Week One Food Composition and Funcion
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What are the most important food components?
water, lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, micronutrients, food additives
What are the most important foods/food products categories are?
meat, dairy products, fruits/ vegetables, seeds/nuts/legumes, cereals, beverages
What is considered food is dependent on what?
social and cultural background of people
What are the most important atoms in food science?
H,C,N,S,
What is an isotope?
Same type of element but different molecular weight because of different neutron amounts in the nucleus
What is the principle quantum number?
n; shell/ energy level; 1,2,3,4
What is the angular momentum?
l; orbital shape; 0<l<n-1; l=0 s orbital, l=1 p orbital, l=2 d orbital
What is the magnetic quantum number?
ml; orbital orientation; -l<ml<l
What is the spin quantum number?
ms; electronic spin; +1/2, -1/2
What is the max number of electrons in the s subshell?
2
What is the max number of electrons in the p subshell?
6
What is the max number of electrons in the d subshell?
10
What is Pauli exclusion principle?
no two electrons in an atom can ahve the same set of four quantum numbers; each orbital holds max 2 electrons with opposite spins
What is Hund’s rule?
electrons fill degenerate orbitals (same energy) singly first with parallel spins
What is aufbau principle?
electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals first
What is electronegativity?
the ability of atoms to attract and hold electrons, increases up and right
What are the key principles of a lewis structure?
each valence electron is represented by a dot; draw the dots on the four sides of the imaginary square with no more than tow dots on any side; put one electron on each side before pairing them up
What are the characteristics of covalent bonds?
smaller difference in electronegativity, electrons are shared by atoms
How is polarity determined in covalent bonds?
by the difference in electronegativity between atoms
What are the characteristics on an ionic bond?
large difference in electronegativity, electrons are taken by atoms
why are intermolecular forces important in food?
they determine important properties like boiling point
Why do intermolecular forces occur?
electrostatic interactions between molecules
What are the characteristics of ion-ion interactions?
ushally between large ionic solids like NaCl, formal charges are inovled
What are the characteristics of ion-dipole interactions?
usually involved in solvation, a dipole ins a polar covalent bond like had and dissolutions of ionic bonds like NaCl in H2O creates an ion-dipole interaction; formal and partial charges are involved
What are the characteristics of dipole-dipole interactions?
partial charges involved, hydrogen bonding is a type of dipole-dipole
What are the characteristics of Van der walls interactions?
occur due to fluctuations in the charge density of particles
How do Van der walls interactions effect food properties?
significantly affect the bulk properties of substance like boiling and melting point, helps in stabilizing proteins structures and polymer chain, accounts for physical adsorption of molecules to solid surfaces, responsible for adhesion and stability of colloids
What defines a polar molecule?
there are different terminal atoms or lone pair of electrons around the central atom, difference in electronegativity between atoms, in organic compounds O, Cl, N in comparison to C
What is the relationship between reactivity and stability?
reactivity generally has an inverse relationship with stability
What are the characteristics of a reactive molecule?
formal charges, partial charges, pie bonds, steric effects
Lewis Structure
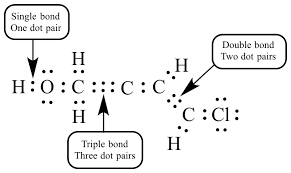
Structural Formular
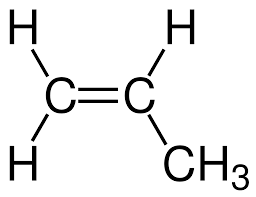
Geometric structure
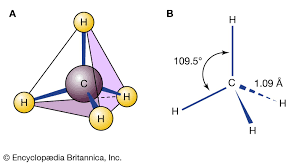
skeletal formula
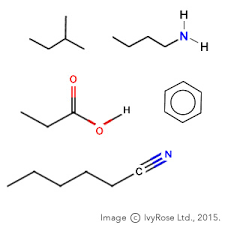
Condensed structural formula
CH3CH2CH3
Molecular Formula
C3H8
What are structural isomers?
two different molecules but with the same molecular formula
What indicates a chiral center?
4 different things attached to the carbon looking at
What are enantiomers?
a pair of molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other
What are diastereomers?
stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other
What is the ending for single bonds?
ane
What is the ending for double bonds?
ene
What is the ending for triple bonds?
yne
What is the naming in order of number of atoms?
meth, eth, prop, bute, pent, hex, hept, oct, non, dec
What is the general naming rules based on?
number of carbons, type of bonds, functional group determines suffix
What is a hydroxyl group?
in alcohols, sugars
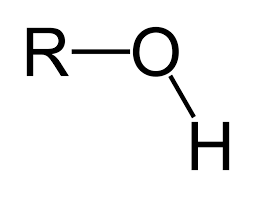
What is a carbonyl?
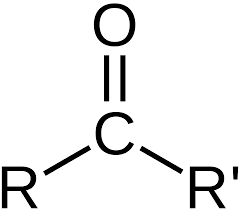
What is a carboxyl group?
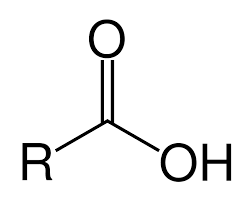
What is a an amino?
in amino acids
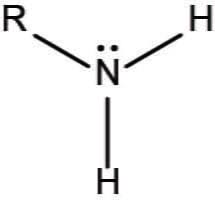
What is an ester?
in fats, flavors
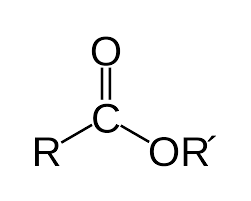
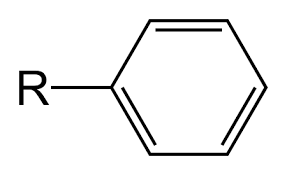
What is a phenyl?
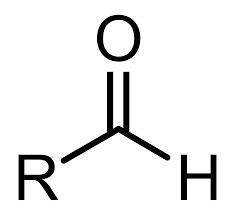
What is an aldehyde?
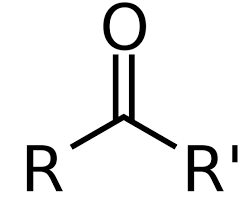
What is a ketone?
What is a thiol?
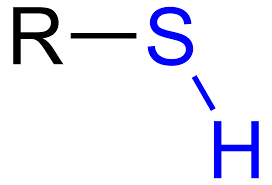
What does R represent?
an alkyl group and hydrophobic acyl chains; can be simple or complex
Why is R used?
to simplify structures when the exact identity of a groups is not important to the concept and makes functional group patterns easier to recognize