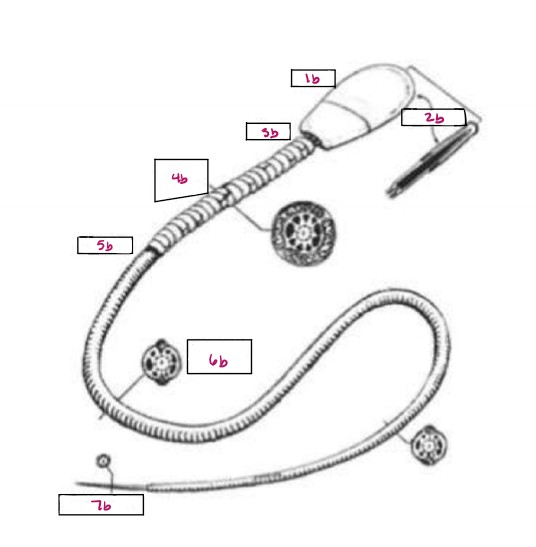
Name 5b
Annulus
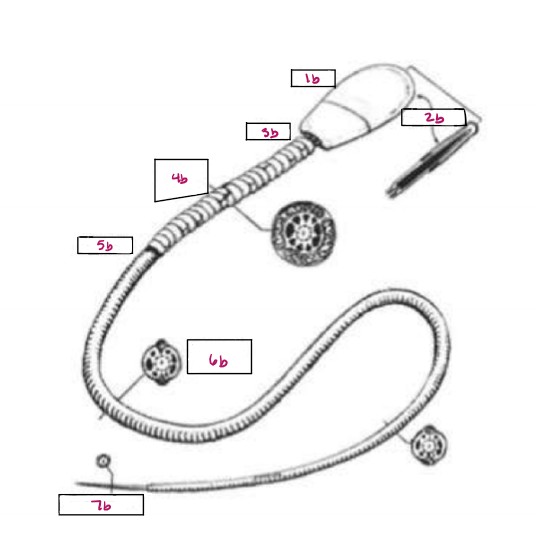
Name 6b
Principal Piece
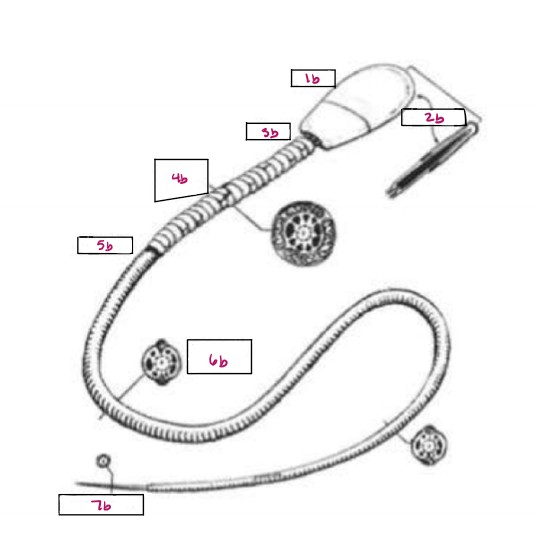
Name 7b
End Piece