Lecture 7 -- Hyoid, Larynx, and Swallowing Flashcards
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is the function of the hyoid apparatus?
Suspends the tongue and larynx from the base of the skull.
List out 4 major muscles of the hyoid apparatus. List out their function, as well as the corresponding nerves.
Sternohyoideus → Draws hyoid caudally → Cervical nerves
Thyrohyoideus → Draw hyoid caudally → Cervical nerves
Mylohyoideus → Draw hyoid rostrally → Trigeminal
Geniohyoideus → Draws hyoid rostrally → Hypoglossal
Which muscle draws the hyoid caudally and is innervated by cervical nerves?
Sternohyoideus.
Which muscle draws the hyoid rostrally and is innervated by the trigeminal nerve?
Mylohyoideus.
What is the roles of the larynx?
Protect the lower respiratory tract from foreign bodies.
Phonation – voice production.
Why the shape and calibre of the passage can be altered?
Some of the cartilages of the larynx are mobile
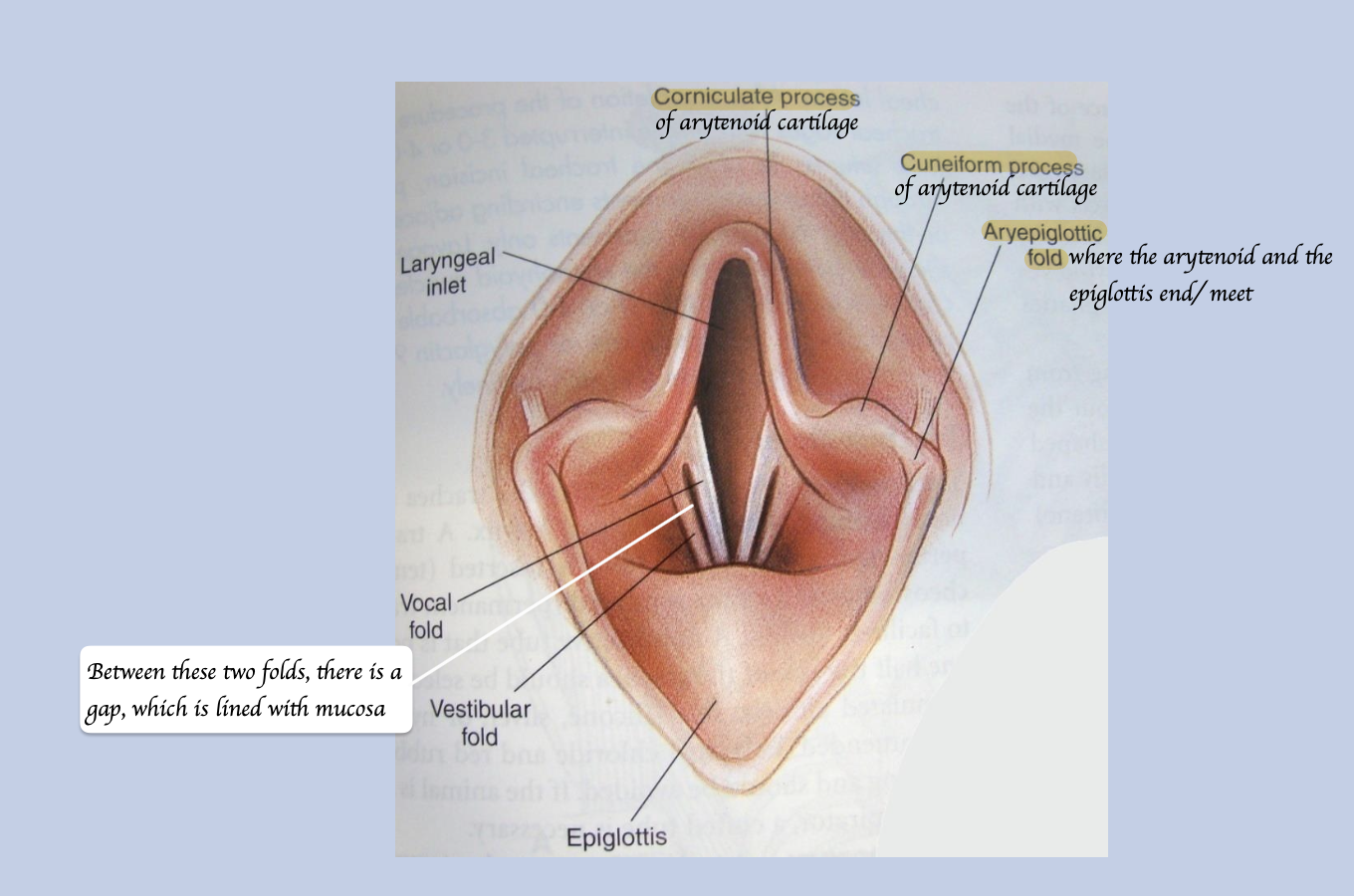
What is the entrance of the vestibule?
Laryngeal aditus
What structures form the roof of the vestibular opening?
Arytenoid cartilage
What structures form the lateral aspect of the vestibular opening?
Aryepiglottic folds (that joins the epiglottis to the arytenoids)
What structures form the ventral floor of the vestibular opening?
Epiglottis
What is glottis? What is the name of the actual airway?
Forms a narrow vertical slit
Rima glottidus
What forms the walls of the glottis ventrally?
The paired vocal folds.
What forms the walls of the glottis dorsally?
The arytenoid cartilages.
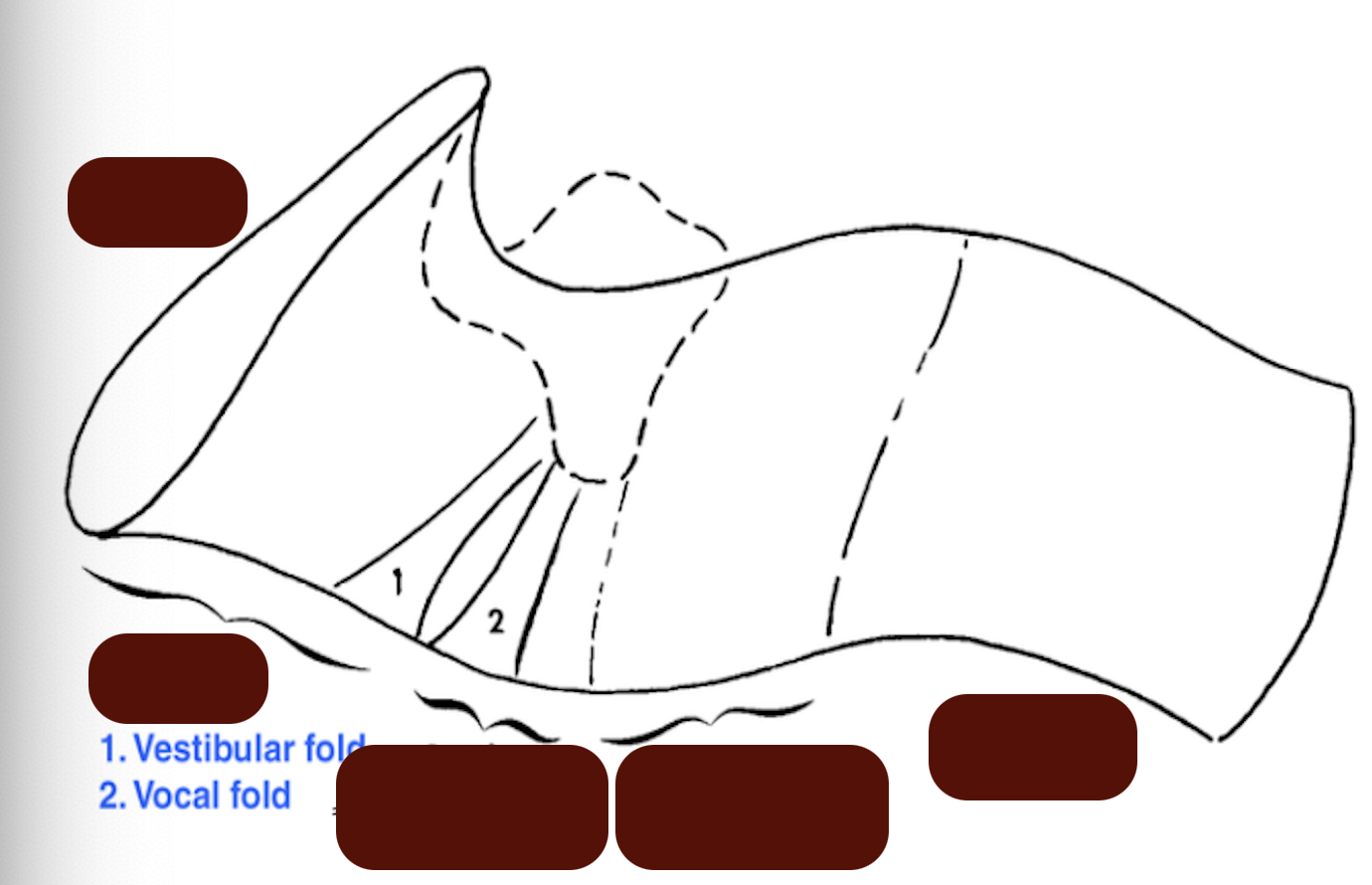
Identify the key feature of the airway of larynx

Identify the key structure of hyoid apparatus and larynx
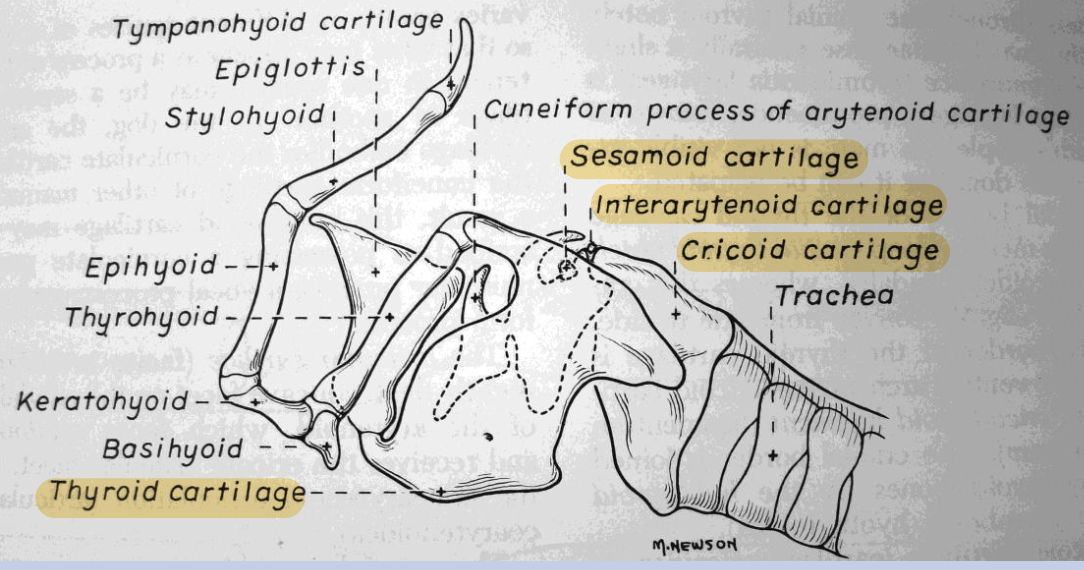
Which of the cartilages of the hyoid apparatus is unpaired?
Basiohyoid
Which laryngeal cartilage is shaped like a signet ring?
Cricoid cartilage
What is the function of the vestibular fold?
Marks the caudal end of the vestibule.
What is the function of the vocal fold?
Responsible for vocalization.
What is the aryepiglottic fold?
Fold from epiglottis to arytenoid.
How many pairs of laryngeal muscles are there?
8 pairs (1 pair opens the glottis + 7 pairs close the glottis)
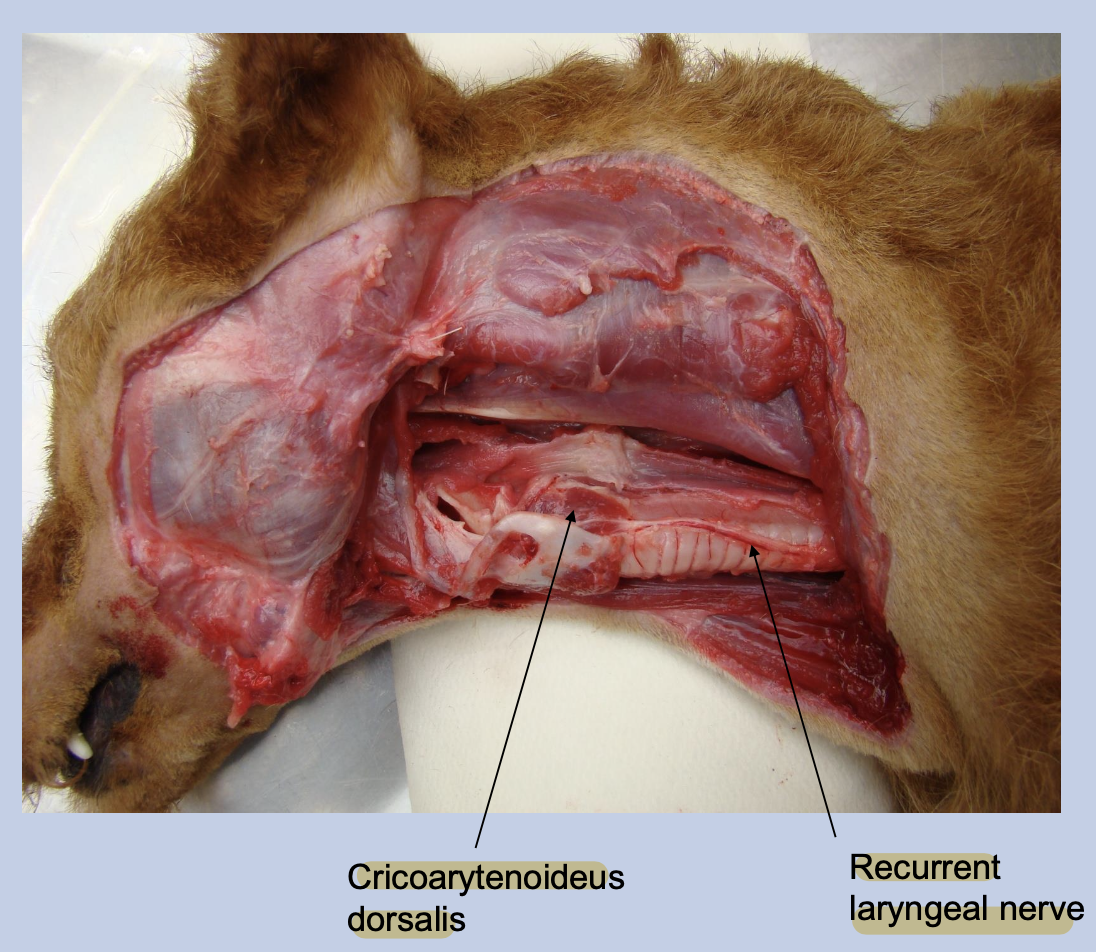
List two important laryngeal muscles and their functions.
Cricoarytenoideus dorsalis: Abducts the arytenoid + Open the glottis
Cricoarytenenous lateralis: Close the glottis
Which nerve innervates all muscles of the larynx except the cricothyroid muscle?
Recurrent laryngeal nerve (Branch of vago-accessory complex)
Which nerve innervates the cricothyroid muscle?
Cranial laryngeal nerve (Branch of vago-accessory complex)
Where is the recurrent laryngeal located?
Beside the trachea
What are the major functions of the cranial laryngeal nerve with respect to laryngeal innervation?
Innervate mucosa of larynx rostral to vocal cords (AA)
Innervate parasympathetic to mucosal gland (SE)
Innervate cricothryoideus muscle (SVE)
What are the major functions of the cranial laryngeal nerve with respect to laryngeal innervation?
Innervate mucosa of larynx caudal to vocal folds (AA)
Innervate parasympathetic to mucosal glands (AE)
Innervates all muscles of larynx except cricothyroid (SVE)
Describe the course of the recurrent laryngeal nerve
Left recurrent laryngeal → Curves around the aorta → Passes between aorta and pulmonary trunk before reascending back up to the neck
Right recurrent laryngeal - Give of caudal to right subclavian artery -> Returns up the neck
What defines Brachycephalic Obstructive Airway Syndrome?
Stenotic nares
Abnormal shape/ position of nasal turbinates
Extra long soft palate
Everted laryngeal saccules
Narrow trachea.
During stage 1 of laryngeal collapse in brachycephalic dogs what occurs?
Laryngeal saccule eversion.
What is dorsal displacement of the soft palate in horses?
When the soft palate sits above the epiglottis → Inhale into the larynx on inspiration → Cause coughing
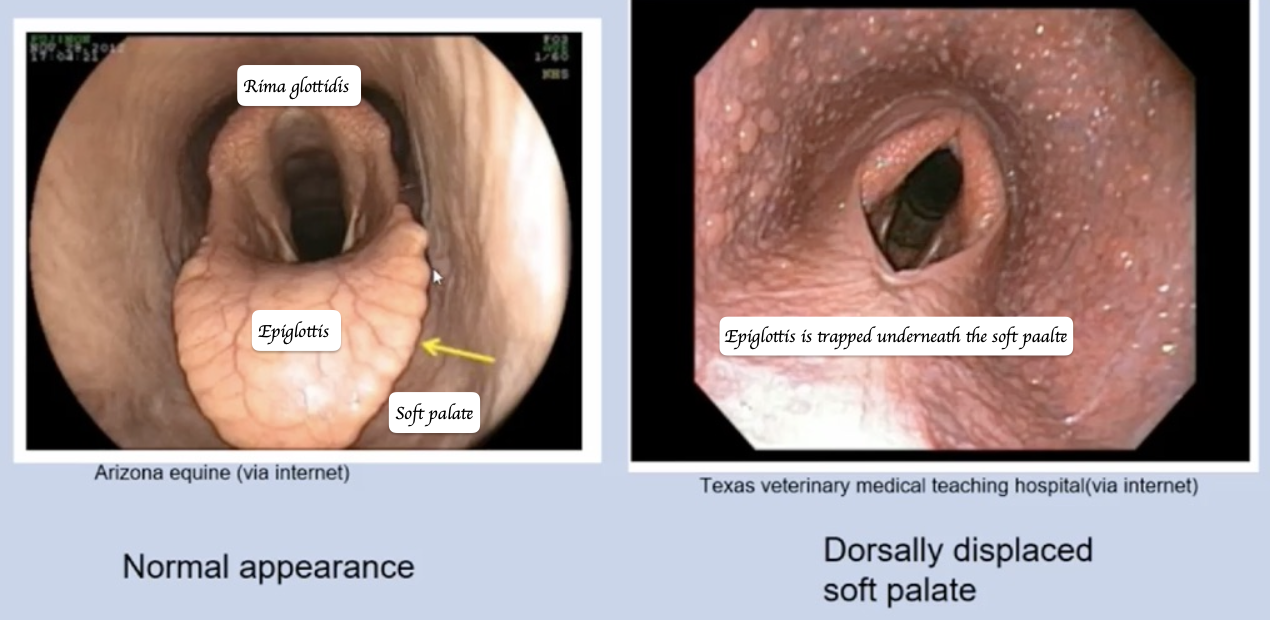
What causes total paralysis of the left arytenoid in horses?
Failure of the left cricoarytenoideus dorsalis muscle to contract due to recurrent laryngeal neuropathy.
What is laryngeal reflexes?
Laryngeal mucosa is very sensitive to mechanical stimulation + stimulation from small particles → Initiate coughing or reflex closure of glottis
Which species need local anaesthesia for intubation?
Cats and rabbis → Because these species have very sensitive laryngeal mucosa