AP Chemistry Unit 2
1/66
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
chemical bonds
the attractive forces that hold atoms together
ionic bond
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
metallic bond
a bond formed by the attraction between positively charged metal ions and the electrons around them
octet rule
States that atoms lose, gain or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons
lattice energy
the energy released when one mole of an ionic crystalline compound is formed from gaseous ions
single bond
a covalent bond in which two atoms share one pair of electrons
double bond
A covalent bond in which two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms
triple bond
a covalent bond in which two atoms share three pairs of electrons
bond length
the average distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms
bond polarity
a measure of how equally or unequally the electrons in any covalent bond are shared
polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
nonpolar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally by the two atoms
electronegativity
A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons
polar molecule
A molecule that has electrically charged areas.
dipole
created by equal but opposite charges in a polar molecule
formal charge
The number of valence electrons in an isolated atom minus the number of electrons assigned to the atom in the Lewis structure
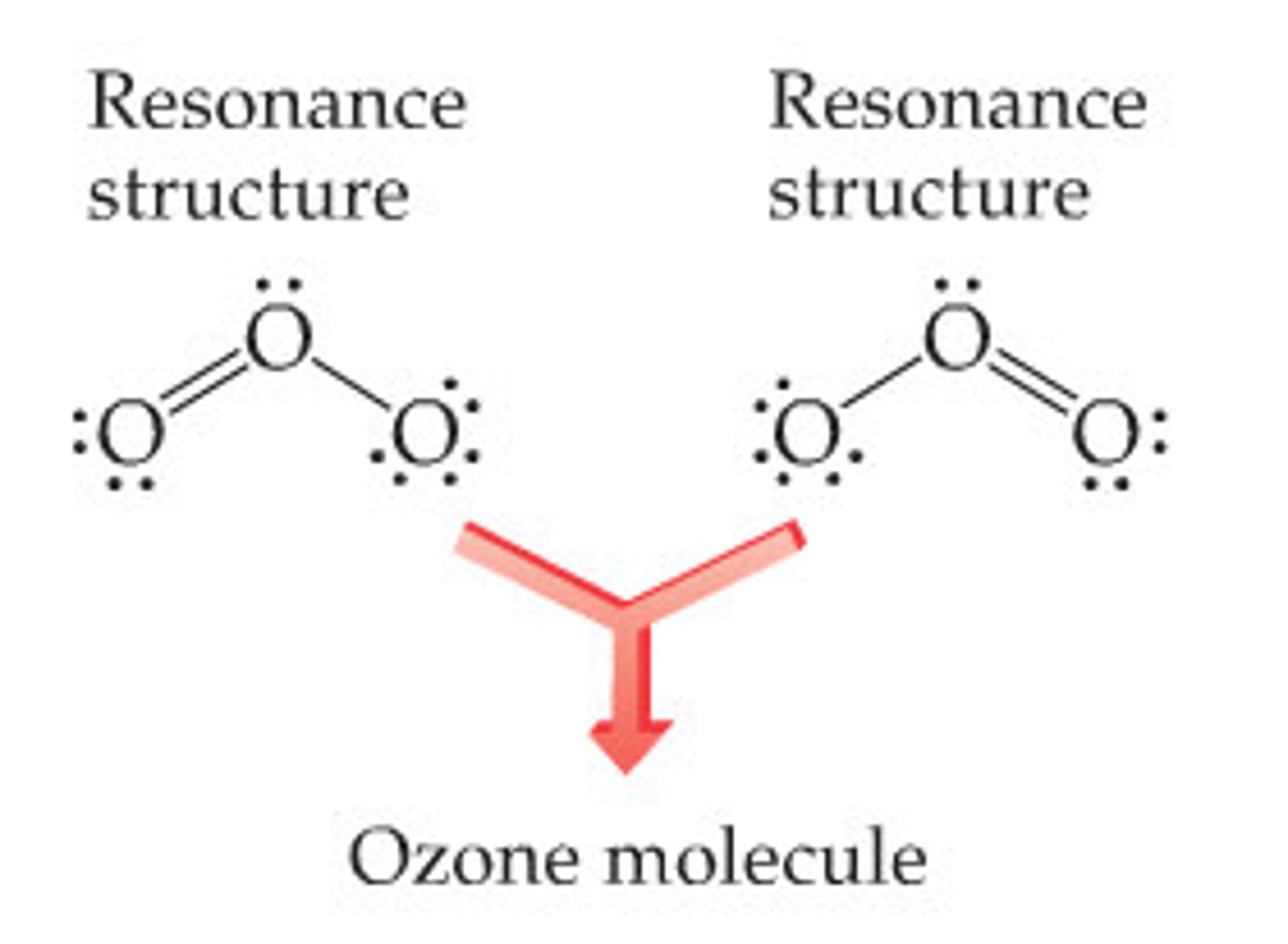
resonance structure
one of the two or more equally valid electron dot structures of a molecule or polyatomic ion
bond angle
the angle formed by two bonds to the same atom
VSEPR theory
Valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory; because electron pairs repel, molecules adjust their shapes so that valence electron pairs are as far apart as possible
electron domain
in the VSEPR model, a region about a central atom in which an electron pair is concentrated (could be unshared or bonded pair)
bonding pair
an electron pair found in the space between two atoms
nonbonding pairs
two paired valence electrons that tend not to participate in a chemical bond
bond dipole
separation of electrical charge created when atoms with different electronegativities form a covalent bond
hybrid orbitals
orbitals of equal energy produced by the combination of two or more orbitals on the same atom
hybridization
the mixing of several atomic orbitals to form the same total number of equivalent hybrid orbitals
sp hybridization
linear; bond angle: 180
a type of bonding where the 2s orbital mixes with only one of the three p-orbitals resulting in two sp orbitals and two remaining unchanged p orbitals
sp2 hybridization
1. Trigonal planar structure
2. sp2 hybridization creates 3 identical orbitals of intermediate energy and length and leaves one unhybridized p orbital
3. 3 effective pairs of electrons surround the carbon (double bond treated
as one effective pair)
sp3 hybridization
A type of hybridization that results from the combination of the s orbital and all three p orbitals in the second energy level of carbon, resulting in four hybrid orbitals and occurs when a carbon atom is bonded to four other atoms. The geometric arrangement of those four hybrid orbitals is called tetrahedral.
sigma bond
a bond formed when two atomic orbitals combine to form a molecular orbital that is symmetrical around the axis connecting the two atomic nuclei
pi bond
a bond that is formed when parallel orbitals overlap to share electrons.
metallic solids
solids that have metal atoms occupying the crystal lattice and held together by metallic bonding
ionic solids
solids whose composite units are ions; they generally have high melting points
alloys
a mixture composed of two or more elements, at least one of which is a metal
substitutional alloy
some of the host metal atoms are replaced by other metal atoms of similar sizes
interstitial alloy
a mixture formed when small atoms fill holes in a metallic crystal
electron sea model
Proposes that all metal atoms in a metallic solid contribute their valence electrons to form a "sea" of electrons, and can explain properties of metallic solids such as malleability, conduction, and ductility.
delocalized electrons
electrons that are free to move
linear
180 degrees
trigonal planar
120 degrees
tetrahedral
109.5 degrees
trigonal bipyramidal
120, 180, and 90 degrees
octahedral
90 and 180 degrees
trigonal pyramidal
3 bonds, 1 lone pair
bent
2 bonds, 2 lone pairs
see-saw
4 bonds, 1 lone pair
T-shape
3 bonds, 2 lone pairs
square pyramidal
5 bonds, 1 lone pair
square planar
4 bonds, 2 lone pairs
luster
(n.) the quality of giving off light, brightness, glitter, brilliance
malleable
easy to shape or bend
ductile
can be drawn into wires
electronegativity difference
The difference in electronegativity between two elements in a bond.
Coulomb's Law
F=K q₁*q₂/r², magnitude of force between two charges
ion
A charged atom
polyatomic ion
a tightly bound group of atoms that behaves as a unit and has a positive or negative charge
bond distance (bond length)
the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms
free radical
an atom or a group of atoms that has one unpaired electron
resonance
the bonding in molecules or ions that cannot be correctly represented by a single Lewis structure
bond order
the number of bonds between atoms: 1 for a single bond, 2 for a double bond, and 3 for a triple bond
diatomic molecule
a molecule containing only two atoms
oxyacid
an acid that is a compound of hydrogen, oxygen, and a third element, usually a nonmetal
electrical conductivity
the ability of an object to transfer electric current
molten
made liquid by heat; melted
partial charge
unequal distribution of electrons caused by a polar covalent bond
valence electron
an electron that is found in the outermost shell of an atom and that determines the atom's chemical properties
brittle
easily broken