Pulmonary Exam 1: Pulmonary Pathology (Dr. Menon)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Define the following:
Collapse of lung
Atelectasis
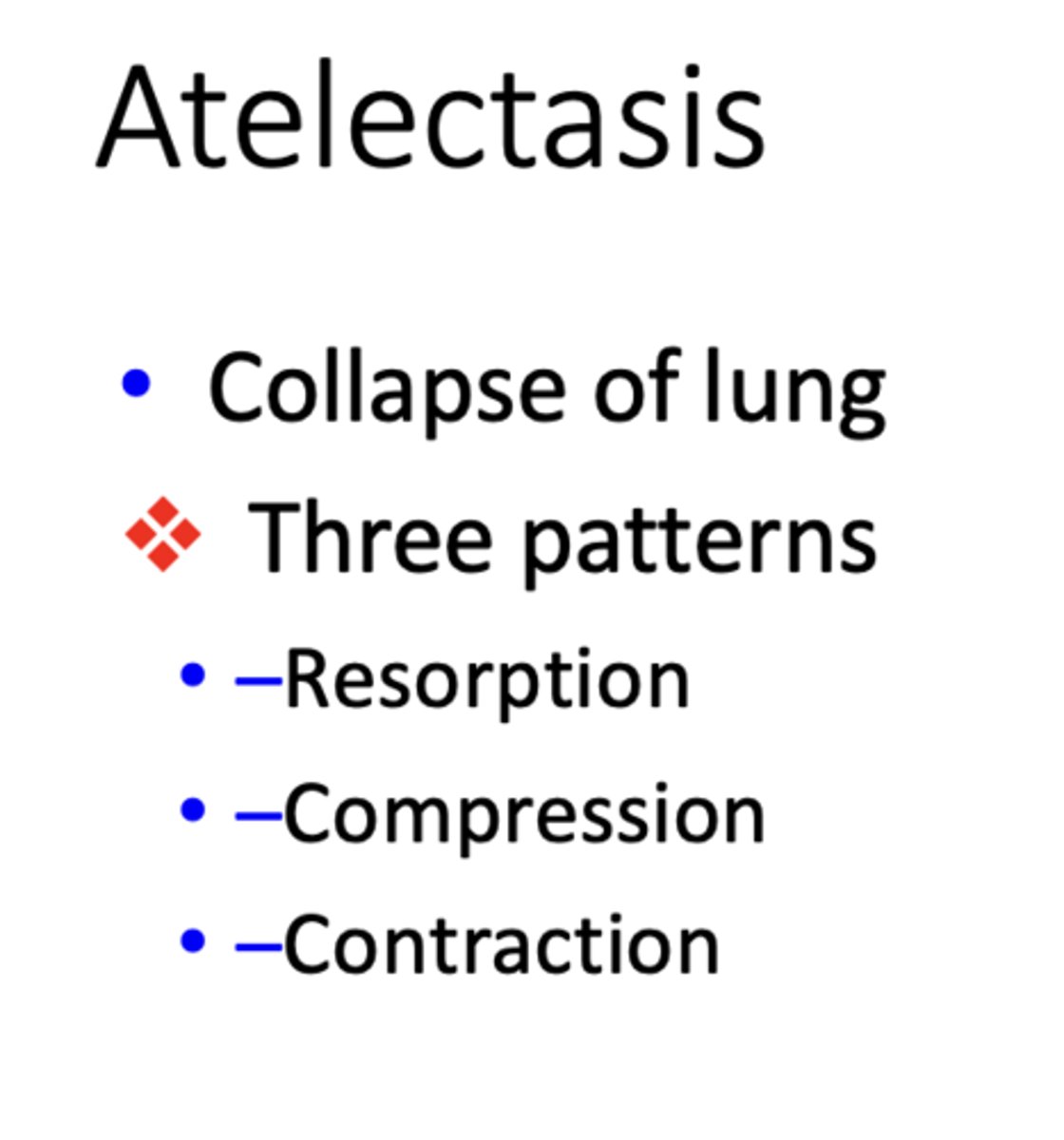
3 patterns for Atelectasis:
- Resorption
- Compression
- Contraction
type of Atelectasis:
- Due to obstruction in airway
- Potentially reversible
Resorption

type of Atelectasis:
- Due to fluid, blood, or air accumulation in pleural cavity
- Potentially reversible
Compression

type of Atelectasis:
- Cicatrization atelectasis
- Due to scarring causing contraction of parenchyma
- Only irreversible pattern
Contraction

Results from increased fluid in alveolar wall, usually from left ventricular failure:
Pulmonary Edema

Macrophages within alveolar spaces that have phagocytosed hemoglobin:
“Heart Failure Cells”

“Heart Failure Cells” are associated with what pathology of the lungs?
Pulmonary Edema

What has the following characteristics?
- Defined as arterial pressure at least one-quarter of systemic circulation
- Results in increased work and right heart failure
- Secondary is more common
Pulmonary Hypertension

This lung pathology causes:
- 50,000 deaths/year in USA
- May be virtually instantaneous
- True incidence unknown
- Typically seen with venous stasis
Pulmonary Emboli
_____________ is due to tumor, fat/bone marrow, amniotic fluid, foreign material (rarely due to other material)
pulmonary emboli
What has the following characteristics?
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- Formerly Wegener granulomatosis
- >80% develop respiratory manifestations
– Necrotizing granulomatous inflammation
– Vasculitis
– Nose, renal, and oral lesions
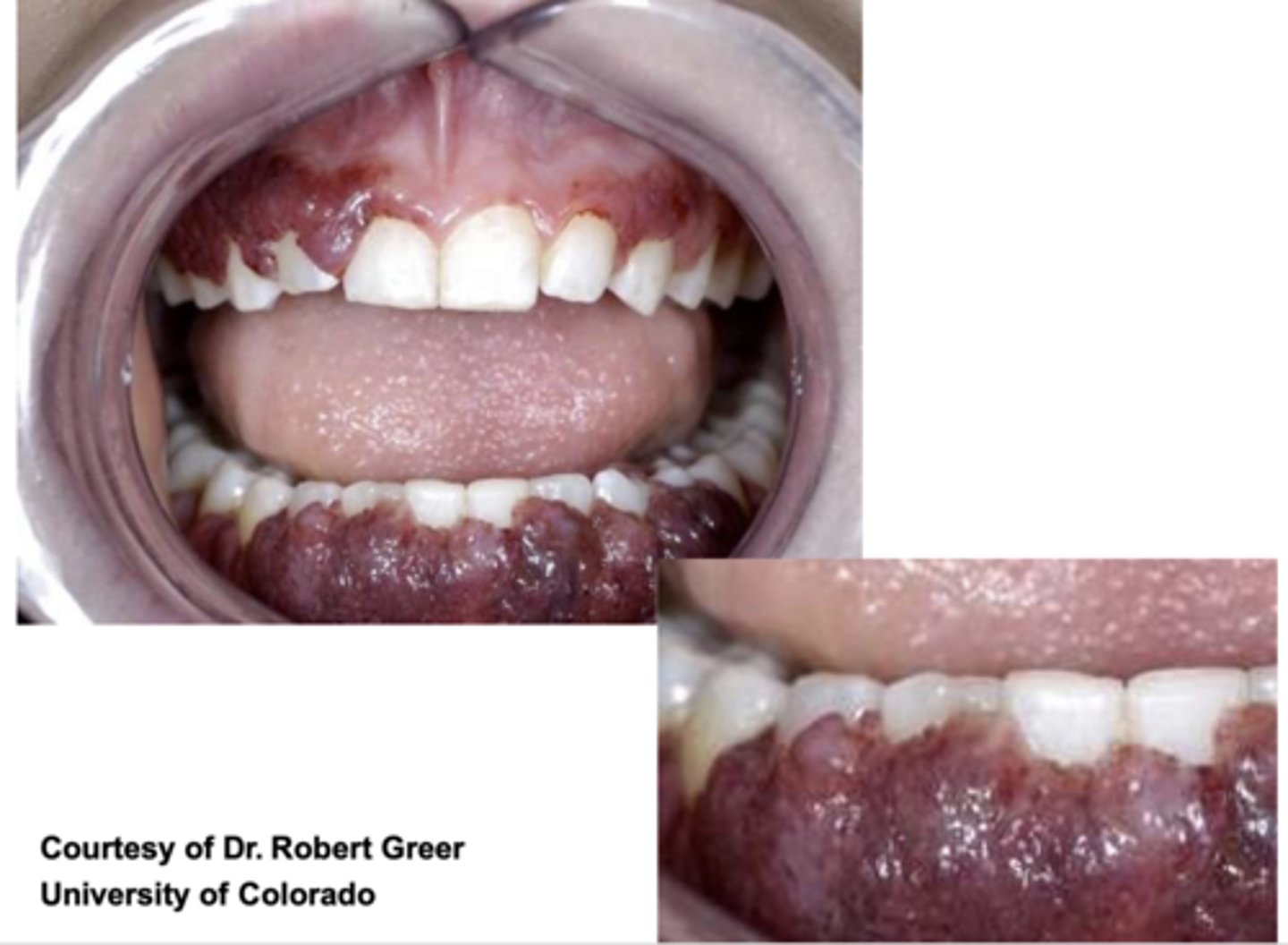
*Strawberry gingivitis
Pulmonary Vasculitis

Strawberry gingivitis is associated with what lung pathology?
Pulmonary Vasculitis
Pulmonary edema most commonly caused by _________ ventricular failure
left

Pulmonary hypertension causes _____-sided heart failure
right

most commonly caused from deep leg veins
-5% may cause sudden death, cor pulmonale, or shock
pulmonary emboli

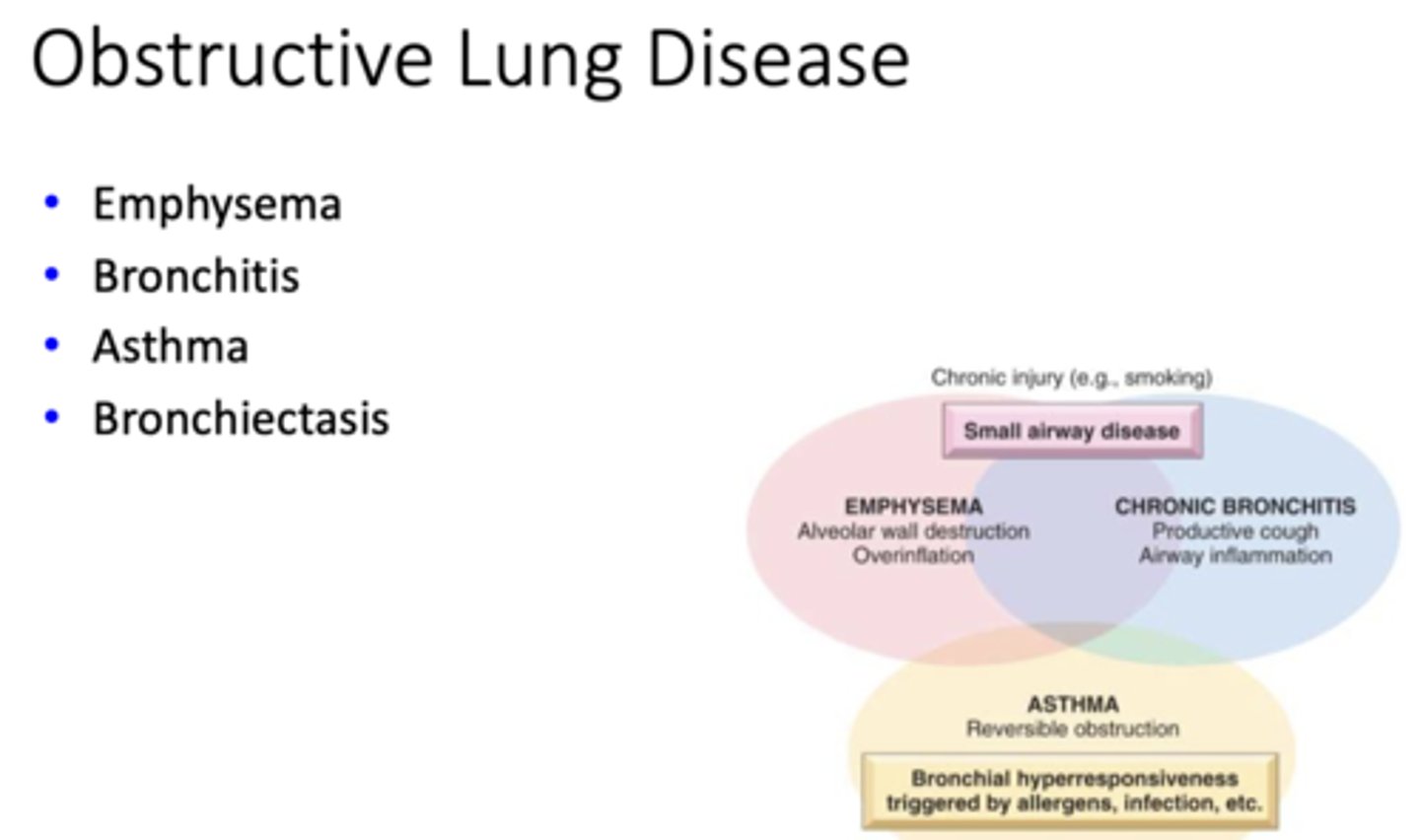
Obstructive or restrictive disease?
- Reduced expansion of lung parenchyma
- Capacity decreased
Restrictive

Obstructive or restrictive disease?
- Emphysema
- Bronchitis
- Asthma
- Bronchiectasis
Obstructive
What has the following characteristics?
- Abnormal enlargement of airspaces distal to terminal bronchioles
- Destruction of alveolar walls
- Absence of scarring
- Strongly associated with cigarettes
Emphysema

which form of Emphysema is the most common clinically significant pattern?
Centriacinar (centrilobular) emphysema

form of Emphysema:
- Most common clinically significant pattern
- More common and severe in upper lobes
- Most commonly associated with smoking
- NOT associated with a1-antitrypsin deficiency
Centriacinar (centrilobular) emphysema

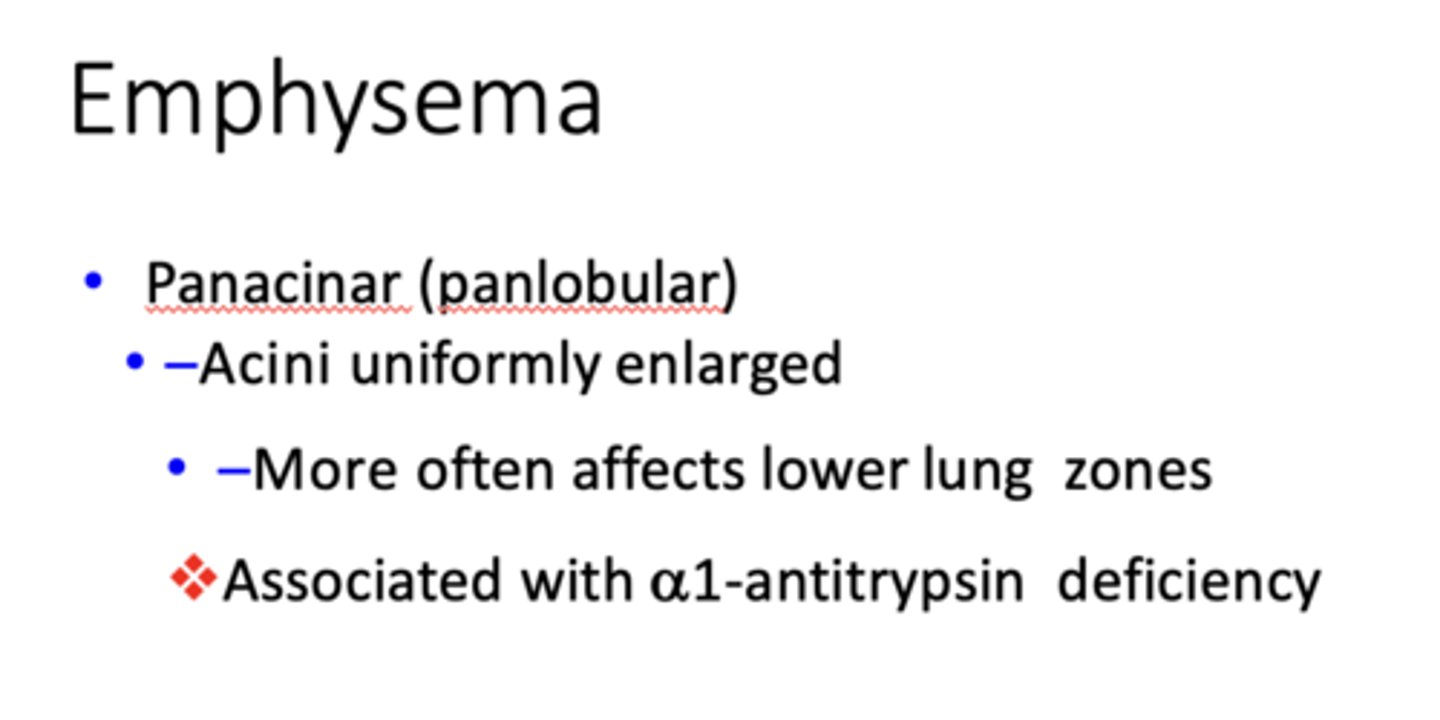
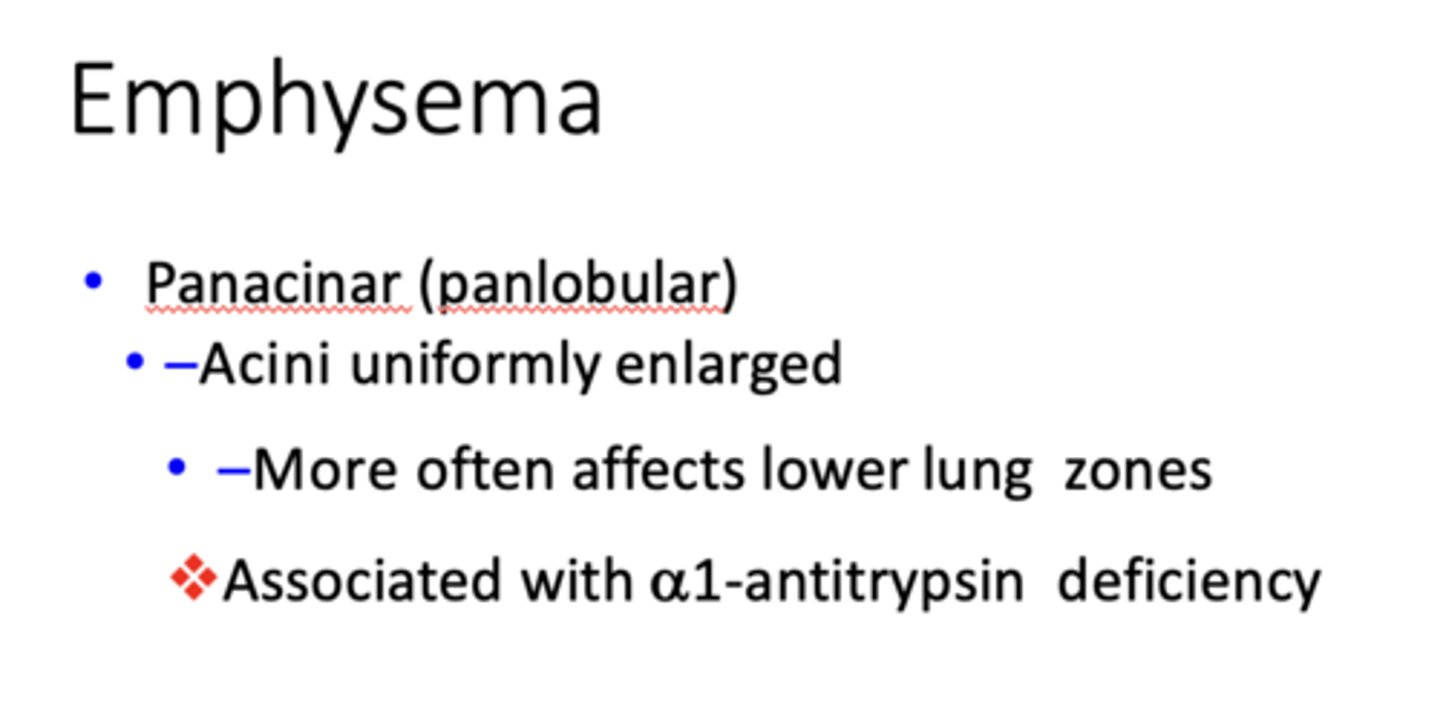
form of Emphysema:
- Acini uniformly enlarged
- More often affects lower lung zones
- Associated with a1-antitrypsin deficiency
Panacinar (panlobular) emphysema
Which form of emphysema is associated with a1-antitrypsin deficiency
panacinar (panlobular)
What has the following characteristics?
- Proximal acinus spared
- Idiopathic
- Occurs adjacent to areas of fibrosis
Distal acinar

What has the following characteristics?
- Usually with scarring
– Irregular involvement
- Most common pattern for emphysema, though usually asymptomatic
irregular
Pathogenesis for this condition include:
- Results from insufficient wound repair
- Exposure to toxins induces chronic inflammation
- Imbalance between proteases and protease inhibitors
Emphysema

What has the following characteristics?
- Progressive dyspnea
- Without bronchitic component, may maintain adequate oxygenation with prominent dyspnea ("Pink puffers")
- With pronounced bronchitis, patients exhibit hypoxia ("Blue bloaters")
Emphysema

What complication of emphysema?
- Secondary pulmonary hypertension
- Death from pulmonary failure with respiratory acidosis, hypoxia, coma, or right-sided heart failure
Chronic bronchitis

Persistent productive cough for at least 3 consecutive months in 2 consecutive years:
Chronic Bronchitis

_________ is clearly linked to cigarette smoking
chronic bronchitis

Airway obstruction due to hypersecretion of mucus:
Chronic Bronchitis
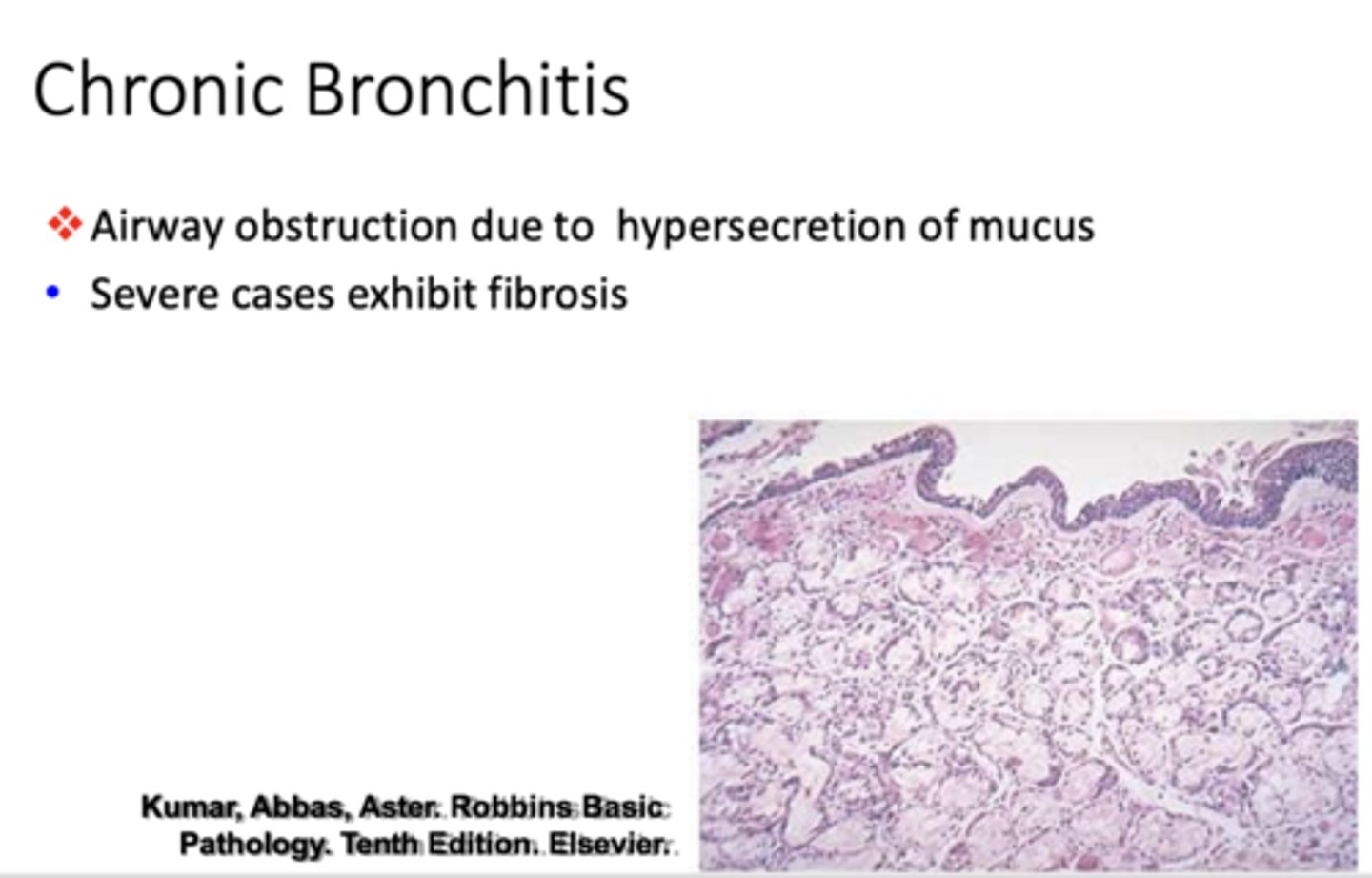
Hallmarks of this disease:
- Intermittent and reversible airway obstruction
- Chronic bronchial inflammation
- Bronchial smooth muscle cell hypertrophy
- Increased mucus secretion
- Eosinophilic infiltrate with Charcot- Leyden crystals
Asthma

Eosinophilic infiltrate with Charcot- Leyden crystals is associated with:
Asthma

What has the following characteristics?
- Type I hypersensitivity response
- Begins in childhood, usually in families with history of allergy
Atopic asthma

What has the following characteristics?
- Associated with viruses or pollutants
- Usually begins in adult life and not associated with a history of allergy
Non-atopic asthma

The following are triggers of what?
- Allergy
- Infection
- Occupational exposure
- Drug-induced
- Irritant gases
- Psychological stress
- Exertion
- Cold air
Asthma

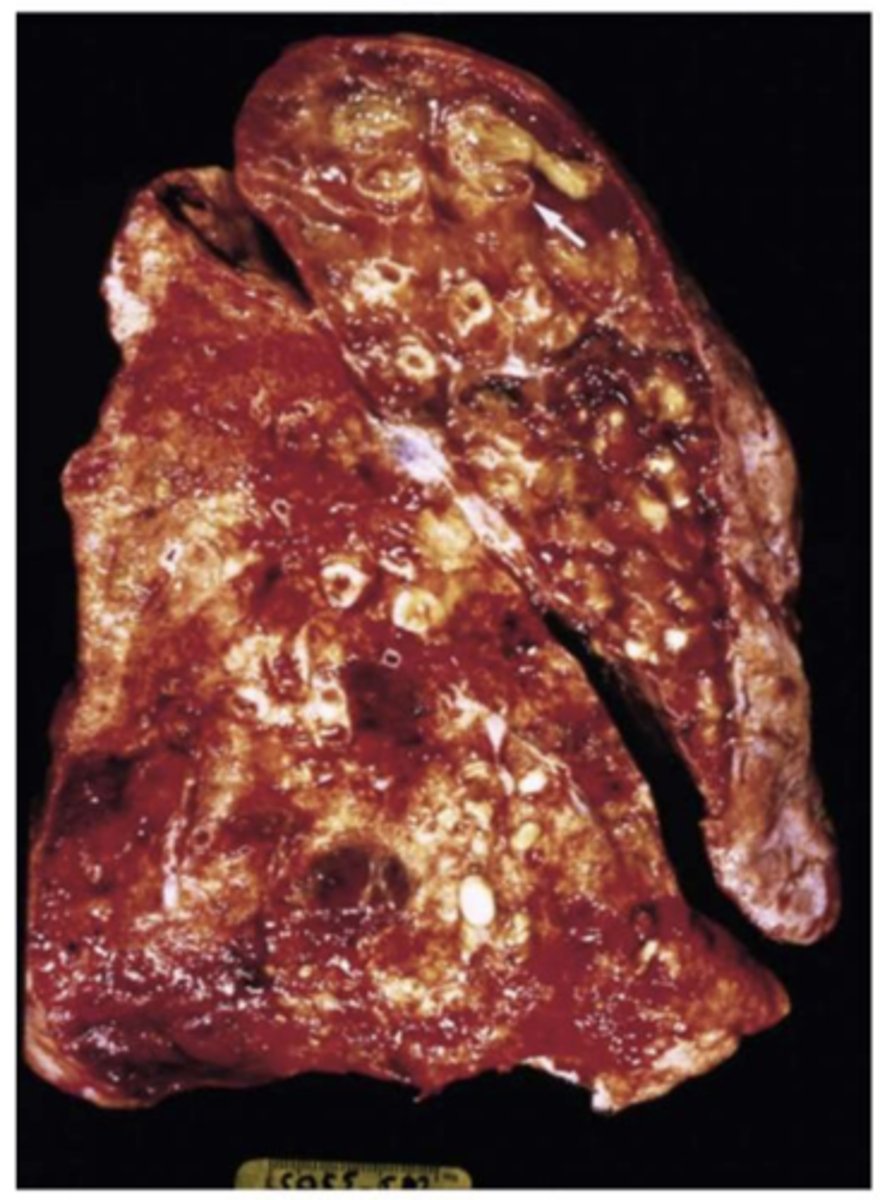
What has the following characteristics?
- Dilation of bronchi and bronchioles
- Predisposing conditions: Bronchial obstruction, cystic fibrosis, and immunodeficiency
- Associated with Necrotizing pneumonia
Bronchiectasis
What has the following characteristics?
• Recurrent cough and hemoptysis
• Expectoration of purulent sputum
• Recurrent chest infection
• Airway diameter typically 4 times larger
Bronchiectasis
type of lung disease:
–Limitation of airflow
–Normal capacity
Obstructive

type of lung disease:
– Reduced expansion of lung parenchyma
– Capacity decreased
- Forced vital capacity reduced
- Expiratory flow rate reduced proportionately
- Normal FEV:FVC ratio
Restrictive
Obstructive or restrictive disease?
- Chest wall disorders with normal lungs (Obesity, diseases of pleura, neuromuscular disorders)
- Interstitial lung diseases (chronic and acute)
Restrictive

What are four categories of chronic interstitial lung disease?
- Fibrosing
- Granulomatous
- Eosinophilic
- Smoking-related

What has the following characteristics?
• Patchy progressive bilateral interstitial fibrosis
• 2/3 of patients are >age 60
• Male predilection
• Treated with lung transplantation
• Survival = 3-5 years
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis

T/F: CDC stopped short of labeling dentistry as an occupational risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, but did advise:
"Further investigation of the risk for dental personnel and IPF is warranted to develop strategies for prevention of potentially harmful exposures."
True

What has the following characteristics?
Lung reaction to inhalation of organic or inorganic particles
Pneumoconioses

Most common mineral duct pneumoconioses (restrictive pulm. disease) are due to :
- Coal dust
- Silica
- Asbestos

t/f: tobacco smoking worsens effects of all inhaled mineral dusts, especially asbestos within pneumoconioses
True

What has the following characteristics?
- Asymptomatic anthracosis
- Simple coal worker's pneumoconiosis (CWP)
- Complicated CWP/Progressive massive fibrosis
Coal worker's pneumoconiosis

What has the following characteristics?
- Most prevalent chronic disease worldwide
- Caused by inhalation of silica, especially in crystalline form
Silicosis

this pathology is associated with an increase susceptibility to tuberculosis and carcinogenesis:
Silicosis

This pathology is linked to multiple diseases:
- Interstitial fibrosis
- Lung carcinoma
- Mesothelioma
- Laryngeal carcinoma
- Increased cancer risk in family of exposed
Asbestosis

Define the following:
Fibrous silicate historically used as a building, insulating, and fire-resistant material
Asbestos

This pathology has a long latent period often seen between exposure and onset of clinical disease:
Asbestosis

What idiopathic multisystem disorder has the following characteristics?
- Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
- Eye lesions
- Skin lesions
- Noncaseating granulomas
- High incidence in Swedish, Danish, and African-American populations
- Predilection for adults
Sarcoidosis

What is the idiopathic multiple system disorder with NONCASEATING GRANULOMAS?
sarcoidosis

What has the following characteristics?
- 190,000 cases diagnosed annually
- Produced by diffuse alveolar capillary and epithelial damage
- Life-threatening respiratory insufficiency, cyanosis, and severe arterial hypoxemia
- May progress to multisystem organ failure
- Histopathologic manifestation in lungs is diffuse alveolar damage (DAD)
Acute respiratory distress syndrome

What has the following treatment:
– Continuous positive airway pressure ventilation with support of cardiac, circulatory, and renal function
- Mortality reduced to 40%
– Death usually from systemic inflammatory response syndrome with multi-organ failure
Acute respiratory distress syndrome

In acute respiratory distress syndrome, mortality is reduced to ______% with treatment
40%
