B4 - Animal & plant tissues, organ systems
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What does the left ventricle pump
blood around the body
what does the right ventricle pump
low oxygen, high carbon dioxide blood into the lungs
where does gas exchange take place
lungs/alveoli
in gas exchange, which gas is diffused into the alveoli
carbon dioxide
in gas exchange, which gas is diffused into the bronchial tubes
oxygen
What is the thickest blood vessel type
artery
where do arteries carry blood to
away from the heart
where do veins carry blood to
towards the heart
capillaries connect what
connect arteries and veins
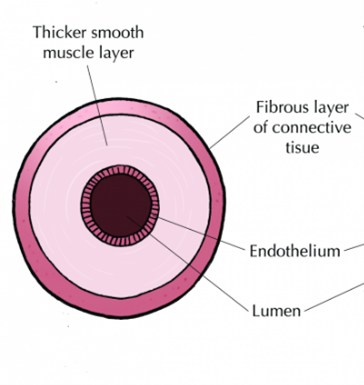
Which blood vessel is this
Artery
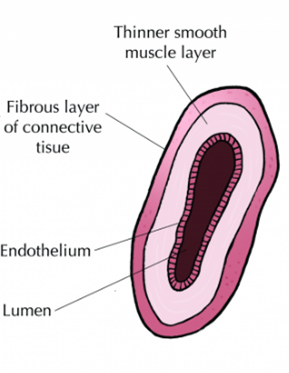
which blood vessel is this
vein

which blood vessel is this
capillary
Do arteries carry de/oxygenated blood
carry oxygenated, except pulmonary artery
Do veins carry de/oxygenated blood
carry de oxygenated except pulmonary vein
Platelets
cell fragments that clot wounds
what does plasma transport
cells, CO2, hormones and waste
Atherosclerosis definition
building of fat in the coronary arteries
Atherosclerosis causes
-smoking (high blood pressure)
-high cholesterol (fatty substance carried in blood)
-lack of exercise ( increase in blood pressure and cholesterol)
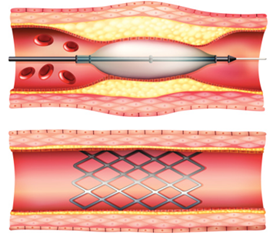
What dew schtents dew
Inserted into the narrow artery then expand inside to increase oxygen flow to the heart
What are statins
Drugs that lower the amount of harmful cholesterol in blood, also stops the liver from producing too much cholesterol
cardiomyopathy symptoms
walls of the heart are stretched, thickened or stiff preventing blood from pumping
congenital heart disease
birth defect affecting the heart
Faulty valves
heart valves that are faulty, preventing the valve from opening or closing completely
faulty valves symptoms
-short of breath
-swelling of ankles and feet
-fatigue
faulty valves causes
-congenital
-rheumatic fever
-cardiomyopathy
-heart attack damage
-old age
-endocarditis ( bacterial infection in heart)
wuh is epidermal
waxy surface on plant
palisade mesophyll
site of photosynthesis, lotta chloroplasts
spongy mesophyll
space for gas exchange, also photosynthesis
meristem
tips of roots and shoots, site of cell differentiation
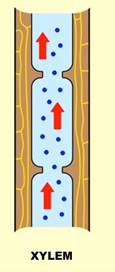
transpiration
Xylem transporting water + mineral ions from roots to stem and leaves
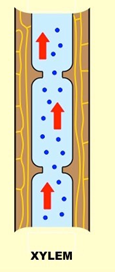
Xylem characteristics
-hollow tubes, strengthened by lignin
-one way flow
-transpiration increases with temp, humidity, wind, light
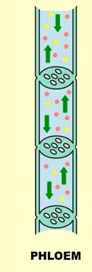
translocation
Phloem transporting dissolved sugar from leaves to rest of plant for use or storage
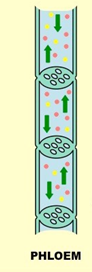
phloem characteristics
-made of elongated cells
-two way flow