[BIO 120.11] Module 3 Part 2: Culturing Bacteria - Incubation Conditions
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Temperature, Molecular oxygen
What are 2 factors that are considered for incubation conditions?
Minimum Cardinal Temperature
Cardinal Temperature: Membrane gelling
Minimum Cardinal Temperature
Cardinal Temperature: Transport processes so slow that growth cannot occur
Optimum Cardinal Temperature
Cardinal Temperature: Enzymatic reactions occurring at maximal possible rate
Maximum Cardinal Temperature
Cardinal Temperature: Protein denaturation
Maximum Cardinal Temperature
Cardinal Temperature: Collapse of the cytoplasmic membrane occurs
Maximum Cardinal Temperature
Cardinal Temperature: Thermal lysis
Psychrophile, Polaromonas vacuolata
Microorganism category and example that grow optimally at 4 degrees Celsius
4 deg C
What is the optimal temperature for psychrophiles?
Mesophile, E. coli
Microorganism category and example that grow optimally at 39 degrees Celsius
39 deg C
What is the optimal temperature for mesophiles?
Thermophile, Geobacillus stearothermophilus
Microorganism category and example that grow optimally at 60 degrees Celsius
Hyperthermophile, Thermococcus celer, Pyrolobus fumarii
Microorganism category and example that grow optimally at 88 and 106 degrees Celsius, respectively
60 deg C
What is the optimal temperature for thermophiles?
88 deg C
What is the optimal temperature for hyperthermophiles (below boiling temperature)?
106 deg C
What is the optimal temperature for hyperthermophiles (above boiling temperature)?
Mesophile
Psychrotolerant and thermotolerant bacteria can still fall under what category of bacteria based on temperature requirement?
TRUE
T/F: Molecular oxygen (O2) is an essential nutrient for many microbes, but can also be lethal to some microbes
FALSE
T/F: Molecular oxygen (O2) is an essential nutrient for all microbes
TRUE
T/F: All microorganisms convert O2 to toxic oxygen byproducts during respiration or by cellular electron carriers
FALSE
T/F: Only some microorganisms convert O2 to toxic oxygen byproducts during respiration or by cellular electron carriers
Respiration, Cellular electron carriers, Flavoproteins
Fill in the blank: All microorganisms convert O2 to toxic oxygen byproducts during ___ or by ___ (e.g. ____)
TRUE
T/F: Oxygen is toxic to all microorganisms
FALSE
T/F: Oxygen is only toxic to some microorganisms
Superoxide anion (O2-), Hydroxyl radical (OH), Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
What are 3 examples of toxic oxygen byproducts? SHH
Macromolecules
What do superoxide anions (O2-) oxidize?
Superoxide anion (O2-), Hydroxyl radical (OH)
What oxygen byproducts can oxidize macromolecule?
Macromolecules
What do hydroxyl radicals (OH) oxidize?
Damages cell components
What does hydrogen peroxide do as an oxygen by-product?
TRUE
T/F: H2O2 is less toxic than O2- and OH
FALSE
T/F: H2O2 is more toxic than O2- and OH
Catalase
What enzyme can be used to detoxify 2 hydrogen peroxides?
Catalase
What enzyme is responsible for the reaction shown in the image?
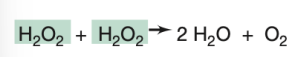
Peroxidase
If you have a hydrogen peroxide and NADH, what enzyme can be used to detoxify the hydrogen peroxide?
Superoxide dismutase
What enzyme can be used to detoxify two superoxide anions to produce hydrogen peroxide?
Superoxide dismutase / catalase in combination
What enzyme can be used to detoxify superoxide anion to water and oxygen molecules?
Superoxide reductase
What enzyme can be used to detoxify superoxide anion to hydrogen peroxide and oxidized rubredoxin?
Peroxidase
What enzyme is responsible for the reaction shown in the image?
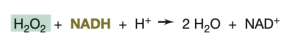
Superoxide dismutase
What enzyme is responsible for the reaction shown in the image?
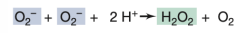
Superoxide dismutase / catalase in combination
What enzyme is responsible for the reaction shown in the image?
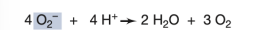
Superoxide reductase
What enzyme is responsible for the reaction shown in the image?

Obligate aerobe, Micrococcus luteus
Microorganism Type and Example: Thrives in the presence of atmospheric oxygen, will not grow without oxygen
(+) SOD, (+) Catalase
Enzyme content of obligate aerobes
(+) SOD, (+) Catalase
Enzyme content of facultative anaerobes
Facultative anaerobe, E. coli
Microorganism Type and Example: Does not require oxygen, but it is advantageous or it promotes their growth
Aerotolerant Anaerobe, Streptococcus mutans
Microorganism Type and Example: Not affected by oxygen, but usually in experiments, they are provided with oxygen (less complicated)
(+) SOD, (-) Catalase
Enzymes for Aerotolerant anaerobes
(-) SOD, (-) Catalase
Enzymes for strict anaerobes
Strict anaerobe, Methanobacterium formicicum
Microorganism Type and Example: Thrives without oxygen, it is lethal for them
(+) SOD, (±) Catalase at low levels
What is the enzyme content for microaerophiles?
Microaerophile, Spirillum volutans
Microorganism Type and Example: They need oxygen, but the concentration should be below atmospheric level
Hydrogen peroxide, oxidoreductase, superoxide anion
Catalase disproportionates ___, and SOD is an ___ that serves to dismutate the ___.
Use Shaker Incubator
What can I do in a laboratory if I need to grow bacteria in a broth?
Sparging System
Aside from shaker flasks, what is another equipment used to promote aeration? Usually used in bioreactors
Nitrogen gas
What gas can be used to remove or displace oxygen from a system?
Microaerophilic Jar or can (Candle inside jar)
What can be used to cultivate microaerophiles?
Anoxic Jar, Anoxic Glove Bag
What can be used to cultivate anaerobes?
Kitchen jars with oxygen absorbers
What can be used as an alternative for anoxic jars?