APUSH Time Period 4 (CH 8.9 - 11)
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Jefferson’s goals in power
dismantle the Federalist system
reduce importance of the national gov. in daily life
free trade, religion, + press
Peace w/ all nations, but no entangling alliances
Economy in the government
Marbury vs Madison
William Maybury never receieved his appointment papers by John Adams (midnight judges), and he sued new Secretary of State James Madison. This established the Supreme Courts right to “judicial review”: the right to determine weather an act of congress violates the constitution.
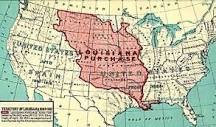
Louisiana Purchase
This exchanged 530,000,000 acres of territory in North America that the United States purchased from France in 1803 for $15 million. It was Jefferson's greatest achievement, but Jefferson violated the Constitution by buying land from a foreign power. Federalists hated this deal because the US already had “too much land and not enough money”. Slaves who had been living in this territory now had reduced freedoms and free blacks faced a decline in status. Women retained principles of “community property” since Spanish + French civil codes recognized women as co-owners of family property.
Lewis + Clark
Their goals were to study the plants, animals, + geography of the area as well as how to economically exploit the region. They ended up bringing lots of info + specimen, but didn’t find a commercial route to Asia.
Barbary Wars
1801-1815 This was the first war fought by the US. The US was trying to protect commerce since the Barbary States had preyed on shipping, including demanding tribute. In 1801 Jefferson refused to pay the higher price and so the Pasha (ruler) of Tripoli declared war on the US. The naval conflict ended in 1804 with the US victory at Tripoli Harbor, but the harassment didn’t end til after the War of 1812. It also established the US view of Muslims as exotic people who didn’t adhere to Western standards.
Embargo Act
1807 - closed U.S. ports to all exports and restricted imports from Britain. It was a large exercise of federal power considering Jefferson believed in limited government. Americans exports dropped by 80% by 1808 but neither France nor Britain noticed. This act devastated the economies of American cities (esp. yoemen), and the act was violated by American shippers + other people whose income was based on trade.
War Hawks
Young congressmen, enthusiastic nationalists, who were pushing to go to war w/ Britain. Some members wanted to annex Canada or conquer Florida. They wanted to restore free trade + stop European infringements on American independence.
Tecumseh
Shawnee brother of Tenskwatawa, he was a religion prophet who called for complete separation from whites, since they are the source of all evil. He believed that Indians should abandon American alcohol, food, clothes, etc.
Tenskwatawa
Shawnee brother of Tecumseh, he traveled the MI Valley encouraging a pan - Indian alliance like that of the 1760’s. “The option is to resist or be exterminated”
Battle of Tippecanoe
1810 Tenskwatawa had called for attacks on American Frontier settlements. While he was absent, American forces destroyed Prophetstown.
War of 1812 CAUSES
The assaults on American shipping had continued, + Madison asked Congress for a declaration of War. Feds + Reps in the North voted against the war (bc this was where mercantile + financial resources were located). The South + West voted for the war.
Why was is foolish for the US to go to war with Britain?
US was disunited and had an unprepared military going against 1 of 2 major world powers at the time. US was struggling financially since the charter of the Bank of the US ended in 1811 + northern merchants refused to loan money. Britain was preoccupied w/ European conflicts until they beat Napolean + invaded US + burned the White House and Capitol.
US Military Successes in War of 1812
1812 - American frigate Constitution defeated British warship Guerriere
1813 - Commodore H. Perry defeated British naval force on Lake Erie.
Fort Mchenry withstood British bombardment on Baltimore Harbor (Star Spangled Banner!)
Defeated Indian attacks (ended Creeks) + gained 23 million acres to fed. gov.
Battle of New Orleans
At this battle, Andrew Jackson fought off a British Invasion (1815), recruiting the cities free men of color. News of the Treaty of Ghent hadn’t reached America till after this battle.
Treaty of Ghent
This simply restored the previous system, no territory was exchanged and no agreements relating to impressment or shipping rights were made. This specified that Britain must return the American slaves who had fought for Britain in the War of 1812, but they didn’t. 5 yrs later they decided to end the dispute, and Britain paid a few million in compensation.
War of 1812 Significance
confirmed the ability of a Republican gov. to conduct war w/o surrendering its institutions.
Jackson became a national hero
Completed conquest of land east of MI River
Solidified the border b/w US + Canada
Created a growing sense of Canadian nationalism + Canada was glad to be independent of US domination.
Both US and Canada grew stereotypical views of each other (US as prone to violence + and Canada as monarchical)
End of the Federalist Party
The Feds held unpopular opinions on the war and commercial + financial interests. They also distrusted popular self government (but the people were feeling patriotic). “accused of being unpatriotic”.
Hartford Convention (see other flashcard)
Hartford Convention
1814 New England Federalists gathered to give voice to their parties’ grievances: domination of the federal government by VA presidents + their own regions declining influence due to new Western states. The Federalists wanted to eliminate the 3/5 Clause and require 2/3 Congress votes for admitting new states, declaring war, and to create laws restricting trade.
Market Revolution
Caused by innovations in transportation + communication, this was an economic transformation. Most people had been self sufficient, with little access to markets, but that changed.
Erie Canal
The completion of this allowed goods to flow between NY + the Great Lakes
Attracted lots of farmers migrating from New England
Acted as fertilizer, causing new towns to spring up.
Market Revolution Inventions
Innovations such as the steamboat, canal, railroad, and telegraph opened new land to settlement lowered transportation costs, and allowed for economic enterprises to sell products. Steamboats made upstream commerce possible as well as transport across the Great Lakes + eventually Atlantic Ocean. Railroads opened new areas of the American interior to settlement + stimulated coal mining + iron manufacturing. The telegraph made instantaneous communication possible throughout the entire nation.
Western Growth
1815 - 1821 6 new states entered Union
1790 - 1840 4.5 mill people crossed the Appalachian mts.
Spain sold Florida to US in 1819 (Adam Onis Treaty)
Cotton Gin
This invention quickly separated the seed from the cotton + allowed the growing + selling of cotton on a large scale. American slavery had been dying out since tobacco was exhausting the soil, but now greatly expanded. SC even re-opened the African Slave Trade from 1803-1808. Slaves were transferred from the older slave states to the new lower South in slave coffles (groups chained to one another and forced to march).
Farming Inventions
The steel plow made it possible to quickly transform the Western prairies into farmable land. The reaper (horse drawn machine) increased the amount of wheat a farmer could harvest.
Factory System
This gathered large groups of workers under central supervision + replaced hand tools w/ power driven machinery. Lowell’s Mills were modern textile factories that spun thread + eventually wove + finished cloth. Lowell’s Mills employed 10k people!
American System of Manufacturers
The mass production of interchangeable parts that could be quickly assembled into standardized finished products. Produced not only textiles, but tools, firearms, shoes, clocks, ironware, and agriculture machinery.
Market Revolution Effect on Workers
The Market revolution changed Americans concept of time itself
Farm time was regulated by the season, but in cities there was a clear mark of what was leisure time and what work time.
Wage became common language
Increased reliance on railroads
NE textile mills relied heavily on female + child labor
The early labor movement also called for the end of imprisonment due to debts, the opportunity for free education, and a 10-hour-per-day working limit.
Market Revolution Impact on Immigration
90% of immigrants went to northern states bc of job opportunities + lack of slave competition.
Peasants and trade crafts had been pushed off of European land, and ocean-going steamships + railroad made distance travel more practical
Germans had more skilled craftsmen than the Irish and settled in tightly knit neighborhoods.
Nativism
“Anti immigrant”, this is the political policy of promoting the interests of native inhabitants against those of immigrants. Some people feared the impact that immigrants would have on american political + social life. These people blamed immigrants for urban crime, political corruption, and fondness of liquor. They saw the immigrants as undercutting native born laborers by working for much lower wages.
Corporation
This has special privileges and powers granted in a government charter. Investors and directors are not personally liable for debts, therefore they were able to raise more capital then a traditional enterprise forms. Courts opposed efforts by established firms to limit competition from newcomers.
Manifest Destiny
“The US had a divinely appointed mission to occupy all of North America. Their right to do so was proven by the nations divinely inspired mission to extend the area of freedom.”
Transcendentalists
New England intellectuals who insisted on the priority of individual judgement over existing social traditions + institutions.
Individualism
The idea that ownership of oneself instead of one’s property made someone virtuous. This was ironic because people promoted the idea of the “sovereign individual” but at the same time the market revolution promoted commercial connections between far flung people.
Henry David Thoreau
He was a writer from Concord, MA who believed in individual self-reliance. He believed modern society stifled individual judgement by trapping them in the jobs and obsession with wealth. “People have no time to appreciate the beauties of nature”, he wanted people to find freedom within and “simplify” their lives.
Second Great Awakening
Popular Religious revivals added a religious foundation on the emerging ideas of self-improvement , reliance, and determination. This was started by religious leaders alarmed at dropping church rates, but the efforts expanded quickly. Methodism + Christianity grew, while deism waned. The revivalists used the market revolution to their advantage to spread religion and technically promoted the market culture, even though scramble for wealth was seen as the law of Satans Empire.
The ending of gov. funding for established churches promoted religious pluralism (new churches, and splits)
Inspired the growth of reform movements, especially abolitionism.
Mormons
This group was founded in 1820 by NY famer Joseph Smith. It responded to disruptions cause by the market revolution, + was self consciously democratic. It admitted everyone who accepted Smith’s message. Smith allowed polygamy (allows men to have more than 1 wife). This group had the unique practice of posthumous baptism (baptize long dead ancestors). They believed Christ had been in the Americas (Smith claimed he found a set of gold plates that explained this).
Self-Made Man
This meant that those who achieved success did so not as a result of hereditary privilege or the government like in Europe, but through their own hard work and intelligence . The market revolution made a new middle class.
Cult of Domesticity
evolved from Republican Motherhood
virtue shifted to describe the personal moral quality associated with women
Virtue meant sexual innocence, beauty, frailty, and dependence on men
Married women couldn’t sign contracts, sue in their name, or control their wages til after the Civil War
Became respectable for wives to stay at home, outside of the new market economy.
Andrew Jackson
He came from humble beginnings + was self-made. “The coming to power of the “common man”. He was orphaned during the American Revolution and served as a courier (messenger) while still in his youth for the War of Independence. During his career, there were major developments in the market revolution, expansion of slavery, westward movement, and the growth of democracy. He was suspicious of banks and paper money and feared the market revolution was a source of moral decay. He didn’t believe in abolition and owned 300 slaves. Presidency: 1829-1837
Property Requirements for Voting
Although VA, NC, and RI didn’t agree, property requirements for voting were removed in 1850 by a Constitutional Convention. The eras ideas of “individualism” shifted people to believe that virtue was determined by ownership of ones self, not ownership of property.
Dorr War
Rhode Island still wanted property qualifications for voting, and in 1841 drafted a new state constitution (it removed blacks from the vote entirely), and inaugurated John Dorr as governor. President John Tyler dispatched federal troops and the movement was shut down. Legislature shortly afterward removed the property qualifications for white and black native-born men.
Alex de Tocqueville + Democracy in America
In his book, he thought that democracy reinforced a sense of equality among those in the nation, but greatened the divide between them and those who weren’t. Americans were defined by their participation in elections, parades, mass meetings, etc. The right to vote was a symbol of American citizenship.
Information Revolution
This was produced by the market revolution and political democracy. This was the expansion of the public sphere, and explosion in printing. The application of steam power to newspaper printing, low postal rates, the emergence of organized political parties, and the “penny press” allowed newspapers to circulate far. The growth of the reading public opened the door for women writers.
“Universal Suffrage”
It only actually applied to white males of age in the nation. Race and gender were used as a natural hierarchy system to bar women and blacks from voting and political participation. During colonial times women were seen as easily swayed, while men ruled by reason. During the 18th century women were seen as too pure to risk contamination by the political world. An elaborate ideology of racial superiority + inferiority, with “scientific” foundations, developed.
Infant Industries
Manufacturing enterprises that sprung up while trade with Britain had been suspended, but now faced intense competition w/ low-cost imported goods. The younger generation of Republicans (had called for war of 1812) wanted these industries to be under national protection. Reps. argued that for the nation to be economically independent from Britain, agriculture needed to be complemented by a manufacturing sector.
American System
Created by Henry Clay, this system had three parts:
a national bank
a tariff on imported manufactured goods (protects US industries)
federal financing for internal improvements (roads + canals)
Government sponsored improvements were the most controversial, as Madison vetoed a bill bc he believed it was outside of the governments power listed in the Constitution.
Tariff of 1816
This protected goods that could be produced outside the US, esp. cotton textiles (Southerners supported)
2nd Bank of the US
This institution was the government’s financial agent: collecting taxes, paying the gov.s debts, + issuing paper money that had real value. But no one knew if the money had any value since the notes were promises to pay a specific amount, and the value of paper money fluctuated wildly since banks often printed more money than specie (gold + silver) in their vaults.
Panic of 1819
This event was caused by:
resumption of trade w/ Europe created huge markets for American cotton + grain
rapid westward expansion stimulated demand for loans to buy land (banks printed more money)
But early 1819 European demand for US farm products returned to normal levels.
Effects:
demand for land plummeted (speculators lost millions as land prices fell)
INFLATION
Banks demanded repayment for loans, but farmers + businessmen who couldn’t pay declared bankruptcy + levels of unemployment rose (esp. Eastern cities).
Deepened distrust of national banks
McCulloch v Maryland
1819: Marshal argued that the bank was a legitimate exercise of national power since the constitution allows Congress to pass all “necessary and proper” laws, it was meant to promote general welfare, + “all means which are not prohibited are Constitutional.”. States wouldn’t be allowed to tax, since that “involves the power to destroy” + nothing should be able to destroy something created by the government. After the decision of this case, Congress maintained the Second National Bank of the US until 1836.
Era of Good Feelings
1815-1825: Monroe’s two terms in office were called BLANK because it was a one-party government at the time.
Missouri Compromise
1820 MI wanted to form a constitution for admission to the union as a state. MI wanted to have slavery, but republican congressmen didn’t. This deal said that MI would be able to create a constitution w/o the slave restriction, but Maine (prohibited slavery) would be admitted to the union to balance free + slave states. Slavery would be prohibited in all remaining Louisiana purchase territory North of lat 36 degrees 30’. This allowed MI to create a constitution that outlawed free blacks from entering the state, which was removed in the 2nd Missouri Compromise in 1821 since it violated the COMITY clause.
Westward Expansion + Question of Slavery
Division was created on how to decide weather new states would be free or slave states. Republicans voted against slavery in new states only bc they were upset at the South’s influence in Washington, with 28 years of VA presidents, besides John Adams.
COMPARE Spanish-American revolutions vs American Revolution
Both ignited because the imperial country wanted colonies to finance them. Local colonial elites in both revolutions wanted to be seen as equal to the imperial powers. Both their declarations of independence took inspiration from Jefferson’s Declaration of Independence. However unlike the British, the Spanish Empire became 17 different nations (bc too vast and disconnected). The Latin American constitutions were more democratic then the US, extending the vote to indians and blacks. The Latin American independence wars were longer + more destructive (sometimes followed by civil war, which made it much harder for these countries to economically develop).
Monroe Doctrine
1823 -
US would oppose any colonization efforts in the Americas
US would abstain from involvement in European wars
Warned European powers not to interfere with the newly independent Latin American states
It claimed the US as the dominant power in the New World / Western Hemisphere.
“America’s diplomatic declaration of independence”
Henry Clay “corrupt bargain”
Clay received the last electoral votes out of 4 candidates, and was eliminated from the prez race. Clay gave his support to Adam, since he was most likely to promote the American system and voting for the westerner Jackson would impede his own ambitions to be president. Henry shortly became secretary of state for Adam and people believed he had traded critical votes in order to hold the public office. It made it impossible for him to reach the White House.
John Quincy Adams
6th president, from 1825 - 1829
He was originally a federalist, but abandoned it later.
Wanted legislation promoting agriculture, commerce, manufacturing, + “mechanical + elegant arts”.
He wanted to establish a national university, astronomical observatory, and naval academy.
Wanted the US to adopt metric system :0
“Liberty is Power”
Martin Van Buren
8th president, 1837 - 1841
He didn’t believe that political parties were dangerous or decisive, but a necessary + desirable part of political life. Competition b/w parties gave a check on those in power + gave voters a real choice in elections. National political parties formed a bond of unity in a divided nation.
Election Campaign of 1828
This campaigns of this election were scurrilous (spreading scandalous claims) because Jackson’s supporters accused Adams of having a series of mistresses while was a diplomat in Europe and Jackson’s opponents called him a murderer for executing army deserters + killing men in duels. :(
Early 19th Century Democrat
This group is alarmed by the widening gap b/w social classes
Believed non-producers (bankers, merchants) were trying to take advantage of their government connections to gain wealth at the dispense of the “producers” (farmers, laborers, artisans)
Wanted government out of the economy
Farming regions (lower NW, South backcountry) and slave holders voted democratic.
Believed that the key to freedom was individual action.
Early 19th Century Whig
This group believed the government could guide economic development through tariffs, a national bank, and aid to internal improvements.
Supported by established businessmen, bankers, farmers, near water (benefited from economic change), and large southern planters
Believed that liberty and power reinforced each other, freedom could be enhanced and promoted by government action.
Viewed society as a hierarchy of social classes
They rejected the idea that the gov. shouldn’t interfere in private life.
The Spoils System
The Principle of rotation in office. Jackson had wanted government posts to be open to the people. It meant that loyalty to the party became the main qualification for jobs like postmaster or custom officials. This led to widespread incompetence and corruption bc its like “I like you, you get the job”.
Tariff of Abominations
1828 This raised taxes on imported manufactured goods of wool and raw materials (iron). This angered the south, which claimed that it raised prices paid by the southern consumers to benefit the north.
Nullification Crisis
1832-33 This was a confrontation between SC and the federal government about nullification and tariffs. (btw nullification is the constitutional theory that individual states can invalidate federal laws or judicial decisions they deem unconstitutional)
Webster Hayne Debate:
Webster called nullification illegal and treasonous
Hayne was a disciple of Calhoun
Indian Removal Act
1830 the uprooting of the 5 civilized tribes. Jackson had wanted to assert the US’s sovereignty, and to extend slavery they needed to turn Indian soil into slave soil. This act rejected the idea that Indians could be assimilated into American society. Chief Justice John Marshall justified this act by saying that Indians didn’t own the land because they are nomads / hunters and not farmers.
Trail of Tears
1838-1839 The army force 18 thousand Indians into stockades and then forced them west after they refused to leave. ¼ died. The rest of the tribes backed down after this event, expect the Seminoles. This event reinforced the racial definition of American nationhood and freedom.
Views on Banks
Banks symbolized the hopes and fears inspired by the market revolution. Americans such as Jackson distrusted bankers as they were “non producers” who profited off of others labor but contributed nothing to the nations wealth, (banks over-issued money, driving the value down of the income of wage workers).
Bank War
This was conflict b/w Jackson and the head of the national bank Nicholas Biddle. Biddle mentioned to a congress committee that the 2nd US bank had the power to destroy any state bank, but democrats questioned weather any institution should even possess such power. Biddle’s allies tried to convince congress to extend the banks charter, Jackson vetoed it (1832), seeing it as blackmail (the bank would use its resources to oppose his re-election). Jackson presented himself as the protector of the “humble Americans”, since :the rich and powerful often bend the acts of the government of their own selfish purposes.”
This event enhanced the power of the presidency since Jackson proclaimed himself the symbolic representative of all the people.
Jackson was the first to use the veto as a major weapon
Ensured death of the Bank of the US
Pet Banks
These were small local banks who were distributed the money from the destroyed 2nd Bank of America. Without government deposits, the Bank of US couldn’t regulate state banks, who issued more and more money. This caused prices to rise, and wages couldn’t keep up (the value of the wage decreases).
Panic of 1837
This was an economic collapse and depression caused by British distrust of American banknotes, and their demand to be paid in gold or silver only. Britain also lost its demand for American cotton, the US’s major export. Martin Van Buren tried to fix this by removing federal funds from pet banks and put them into the Treasury dept., which would have slowed economic growth had the discovery of gold in California in 1848 not occurred.
Mass Democratic Politics
The advertising of the candidate is more important then the person themselves. “Selling candidates and their image was just as important as the positions for which they stood.”
William Henry Harrison
He died of pneumonia a month into his presidency.
John Tyler
Devoid of accomplishment ☹
“The executive ass”
Most of his cabinet resigned, his party hated him
He showed that a president needed a party behind him to govern.
10th President of US, 1841-1845
Frederick Douglass
This man was born a slave in 1818 (slave mom, white father). He learned to read and write, escaped to the N in 1838, and began advocating for racial equality and abolition. He was also active in movements for women’s rights. He believed slavery could only be overthrown by continual resistance. He argued that slaves were truer to the American beliefs of liberty than the Americans who celebrated the 4th of july while having slaves.
Second Middle Passage
This was the trade of slaves between 1820-1860 from older states to “importing” states of the lower south.
Slavery Impact
Slavery impacted the entire US, not just the South because it determined where people lived, worked, and what conditions they could exercise free speech, assembly, press, etc. The Constitution enhanced the power of the South in the House of Representatives and in the Electoral College. States were also required to return fugitive runaway slaves. Northern manufacturers and merchants participated in the slave economy and shared its profits (helped fund improvements in the North).
Slavery Impact on South
The south limited the growth of industry, discourage immigrants from entering, and was against the technological progress because of slavery. The south experienced less urban growth then the N (banks meant to finance plantations, not manufacturing development).
Support for Slavery
Even families who didn’t own slaves (3/4 white families in south) supported slavery. Small farmers believed their economic and personal freedom relied on slavery. The farmers and plantation owners where united in racism (didn’t want to be the bottom group of society), common qualities, and their participation in a democratic political culture.
The Planter Class
Owned most fertile land
Highest incomes
Dominated leadership of both political parties as well as state and local offices.
Carefully monitored market conditions and invested in enterprises like railroads and canals
some of the richest planters lived lavish lifestyles
Paternalism
This was the belief that men took a personal responsibility for the physical and moral well-being of their dependents (women, children, slaves), Those depending on him must be obedient and provide labor, but they have the right of protection, guidance, subsistence, and care. This outlook masked and justified the true cruelty of slavery. It made slaveowners see themselves as kind and responsible.
View of White Women in South
This group was seen as weak, helpless, and dependent
They were confined to their “domestic circle” even more then Northern women,
Defense for Slavery
Racism was a pillar in the proslavery argument
Slavery was backed up by the bible (servants should obey their masters)
“essential to human progress” (planters believed that w/o slavery people couldn’t develop art and sciences)
Insisted it gave equality to whites since it prevents the growth of a class “destined for labor”
George Fitzhugh
Pro slavery
Believed that universal liberty was not the natural condition of mankind, but slavery was the basis of a normal, civilized society
He said that since the blacks didn’t have economic cares, they really were the happiest and freest in the world.
Slaves under the Law
Illegal to kill slaves except in self-defense
Slaves accused of serious crimes had 1 day in court (white judges and jury)
Slaves could not testify against a white person, acquire property, sign contracts, own firearms, hold meetings w/o white permission or leave the farm w/o the owner's permission.
Illegal to teach a slave to read or write
Owners could interfere in a slave’s choice of marriage and how they spent their free time.
Conditions of Slave Life
some southern states passed laws that slightly improved slave living conditions
Compared to the West Indies and Brazilian slaves, US slaves had better diets, lower infant mortality rates, and longer life expectancies.
Part of this is because the paternalist outlook made owners want to be kinder.
Also, once the slave trade closed and slaves became more expensive, owners were more concerned with the health and living conditions of their slaves
Yet slaves had less access to freedom.
Restrictions on Free Blacks
Couldn’t vote, own firearms or dogs, couldn’t strike a white person, even in self defense.
Couldn’t testify against against whites or serve on juries
Had to always carry their certificate of freedom.
By 1850s most southern states prohibited free blacks from entering their territory.
COMPARE Upper and Lower South
Lower South: Very few free blacks lived in the lower south (2%), they lived in cities and worked as skilled craftsmen. They established their own churches and schools.
Upper South: Had more free blacks, who worked for wages as farm laborers. Planters shifted to grain instead of soil-exhausting tobacco. Planters hired free blacks to work alongside their slaves at harvest time.
Maintaining Control Over Slaves
Slave owners:
Inflicted punishment on slaves (whippings)
Encouraged and exploited division competition b/w slaves (pay 10 cents to those who did good work that day)
Threatened selling their slaves (removes the slave from their immediate family)
Slave Culture
This culture drew from African heritage and centered on family and the church. This culture took music, dances, herbs, and styles of religious worship from African culture. Since US slaves had even male-to-female ratios, it made family creation easier than in the West Indies, and so the family was the center of the slave community. Yet the law didn't recognize the legality of slave marriages.
Slave Gender Roles
The 19th century “cult of domesticity” (women belong in the home) didn’t apply to slave women. Slave men couldn’t act as the providers of the family or protect their wives from abuse. Conventional gender roles applied when slaves did work “on their own time”. Men: fished, chopped wood, hunted. Women: washed, sewed, cared for children.
Religion for Slaves
Religion gave slaves hope for liberation. God didn’t have distinctions b/w sex, color, or anything temporary (like age), Owners forced slaves to go to church, where white ministers preached that theft was immoral and that slaves should obey their masters. Slaves looked up to heros in the bible like Jonah (escaped whale) and David (+Goliath).
Neighborhood Networks
These transmitted information between plantations, skilled craftsmen, ship pilots, etc. They spread news about local and national events. This helped slaves learn about the larger world, which owners didn’t want.
Slave Resistence
Most widespread form: “silent sabotage”: doing poor work, breaking tools, disrupting plantation routine
Slaves said they were sick to avoid work
Theft of food
Arson, poisoning, and armed assaults against whites.
Underground Railroad
An organization of sympathetic abolitionists who hid fugitive slaves in their homes til they sent them to the next station. This was a series of local networks communicating with each other to help fugitives reach safety in free states and Canada.
Amistad
In 1839, 53 slaves took control of this ship, which was transporting the slaves between ports in Cuba, and tried to steer it towards Africa, but landed on the American coast). Since they had been brought recently when the slave trade had been banned, Quincy freed the slaves and most went home to Africa. It may have inspired a similar uprising in the US (Creole Ship).
Denmark Vesey conspiracy
In 1822 a slave from Charleston, SC, Denmark Vesey purchased his freedom after winning the lottery. He was a leader of the African Methodist Church (believed slavery was against the bible). He reflected the combination of American and African culture into black culture. The conspiracy involved planning a major slave revolt, but the plan was discovered.
Nat Turner’s Rebellion
Nat Turner was a slave rebel and preacher who believed God chose him to lead a black uprising. He traveled the US conducting religious services. IN Aug 1831 Nat and some of his followers marched from farm to farm assaulting white inhabitants (militia put it down). Turner was executed. It panicked the white south, hundreds of slaves were whipped or executed. Impact: the VA legislature tightened its grip on bondage, other states followed suit. The South became more isolated as parliament debated a program abolishing slavery. Pro Slavery arguments permeated southern political and intellectual life, abolitionist views were suppressed (freedom of speech violated).
John Adams
The 2nd President of the US (1797-1801).
He was the only non-virginian among the first five presidents. He persuaded many northerners that the South had too much influence in Washington.
Task Labor
A organization system of slave labor where slaves where given a series of daily jobs to be completed at their own pace. It was common on plantations producing rice in South Carolina and Georgia.
Gang System
An organization system of slave labor in which groups of slaves were supervised as they did their work. It is a more violent system than task labor. It was common on plantations in southern Louisiana where sugarcane was cultivated.