EPS SCI 17 Midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:20 AM on 5/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
Paleontology
the study of the remains of ancient life, including body, chemical, and trace fossils - not just the study of dinosaurs
2
New cards
Gideon and Mary Ann Mantell
named the iguanodon
3
New cards
dinosauria
"terrible lizards" - coined by Sir Richard Owen (1804-1892)
4
New cards
Endothermic
saying that dinosaurs generated their own heat to maintain an optimal body temperature
5
New cards
Edward Drinker Cope
\- 1840-1897 - Worked at the Academy of Natural Sciences in Philadelphia
- Published over 1,400 papers
\- Named more than 1,000 vertebrate species
- Published over 1,400 papers
\- Named more than 1,000 vertebrate species
6
New cards
Gastroliths
Swallowed stones in the stomach that aid in digestion
7
New cards
Paleobiology
Paleobiology is a growing and comparatively new discipline which combines the methods and findings of the life science biology with the methods and findings of the earth science paleontology.
8
New cards
Ice age mammals
are not considered dinosaurs for a multitude of reasons
ex. did not live in the same era (Cenozoic - Quaternary)
ex. did not live in the same era (Cenozoic - Quaternary)
9
New cards
Dinosaur Hips
Ornithiscian - bird hips
Saurischian - lizard hips (sauropods and theropods)
Saurischian - lizard hips (sauropods and theropods)
10
New cards
Digitigrade
tiptoe walking
11
New cards
facultative
capable of but not restricted to a particular function or mode of life
ex. ornithopods = bipeds or facultative quadrapeds
ex. ornithopods = bipeds or facultative quadrapeds
12
New cards
Battery teeth
\
hundreds of ***teeth*** which were stacked in rows upon rows and formed a grinding surface to process plant foods
hundreds of ***teeth*** which were stacked in rows upon rows and formed a grinding surface to process plant foods
13
New cards
If you wanted to take your time machine and go hunting for Carcharodontosaurs what's the best place you could travel to to have a chance of seeing one?
Any of these, they were cosmopolitan (worldwide)
14
New cards
Which dinosaur would have been the "butcher of the Jurassic" in North America?
Allosaurus Fragilis
15
New cards
Which of the following characters relate to enhancing bipedal movement in theropods?
stiffened tails
16
New cards
Which of the following does NOT belong in tetanurans?
ornithopods
17
New cards
The K/T (End Cretaceous) Extinction is at the END of which ERA?
Mesozoic
18
New cards
Which of these dinosaurs or dinosauromorphs lived in the Triassic?
\- Eoraptor
\- Herrerasaurus
\- Coelophysis
\- Herrerasaurus
\- Coelophysis
19
New cards
If you wanted to take your time machine and go hunting for sauropods what's the WORST time/place you could travel to to have a chance of seeing one?
Cretaceous of North America
20
New cards
What are some geological reasons that we are able to reconstruct the members of Late Jurassic dinosaur communities so well?
Dinos were abundant and fossil-filled rock formations are exposed to the surface
21
New cards
Post-orbital
behind the eye
22
New cards
synapsid
only 1 post-orbital fenestrae
23
New cards
diapsid
2 post-orbital fenestrae (one behind eye and one behind and above the eye)
24
New cards
amniotic egg
an egg with a shell and internal membranes that keep the embryo moist, fluid helps to protect the developing embryo from physical danger
25
New cards
William Buckland (1784-1856)
\- first to name a dinosaur (Megalosaurus - a theropod)
\- coined the term "paleontology"
\- coined the term "paleontology"
26
New cards
transitional fossil
fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group
\- ex. first = Archaeopteryx
\- ex. first = Archaeopteryx
27
New cards
Othniel Charles Marsh
\
\- 1831-1899
\- Helped found the Yale-Peabody Museum
\- Worked at the US Geological Survey and was president of the National Academy of Sciences
\- Named 26 genera of dinosaurs, including *Apatosaurus*, *Allosaurus*, *Diplodocus*, *Stegosaurus*, and *Triceratops*
\- 1831-1899
\- Helped found the Yale-Peabody Museum
\- Worked at the US Geological Survey and was president of the National Academy of Sciences
\- Named 26 genera of dinosaurs, including *Apatosaurus*, *Allosaurus*, *Diplodocus*, *Stegosaurus*, and *Triceratops*
28
New cards
Marsh and Cope
\- Both found the large collections of bones in the American West
\- Both did much to promote dinosaur research in the late 1800's
\- Both did much to promote dinosaur research in the late 1800's
29
New cards
hypothesis vs. theory
A hypothesis is either a suggested explanation for an observable phenomenon, or a reasoned prediction of a possible causal correlation among multiple phenomena. In science, a theory is a tested, well-substantiated, unifying explanation for a set of verified, proven factors.
30
New cards
melanin
A pigment that gives the skin its color
31
New cards
Iridiophores
pigment cells that reflect light using plates of crystalline chemochromes made from guanine. When illuminated they generate iridescent colours because of the diffraction of light within the stacked plates.
32
New cards
countershading
Dark colors (top) visible from above when the background is dark ground and light colors (bottom) visible when the animal is backlit
33
New cards
Ecology
The study of how living things interact with each other and their environment
34
New cards
Mammutus
has hair, live birth = not dino
35
New cards
archosaurs
Archosaurs are a group of diapsid amniotes and are broadly classified as reptiles. The living representatives of this group consist of birds and crocodilians.
\- crooked ankle
\- crooked ankle
36
New cards
Phylogeny of dino relatives
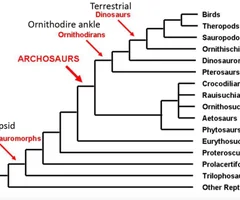
37
New cards
homologous
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry.
38
New cards
tetrapod
vertebrate with four limbs
39
New cards
Why move to land?
1. escape predation
2. less competition
3. more resources (oxygen, sunlight, and food?)
4. easier to move around
40
New cards
absolute dating
any method of measuring the age of an event or object in years
41
New cards
Taxa (taxon)
a grouping of organisms
ex. a species, a genus
ex. a species, a genus
42
New cards
traits
Characteristics that are inherited
43
New cards
antiorbital fenestra
ahead of the orbit
44
New cards
The early dinosaurs lived on which continent?
Pangea
45
New cards
What process powers continental drift?
Convection within the earth
46
New cards
Which organisms were the dominant, top predators in the Triassic?
Pseudosuchians
47
New cards
What is the term for two groups of organisms that resemble each other because of similarities in lifestyle and environment (not close ancestry and shared traits)?
Convergent
48
New cards
The hot and extreme weather in the Triassic was caused by?
High levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
49
New cards
The early dinosaurs lived on which continent?
Pangea
50
New cards
In science, the usefulness of a claim (or hypothesis) is directly related to:
the testability of the claim
51
New cards
Which of these has __all__ of the same skeletal traits we have used to define a dinosaur?
Billie, Professor Brown's parrot
52
New cards
Dinosaur fossils greater than 200 million years old would be found in which time PERIOD? Use the time scale from lecture, online, or the first pages of Rise of the Dinosuars
Triassic
53
New cards
All theropods were carnivorous
False
54
New cards
If energy present at each step in the food chain is visualized as a pyramid of consumers, plants are on the bottom and apex predators are at the top. The available energy at each level narrows down substantially. Where does most of the lost energy go?
Into heat
55
New cards
What does it mean when we say theropods were "airheads"?
Their skulls were filled with air sacs
56
New cards
The name Tetanurae refers to which shared character (trait) of this theropod group?
Stiff Tails
57
New cards
Why is the tyrannosaurid group of dinosaurs found globally when so many other dinosaur groups were restricted to one place and time?
tyrannosaurids originated early enough that Pangea existed and they occupied it before it broke up
58
New cards
You're wandering around Africa in the Cretaceous and you see a brutal scene of a theropod killing a baby titanosaur. Which of the following taxa does the theropod most likely belong to?
Abelisaurs
59
New cards
Which of these is not a rock type that would preserve fossils?
Igneous Rock
60
New cards
fenestrae
a small natural hole or opening, especially in a bone
61
New cards
Ceratosaurus
Allosaurid Theropod
Smallest Allosaurid
It was the only carnivorous dinosaur that had three horns.
Smallest Allosaurid
It was the only carnivorous dinosaur that had three horns.
62
New cards
Archaeopteryx
Saurischian Theropod
Late Jurassic
An intermediate fossil that shows both reptile and bird characteristics.
Late Jurassic
An intermediate fossil that shows both reptile and bird characteristics.
63
New cards
Herrerasaurus
Saurischian
Late Triassic
One of the earliest known dinosaurs
Late Triassic
One of the earliest known dinosaurs
64
New cards
Majungasaurus
Abelisaurid Theropod
Tiny arms
Late Cretaceous
Had evidence that Majungasaurus and Majugatholus were the same animal
Tiny arms
Late Cretaceous
Had evidence that Majungasaurus and Majugatholus were the same animal
65
New cards
Tyrannosaurus Rex
Last large theropod to rule
Late Cretaceous
Robust wide skull, heaviest land animal, crushing bite. King of Cretaceous
Late Cretaceous
Robust wide skull, heaviest land animal, crushing bite. King of Cretaceous
66
New cards
Deinonychus
Dromaeosaurid Theropod
Early Cretaceous
"Terrible claw"; a genus of carnivorous dromaeosaurid coelurosaurian dinosaurs, with one described species
Led to start of the dinosaur renaissance
Early Cretaceous
"Terrible claw"; a genus of carnivorous dromaeosaurid coelurosaurian dinosaurs, with one described species
Led to start of the dinosaur renaissance
67
New cards
Velociraptor
Dromaeosaurid Theropod
Late Cretaceous
Had a large manus "hand" with three strongly curved claws, which were similar in construction and flexibility to the bones of modern birds
May have had feathers
Late Cretaceous
Had a large manus "hand" with three strongly curved claws, which were similar in construction and flexibility to the bones of modern birds
May have had feathers
68
New cards
Compsognathus
FIRST Theropod
Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous
Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous
69
New cards
Spinosaurus
Spinosauridae Theropod
Cretaceous
Likely the largest and tallest Dino. Though very slim and light.
Sail backs and duck bill snout
Semi-aquatic (dense bones)
Cretaceous
Likely the largest and tallest Dino. Though very slim and light.
Sail backs and duck bill snout
Semi-aquatic (dense bones)
70
New cards
Allosaurus
Theropod
Late Jurassic
One of the earliest dinosaurs found. Gave name to HUGE allosaurids
Reduce bone strength but very light
Late Jurassic
One of the earliest dinosaurs found. Gave name to HUGE allosaurids
Reduce bone strength but very light
71
New cards
Oviraptor
Theropod
Late Cretaceous
Carried eggs, may have eaten eggs
Possibly omnivore
Late Cretaceous
Carried eggs, may have eaten eggs
Possibly omnivore
72
New cards
Ornithomimus
Late Theropod
Very fast
Cretaceous of Laurasia, possible also Gondwana
Some have bizzare feeding adaptations (duck-like beaks, diverse in size and diet)
Very fast
Cretaceous of Laurasia, possible also Gondwana
Some have bizzare feeding adaptations (duck-like beaks, diverse in size and diet)
73
New cards
Therizinosaurus
Theropod
Late Cretaceous
Known for their huge claws and resembled sloths
Possibly herbivores
Late Cretaceous
Known for their huge claws and resembled sloths
Possibly herbivores
74
New cards
Microraptor
Dromaeosaur Theropod
Early Cretaceous
Among the smallest-known non-avian dinosaurs (1kg)
Early Cretaceous
Among the smallest-known non-avian dinosaurs (1kg)
75
New cards
Camarasaurus
Sauropod
Late Jurassic
Giant herbivores
Hollow chamber in vertebrae
Late Jurassic
Giant herbivores
Hollow chamber in vertebrae
76
New cards
Diplodocus
Herbivorous dinosaur with a long neck and tail, lived during the Late Jurassic period. One of the largest land animals ever discovered, reaching up to 90 feet in length and weighing up to 25 tons.
77
New cards
Plateosaurus
Sauropod-ish
Late Triassic North America
Facultative Bipeds- capable of walking or running on two legs often for a limited period in spite of normally walking or running on four limbs or more
\-Shows transition
Social
Late Triassic North America
Facultative Bipeds- capable of walking or running on two legs often for a limited period in spite of normally walking or running on four limbs or more
\-Shows transition
Social
78
New cards
Giraffatitan
Sauropod
Cretaceous East Africa
Largest dino until 1990
Reconstructed with upright neck
Controversially located in Berlin
Cretaceous East Africa
Largest dino until 1990
Reconstructed with upright neck
Controversially located in Berlin
79
New cards
Iguanodon
Ornithopod
Mid-Jurassic to Late Cretaceous
Second dino to ever be identified and named
First described herbivorous dino
Mid-Jurassic to Late Cretaceous
Second dino to ever be identified and named
First described herbivorous dino
80
New cards
Maiasaurus Peeblesorum
Hadrosaurid Ornithopod
Jurassic/Cretaceous
Evidence of parental care
Transition between fast bipedal and duckbilled quadriped herbivores
Jurassic/Cretaceous
Evidence of parental care
Transition between fast bipedal and duckbilled quadriped herbivores
81
New cards
Phytosaurs
Croc Relatives
Triassic
Sprawled limbs, robust tails, armor plates embedded in the skin, elongate skulls lined with sharp cone-shaped teeth, nostrils faced upwards.
Triassic
Sprawled limbs, robust tails, armor plates embedded in the skin, elongate skulls lined with sharp cone-shaped teeth, nostrils faced upwards.
82
New cards
Pseudosuchians
Croc relatives
Triassic
Top Predator in Triassic
Triassic
Top Predator in Triassic
83
New cards
Homo sapiens
Modern humans
84
New cards
Dimetrodon
carnivorous mammal like reptile, of the genus Dimetrodon
Permian Era North America
Long and usually bearing spinal sails. Look like dinos but only one postorbital fenestra
Permian Era North America
Long and usually bearing spinal sails. Look like dinos but only one postorbital fenestra
85
New cards
How did the concept of dinosaurs come to its current state over the past 200 years?
Paradigm shift in the 60s: in 1964, an expedition from Yale University discovers, in Montana, a sickle-clawed "raptor" theropod (deinonychus) One of the Yale paleontologists, John Ostrom, noted that the fossil recovered and related predators presented several bird-like skeletal features. Subsequent studies and research made scientists conclude that birds, and not reptiles, are in fact direct descendants of dinosaurs. Ostrom argued for warm-blooded, active dinosaurs. One of his students, Bakker, argued that Tyrannosaurs and its carnivorous kin were agile predators, able to run fast (almost 40 mph). More recent work indicates that Tyrannosaurus & co actually could barely run. For what concerns herbivores, there's scientific debate going on on whether sauropods could rear up on their hind legs and elevate their necks above the horizontal.
86
New cards
What are the origins of dinosaurs in time and on Earth?
Scientists first began to study dinosaurs during the 1820s when they discovered the bones of a large land reptile they dubbed as Megalosaurus (named by William Buckland) buried in the English countryside. In 1842, Sir Richard Owen first coined the term "Dinosauria". There are "stem reptiles" or early amniotes from 300 Ma, where mammals, birds, dinosaurs, and reptiles all stem from (synapsids and diapsids split from here)
\-Dinosaurs and their relatives share traits: jaws and teeth, vertebral column, amniotic eggs (ancestrally), terrestrial (ancestrally)Synapsids (mammal-like reptiles, not dinos)
\-One postorbital fenestra (skull hole)Diapsids (dinos, birds, living reptiles)-Two postorbital fenestra Archosaurs: closest dino relatives (all about the ankles)
\-Split in ankle anatomy between croc-like animals and dinos/pterosaursOrnithodirans: dinosaur/pterosaur divide
-Split determined by flight... archosaurs minus flying pterosaurs (leaving all terrestrial)
Dinosaurs: terrestrial diapsids with ornithodire ankles that lived in the Mesozoic, or all the ancestors of the pigeon and Triceratops
\-Dinosaurs and their relatives share traits: jaws and teeth, vertebral column, amniotic eggs (ancestrally), terrestrial (ancestrally)Synapsids (mammal-like reptiles, not dinos)
\-One postorbital fenestra (skull hole)Diapsids (dinos, birds, living reptiles)-Two postorbital fenestra Archosaurs: closest dino relatives (all about the ankles)
\-Split in ankle anatomy between croc-like animals and dinos/pterosaursOrnithodirans: dinosaur/pterosaur divide
-Split determined by flight... archosaurs minus flying pterosaurs (leaving all terrestrial)
Dinosaurs: terrestrial diapsids with ornithodire ankles that lived in the Mesozoic, or all the ancestors of the pigeon and Triceratops
87
New cards
What is a dinosaur?
Terrestrial diapsids with ornithodire ankles that lived in the Mesozoic, all ancestors of the common ancestor of pigeons and triceratops
123 hand
234 foot
Several holes in skull (two postorbital fenestra)
Kinetic skull
Upright posture
Hole in hip
Unusual ankle
Terrestrial (no dinosaur was ever fully aquatic or able to fly)
123 hand
234 foot
Several holes in skull (two postorbital fenestra)
Kinetic skull
Upright posture
Hole in hip
Unusual ankle
Terrestrial (no dinosaur was ever fully aquatic or able to fly)
88
New cards
Which vertebrates are the closest relatives of the dinosaurs?
Archosaurs (including crocodilians), can be identified by the ankles, which have a crurotarsal ankle joint (dinosaurs and pterosaurs have a mesotarsal ankle joint)
89
New cards
What major characteristics define Ornithodires?
Ornithodires: Archosaurs that more closely resemble birds than crocodilians
\-Mesotarsal ankles
\-Covered in feathers
\-Lineage where dinosaurs and pterosaurs split
\-Mesotarsal ankles
\-Covered in feathers
\-Lineage where dinosaurs and pterosaurs split
90
New cards
What major characteristics define Ornithischians?
Any herbivorous dinosaur of the suborder Ornithopoda whose members usually walked erect on their hind legs
\-kinetic skull
\-'bird' hips
\-leaf shaped teeth
\-lower jaw with a predentary bone
\-network of bony ligaments (ossified tendons)
\-stiffen backbone
-North America
\-Ornithischians
\-kinetic skull
\-'bird' hips
\-leaf shaped teeth
\-lower jaw with a predentary bone
\-network of bony ligaments (ossified tendons)
\-stiffen backbone
-North America
\-Ornithischians
91
New cards
What characteristics define Saurischians?
\-Loss of distal carpal V
\-Lizard hipped dinos
-Pubis runs anteriorly and downward
-Twisted thumb (carpal I)
-Includes theropods and brachiosaurus things
\-Lizard hipped dinos
-Pubis runs anteriorly and downward
-Twisted thumb (carpal I)
-Includes theropods and brachiosaurus things
92
New cards
What are the 2 main traits that divide Sauropods into Diplodocids vs Macronarians?
Diplodocids
\-single nostril
\-peg teeth
Macronarians
-2 nostrils
\-leaf teeth
\-single nostril
\-peg teeth
Macronarians
-2 nostrils
\-leaf teeth
93
New cards
Which locomotion-related traits divide Ornithopods into Heterodontids vs Iguandodontids+Hadrosaurs?
Heterodontids -bipedal
Iguanodontids+Hadrosaurs -faculative quadripeds if not pure quadripeds
Iguanodontids+Hadrosaurs -faculative quadripeds if not pure quadripeds
94
New cards
Which feeding-related traits divide Iguanodontids, Hadrosaurids and Lambeosaurs?
Iguanodontids -not as many replacement teeth
Hadrosaurids -duck bill mouth
Lambeosaurs -staggered replaceable teeth
Hadrosaurids -duck bill mouth
Lambeosaurs -staggered replaceable teeth
95
New cards
Which diet characterizes each branch of the Ceolurosaur theopod family tree? Can you point out a skull or forelimb trait to support that answer?
Therazinosaurs
\-Possibly herbivore
\-Sloth appearance and long claws don't suggest hunting or tearing flesh
\
Oviraptors
\-Possibly ate eggs, fish, and shellfish
\-beak, no teeth, great crushing power
\
Ornithomimids
\-Not carnivore, Omnivore possibly
\-No teeth and very light and fast build
\-Possibly herbivore
\-Sloth appearance and long claws don't suggest hunting or tearing flesh
\
Oviraptors
\-Possibly ate eggs, fish, and shellfish
\-beak, no teeth, great crushing power
\
Ornithomimids
\-Not carnivore, Omnivore possibly
\-No teeth and very light and fast build
96
New cards
What techniques are used to obtain a relative date for a fossil? An absolute date?
Absolute date: radiometric dating (for rocks not fossils)
\
Relative date: Superposition (older vs. younger rocks), principle of original horizontality
\
Relative date: Superposition (older vs. younger rocks), principle of original horizontality
97
New cards
When was the Mesozoic and what time periods are in it, in order?
250m to 66m years ago
Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous
Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous
98
New cards
In what time period did the ancestors of most animals (including that of vertebrates) show up?
Cambrian
99
New cards
How did vertebrates combat dessication?
Adults - thick skin
Young - amniotic egg
Young - amniotic egg
100
New cards
What happened in the Permian era before the Triassic
amniotes ruled the land, vertebrates overtook arthropods for goodarchosaurs relatively small and uncommon, except in freshwater realm